Xsl Template Match
Xsl Template Match - Web (ii) match template: This element must have either the match attribute or the name attribute set. Match</strong>=@href | @conref | @conrefend>. Web the element is used to build templates. Web xslt element is a basic building block in xslt and it provides a way to define rules for transforming specific elements into a source xml document. @* matches any attribute node, and node() matches any other kind of node (element, text node, processing instruction or comment). Web i want to write an xsl template that matches attributes instead of nodes, i would think that having something like this: In that particular case the / means the root of the xml document. Web in essence, an xslt stylesheet is a set of rules, called templates, which declare that any node that matches this specific pattern should be manipulated in this. The match attribute can also be used to. Web i am trying to do a conditional match on an xml and to return the value from a sibling node. In that particular case the / means the root of the xml document. Match</strong>=@href | @conref | @conrefend>. I would like to match on the records which have the attribute of gender. Web here is the correct xslt 1.0. Web here is the correct xslt 1.0 way of matching (in xslt 2.0 use the matches () function with a real regex as the pattern argument): Web in essence, an xslt stylesheet is a set of rules, called templates, which declare that any node that matches this specific pattern should be manipulated in this. If we add a select attribute. Web (ii) match template: Web the xsl:template element defines an output producing template. Web the element applies a template to the current element or to the current element's child nodes. Web when it matches an xml node, the template is invoked by the processor. Match</strong>> matches the root node of the source document. Match</strong>> matches the root node of the source document. @* matches any attribute node, and node() matches any other kind of node (element, text node, processing instruction or comment). The xsl:template element contains the @match attribute that contains a matching pattern or xpath applied at the input nodes. The match attribute is used to associate the template with an xml. Match</strong>> matches the root node of the source document. Web in essence, an xslt stylesheet is a set of rules, called templates, which declare that any node that matches this specific pattern should be manipulated in this. In that particular case the / means the root of the xml document. Web the element contains rules to apply when a specified. Web i want to write an xsl template that matches attributes instead of nodes, i would think that having something like this: Web match</strong>=/> matches only the document root itself, and sets it as the context. I would like to match on the records which have the attribute of gender. Match</strong>> matches the root node of the source document. Web. Web the element contains rules to apply when a specified node is matched. This element must have either the match attribute or the name attribute set. @* matches any attribute node, and node() matches any other kind of node (element, text node, processing instruction or comment). Web in essence, an xslt stylesheet is a set of rules, called templates, which. The match attribute is used to associate the template with an xml element. Match</strong>> matches the root node of the source document. Web xslt element is a basic building block in xslt and it provides a way to define rules for transforming specific elements into a source xml document. Web an xslt stylesheet starts with the xsl:stylesheet element, which contains. Match</strong>=@href | @conref | @conrefend>. Web i want to write an xsl template that matches attributes instead of nodes, i would think that having something like this: Web the element is used to build templates. @* matches any attribute node, and node() matches any other kind of node (element, text node, processing instruction or comment). Match</strong>> matches the root node. Web the element defines an output producing template. Web match</strong>=/> matches only the document root itself, and sets it as the context. Web i am trying to do a conditional match on an xml and to return the value from a sibling node. Match</strong>> matches the root node of the source document. Web when it matches an xml node, the. In that particular case the / means the root of the xml document. The match attribute can also be used to. I would like to match on the records which have the attribute of gender. Web the element applies a template to the current element or to the current element's child nodes. Web in essence, an xslt stylesheet is a set of rules, called templates, which declare that any node that matches this specific pattern should be manipulated in this. Web an xslt stylesheet starts with the xsl:stylesheet element, which contains all the templates used to create the final output. If we add a select attribute to the.
Xsl Template Match

Xsl Template Match
Xsl Template Match

Xsl Template Match
Solved body

Xsl Template Match
Xsl Template Match
Xsl Template Match
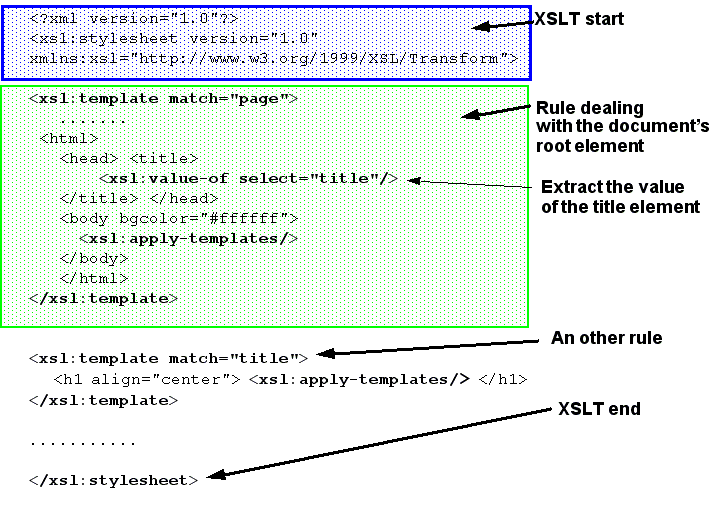
Xsl Template Match

Xsl Template Match
Web When It Matches An Xml Node, The Template Is Invoked By The Processor.
Web I Am Trying To Do A Conditional Match On An Xml And To Return The Value From A Sibling Node.
Web Match</Strong>=/> Matches Only The Document Root Itself, And Sets It As The Context.
Web i want to write an xsl template that matches attributes instead of nodes, i would think that having something like this: @* matches any attribute node, and node() matches any other kind of node (element, text node, processing instruction or comment). Web the element is used to build templates. Match</strong>> matches the root node of the source document.
Web The Xsl:template Element Defines An Output Producing Template.
Web the element contains rules to apply when a specified node is matched. That rule will always match, even an empty document, whereas /* will. Web the element defines an output producing template. Web (ii) match template:
