Lipids Carbohydrates Proteins Nucleic Acids Chart
Lipids Carbohydrates Proteins Nucleic Acids Chart - Carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids. Web biomolecule, any of numerous substances that are produced by cells and living organisms. While they have different structures and functions, they are all composed of long complex chains of molecules (polymers) made up of simpler, smaller subunits (monomers). And fats or lipids are provided by oils, fatty fish, nuts and red meat. Hundreds of monosaccharides joined by glyosidic bond. Breakdown of these macromolecules provides energy for cellular activities. Their functions are to be the main source of energy and reserve, they are structural components and they play a key role in the immune recognition of cells. Made up of carbon, hydrogen and oxygen. It forms long chains with itself. They are all composed of only three atoms: Unit 6 structure of a cell. Web the four major classes of biological macromolecules are carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids. The simple sugars are catabolized during glycolysis. Each is an important cell component and performs a wide array of functions. The main substances found in every cell are a combination of lipids, carbohydrates, nucleic acids and proteins. Unit 7 more about cells. Proteins are created by linking together amino acids into protein links. Web unit 1 intro to biology. While they have different structures and functions, they are all composed of long complex chains of molecules (polymers) made up of simpler, smaller subunits (monomers). Study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like elements present in carbohydrates,. Carbohydrates are organic compounds that consist primarily of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen. Unit 2 water, acids, and bases. Web function of nucleic acids. Web foods that supply carbohydrates include grains, fruits and vegetables; Web unit 1 intro to biology. They are all composed of only three atoms: These are sugars and starches. Each of them is discussed below. Lets compare these four biomolecules essential for life. Web function of nucleic acids. The four major classes of biological macromolecules are carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids. Study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like elements in carbohydrates, carbohydrates monomer, functions of. Each type has its own monomer subunit which joins to other monomers in specific ways. Web proteins are broken down by the enzymes pepsin and peptidase, and by hydrochloric acid.. Unit 5 energy and enzymes. Web the four major biomolecules also called as macromolecules are proteins, carbohydrates, lipids, and nucleic acids. Protein is found in animal products and beans; The four major classes of biological macromolecules are carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids. Made up of monosaccharides joined by glyosidic bond. Found in all living things. The main substances found in every cell are a combination of lipids, carbohydrates, nucleic acids and proteins. Breakdown of these macromolecules provides energy for cellular activities. Cho, in a ratio of 1:2:1. Unit 8 membranes and transport. The main substances found in every cell are a combination of lipids, carbohydrates, nucleic acids and proteins. Lets compare these four biomolecules essential for life. Web for instance, carbohydrates are broken down by amylase, sucrase, lactase, or maltase. Biological macromolecules are important cellular components and perform a wide array of functions necessary for the survival and growth of living organisms.. Protein is found in animal products and beans; Biological macromolecules are important cellular components and perform a wide array of functions necessary for the survival and growth of living organisms. What makes carbon such an important element? Lets compare these four biomolecules essential for life. Biomolecules have a wide range of sizes and structures and perform a vast array of. Click the card to flip 👆. Biological macromolecules are important cellular components and perform a wide array of functions necessary for the survival and growth of living organisms. Unit 9 more about membranes. It forms long chains with itself. Unit 5 energy and enzymes. Unit 8 membranes and transport. Carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, nucleic acids. Carbohydrates are chemically defined as polyhydroxy aldehydes or ketones or compounds which produce them on hydrolysis. Carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids. Click the card to flip 👆. Unit 6 structure of a cell. Protein is found in animal products and beans; Within all cells, small organic molecules are joined together to form larger molecules. Carbohydrates are organic compounds that consist primarily of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen. Hundreds of monosaccharides joined by glyosidic bond. Web carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids. Found in all living things. Web there are four major classes of biological macromolecules (carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids); These are sugars and starches. Web the four major biomolecules also called as macromolecules are proteins, carbohydrates, lipids, and nucleic acids. The four major types of biomolecules are carbohydrates, lipids, nucleic acids, and proteins.
Carbs Lipids Proteins Nucleic Acids Chart

Compare The Chemical Structure And Functions Of Carbohydrates Lipids
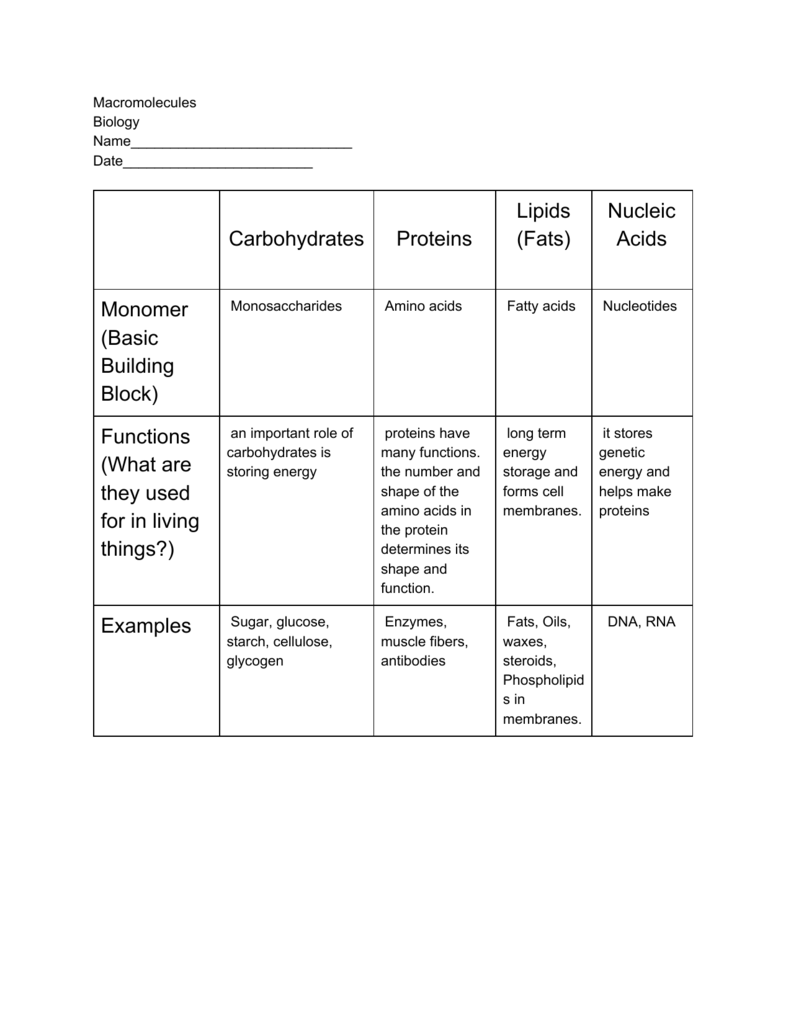
Carbohydrate Lipid Protein Nucleic Acid Chart
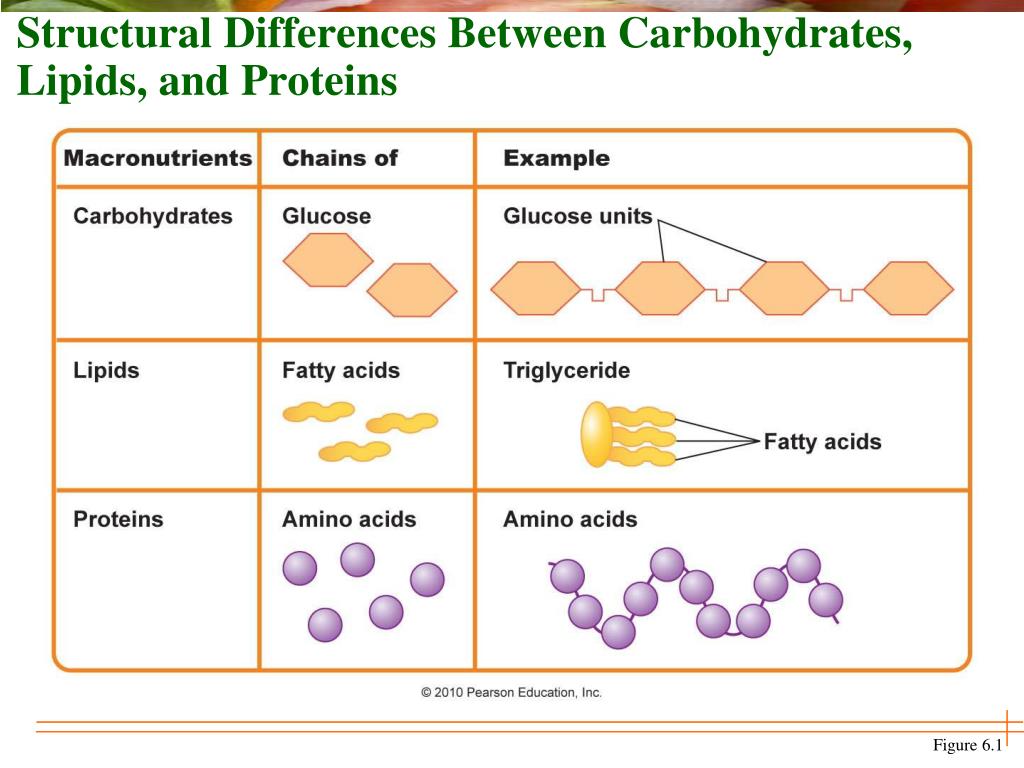
Carbohydrate Lipid Protein Nucleic Acid Chart

Carbohydrates Lipids Proteins And Nucleic Acids Chart
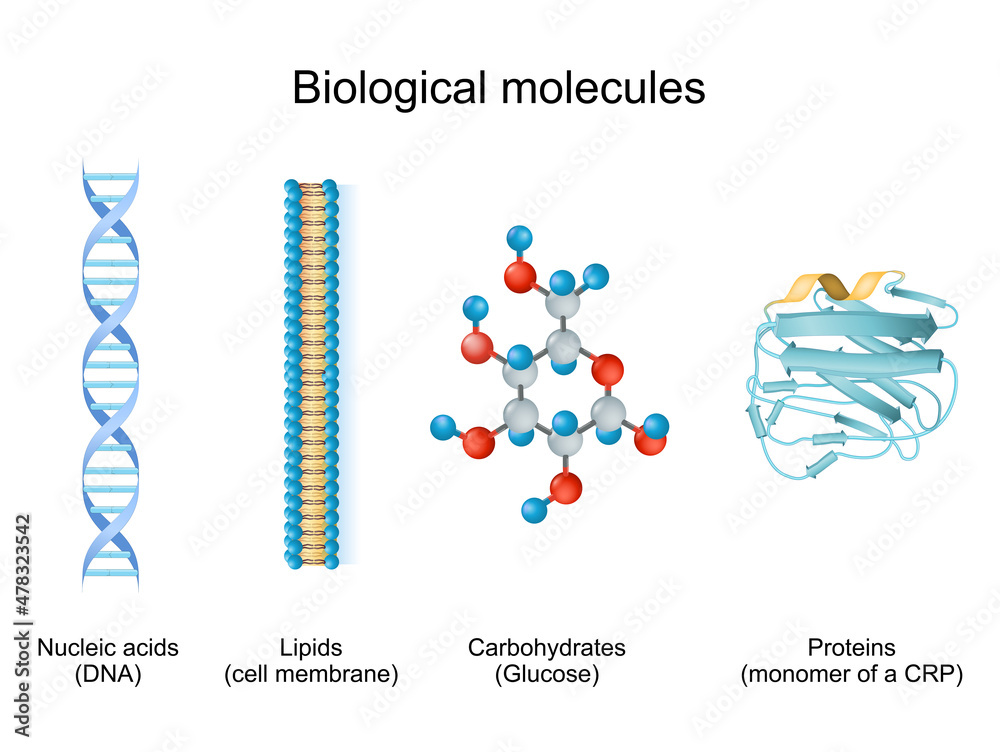
Carbohydrates Lipids Proteins And Nucleic Acids Chart vrogue.co

Compare The Chemical Structure And Functions Of Carbohydrates Lipids
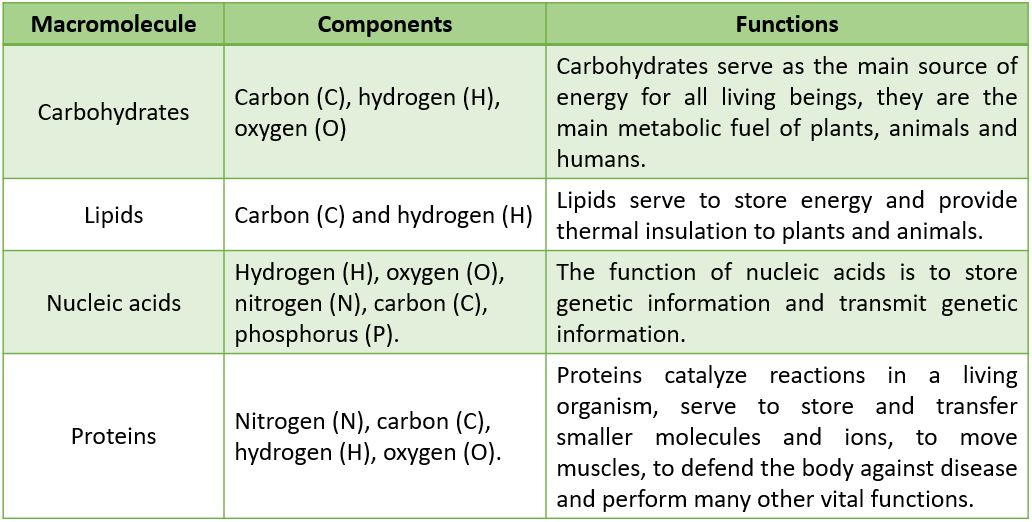
Carbohydrates Lipids Proteins And Nucleic Acids Chart vrogue.co

Four Biomolecules Structure and Function Comparison Chart

Carbohydrates Lipids Proteins And Nucleic Acids Chart
Cho, In A Ratio Of 1:2:1.
Visit This Site To See Visual Representations Of Dehydration Synthesis And Hydrolysis.
Their Functions Are To Be The Main Source Of Energy And Reserve, They Are Structural Components And They Play A Key Role In The Immune Recognition Of Cells.
The Fatty Acids From Fats Connect With Glucose Catabolism Through Acetyl Coa.
Related Post: