Chart Of Electromagnetic Radiations
Chart Of Electromagnetic Radiations - Web these radiations differ in wavelength and frequency, creating a vast spectrum used in various scientific and practical applications. Classically, electromagnetic radiation consists of electromagnetic waves, which are synchronized oscillations of electric and magnetic fields. Sometimes denoted by ν instead) and wavelength λ (the greek letter lambda) associated with it. Web since electromagnetic radiation acts as a wave, then any particular electromagnetic wave will have a frequency ( f ; Web a diagram of the electromagnetic spectrum, showing various properties across the range of frequencies and wavelengths. Web this map is printed on premium 32lb matte paper with fade resistant, premium inks and includes a white border on all sides to allow for matting and framing. The spectrum is divided into separate bands, with different names for the electromagnetic waves within each. Web in physics, electromagnetic radiation (emr) consists of waves of the electromagnetic (em) field, which propagate through space and carry momentum and electromagnetic radiant energy. Web define the electromagnetic spectrum, and describe it in terms of frequencies and wavelengths; Radio waves have the longest wavelength, and gamma rays have the shortest wavelength. Web these radiations differ in wavelength and frequency, creating a vast spectrum used in various scientific and practical applications. In this wave the electric and magnetic fields change their magnitude and direction each second. The electromagnetic spectrum can be expressed in terms of energy, wavelength or frequency. Web electromagnetic radiation, in classical physics, the flow of energy at the speed. This is a reproduction of the chart of electromagnetic radiations, characterized by a common speed in a vacuum. Describe and explain the differences and similarities of each section of the electromagnetic spectrum and the applications of radiation from those sections To the left of the electromagnetic spectrum are radio waves, the lowest frequency form of radiation with the longest wavelengths.. This classification is known as the electromagnetic spectrum. This is a reproduction of the chart of electromagnetic radiations, characterized by a common speed in a vacuum. The following table shows us this spectrum, which consists of all the types of electromagnetic radiation that exist in our universe. The spectrum is divided into separate bands, with different names for the electromagnetic. Radio waves have the longest wavelength, and gamma rays have the shortest wavelength. This is a reproduction of the chart of electromagnetic radiations, characterized by a common speed in a vacuum. Web these radiations differ in wavelength and frequency, creating a vast spectrum used in various scientific and practical applications. The spectrum is divided into separate bands, with different names. Web each section of the electromagnetic (em) spectrum has characteristic energy levels, wavelengths, and frequencies. Web this map is printed on premium 32lb matte paper with fade resistant, premium inks and includes a white border on all sides to allow for matting and framing. The part of the electromagnetic spectrum with the longest wavelength and lowest frequency is radio. Web. Longer wavelengths with lower frequencies make up the radio spectrum. The electromagnetic spectrum can be expressed in terms of energy, wavelength or frequency. Web electromagnetic radiation, in classical physics, the flow of energy at the speed of light through free space or through a material medium in the form of the electric and magnetic fields that make up electromagnetic waves. Web these radiations differ in wavelength and frequency, creating a vast spectrum used in various scientific and practical applications. This is a reproduction of the chart of electromagnetic radiations, characterized by a common speed in a vacuum. Web in physics, electromagnetic radiation (emr) consists of waves of the electromagnetic (em) field, which propagate through space and carry momentum and electromagnetic. Web these radiations differ in wavelength and frequency, creating a vast spectrum used in various scientific and practical applications. Radio waves have the longest wavelength, and gamma rays have the shortest wavelength. Classically, electromagnetic radiation consists of electromagnetic waves, which are synchronized oscillations of electric and magnetic fields. Web here are the main classes of electromagnetic radiation, listed from lowest. Web these radiations differ in wavelength and frequency, creating a vast spectrum used in various scientific and practical applications. Radio waves have the longest wavelength, and gamma rays have the shortest wavelength. Describe and explain the differences and similarities of each section of the electromagnetic spectrum and the applications of radiation from those sections Web this map is printed on. Web since electromagnetic radiation acts as a wave, then any particular electromagnetic wave will have a frequency ( f ; Web electromagnetic waves can be classified and arranged according to their various wavelengths/frequencies; This is a reproduction of the chart of electromagnetic radiations, characterized by a common speed in a vacuum. Web here are the main classes of electromagnetic radiation,. This is a reproduction of the chart of electromagnetic radiations, characterized by a common speed in a vacuum. Web here are the main classes of electromagnetic radiation, listed from lowest to highest frequency: Web define the electromagnetic spectrum, and describe it in terms of frequencies and wavelengths; In this wave the electric and magnetic fields change their magnitude and direction each second. Web electromagnetic waves can be classified and arranged according to their various wavelengths/frequencies; Web since electromagnetic radiation acts as a wave, then any particular electromagnetic wave will have a frequency ( f ; The electromagnetic spectrum can be expressed in terms of energy, wavelength or frequency. Web these radiations differ in wavelength and frequency, creating a vast spectrum used in various scientific and practical applications. Sometimes denoted by ν instead) and wavelength λ (the greek letter lambda) associated with it. Web this map is printed on premium 32lb matte paper with fade resistant, premium inks and includes a white border on all sides to allow for matting and framing. Web there are seven groups of the electromagnetic spectrum. Describe and explain the differences and similarities of each section of the electromagnetic spectrum and the applications of radiation from those sections Web electromagnetic radiation is, classically speaking, a wave of electric and magnetic fields propagating at the speed of light c through empty space. Radio waves have the longest wavelength, and gamma rays have the shortest wavelength. This classification is known as the electromagnetic spectrum. Web in physics, electromagnetic radiation (emr) consists of waves of the electromagnetic (em) field, which propagate through space and carry momentum and electromagnetic radiant energy.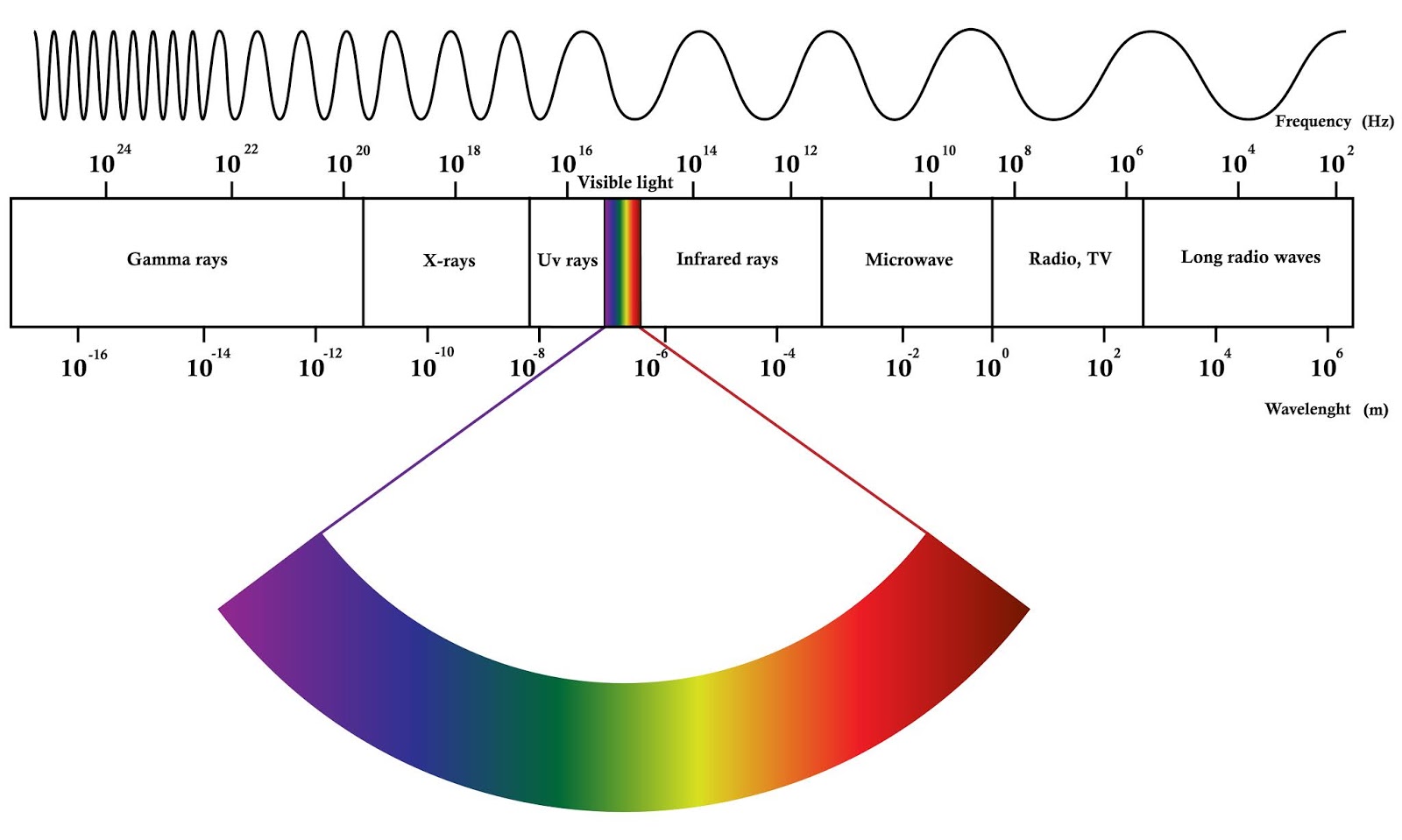
PAPER 604 RADIATION (EMR)

Chart Of Spectrum
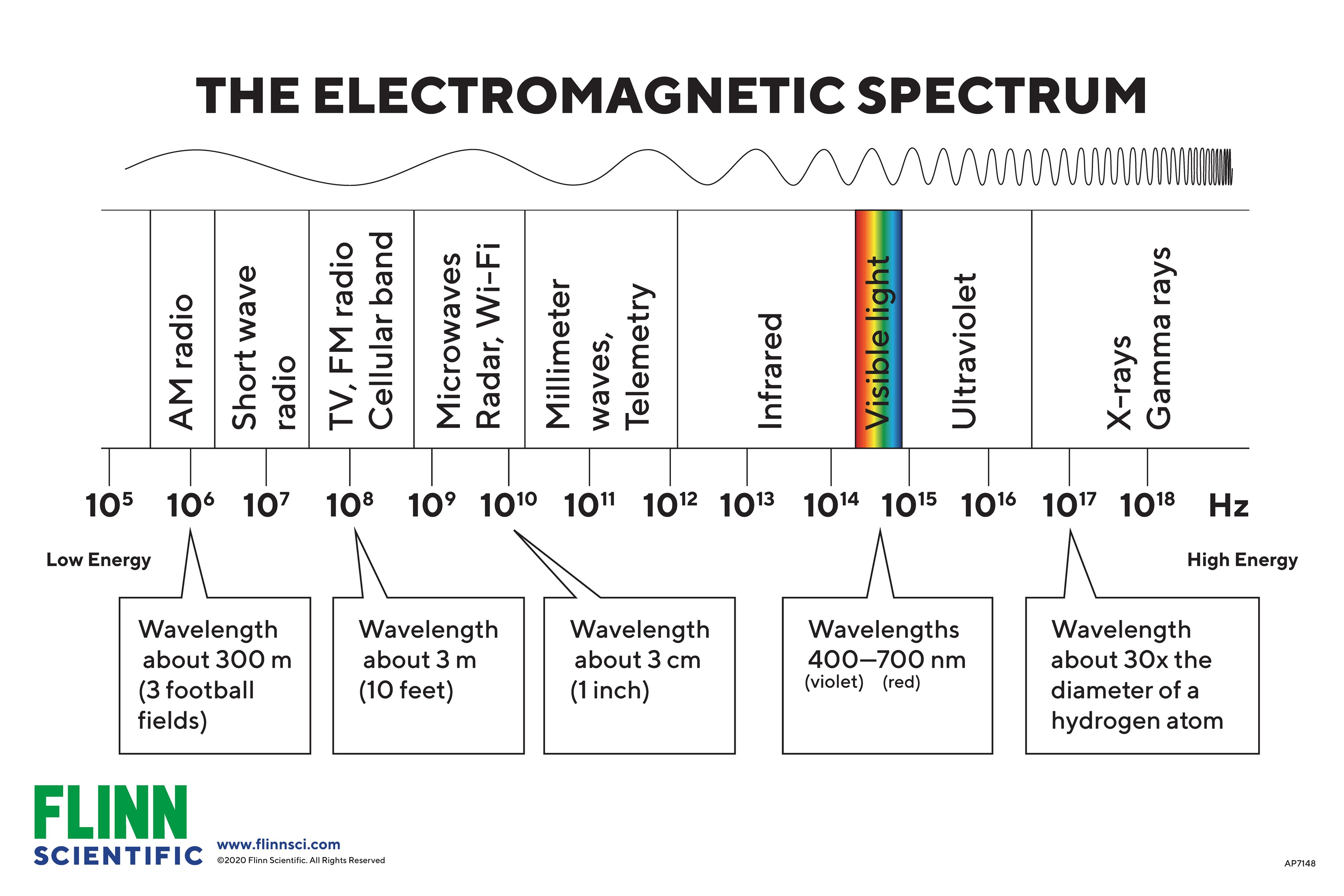
Flinn Spectrum Charts for Physics and Physical Science

The Spectrum HubbleSite

Elektronik Hobi

The Spectrum Mini Physics Learn Physics
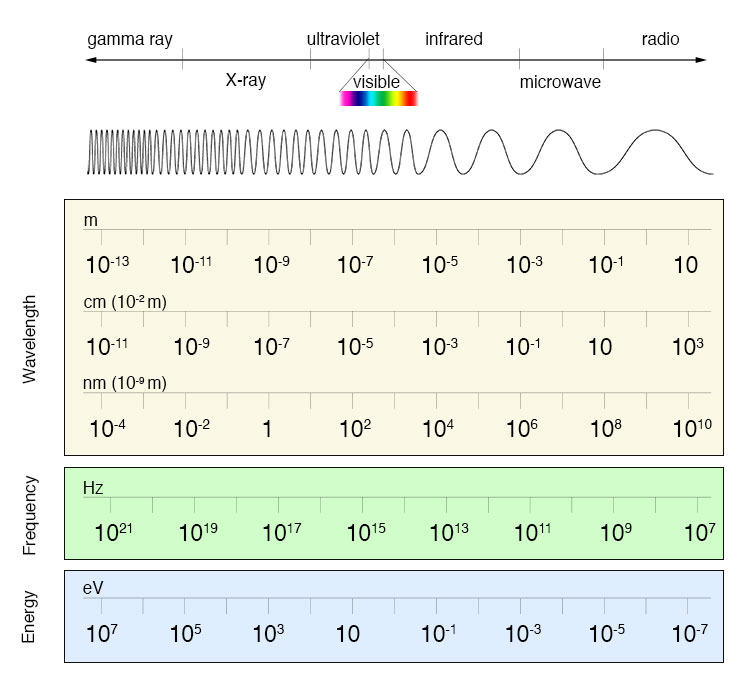
Spectrum
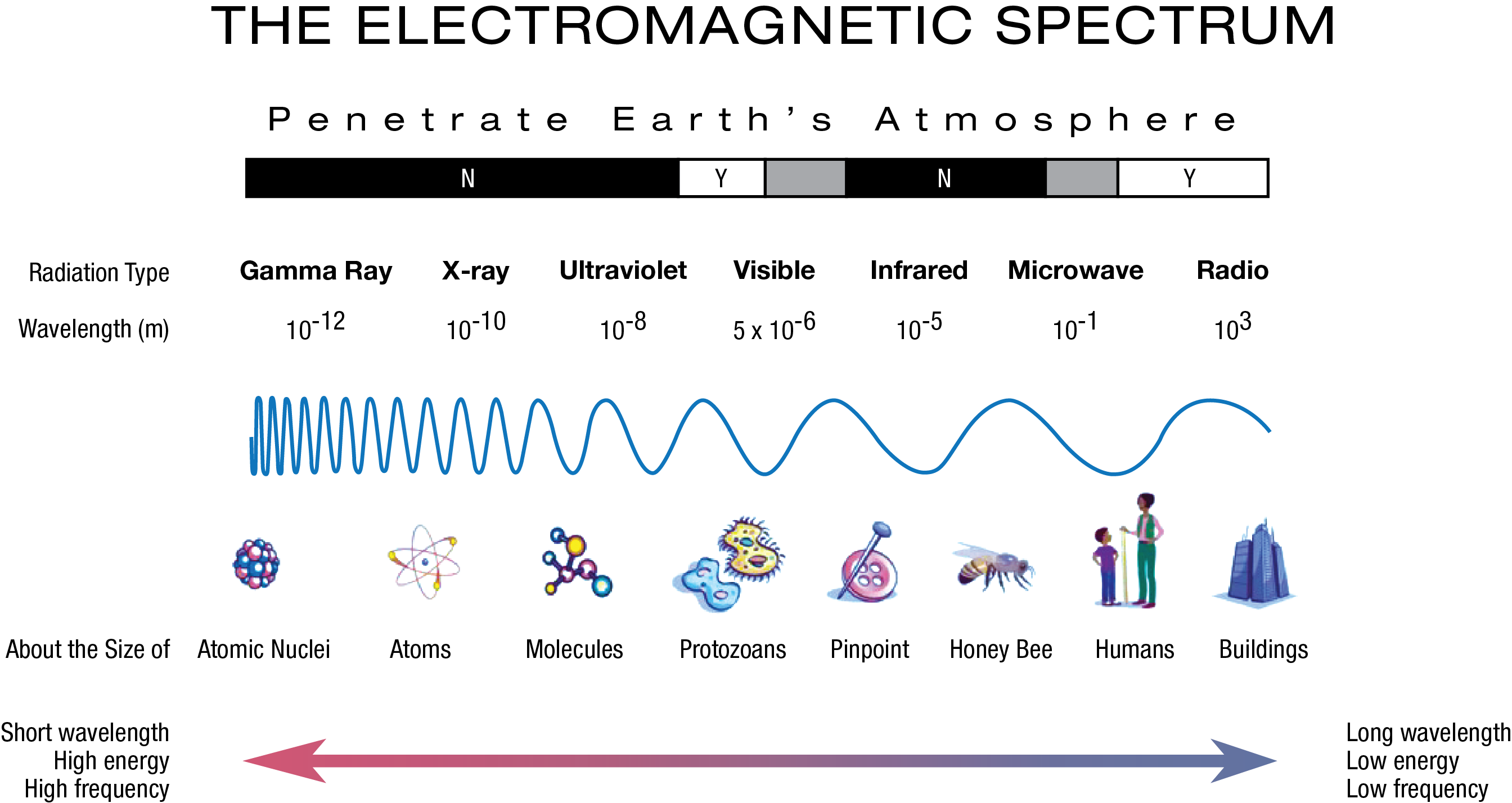
Spectrum Wavelengths Chart

Spectrum and Visible Light Educational Reference Chart
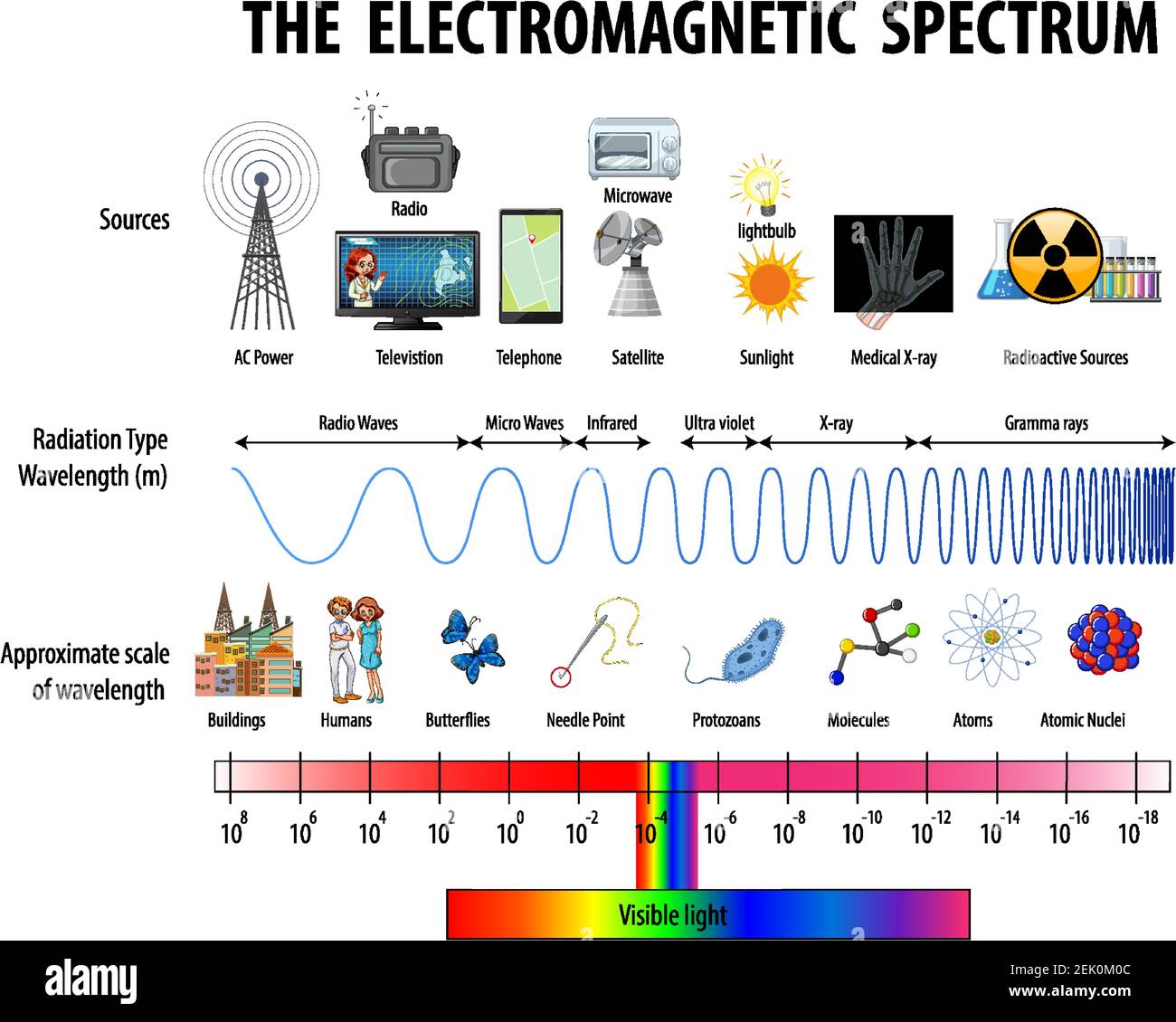
Spectrum Wavelengths Chart
The Electromagnetic Spectrum Is Comprised Of All Frequencies Of Electromagnetic Radiation That Propagate Energy And Travel Through Space In The Form Of Waves.
The Following Table Shows Us This Spectrum, Which Consists Of All The Types Of Electromagnetic Radiation That Exist In Our Universe.
Web Each Section Of The Electromagnetic (Em) Spectrum Has Characteristic Energy Levels, Wavelengths, And Frequencies.
Web Electromagnetic Radiation, In Classical Physics, The Flow Of Energy At The Speed Of Light Through Free Space Or Through A Material Medium In The Form Of The Electric And Magnetic Fields That Make Up Electromagnetic Waves Such.
Related Post: