Solder Melting Temperature Chart
Solder Melting Temperature Chart - Solder is a metallic material that is used to connect metal workpieces. The alloys listed may be available in forms other than those indicated. The selection of alloy is determined by application, melting temperature and physical properties. Web it contains silver as a primary component and requires high temperatures for melting, making it suitable for applications where mechanical strength is crucial. Further, solder has different composition variations, which leads to the various types we have today. Commonly specified solder alloys are shown in the table. A typical solder such as 60/40, with 60 % tin, and 40 % lead, has a melting point approximately between 183 °c to 188 °c. What’s the proper soldering iron temperature for standard.031 60/40 solder? Other solder alloys are also available. The selection of alloy is determined by application, melting temperature and physical properties. If you’ve worked on ems pcba projects, you know that soldering is critical to making. Welcome to our comprehensive guide on the melting point of solder! Your soldering iron plays an essential role. The eutectic composition (37% pb, 63% sn) has a melting point of approximately 183°c (361°f). Web solder alloy melting temperature metal weight percent melting temperature. So, your soldering iron temperature should be higher by 68 to 86 degrees fahrenheit (20 to 30 degrees celsius). Web charts & graphs | 10/28/2020. Web solder with a composition of 60% tin and 40% lead has a varying melting range but will begin turning into liquid at 361.4°f (183°c), then completely turn into liquid at 375.8°f (191°c). Web most. So, your soldering iron temperature should be higher by 68 to 86 degrees fahrenheit (20 to 30 degrees celsius). Web solder with a composition of 60% tin and 40% lead has a varying melting range but will begin turning into liquid at 361.4°f (183°c), then completely turn into liquid at 375.8°f (191°c). Commonly specified solder alloys are shown in the. Selecting a soldering temperature for your iron. The selection of alloy is determined by application, melting temperature and physical properties. Save this chart for quick reference. Commonly specified solder alloys are shown in the table. Solder is a metallic material that is used to connect metal workpieces. There are few things that will impact the soldering temperature that you need on your soldering iron. Commonly specified solder alloys are shown in the table. Selecting a soldering temperature for your iron. This temperature chart shows the different solders that are available and their melting temperatures. Whether you are a seasoned soldering pro or just starting out, understanding the. As you progress through assembly use a lower temperature solder. The selection of alloy is determined by application, melting temperature and physical properties. The selection of alloy is determined by application, melting temperature and physical properties. With balanced ratios (50% tin and 50% lead), the melting range widens to between 361°f and 421°f. Thickness (μm) of intermetallics in solder alloys. Web solder with a composition of 60% tin and 40% lead has a varying melting range but will begin turning into liquid at 361.4°f (183°c), then completely turn into liquid at 375.8°f (191°c). Commonly specified solder alloys are shown in the table. Web charts & graphs | 10/28/2020. With balanced ratios (50% tin and 50% lead), the melting range widens. Soldering is accomplished by quickly heating the metal parts to be joined, and then applying a flux and a solder to the mating surfaces. Welcome to our solder melting temperature guide! An anonymous man soldering a pcb. The eutectic composition (37% pb, 63% sn) has a melting point of approximately 183°c (361°f). Web charts & graphs | 10/28/2020. Indium solder is a type of solder that contains indium as the primary component. An anonymous man soldering a pcb. Commonly specified solder alloys are shown in the table. Low temperature solder types and their melting points. Save this chart for quick reference. Further, solder has different composition variations, which leads to the various types we have today. The eutectic composition (37% pb, 63% sn) has a melting point of approximately 183°c (361°f). Commonly specified solder alloys are shown in the table. Web below is an alloy temperature chart for reference. Solder is a metallic material that is used to connect metal workpieces. This chart includes the alloy’s melting temperature and lists the available forms for each alloy. Commonly specified solder alloys are shown in the table. Low temperature solder types and their melting points. Indium solder is a type of solder that contains indium as the primary component. Welcome to our solder melting temperature guide! Selecting a soldering temperature for your iron. Thickness (μm) of intermetallics in solder alloys aged at 150 ºc. Web the alloy temperature chart lists the alloys that are available from kester. Other solder alloys are also available. There are few things that will impact the soldering temperature that you need on your soldering iron. A typical solder such as 60/40, with 60 % tin, and 40 % lead, has a melting point approximately between 183 °c to 188 °c. The eutectic composition (37% pb, 63% sn) has a melting point of approximately 183°c (361°f). When assembling a piece start with the highest melting point solder. Web melting temperatures of solder are determined by the zinc content: An anonymous man soldering a pcb. Commonly specified solder alloys are shown in the table.
Solder Melting Temperature Chart
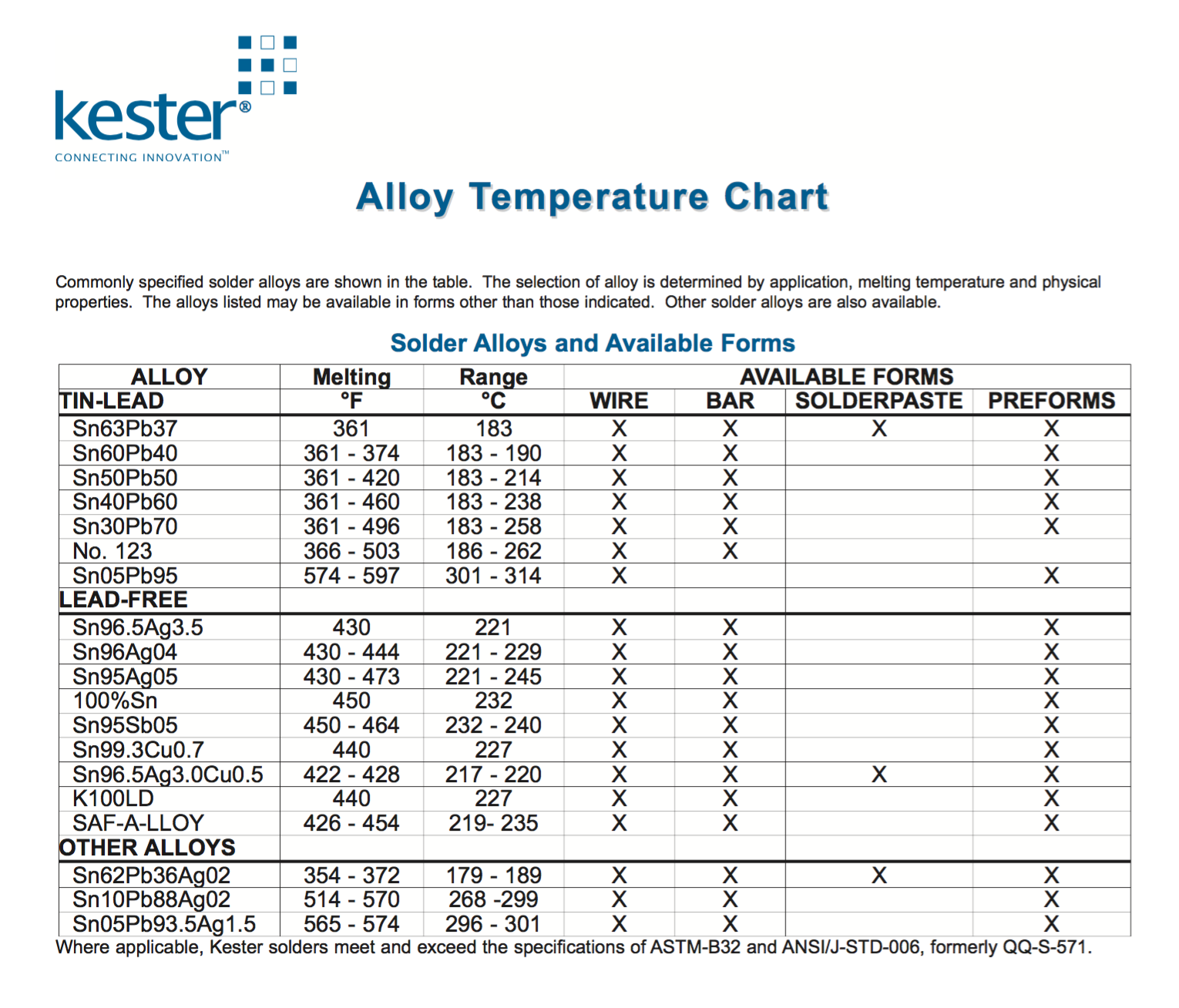
Solder Iron Temperature Chart
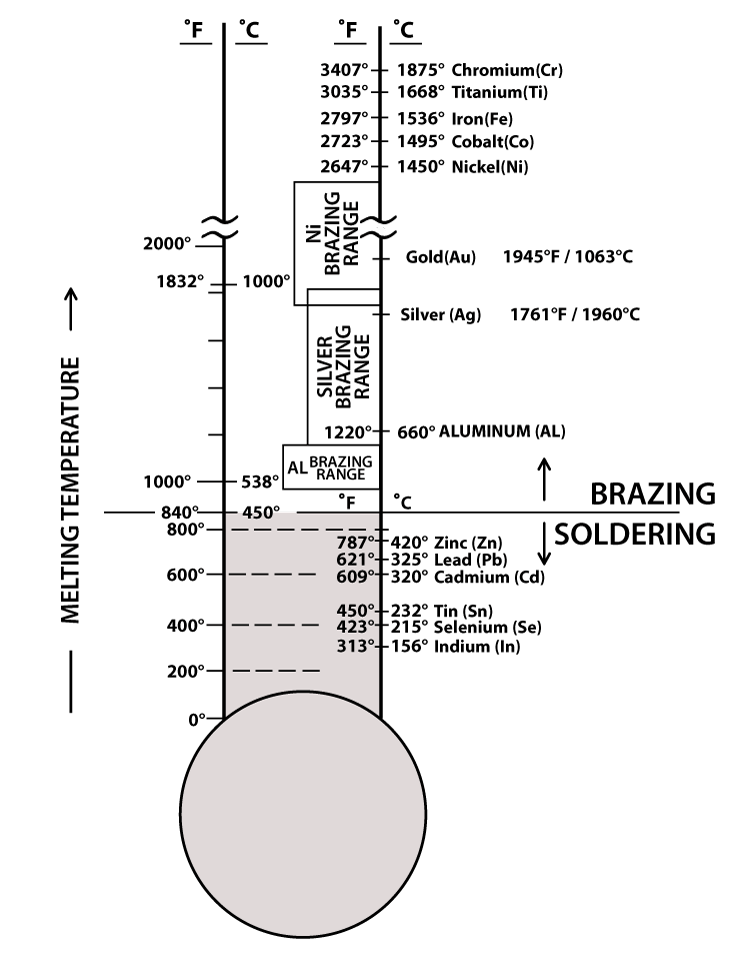
Solder Melting Point Chart
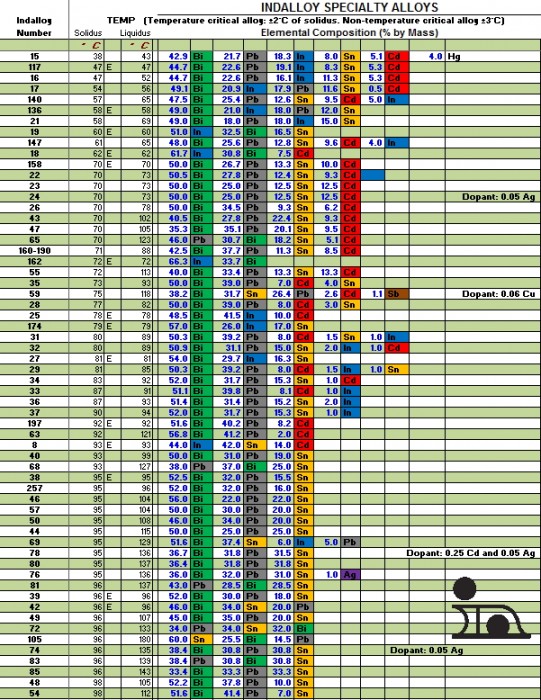
Solder Melting Point Chart

Solder Melting Point Chart

Solder Melting Temperature Chart
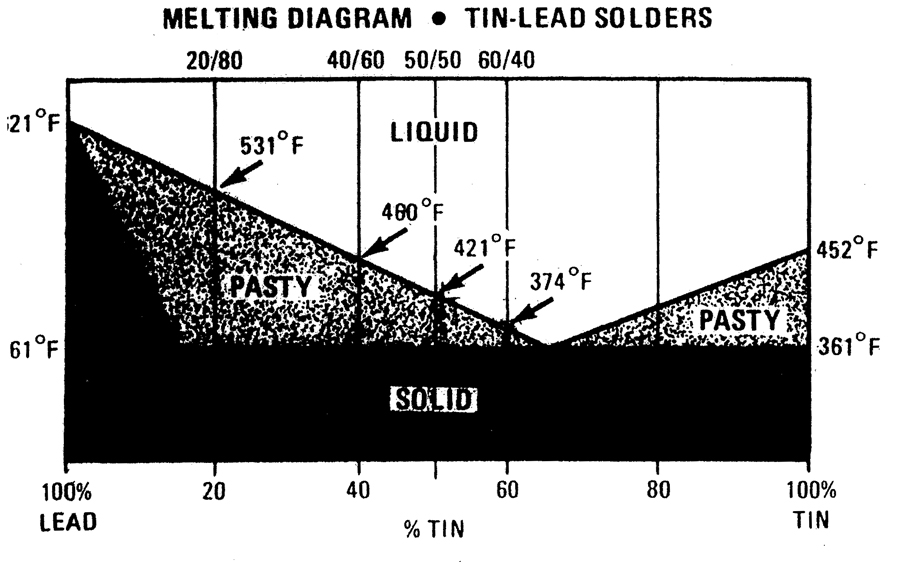
Silver Solder Melting Temperature Chart

Solder Melting Point Chart

Silver Solder Melting Temperature Chart

Solder Melting Point Chart
Other Solder Alloys Are Also Available.
So We Have To Get The Solder Joint Hotter Than This.
Web It Contains Silver As A Primary Component And Requires High Temperatures For Melting, Making It Suitable For Applications Where Mechanical Strength Is Crucial.
The Choice Of Specific Solder Alloys Depends On Their Melting Point, Chemical Reactivity, Mechanical Properties, Toxicity, And Other Properties.hence A Wide Range Of Solder Alloys Exist, And Only Major Ones Are.
Related Post: