Cathodic Protection Design
Cathodic Protection Design - Web cathodic protection is an industrial technique for controlling metallic corrosion. (a) parameters that define the anode bed, (b) parameters that define the structure to be protected (cathode), and (c). Uncoated, coated, concrete reinforcing steel, pipeline). A simple method of protection connects the metal to be protected to a more easily corroded sacrificial metal to act as the anode. Web cathodic protection (cp) is a technique used for prevention of corrosion by making a metal, which would ordinarily behave like an anode and corrode, instead behave like a cathode and reduce or eliminate corrosion attack. Web steel monopile support structures for offshore wind turbines require protection from corrosion and consideration with respect to biofouling on their external and internal surfaces. Web design and installation of cathodic protection systems. Web cathodic protection (cp) is an important component for the sustainability of many metal structures. Sce as the protection limit for stainless steels. It can be applied in any situation where the environment surrounding the metal acts as a conductor for electric current. Web the basic principles for the design of sacrificial anode cathodic protection systems are: The sacrificial metal then corrodes. While localized damaged surfaces can be patched, ongoing degradation may weaken the integrity of the overall infrastructure. Here we discuss 12 things to consider. The corrosion process and afecting factors. When applied properly, cp stops the corrosion reaction from occurring to protect the integrity of metallic structures. The most common impressed current voltage sources are rectifiers, which can break down. It can be applied in any situation where the environment surrounding the metal acts as a conductor for electric current. Web the basic principles for the design of sacrificial anode. First, the total amount of current is determined, then the output per anode is determined. The corrosion process and afecting factors. 5.1.1 uncoated steel three design current densities are given: (a) parameters that define the anode bed, (b) parameters that define the structure to be protected (cathode), and (c). Web cathodic protection (cp) is an important component for the sustainability. Web cathodic protection is an industrial technique for controlling metallic corrosion. Web cathodic protection is a popular protection method for preventing corrosion in pipelines, offshore oil platforms and other steel structures. Cathodic protection is commonly used on buried and submerged metallic structures like pipelines, underground storage tanks, locks, subsea equipment, offshore floaters, harbors, and. The prevailing cp standards do not. Web cathodic protection (cp) is an important component for the sustainability of many metal structures. However, cathodic protection, often in conjunction with protective coatings, is also used to protect immersed parts of bare steel surfaces (including coating damaged areas) from corrosion. Cathodic protection can affect the corrosion fatigue properties of the structure. Web examples of cathodic protection and cathodic prevention. / k æ ˈ θ ɒ d ɪ k / ⓘ) is a technique used to control the corrosion of a metal surface by making it the cathode of an electrochemical cell. When applied properly, cp stops the corrosion reaction from occurring to protect the integrity of metallic structures. Uncoated, coated, concrete reinforcing steel, pipeline). (a) parameters that define the. Web cathodic protection design for stainless steel. In general, cathodic protection can have following effects on the fatigue: Web protective coatings are the most efficient way to protect ship steel structures from corrosion. Web designing a galvanic anode cp system using formulas ‐ example. As it will be described in detail below, there are two kinds of cathodic protection: Web cathodic protection (cp) is a technique used for prevention of corrosion by making a metal, which would ordinarily behave like an anode and corrode, instead behave like a cathode and reduce or eliminate corrosion attack. Web the basic principles for the design of sacrificial anode cathodic protection systems are: Web pipeline cathodic protection design requires a wide number of. As it will be described in detail below, there are two kinds of cathodic protection: Web steel monopile support structures for offshore wind turbines require protection from corrosion and consideration with respect to biofouling on their external and internal surfaces. 5.1.1 uncoated steel three design current densities are given: Web metallic structures in contact with water, soil, concrete, and moist. The corrosion process and afecting factors. Sce as the protection limit for stainless steels. Web protective coatings are the most efficient way to protect ship steel structures from corrosion. In general, cathodic protection can have following effects on the fatigue: Web cathodic protection (cp) is an important component for the sustainability of many metal structures. Web properly designed cathodic protection systems can reduce the corrosion rate to negligible amounts. Cathodic protection is commonly used on buried and submerged metallic structures like pipelines, underground storage tanks, locks, subsea equipment, offshore floaters, harbors, and. Web the ‘initial’ and ‘final’ design current densities, ici (initial) and icf (final), respectively, give a measure of the anticipated cathodic current density demand to achieve cathodic protection of a bare metal surface within a reasonably short period of time. Web the basic principles for the design of sacrificial anode cathodic protection systems are: Web cathodic protection is a popular protection method for preventing corrosion in pipelines, offshore oil platforms and other steel structures. Web cathodic protection and coatings are common methods for protecting buried metal structures, including pipelines, in soil and water. Web protective coatings are the most efficient way to protect ship steel structures from corrosion. The most common impressed current voltage sources are rectifiers, which can break down. When applied properly, cp stops the corrosion reaction from occurring to protect the integrity of metallic structures. Cathodic protection (cp) works effectively to protect the external surfaces of monopiles, but internally, byproducts from aluminum sacrificial anode cp (sacp) and. As it will be described in detail below, there are two kinds of cathodic protection: Uncoated, coated, concrete reinforcing steel, pipeline). Sce as the protection limit for stainless steels. In general, cathodic protection can have following effects on the fatigue: The prevailing cp standards do not give detailed guidelines for cp of stainless steel, especially related to current demand. Corrosion types based on mechanism.
Impressed Current Cathodic Protection ICCP Systems
Schematic showing cathodic protection methods using sacrificial anode
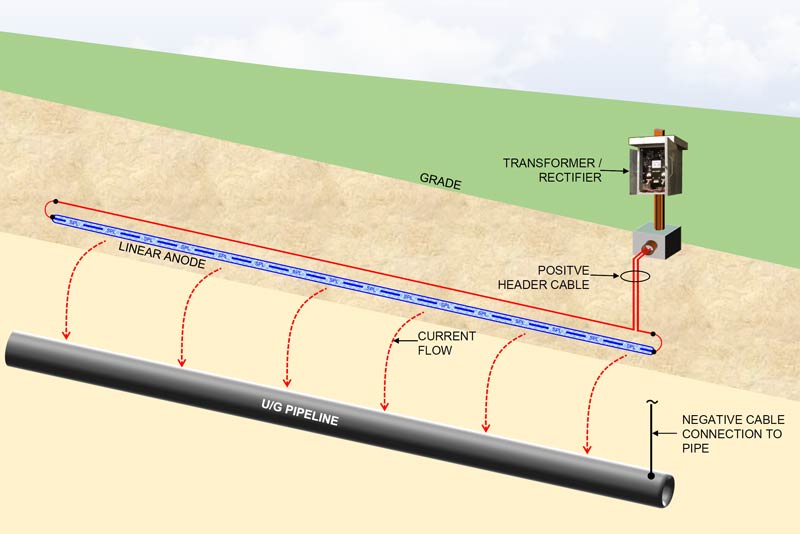
cathodic protection ground bed design gabrielleephotography

Cathodic Protection System Services B&B Lightning Protection — B&B
CATHODIC PROTECTION & CORROSION CONTROL MR Vision Oilfield Services

Cathodic Protection System Drawings

Cathodic Protection Pipeline Protection

Cathodic Protection 101
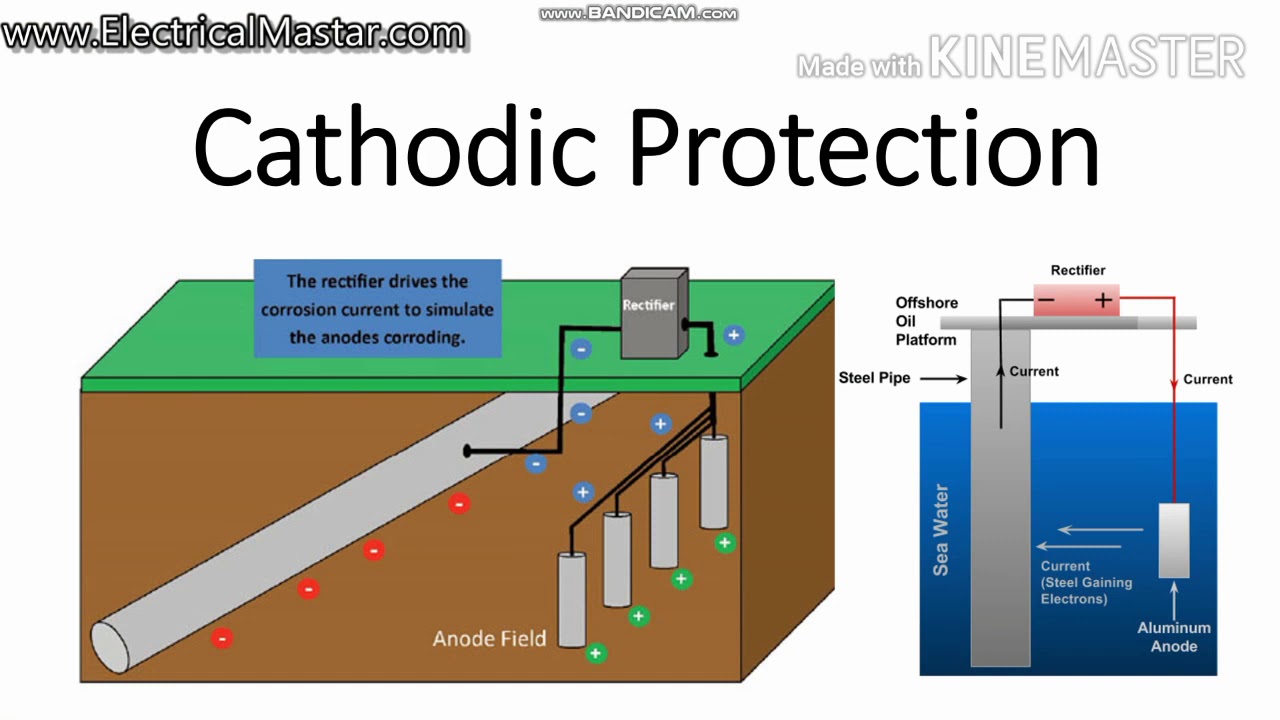
Cathodic Protection Electrical System
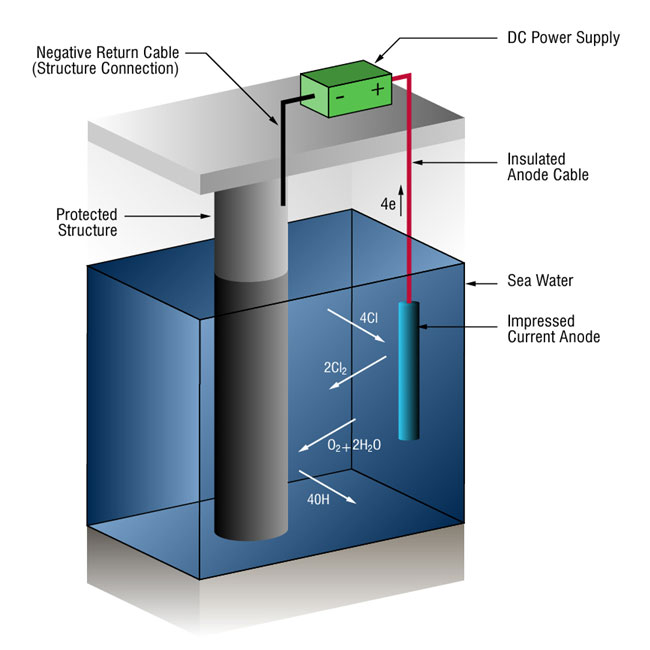
Cathodic Protection
Web Cathodic Protection (Cp) Is A Technique Used For Prevention Of Corrosion By Making A Metal, Which Would Ordinarily Behave Like An Anode And Corrode, Instead Behave Like A Cathode And Reduce Or Eliminate Corrosion Attack.
5.1.1 Uncoated Steel Three Design Current Densities Are Given:
Cathodic Protection Can Affect The Corrosion Fatigue Properties Of The Structure.
Cathodic Protection (Cp) Is One Of The Few Methods That Successfully Mitigates Corrosion.
Related Post: