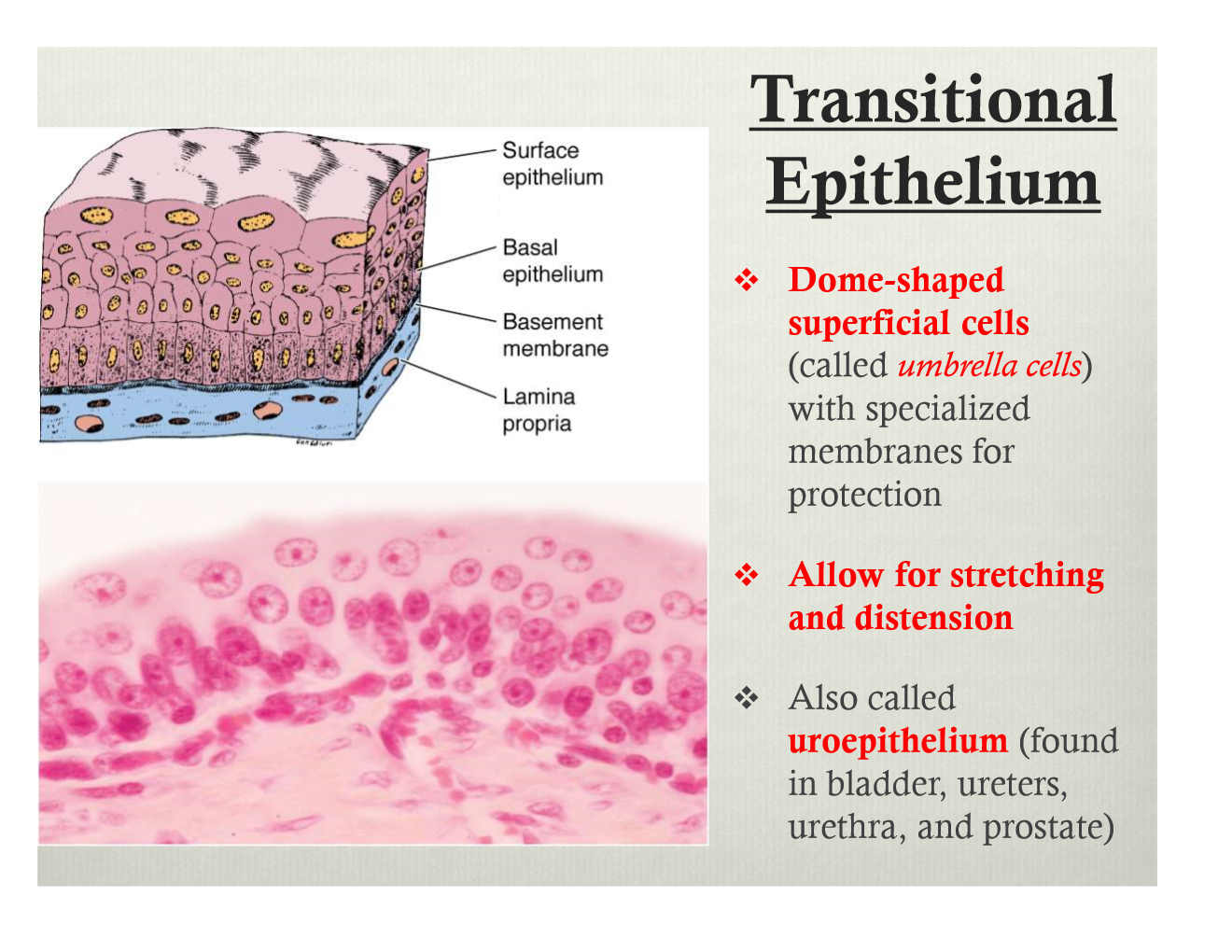
Transitional Epithelium Drawing
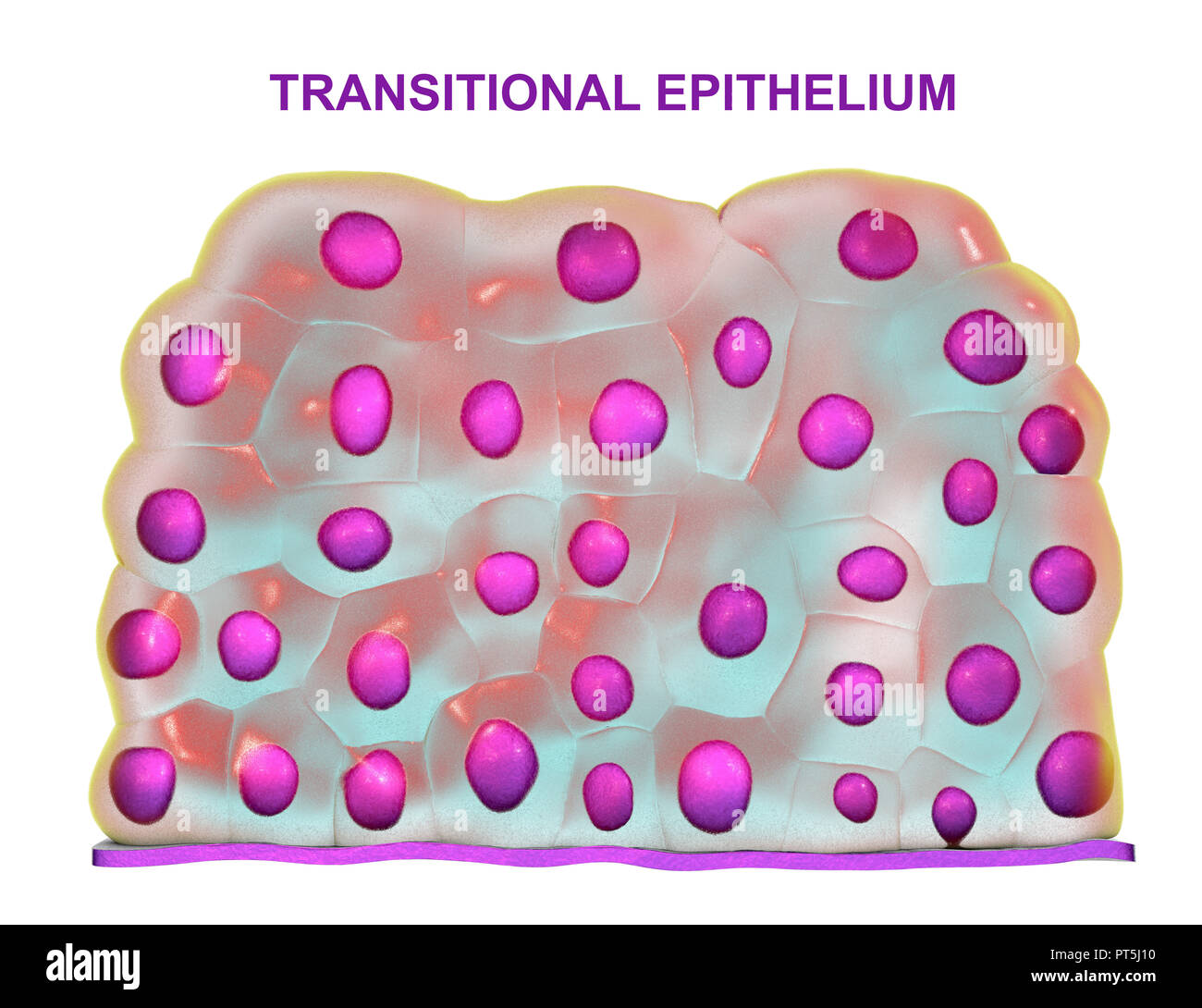
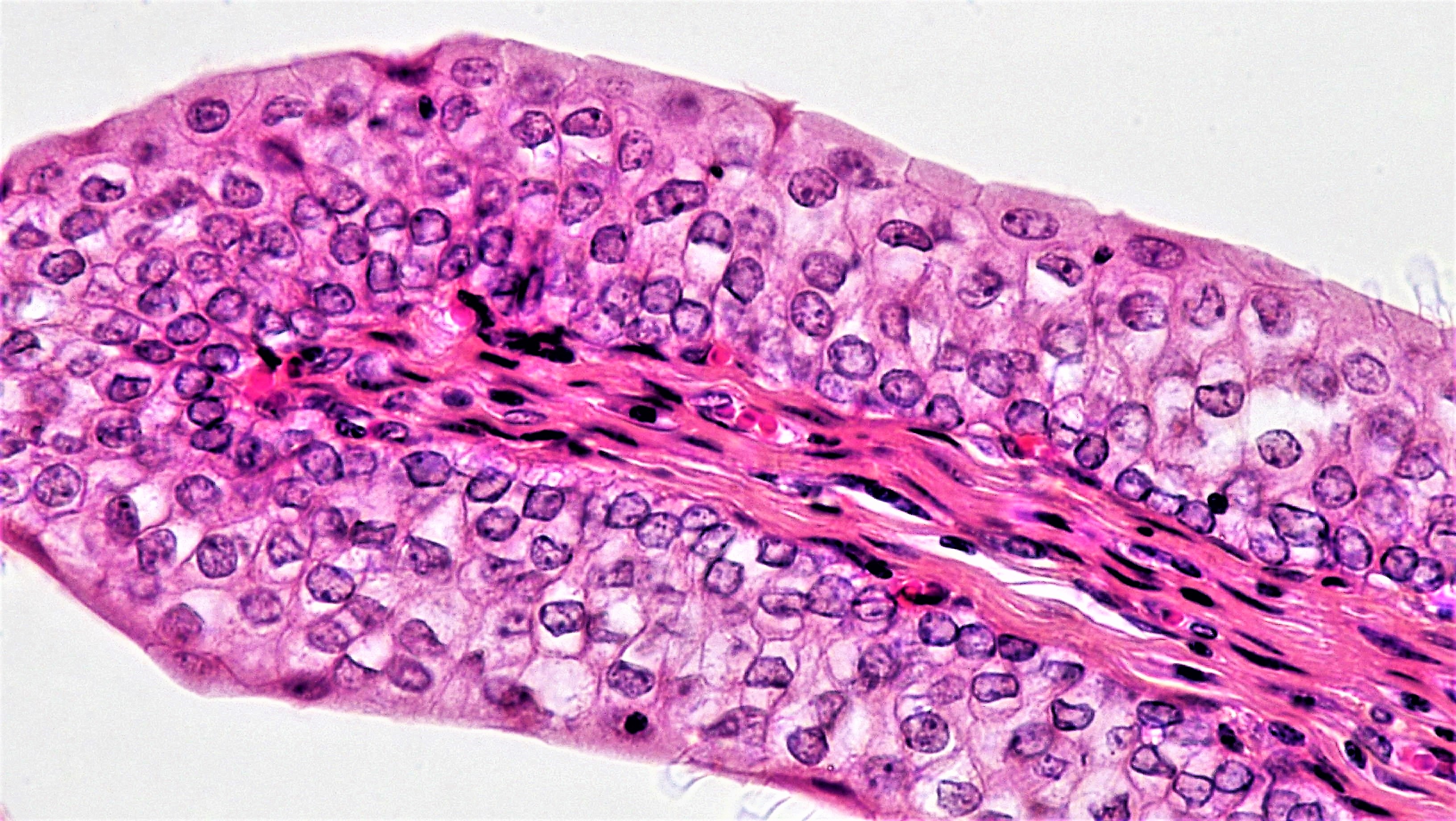
Transitional Epithelium Drawing - Web transitional epithelium (urothelium) is a specialized stratified epithelium found in the lower urinary tract. Web learn about the structure and function of transitional epithelium, a stratified tissue that lines the urinary tract. Transitional cells line the whole of the urinary tract from the inside of the kidney, down the ureters, into the bladder and all but the last part of the urethra. The thickness of transitional epithelium depends on the state of distension of the organ. It rapidly adapts to distention and contraction by changing from a taller to. In its relaxed state, the cells usually appear more cuboidal or. Web transitional epithelium is a layer of cells that forms the mucosal lining of your ureters, a portion of your urethra, and your urinary bladder. When the organ is contracted, many layers of cells are present and the. Web transitional epithelium, high power. The bladder is contracted so the epithelium is thick. The thickness of transitional epithelium depends on the state of distension of the organ. Cells of simple squamous epithelium have the following. The bladder is contracted so the epithelium is thick. Web learn about the structure and function of transitional epithelium, a stratified tissue that lines the urinary tract. Web transitional epithelium, high power. See images, diagrams, and interactive activities to identify and. The thickness of transitional epithelium depends on the state of distension of the organ. Web transitional epithelium is a stratified epithelium in which the shape of the surface cells changes (undergoes transitions) depending on the degree of stretch. Web transitional epithelium is found solely in the urinary tract. Web transitional epithelial. Transitional cells line the whole of the urinary tract from the inside of the kidney, down the ureters, into the bladder and all but the last part of the urethra. Web learn about the structure and function of transitional epithelium, a stratified tissue that lines the urinary tract. The thickness of transitional epithelium depends on the state of distension of. Web transitional epithelium is found solely in the urinary tract. Transitional cells line the whole of the urinary tract from the inside of the kidney, down the ureters, into the bladder and all but the last part of the urethra. It rapidly adapts to distention and contraction by changing from a taller to. Cells of simple squamous epithelium have the. When the organ is contracted, many layers of cells are present and the. Cells of simple squamous epithelium have the following. Web description and photographs of transitional epithelium in the kidney and bladder, including electron micrographs showing distensible surface cells. Web transitional epithelium is a layer of cells that forms the mucosal lining of your ureters, a portion of your. When the organ is contracted, many layers of cells are present and the. Web transitional epithelium is found solely in the urinary tract. It changes shape in response to stretch. In its relaxed state, the cells usually appear more cuboidal or. It rapidly adapts to distention and contraction by changing from a taller to. Web transitional epithelium is a layer of cells that forms the mucosal lining of your ureters, a portion of your urethra, and your urinary bladder. Cells of simple squamous epithelium have the following. Web transitional epithelium is a type of stratified epithelium composed of several layers of cells, with the morphology of cells varying depending on the function of the. In its relaxed state, the cells usually appear more cuboidal or. Cells of simple squamous epithelium have the following. It changes shape in response to stretch. The first pages illustrate introductory concepts for those new to. Web transitional epithelium, high power. Web transitional epithelium is a layer of cells that forms the mucosal lining of your ureters, a portion of your urethra, and your urinary bladder. Web transitional epithelium is found solely in the urinary tract. Web learn about the structure and function of transitional epithelium, a stratified tissue that lines the urinary tract. Cells of simple squamous epithelium have the. See images, diagrams, and interactive activities to identify and. Cells of simple squamous epithelium have the following. It rapidly adapts to distention and contraction by changing from a taller to. Web transitional epithelium (urothelium) junctional complexes. Web transitional epithelial cells are epithelial cells specialized to change shape if they are stretched laterally. Web transitional epithelium, high power. When the organ is contracted, many layers of cells are present and the. Web learn about the structure and function of transitional epithelium, a stratified tissue that lines the urinary tract. It rapidly adapts to distention and contraction by changing from a taller to. Web transitional epithelium (urothelium) is a specialized stratified epithelium found in the lower urinary tract. Web description and photographs of transitional epithelium in the kidney and bladder, including electron micrographs showing distensible surface cells. Transitional cells line the whole of the urinary tract from the inside of the kidney, down the ureters, into the bladder and all but the last part of the urethra. Web transitional epithelium is found solely in the urinary tract. Web transitional epithelium is a layer of cells that forms the mucosal lining of your ureters, a portion of your urethra, and your urinary bladder. Web transitional epithelium (urothelium) junctional complexes. See images, diagrams, and interactive activities to identify and. Web transitional epithelium is a stratified epithelium in which the shape of the surface cells changes (undergoes transitions) depending on the degree of stretch. In its relaxed state, the cells usually appear more cuboidal or. Web transitional epithelium is a type of stratified epithelium composed of several layers of cells, with the morphology of cells varying depending on the function of the organ. It changes shape in response to stretch. The first pages illustrate introductory concepts for those new to.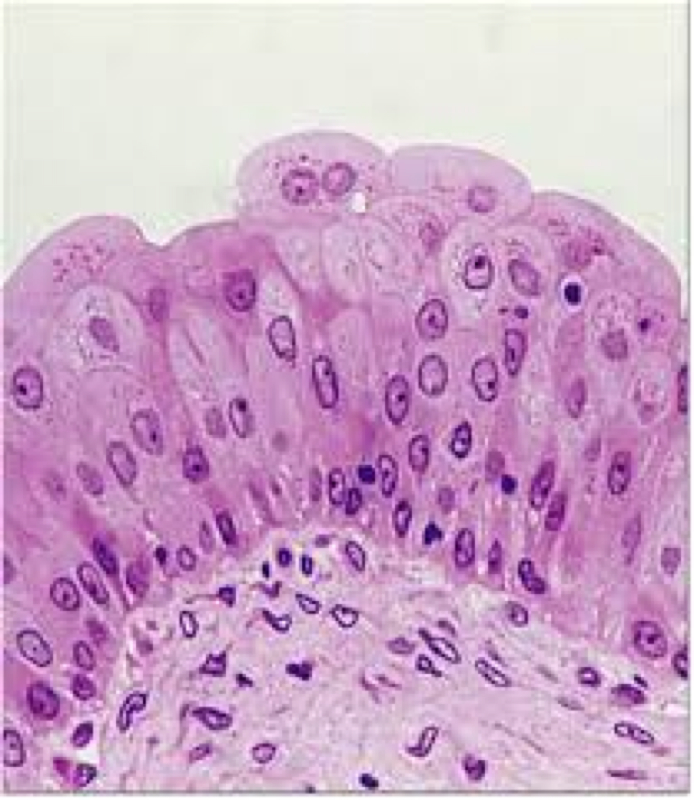
Epithelial Tissues Anatomy 101
Transitional Epithelium Anatomy And Physiology Histol vrogue.co

Transitional Epithelium Histology

Transitional Epithelium Diagram Quizlet

Transitional epithelium Histology slides, Medical laboratory science
Transitional epithelium hires stock photography and images Alamy

Image Gallery transitional epithelium

transitional epithelium Diagram Quizlet

Tissue The Living Fabric Tissue biology, Human anatomy and
Simple For Transitional Epithelium Professional 2 Easily Interior
The Thickness Of Transitional Epithelium Depends On The State Of Distension Of The Organ.
Cells Of Simple Squamous Epithelium Have The Following.
Web Transitional Epithelial Cells Are Epithelial Cells Specialized To Change Shape If They Are Stretched Laterally.
The Bladder Is Contracted So The Epithelium Is Thick.
Related Post: