Unix Permissions Chart
Unix Permissions Chart - Web understanding linux permissions is critical for anyone looking to control access to files and directories on their system. This guide aims to provide you with a. Grants the capability to read,. Web on linux, there are three different permission types for files and directories: Linux file permissions, chmod, & umask. These permissions are assigned to three categories of users: Web everyone ( o) based on these three groups, i now know that: Web let us say you wish to give full permission to owner, read & execute permission to group, and read only permission to others, then you need to calculate. If the file is owned by the user, the user permissions determine the access. Files and directories are owned by a user. Files and directories are also assigned to a group. Understanding and setting unix file permissions. Web chmod is a command that lets you change the permissions of a file or directory to all types of users. Web understanding linux permissions is critical for anyone looking to control access to files and directories on their system. Web based on these articles: Web this article will cover standard linux file systems permissions, dig further into special permissions, and wrap up with an explanation of default permissions using. Web use this handy cheat sheet with examples for how to manage linux users and permissions. Web our linux permissions cheat sheet covers important file and directory access commands to help you understand and manipulate. Here’s the syntax of the chmod command: Web understanding linux permissions is critical for anyone looking to control access to files and directories on their system. Web what permissions do they have? Web every file on a linux system has three types of permissions: If the file is owned by the user, the user permissions determine the access. How to use setuid setgid and stickybit. Web based on these articles: Web understanding linux permissions is critical for anyone looking to control access to files and directories on their system. Linux file permissions, chmod, & umask. Web use this handy cheat sheet with examples for how to manage linux users and permissions. Web understanding linux permissions is critical for anyone looking to control access to files and directories on their system. Web everyone ( o) based on these three groups, i now know that: The read permission means that the file/directory is readable. This guide aims to provide you with a. These permissions are assigned to three categories of users: Grants the capability to read,. Web access to a file has three levels: Web this article will cover standard linux file systems permissions, dig further into special permissions, and wrap up with an explanation of default permissions using. Files and directories are also assigned to a group. Files and directories are owned by a user. Web access to a file has three levels: The read permission means that the file/directory is readable. Web every file on a linux system has three types of permissions: Web the basic building blocks of unix permissions are the read, write, and execute permissions, which have been described below −. Grants the capability to read,. Linux file permissions, chmod, & umask. How to use setuid setgid and stickybit. Web chmod is a command that lets you change the permissions of a file or directory to all types of users. Web access to a file has three levels: Understanding and setting unix file permissions. Web permissions on linux systems are split into three classes: Here’s the syntax of the chmod command: If the group of the file. If the file is owned by the user, the user permissions determine the access. Web understanding linux permissions is critical for anyone looking to control access to files and directories on their system. These permissions are assigned to three categories of users: Files and directories are owned by a user. Web everyone ( o) based on these three groups, i now know that: Web chmod is a command that lets you change the permissions of a file or directory to all types of users. Here’s the syntax of the chmod command: Web let us say you wish to give full permission to owner, read & execute permission to group, and read only permission to others, then you need to calculate. Web in linux, access to the files is managed through the file permissions, attributes, and ownership. Web the basic building blocks of unix permissions are the read, write, and execute permissions, which have been described below −. Web chmod is a command that lets you change the permissions of a file or directory to all types of users. Web on linux, there are three different permission types for files and directories: Web this article will cover standard linux file systems permissions, dig further into special permissions, and wrap up with an explanation of default permissions using. These permissions are assigned to three categories of users: If the group of the file. Grants the capability to read,. Files and directories are owned by a user. This ensures that only authorized users and processes can. This guide aims to provide you with a. Web every file on a linux system has three types of permissions: Linux permissions cheat sheet by seth kenlon add. Web use this handy cheat sheet with examples for how to manage linux users and permissions. Here’s the syntax of the chmod command:
Linux Permissions Chart A Visual Reference of Charts Chart Master
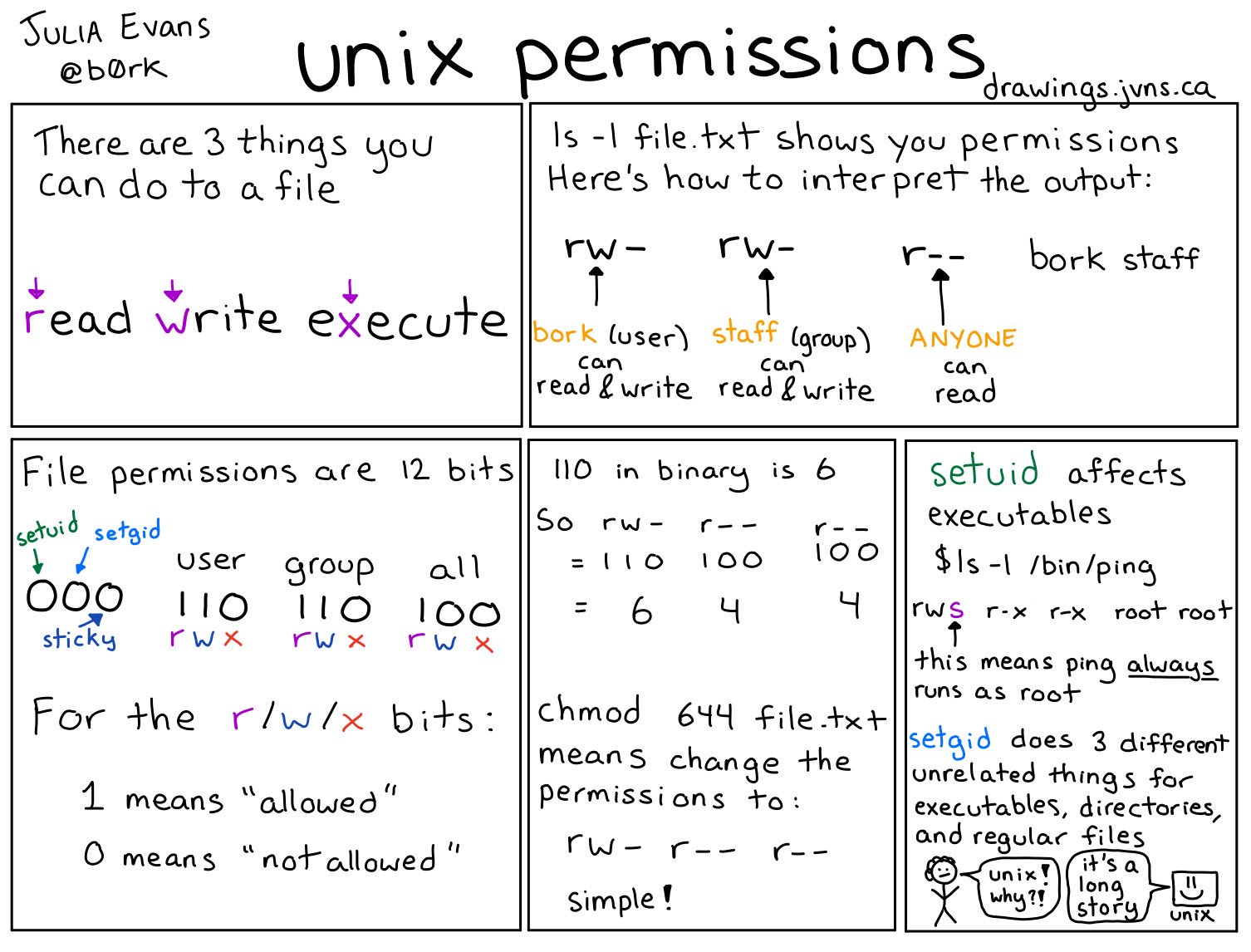
🔎Julia Evans🔍 on Twitter "unix permissions…

Unix File Permissions Chart

Numeric permissions table. Linux, Linux permissions, Sample resume

linux Understanding UNIX permissions and file types Unix & Linux
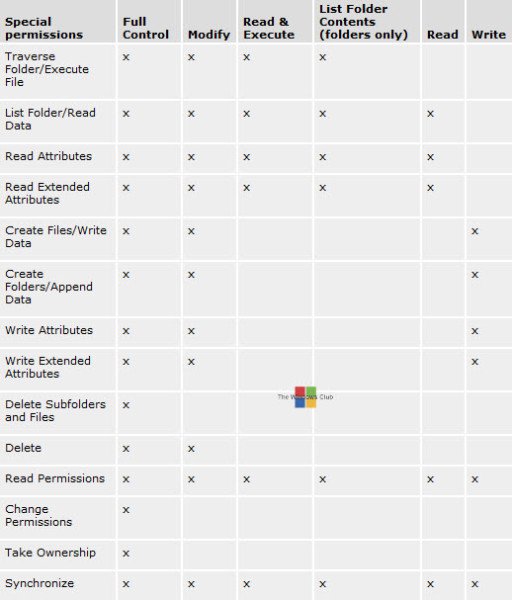
Unix File Permissions Chart
Practice Linux Permissions Basics with 7 Activities [Part II] by

Unix Permissions — The Easy Way. Index of all chmod permutations by
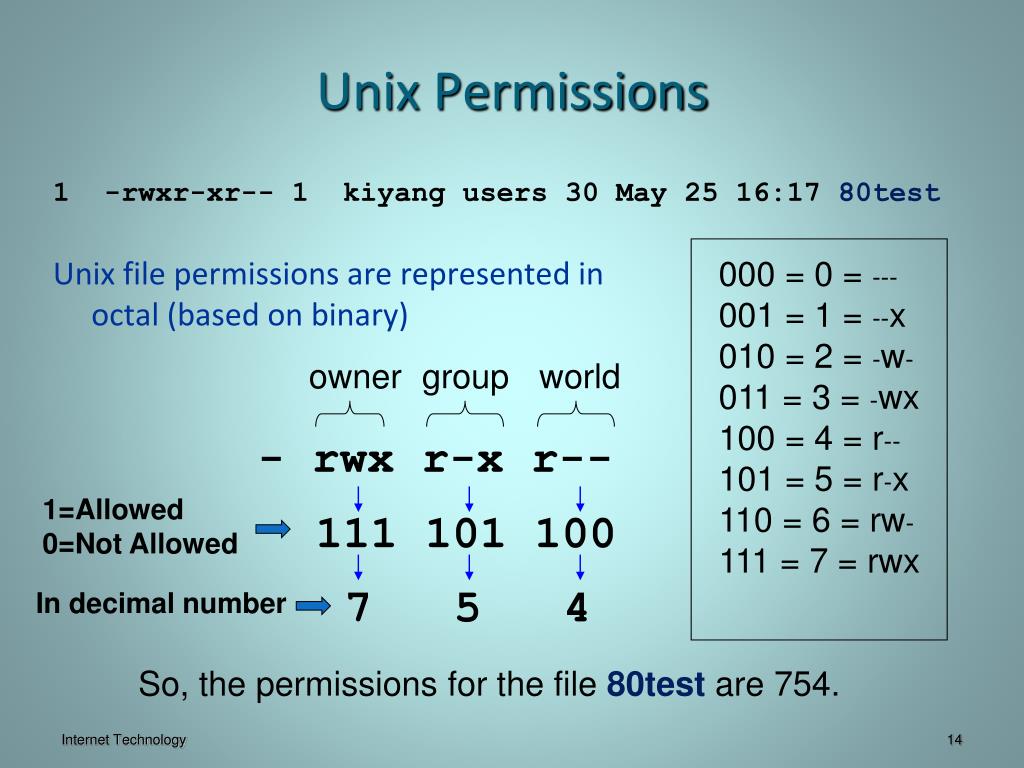
PPT UNIX Basics PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID3891007

Unix File Permissions Chart
How To Use Setuid Setgid And Stickybit.
Web Access To A File Has Three Levels:
Files And Directories Are Also Assigned To A Group.
Web Understanding Linux Permissions Is Critical For Anyone Looking To Control Access To Files And Directories On Their System.
Related Post: