Suboccipital Referral Pattern
Suboccipital Referral Pattern - Web cervicogenic headaches are associated with musculoskeletal dysfunction and muscle imbalance with characteristic patterns of muscle weakness and tightness. You can relieve these points and tensions yourself. Web the diagnosis of suboccipital trigger points is made when there is tenderness in the suboccipital region, referred pain with maintained pressure for 10 seconds, and increased referred pain on muscle contraction. If they are tense or carry active trigger points, they can trigger headaches and restrict the mobility of the neck. Web a cervicogenic headache is thought to be referred pain arising from irritation caused by cervical structures innervated by spinal nerves c1, c2, and c3; The x is where trigger points create tension, and the red dots are where pain is commonly produced from these trigger points. Travell and simons have divided tps into subtypes, including active, associated, attachment, central,. Web the referred pain area elicited by suboccipital trps was significantly larger than the referred pain elicited from the remaining muscles ( p < 0.001) within the fms, but smaller within the tmd ( p < 0.01). Web the suboccipital muscles consist of four small muscles at your cervical spine. Web activated trigger points on the suboccipital muscles can result in a referred pain pattern that spreads to one and/or both sides of the head above the occipital and temporal bones [ 106 ]. You can relieve these points and tensions yourself. Web the referred pain area elicited by suboccipital trps was significantly larger than the referred pain elicited from the remaining muscles ( p < 0.001) within the fms, but smaller within the tmd ( p < 0.01). Web a cervicogenic headache is thought to be referred pain arising from irritation caused by. A thorough history and clinical examination will lead to an accurate diagnosis. Web a picture below illustrates this specific referral pattern. Web the diagnosis of suboccipital trigger points is made when there is tenderness in the suboccipital region, referred pain with maintained pressure for 10 seconds, and increased referred pain on muscle contraction. Web a cervicogenic headache is thought to. The x is where trigger points create tension, and the red dots are where pain is commonly produced from these trigger points. Web injection with lidocaine has been shown to be effective in patients who have symptomatic active trigger points that produce a twitch response to pressure and create a pattern of referred pain. Travell and simons have divided tps. The x is where trigger points create tension, and the red dots are where pain is commonly produced from these trigger points. Travell and simons have divided tps into subtypes, including active, associated, attachment, central,. Web cervicogenic headaches are associated with musculoskeletal dysfunction and muscle imbalance with characteristic patterns of muscle weakness and tightness. Web activated trigger points on the. Web the diagnosis of suboccipital trigger points is made when there is tenderness in the suboccipital region, referred pain with maintained pressure for 10 seconds, and increased referred pain on muscle contraction. Web a cervicogenic headache is thought to be referred pain arising from irritation caused by cervical structures innervated by spinal nerves c1, c2, and c3; A thorough history. Web the diagnosis of suboccipital trigger points is made when there is tenderness in the suboccipital region, referred pain with maintained pressure for 10 seconds, and increased referred pain on muscle contraction. Web the suboccipital muscles consist of four small muscles at your cervical spine. Web the spot will normally be painful to compression and produce a stereotypical referral pattern. Web activated trigger points on the suboccipital muscles can result in a referred pain pattern that spreads to one and/or both sides of the head above the occipital and temporal bones [ 106 ]. A thorough history and clinical examination will lead to an accurate diagnosis. Web a picture below illustrates this specific referral pattern. Web the diagnosis of suboccipital. Travell and simons have divided tps into subtypes, including active, associated, attachment, central,. The x is where trigger points create tension, and the red dots are where pain is commonly produced from these trigger points. Web activated trigger points on the suboccipital muscles can result in a referred pain pattern that spreads to one and/or both sides of the head. You can relieve these points and tensions yourself. Web activated trigger points on the suboccipital muscles can result in a referred pain pattern that spreads to one and/or both sides of the head above the occipital and temporal bones [ 106 ]. Web a picture below illustrates this specific referral pattern. If they are tense or carry active trigger points,. Web the referred pain area elicited by suboccipital trps was significantly larger than the referred pain elicited from the remaining muscles ( p < 0.001) within the fms, but smaller within the tmd ( p < 0.01). Web activated trigger points on the suboccipital muscles can result in a referred pain pattern that spreads to one and/or both sides of. Web the suboccipital muscles consist of four small muscles at your cervical spine. Web the spot will normally be painful to compression and produce a stereotypical referral pattern to distant structures. If they are tense or carry active trigger points, they can trigger headaches and restrict the mobility of the neck. You can relieve these points and tensions yourself. Web injection with lidocaine has been shown to be effective in patients who have symptomatic active trigger points that produce a twitch response to pressure and create a pattern of referred pain. The x is where trigger points create tension, and the red dots are where pain is commonly produced from these trigger points. Web the diagnosis of suboccipital trigger points is made when there is tenderness in the suboccipital region, referred pain with maintained pressure for 10 seconds, and increased referred pain on muscle contraction. Web cervicogenic headaches are associated with musculoskeletal dysfunction and muscle imbalance with characteristic patterns of muscle weakness and tightness. A thorough history and clinical examination will lead to an accurate diagnosis. Web activated trigger points on the suboccipital muscles can result in a referred pain pattern that spreads to one and/or both sides of the head above the occipital and temporal bones [ 106 ]. Web the referred pain area elicited by suboccipital trps was significantly larger than the referred pain elicited from the remaining muscles ( p < 0.001) within the fms, but smaller within the tmd ( p < 0.01).
Suboccipital Muscles Headaches, Migraines, Eye Pain The Wellness Digest

Alila Medical Media Trigger points and referred pain patterns for the

Suboccipital Release Technique

The Trigger Point & Referred Pain Guide 13
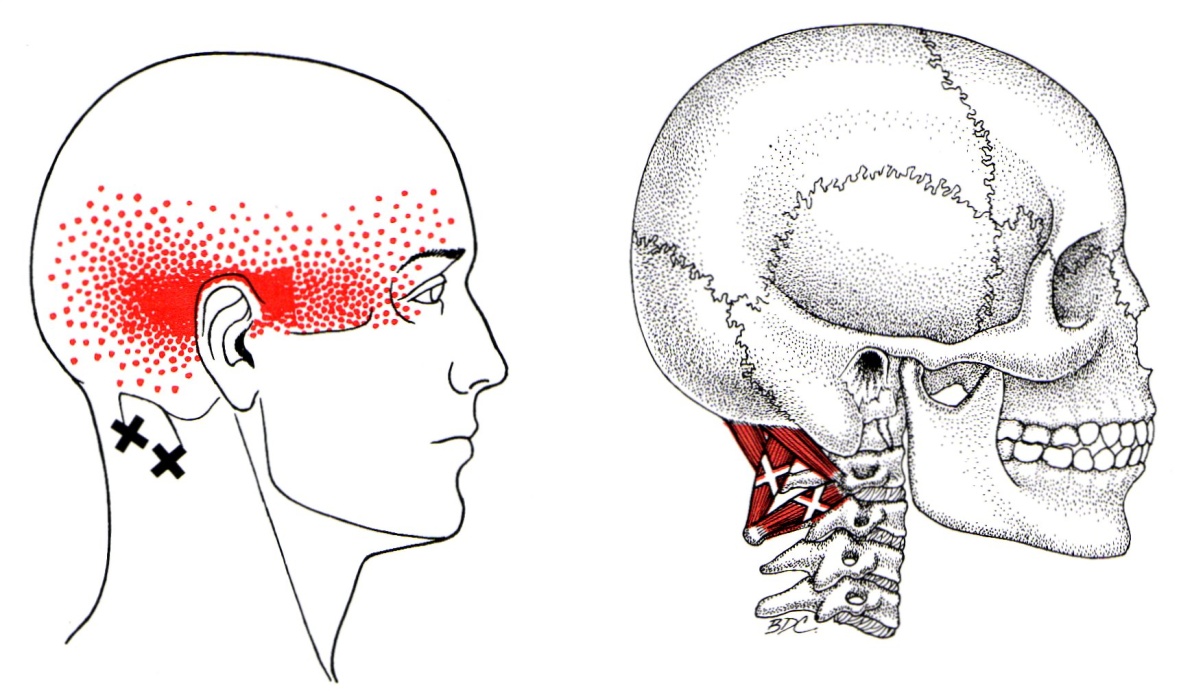
Suboccipital Group The Trigger Point & Referred Pain Guide

Alila Medical Media Trigger points and referred pain patterns for the

Alila Medical Media Trigger points and referred pain patterns for the

Suboccipital Group Trigger Points Learn Muscles

Suboccipital Muscles Trigger Points

Suboccipital Trigger Point Release and Stretch Nourishing Massage
Travell And Simons Have Divided Tps Into Subtypes, Including Active, Associated, Attachment, Central,.
Web A Picture Below Illustrates This Specific Referral Pattern.
Web A Cervicogenic Headache Is Thought To Be Referred Pain Arising From Irritation Caused By Cervical Structures Innervated By Spinal Nerves C1, C2, And C3;
Related Post: