Stoichiometry Chart
Stoichiometry Chart - This chapter will describe how to symbolize chemical reactions using chemical equations, how to classify some common chemical reactions by identifying patterns of reactivity, and how to determine the quantitative relations between the amounts of substances involved in chemical reactions—that is, the reaction. The field of chemistry that is concerned with the relative quantities of reactants and products in chemical reactions and how to calculate those quantities. Web at its core, stoichiometry is the study of the quantitative relationships between the reactants and products in chemical reactions. Stoichiometry ( / ˌstɔɪkiˈɒmɪtri /) is the relationship between the weights of reactants and products before, during, and following chemical reactions. The laws of conservation of mass, energy, and weights or volumes serve as the foundation for the rules used to determine stoichiometric relationships. Web stoichiometry is a general term for relationships between amounts of substances in chemical reactions. Stoichiometry is founded on the law of conservation of mass where the total mass of the reactants equals the. Use balanced chemical equations to derive stoichiometric factors relating amounts of reactants and products. We can use these numerical relationships to write mole ratios, which allow us to convert between amounts of reactants and/or products (and thus solve stoichiometry problems!). The reactants and products, along with their coefficients will appear above. It also describes calculations done to determine how much of a substance will be used in a reaction, left over after a reaction, produced by a. Browse videos, articles, and exercises by topic. Write and balance chemical equations in molecular, total ionic, and net ionic formats. Perform stoichiometric calculations involving mass, moles, and solution molarity. Web flow chart for solving. Relate quantities in a balanced chemical reaction on a molecular basis. Write and balance chemical equations in molecular, total ionic, and net ionic formats. Web explain the concept of stoichiometry as it pertains to chemical reactions. Web stoichiometry is a general term for relationships between amounts of substances in chemical reactions. Determine the number of moles of hydrazine formed when. Write and balance chemical equations in molecular, total ionic, and net ionic formats. Scroll down the page for more examples and solutions. Web stoichiometry is a collective term for the quantitative relationships between the masses, the numbers of moles, and the numbers of particles (atoms, molecules, and ions) of the reactants and the products in a balanced chemical equation. A. Web derive chemical equations from narrative descriptions of chemical reactions. Web to perform a stoichiometric calculation, enter an equation of a chemical reaction and press the start button. This unit is part of the chemistry library. A stoichiometric quantity of a reactant is the amount necessary to react completely with the other reactant(s). Web stoichiometry studies the relative molar ratios. Stoichiometry ( / ˌstɔɪkiˈɒmɪtri /) is the relationship between the weights of reactants and products before, during, and following chemical reactions. Use balanced chemical equations to derive stoichiometric factors relating amounts of reactants and products. (that’s why it’s called “pound cake.”) Determine the number of moles of hydrazine formed when 25.7 g ammonia reacts with excess nitrogen. Perform stoichiometric calculations. (that’s why it’s called “pound cake.”) Mass (g,kg, volume (l, or with. Web stoichiometry is a general term for relationships between amounts of substances in chemical reactions. This unit is part of the chemistry library. This tutorial introduces the concept of reaction stoichiometry, determining the amount of substance that is consumed or produced by a reaction. Moles a moles b grams b before change after. A stoichiometric quantity of a reactant is the amount necessary to react completely with the other reactant(s). Browse videos, articles, and exercises by topic. Web a balanced chemical equation shows us the numerical relationships between each of the species involved in the chemical change. The reactants and products, along with their. A stoichiometric diagram of the combustion reaction of methane. This chapter will describe how to symbolize chemical reactions using chemical equations, how to classify some common chemical reactions by identifying patterns of reactivity, and how to determine the quantitative relations between the amounts of substances involved in chemical reactions—that is, the reaction. Browse videos, articles, and exercises by topic. 1. (that’s why it’s called “pound cake.”) Web at its core, stoichiometry is the study of the quantitative relationships between the reactants and products in chemical reactions. 1 pound of eggs, 1 pound of butter, 1 pound of flour, and 1 pound of sugar. Relate quantities in a balanced chemical reaction on a molecular basis. Web to perform a stoichiometric calculation,. A stoichiometric diagram of the combustion reaction of methane. The field of chemistry that is concerned with the relative quantities of reactants and products in chemical reactions and how to calculate those quantities. (that’s why it’s called “pound cake.”) Moles a moles b grams b before change after. Web stoichiometry describes the relationship between the amounts of reactants and products. Determine the number of moles of hydrazine formed when 25.7 g ammonia reacts with excess nitrogen. It also describes calculations done to determine how much of a substance will be used in a reaction, left over after a reaction, produced by a. Use balanced chemical equations to derive stoichiometric factors relating amounts of reactants and products. The reactants and products, along with their coefficients will appear above. Web a balanced chemical equation shows us the numerical relationships between each of the species involved in the chemical change. Moles a moles b grams b before change after. Consider a classic recipe for pound cake: Rather, it is about having a better conceptual understanding of the process of stoichiometry calculations. Mass (g,kg, volume (l, or with. Web stoichiometry studies the relative molar ratios of the atoms and molecules that participate in chemical reactions, as indicated by the balancing coefficients that are associated with the reaction. This method isn’t about being “easier” or more simple. (that’s why it’s called “pound cake.”) This unit is part of the chemistry library. We can use these numerical relationships to write mole ratios, which allow us to convert between amounts of reactants and/or products (and thus solve stoichiometry problems!). Web stoichiometry is a collective term for the quantitative relationships between the masses, the numbers of moles, and the numbers of particles (atoms, molecules, and ions) of the reactants and the products in a balanced chemical equation. Stoichiometry is founded on the law of conservation of mass where the total mass of the reactants equals the.
Extended Reaction Stoichiometry Road Map — Examples Expii
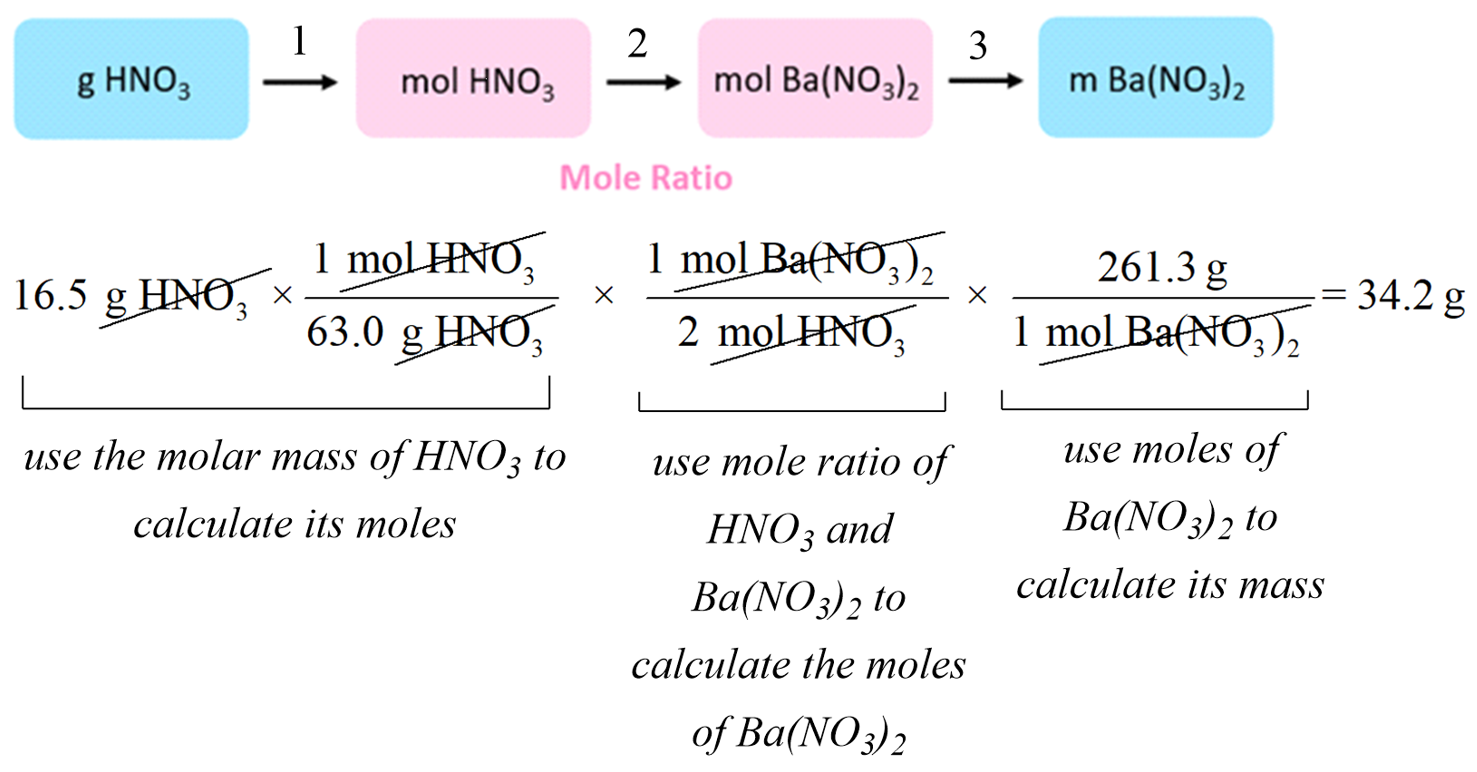
Stoichiometry of Chemical Reactions Chemistry Steps
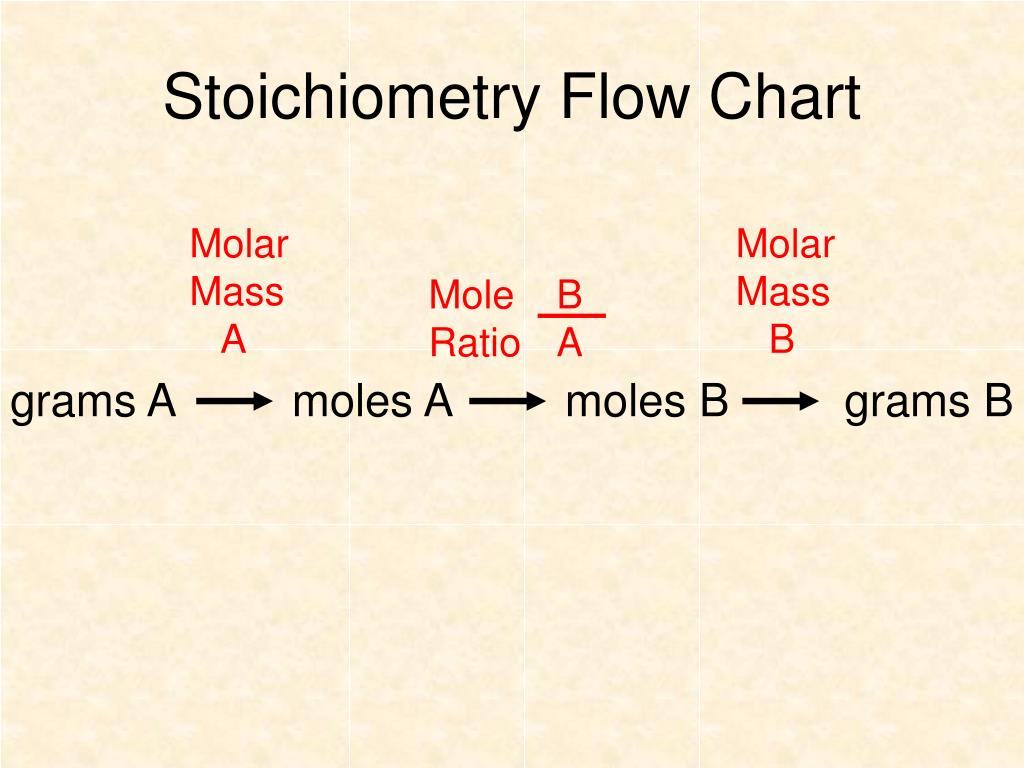
PPT Chapter 12 Stoichiometry PowerPoint Presentation, free download

The Stoichiometric Chart YouTube

Stoichiometry Lessons TES Teaching chemistry, Chemistry education
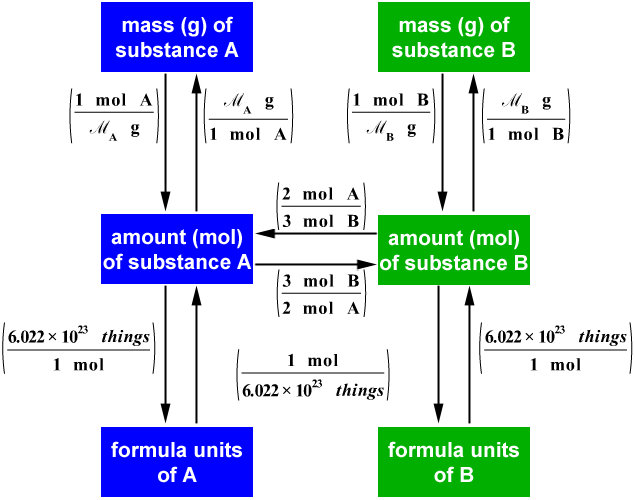
J² + H = Element 119 Kariodisonium Stoichiometry Calculations
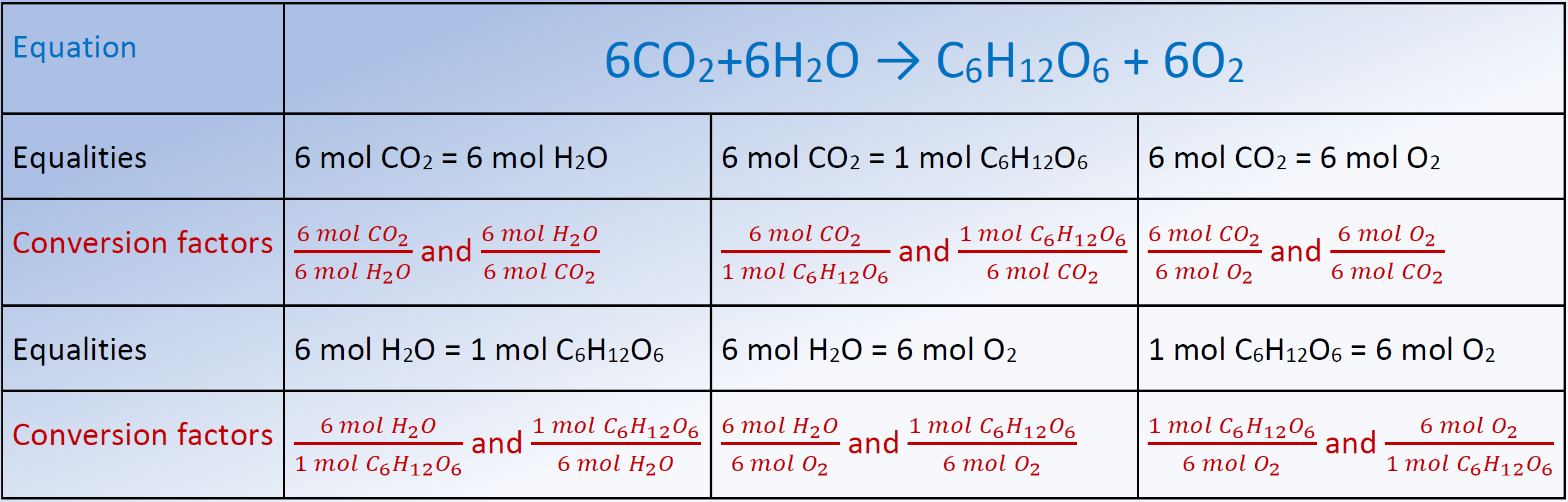
4.7 Stoichiometric calculations Chemistry LibreTexts
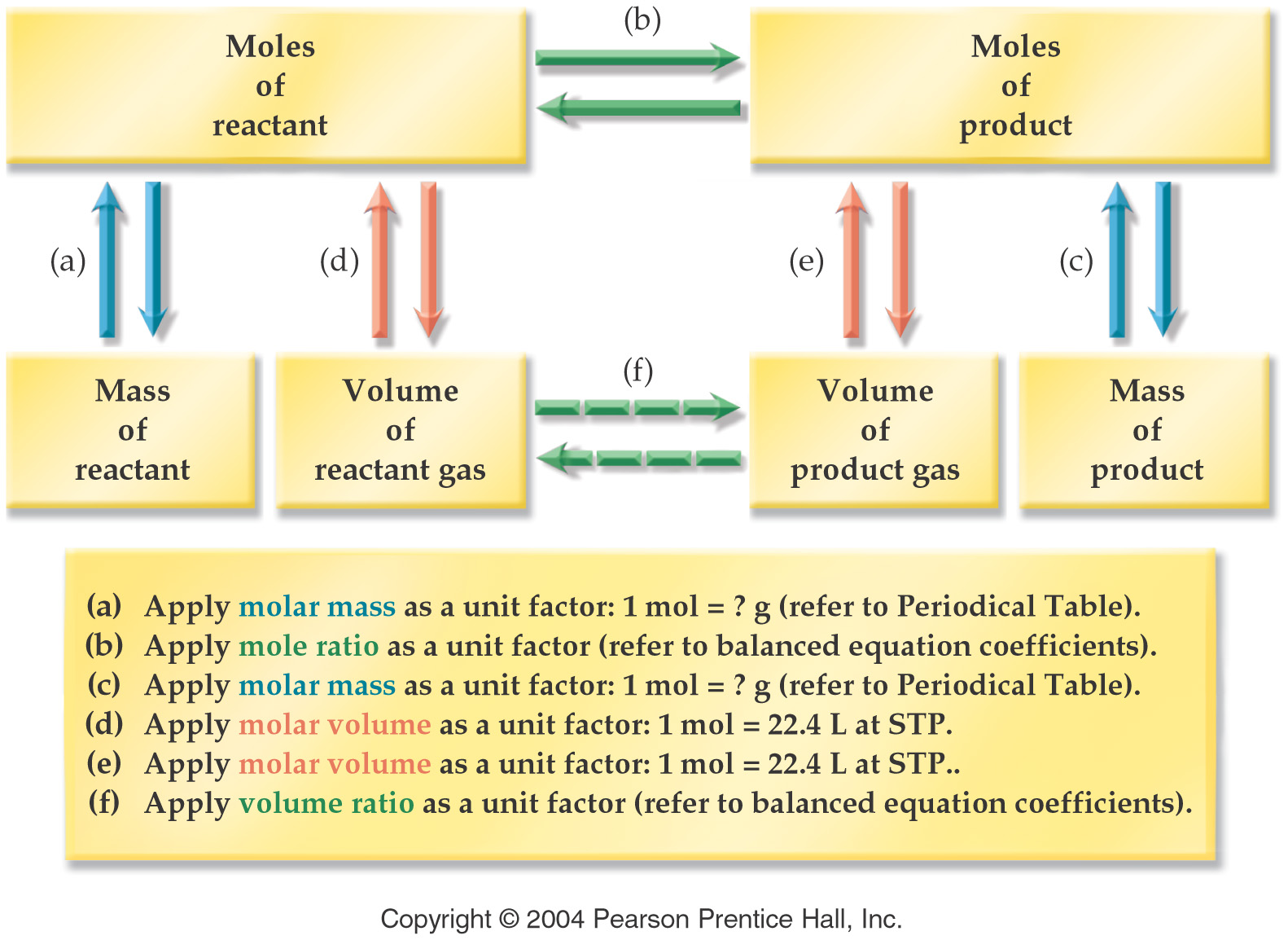
Corwin Text's Image fg10_0105UN.jpg (Stoichiometry Concept Map)
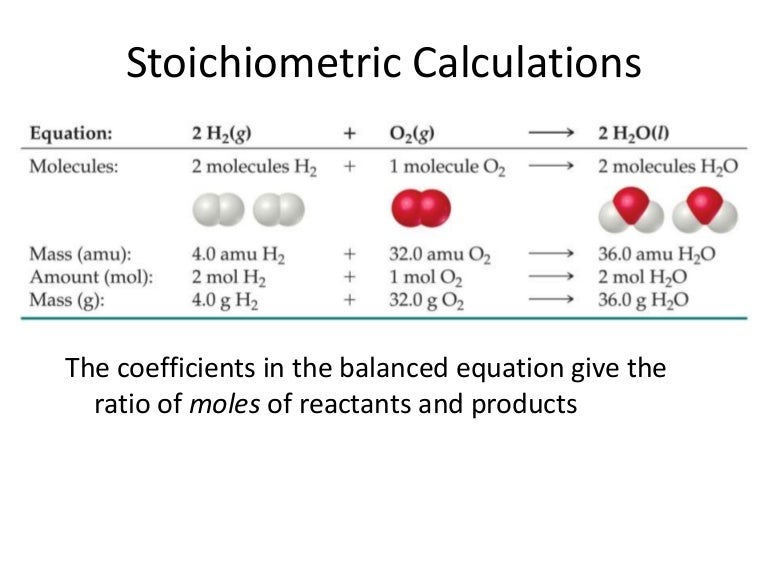
Stoichiometric Calculations

Stoichiometry Chart YouTube
Web The Following Stoichiometry Road Map Gives A Summary Of How To Use Stoichiometry To Calculate Moles, Masses, Volumes And Particles In A Chemical Reaction.
Web The Stoichiometry Chart Is A Roadmap To Show You How Many Fractions Are Needed To Solve The Problem And In What Order Yo.
Figuring Out The Ratios In Which Different Substances Or Elements React To One Another.
One Mole Of Atoms, Ions, Or Molecules Contains Avogadro’s Number Of Those Particles.
Related Post: