Anatomy Chart Back
Anatomy Chart Back - Your latissimus dorsi, or lats,. Web your back muscles are the main structural support for your trunk (torso). The column runs from the cranium to the apex of the coccyx, on the posterior aspect of the body. Your spine starts at the base of your skull (head bone) and ends at your tailbone, a part of your pelvis (the large bony structure between your abdomen and legs). Web the anatomy of the muscles of the back. Sacrum (sacral region) spine anatomy overview video. Web your spine is the long column of bones that extend from your neck to your lower back. Web your lumbar spine consists of the five bones (vertebra) in your lower back. Many of the nerves of the peripheral nervous system, or pns, branch out from the spinal cord and travel to. Web the back performs several important functions including housing and protecting the spinal cord, holding the body and head upright, bearing the weight of the upper body, transmitting this weight to the pelvic girdle and lower limbs when standing or walking, and facilitating the movements of the upper and lower limbs. Web 3d video tutorials and interactive modules on the anatomy of the back including anatomy of the musculature, vertebral column, joints and ligaments. Web this article looks at the anatomy of the back, including bones, muscles, and nerves. Your latissimus dorsi, or lats,. Your spine starts at the base of your skull (head bone) and ends at your tailbone, a. Large areas of the trunk. Superficial back muscles, intermediate back muscles and intrinsic back muscles. The spinal cord begins at the base of the brain and extends into the pelvis. Sacrum (sacral region) spine anatomy overview video. Your spine starts at the base of your skull (head bone) and ends at your tailbone, a part of your pelvis (the large. The spinal cord begins at the base of the brain and extends into the pelvis. The column runs from the cranium to the apex of the coccyx, on the posterior aspect of the body. It contains the osteology, arthrology and myology of the spine and back. Web the anatomy of the muscles of the back. Attached to the shoulder girdle. Other muscles are small and cover much less space. The cervical vertebrae, the thoracic vertebrae, the lumbar vertebrae, the sacrum and the coccyx. Each of these 3 classes have distinct roles in support, movement and/or aiding in specialised functions such as in inspiration/expiration. Web back muscles and low back pain. Your back muscles work together to allow you to bend. Your back consists of a complex array of bones, discs, nerves, joints, and muscles. Web back muscles and low back pain. Web master1305 / shutterstock. It contains and protects the spinal cord. Web your spine is the long column of bones that extend from your neck to your lower back. Each of these 3 classes have distinct roles in support, movement and/or aiding in specialised functions such as in inspiration/expiration. Attached to the posterior thorax. Web the muscles of the back are a group of strong, paired muscles that lie on the posterior aspect of the trunk. Your back consists of a complex array of bones, discs, nerves, joints, and. Web the muscles of the back can be arranged into 3 categories based on their location: Web your spine is the long column of bones that extend from your neck to your lower back. Web the back performs several important functions including housing and protecting the spinal cord, holding the body and head upright, bearing the weight of the upper. Web the muscles of the back can be classified as either deep, intermediate and superficial. Many of the nerves of the peripheral nervous system, or pns, branch out from the spinal cord and travel to. The cervical vertebrae, the thoracic vertebrae, the lumbar vertebrae, the sacrum and the coccyx. Your back muscles work together to allow you to bend over,. Web the muscles of the back are a group of strong, paired muscles that lie on the posterior aspect of the trunk. Web the spine’s four sections, from top to bottom, are the cervical (neck), thoracic (abdomen,) lumbar (lower back), and sacral (toward tailbone). Each of these 3 classes have distinct roles in support, movement and/or aiding in specialised functions. They provide movements of the spine, stability to the trunk, as well as the coordination between the movements of the limbs and trunk. Web back muscles and low back pain. Web the muscles of the back can be classified as either deep, intermediate and superficial. Web 3d video tutorials and interactive modules on the anatomy of the back including anatomy. Your spine starts at the base of your skull (head bone) and ends at your tailbone, a part of your pelvis (the large bony structure between your abdomen and legs). Web learn anatomy as you browse our collection of colorful, large and clearly labeled human body diagrams. These muscles help you move your body, including your head, neck, shoulders, arms and legs. Web the spine’s four sections, from top to bottom, are the cervical (neck), thoracic (abdomen,) lumbar (lower back), and sacral (toward tailbone). The muscles of your back support your spine, attach your pelvis and shoulders to your trunk, and provide mobility and stability to your trunk and spine. The spinal cord runs through its center. The column runs from the cranium to the apex of the coccyx, on the posterior aspect of the body. The back is the body region between the neck and the gluteal regions. Web your back muscles are the main structural support for your trunk (torso). It is part of the axial skeleton and extends from the base of the skull to the tip of the coccyx. Web your back muscles extend from the bones of your neck ( cervical vertebrae) to your lower back (lumbar spine) and then to the base of your lumbar spine ( sacrum) and tailbone ( coccyx ). Web the back performs several important functions including housing and protecting the spinal cord, holding the body and head upright, bearing the weight of the upper body, transmitting this weight to the pelvic girdle and lower limbs when standing or walking, and facilitating the movements of the upper and lower limbs. Web master1305 / shutterstock. The back muscles are divided into two large groups: Web attachments, innervation and functions of the superficial muscles of the back. Skeletal, muscular, cardiovascular, digestive, endocrine, nervous, respiratory, immune/lymphatic, urinary, female reproductive, male reproductive, integumentary.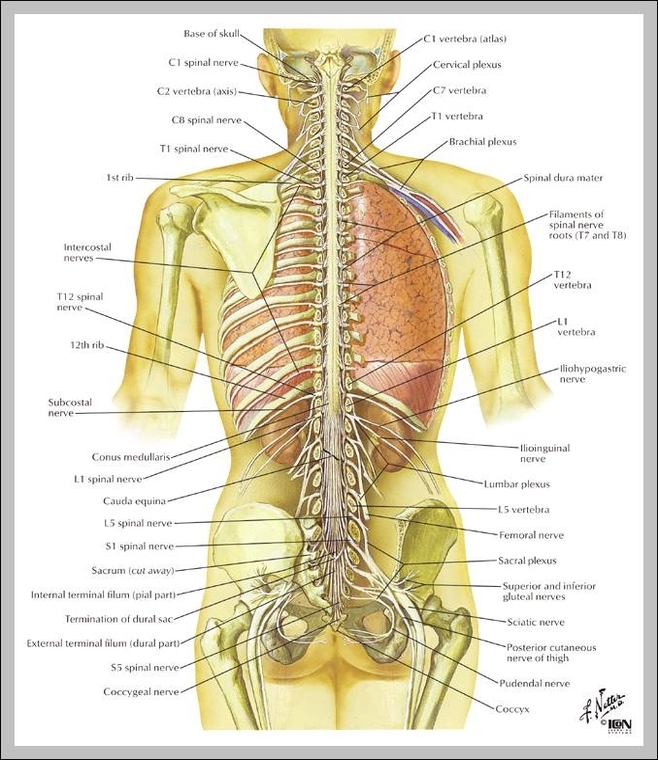
back anatomy Anatomy System Human Body Anatomy diagram and chart images

Anatomy of back muscles Diagram Quizlet

Spinal Anatomy Poster 18" X 24" Clinical Charts and Supplies
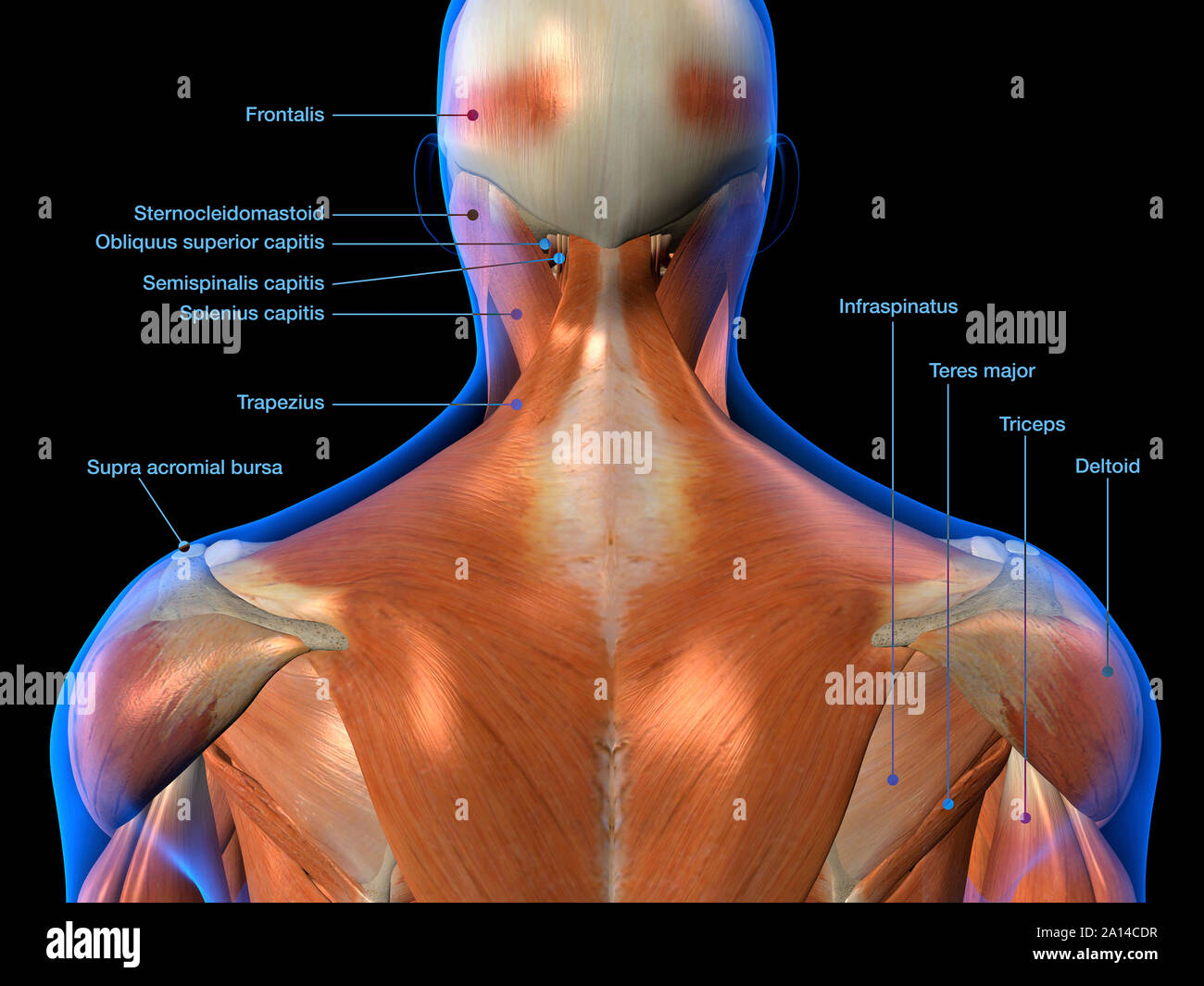
Back Muscles Anatomy Labeled
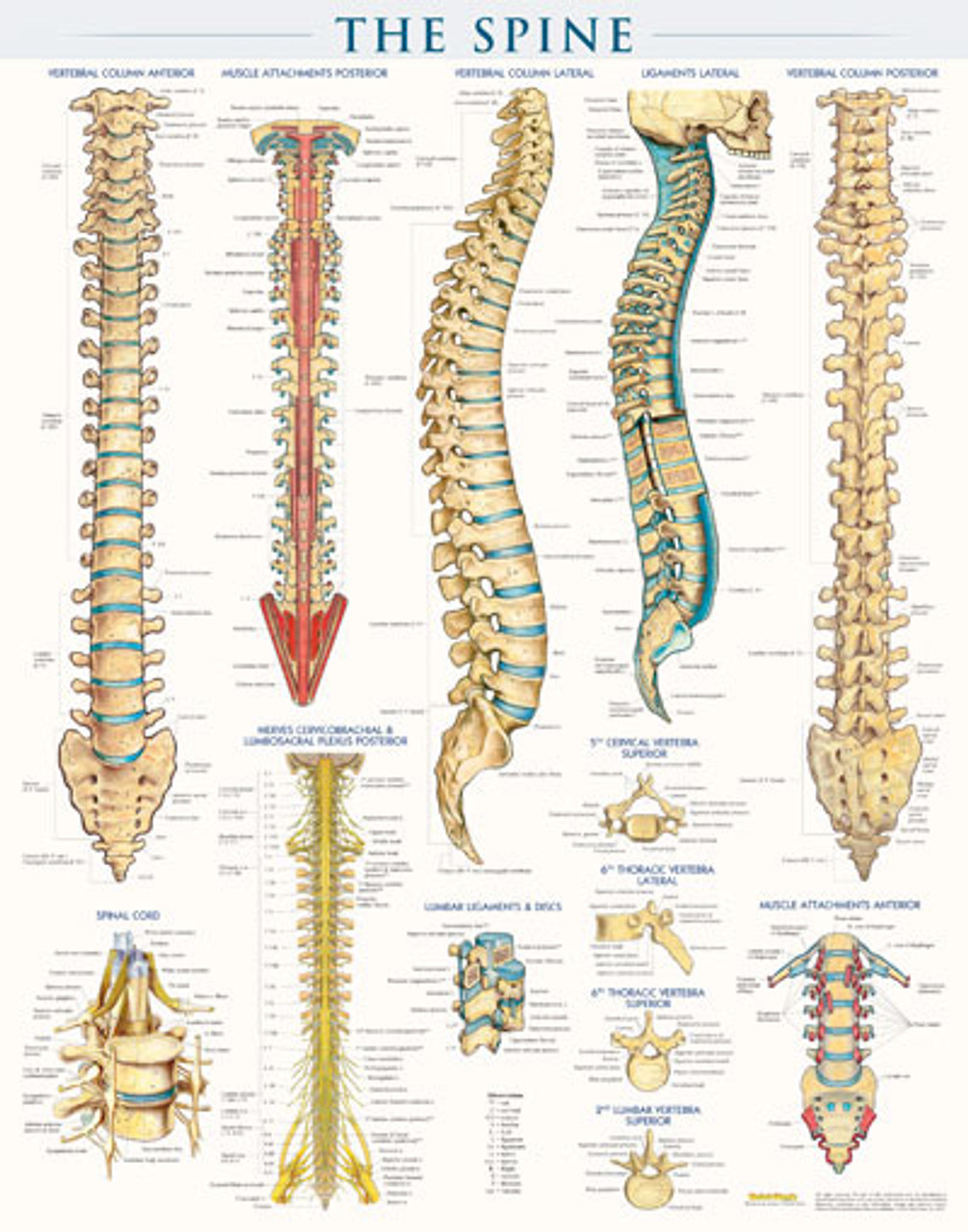
Spine Structure Poster Clinical Charts and Supplies

Lower Back Organ Anatomy Diagram Lower Back Muscle Chart Muscles

The Muscular System Deep Layers, Back Laminated Anatomy Chart Human
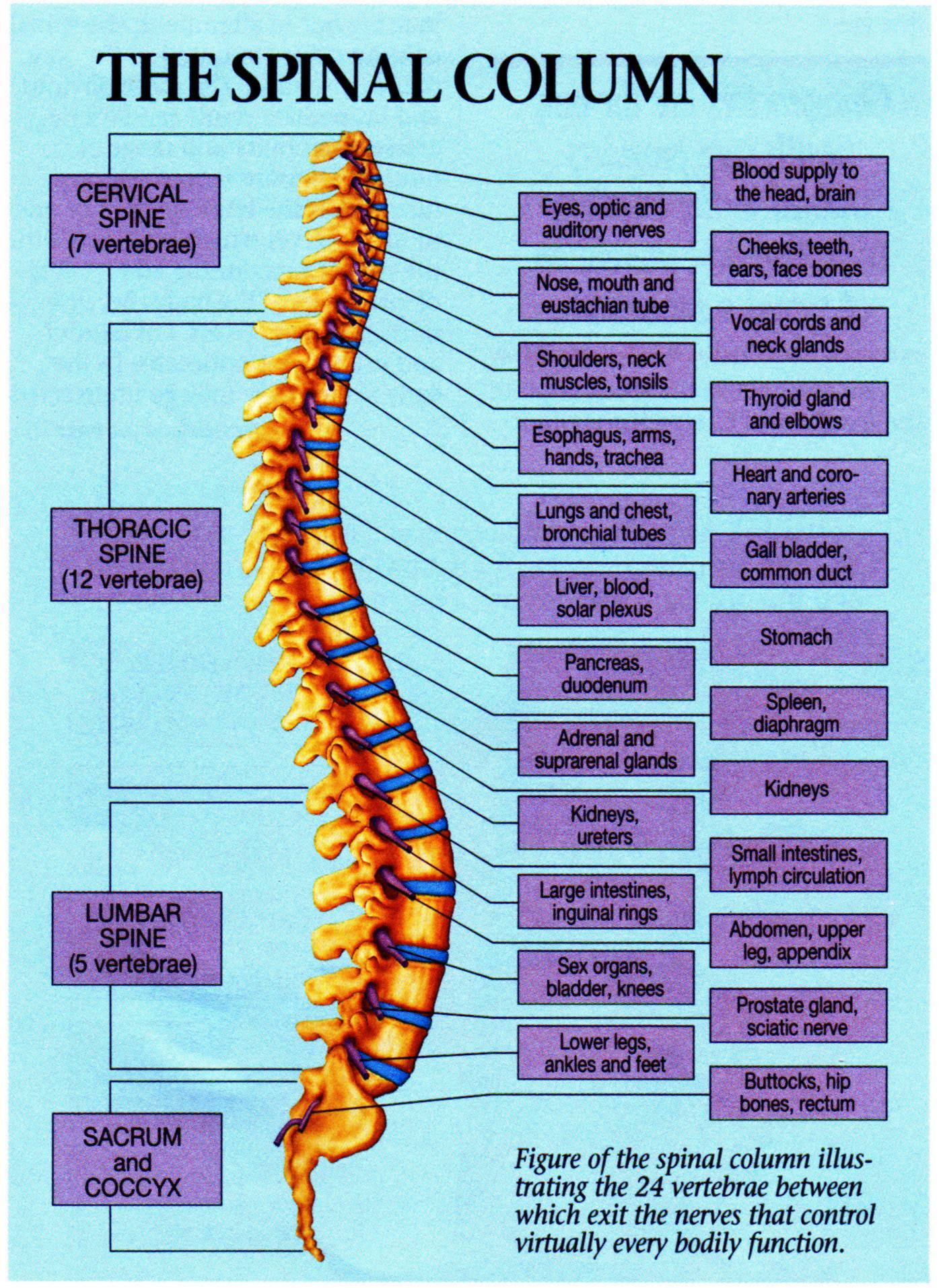
Spine Anatomy Printable Chart Free

Muscles Diagrams Diagram of muscles and anatomy charts
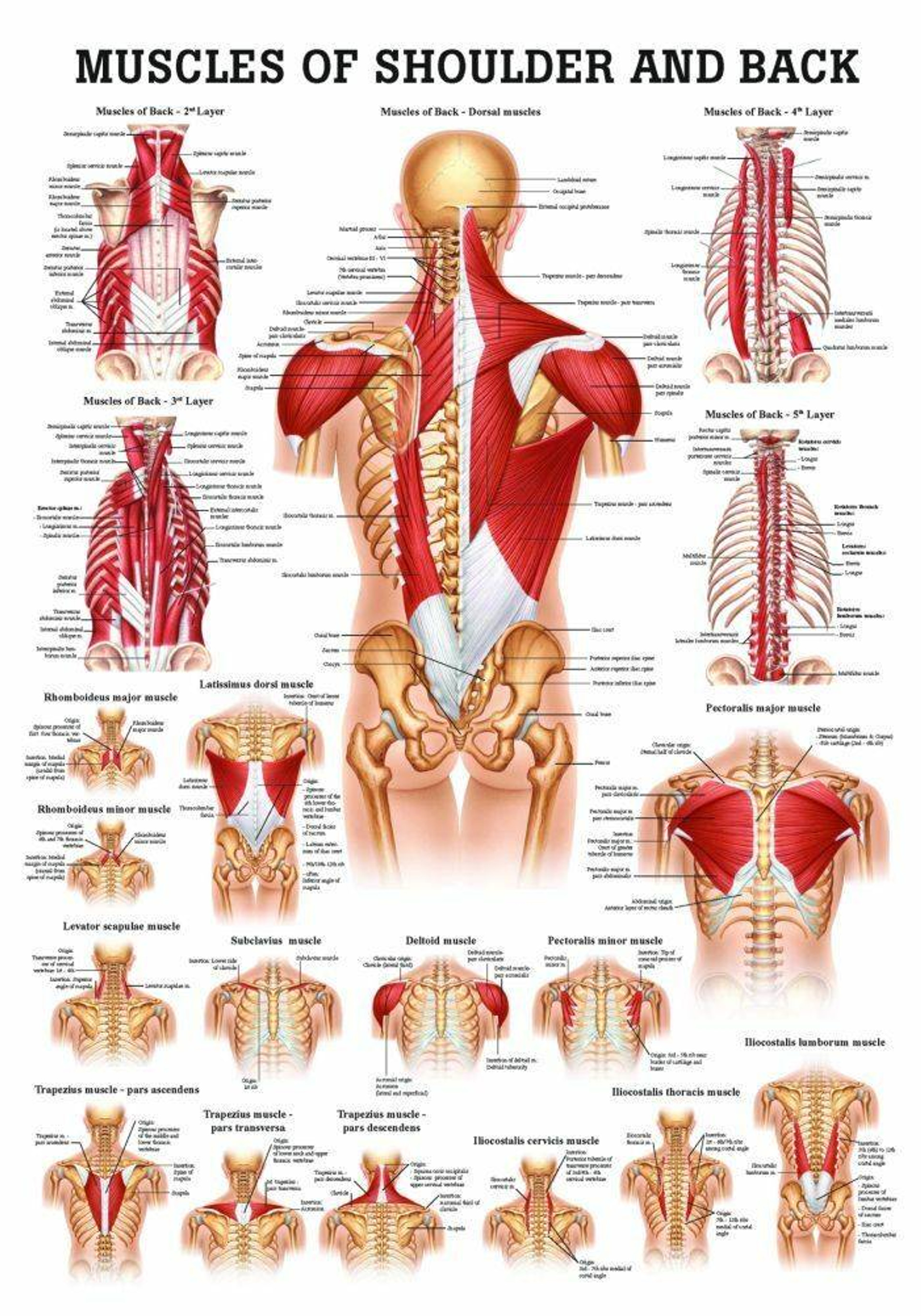
Rudiger Anatomie Muscles of the Shoulder and Back Laminated Anatomy Chart
Your Back Consists Of A Complex Array Of Bones, Discs, Nerves, Joints, And Muscles.
It Contains And Protects The Spinal Cord.
Web Your Lumbar Spine Consists Of The Five Bones (Vertebra) In Your Lower Back.
Here’s An Overview Of The Major Muscles In Your Back That You Can Identify And Effectively Stimulate Through Exercise:
Related Post: