Swamp Cooler Temperature Chart
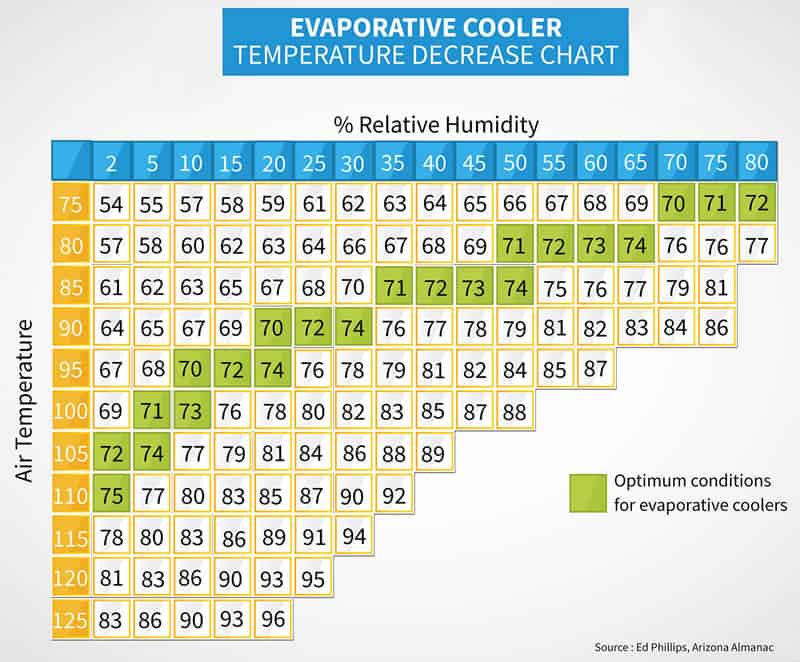
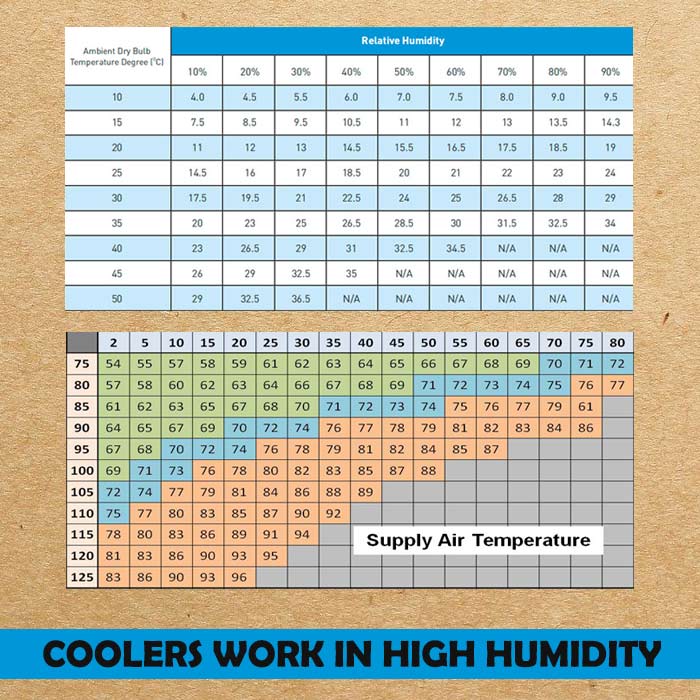
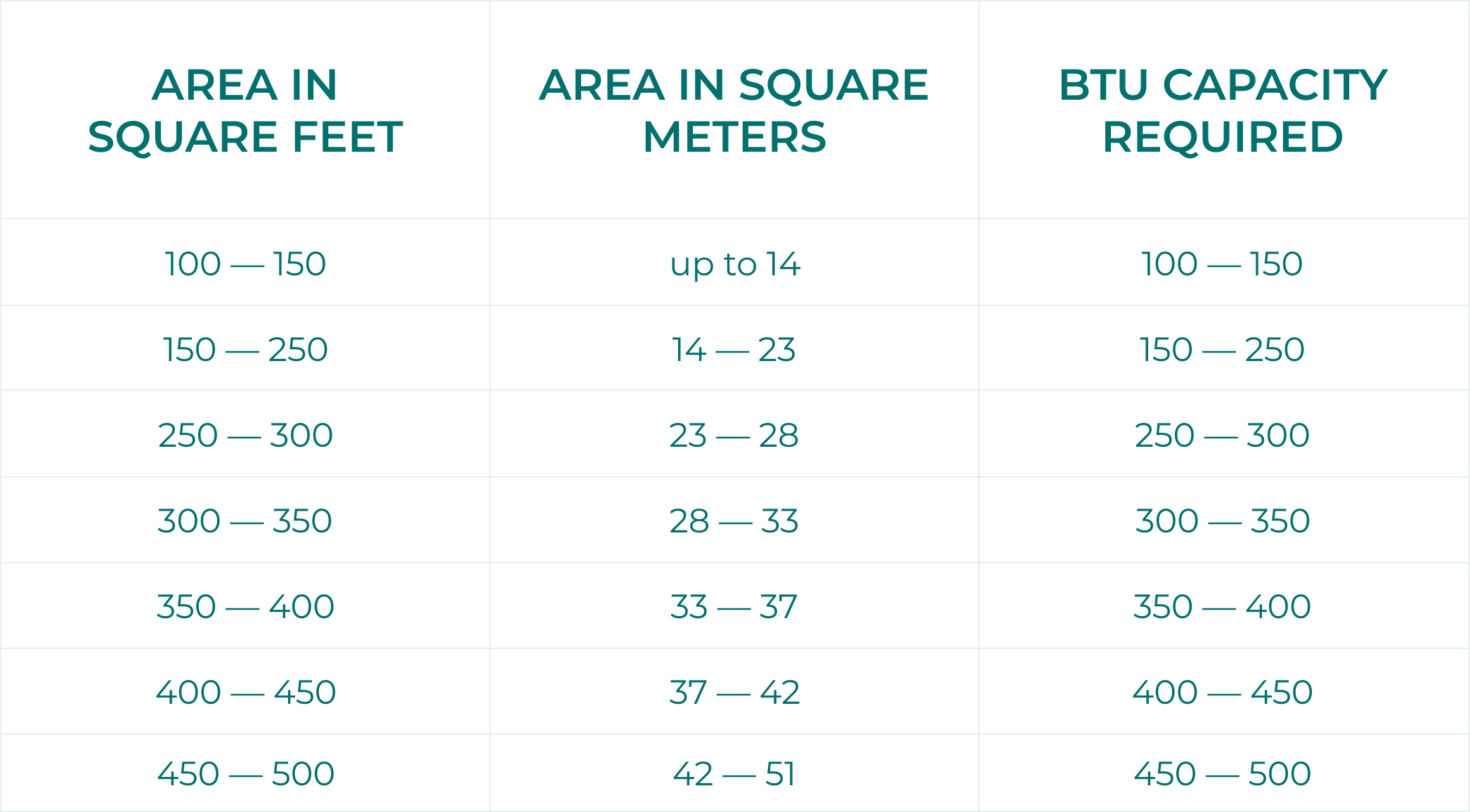
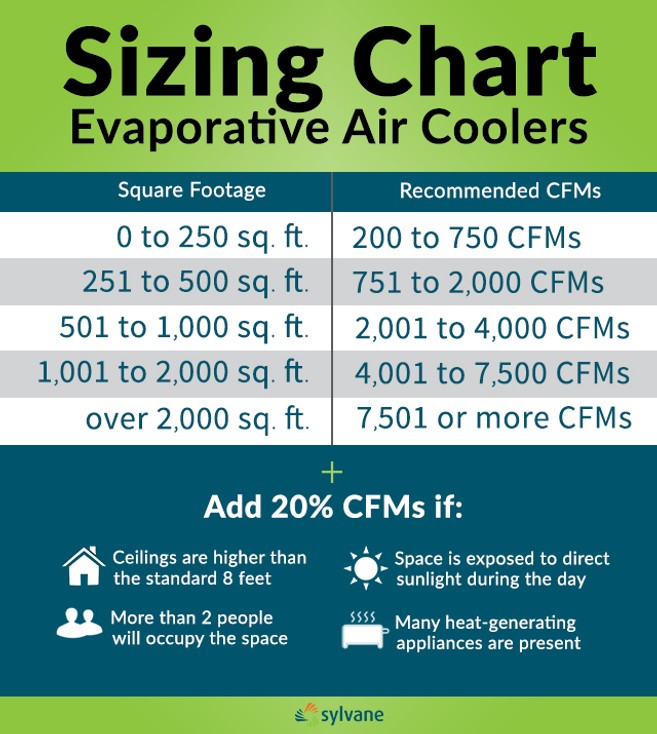
Swamp Cooler Temperature Chart - Web traditional direct evaporative coolers (“swamp coolers”) were often mounted on the roof. Web the next chart shows what temperature differences can be achieved with an evaporative cooler based on indoor air temperature and relative humidity. Web use the calculator below to determine the appropriate cooler sizing based on your needs. Web the direct evaporative cooling process in a psychrometric chart. Web if you take a measurement of the air temperature and relative humidity in your town, you can use this chart to determine if you have optimal conditions to run an evaporative cooler. Just find the intersection of temperature (on the right) and relative humidity (across the top) to the number on the grid where both measurements meet. Web these charts are intended to find the sweet spot for evaporative coolers, where they operate at maximum efficiency have the most appreciable effect on their environment. Web although specifications may vary by unit, most manufacturers recommend operating an evaporative cooler in an area where the temperature is above 80 degrees fahrenheit and below 60% humidity. Web evaporative cooler sizing. These units had multiple inlets and panels of evaporative media. Web at what temperature do swamp coolers stop working? At this point, the air is too cold for evaporation to take place, and the swamp cooler will no longer be effective. The process is indicated in the psychrometric chart below. Generally speaking, most swamp coolers will continue to work until the temperature drops below about 60 degrees fahrenheit. The resulted. Web a swamp cooler operating at 85 percent efficiency can bring the temperature down to a nice, cool 72.3 degrees fahrenheit (22.3 degrees celsius), right in the human comfort zone. Web these charts are intended to find the sweet spot for evaporative coolers, where they operate at maximum efficiency have the most appreciable effect on their environment. Web if you’re. If the humidity in the space is above 60%, it’s best to use a fan or a/c instead. Just find the intersection of temperature (on the right) and relative humidity (across the top) to the number on the grid where both measurements meet. There are big differences between hot and arid climates like arizona versus hot and humid climates like. Web these charts are intended to find the sweet spot for evaporative coolers, where they operate at maximum efficiency have the most appreciable effect on their environment. Next, determine the dry bulb temperature. At this point, the air is too cold for evaporation to take place, and the swamp cooler will no longer be effective. Web although specifications may vary. Directed to serve evaporative cooling professionals , growing by their feedback. For example, if it is 75 degrees in your home and the rh is 20%, air. In addition to dropping the temperature of the air, evaporative cooling offers an additional cooling benefit. In this example, the wet bulb temperature is 30f. First, determine the wet bulb temperature. Start by selecting the a geographic location the cooler will be used in and then cooler model. There are big differences between hot and arid climates like arizona versus hot and humid climates like florida. Air would be pulled in through the sides of the unit, pass through the media,. Web a swamp cooler operating at 85 percent efficiency can. Humidity can allow for less substantial temperature drops. Web the swamp cooler humidity chart spans from 75°f to 125°f temperature and from 2% to 80% relative humidity levels. Web if you’re having trouble getting cold air out of your cooler, try replacing the ice and cold water with room temperature water (never hot water!) and see if the effect is. The chart below can help determine how much airflow will effectively cool your indoor space based on sq. Web at what temperature do swamp coolers stop working? Web evaporative cooler air temperature relative humidity chart. Generally speaking, most swamp coolers will continue to work until the temperature drops below about 60 degrees fahrenheit. Web the swamp cooler humidity chart spans. Web although specifications may vary by unit, most manufacturers recommend operating an evaporative cooler in an area where the temperature is above 80 degrees fahrenheit and below 60% humidity. In this example, the wet bulb temperature is 30f. It tells you at which temperatures and moisture levels using an evaporative cooler is effective. Directed to serve evaporative cooling professionals ,. Next, determine the dry bulb temperature. For example, if you live in a region with a moderately high rh of around 60 percent, the cooler will lower the temperature from 95 to 87 degrees, which. First, determine the wet bulb temperature. Web traditional direct evaporative coolers (“swamp coolers”) were often mounted on the roof. Web although specifications may vary by. Most swamp coolers are rated by cfm, or the cubic feet per minute of airflow. Web evaporative cooler air temperature relative humidity chart. Humidity can allow for less substantial temperature drops. Web the following example outlines how to calculate the swamp cooler efficiency. Web traditional direct evaporative coolers (“swamp coolers”) were often mounted on the roof. It tells you at which temperatures and moisture levels using an evaporative cooler is effective. Web a swamp cooler — the affectionate name for an evaporative cooler — can save you a bundle of money on your electricity bills when temperatures skyrocket during the hot summer months. First, determine the wet bulb temperature. Web a swamp cooler operating at 85 percent efficiency can bring the temperature down to a nice, cool 72.3 degrees fahrenheit (22.3 degrees celsius), right in the human comfort zone. Air at with dry bulb temperature 70 of and relative moisture 60% (state a) is cooled down (state b) by evaporating water. Web a swamp cooler can deliver comfortable air under a wide variety of typical summertime temperature and humidity ranges. In this example, the wet bulb temperature is 30f. Generally speaking, most swamp coolers will continue to work until the temperature drops below about 60 degrees fahrenheit. Air would be pulled in through the sides of the unit, pass through the media,. 96°f and humidity 35% results in an output of 78°f. If the humidity in the space is above 60%, it’s best to use a fan or a/c instead.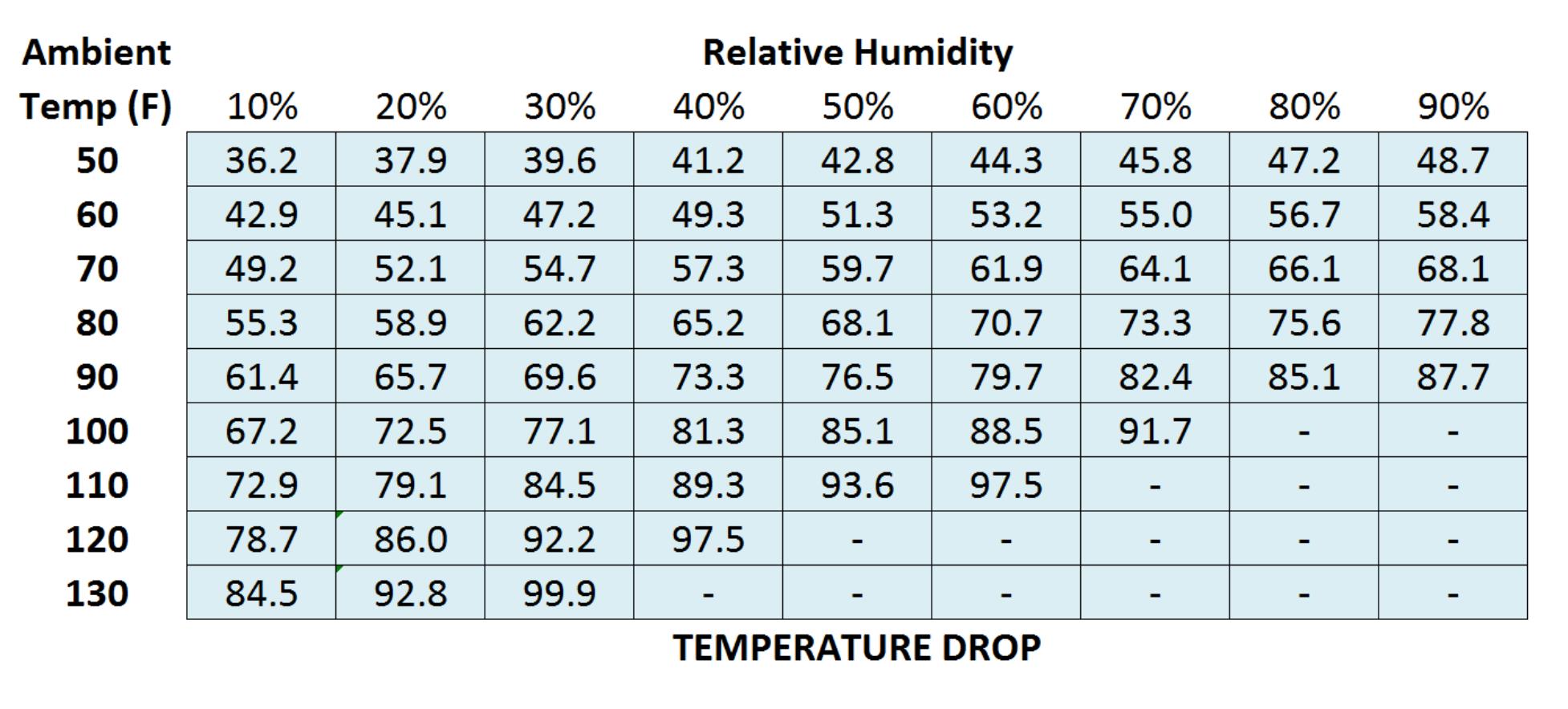
Swamp Cooler Temperature Chart
Swamp Cooler Temperature Chart
Swamp Cooler Temperature Chart
Evaporative Cooler Humidity Chart
Swamp Cooler Cooling Chart

Swamp Cooler Efficiency Chart

Evaporative Cooler Temperature Chart

Swamp Cooler Cooling Chart

How Efficient Is an Evaporative Cooler? (Chart and How it Works)
Swamp Cooler Buying Guide Sylvane
At This Point, The Air Is Too Cold For Evaporation To Take Place, And The Swamp Cooler Will No Longer Be Effective.
The Process Is Indicated In The Psychrometric Chart Below.
Outdoor Evaporative Coolers Called Down Discharge (Or Down Draft) Coolers Are Designed To Be Installed On The Roof And Can Cool An Entire Home.
There Are Big Differences Between Hot And Arid Climates Like Arizona Versus Hot And Humid Climates Like Florida.
Related Post: