Soil Horizon Chart
Soil Horizon Chart - Web special features of each horizon are delineated by lowercase suffixes, such as h (accumulated humus), k (carbonates), n (sodium), o (iron and aluminum oxides), q (silica), s (mixtures of metal oxides and humus), t (silicate clay), v. Different soil horizons show different amounts of alteration. It is operated by the usda natural resources conservation service (nrcs) and provides access to the largest natural resource information system in the world. Web most soils have three major horizons (a, b, c) and some have an organic horizon (o). This soil profile helps scientists. Web a wiki page that provides information on soil horizons and their significance in soil ecology. Web soil description methodology was developed by soil scientists throughout the entire course of the soil survey. Web the major symbols used in describing mineral soil layers in canada are shown in the following tables. During its formation, the soil is arranged in different layers. Smallest and finest soil particles. This layer can be thin, thick, or not present at all, depending on how a soil forms. Each of these layers is called a soil horizon, and when these layers are arranged sequentially one above the other, it. Web special features of each horizon are delineated by lowercase suffixes, such as h (accumulated humus), k (carbonates), n (sodium), o (iron. Web this simple guide for describing soils helps to identify the most important parts of a soil profile and provide an easy way to understand and explain what you see. Web a2 e e horizons: Web soil description methodology was developed by soil scientists throughout the entire course of the soil survey. Web soil horizons layers diagram chart. This soil. Horizons are defined in many cases by obvious physical features, mainly colour and texture. Web there are 7 soil horizons beneath the surface of the earth. Web soil horizons are layers parallel to the soil surface whose physical, chemical and biological characteristics differ from the layers above and beneath. This layer can be thin, thick, or not present at all,. The o horizon is thin in some soils, thick in others, and not present at all in others. This layer can be thin, thick, or not present at all, depending on how a soil forms. Different soil horizons show different amounts of alteration. The o horizon, or organic horizon, is made up mostly of organic matter such as leaf litter. Web match soil horizons with processes occurring within the zone; It is operated by the usda natural resources conservation service (nrcs) and provides access to the largest natural resource information system in the world. Topsoil has the highest proportion of organic material. Web this simple guide for describing soils helps to identify the most important parts of a soil profile. Predict potential management or use challenges based upon given horizon sequence (o) on the surface, but this horizon can also be buried. Web match soil horizons with processes occurring within the zone; Web soil horizons are layers parallel to the soil surface whose physical, chemical and biological characteristics differ from the layers above and beneath. Soil layers include topsoil, subsoil,. Web soil description methodology was developed by soil scientists throughout the entire course of the soil survey. Web soil horizons are layers parallel to the soil surface whose physical, chemical and biological characteristics differ from the layers above and beneath. Web a2 e e horizons: Mostly organic matter such as decomposing leaves. Topsoil is essential for farming. Web soil survey (wss) provides soil data and information produced by the national cooperative soil survey. The o horizon, or organic horizon, is made up mostly of organic matter such as leaf litter and decomposed plant material. The first usda guide for soil horizon identification and description Predict potential management or use challenges based upon given horizon sequence (o) on. Topsoil has the highest proportion of organic material. During its formation, the soil is arranged in different layers. Soil layers include topsoil, subsoil, and the c horizon. A pedon is the smallest unit of land surface that can be used to study the characteristic soil profile of a landscape. Web the major symbols used in describing mineral soil layers in. Different soil horizons show different amounts of alteration. This layer can be thin, thick, or not present at all, depending on how a soil forms. Horizons can be addressed as master horizons (main horizons) are indicated by capital letters. A pedon is the smallest unit of land surface that can be used to study the characteristic soil profile of a. Web soil horizons are layers parallel to the soil surface whose physical, chemical and biological characteristics differ from the layers above and beneath. Learn more about these soil horizons and what impact they can have on your gardening efforts. Web soil horizons are layers in the soil, each with different characteristics. Topsoil is essential for farming. Web this simple guide for describing soils helps to identify the most important parts of a soil profile and provide an easy way to understand and explain what you see. Some humus present, darker in color than layers below. The o horizon, or organic horizon, is made up mostly of organic matter such as leaf litter and decomposed plant material. The assignment of mineral soil layers to each horizon is done by comparing the properties of the horizons in the field to a list of distinctive characteristics, called diagnostic properties. Web special features of each horizon are delineated by lowercase suffixes, such as h (accumulated humus), k (carbonates), n (sodium), o (iron and aluminum oxides), q (silica), s (mixtures of metal oxides and humus), t (silicate clay), v. Different soil horizons show different amounts of alteration. Web soil horizons layers diagram chart. This layer can be thin, thick, or not present at all, depending on how a soil forms. Web a soil horizon is a layer parallel to the soil surface whose physical, chemical and biological characteristics differ from the layers above and beneath. The o horizon is thin in some soils, thick in others, and not present at all in others. Web the soil profile, showing the major layers from the o horizon (organic material) to the r horizon (consolidated rock). The first usda guide for soil horizon identification and description
FileSoil Horizons.svg Wikimedia Commons
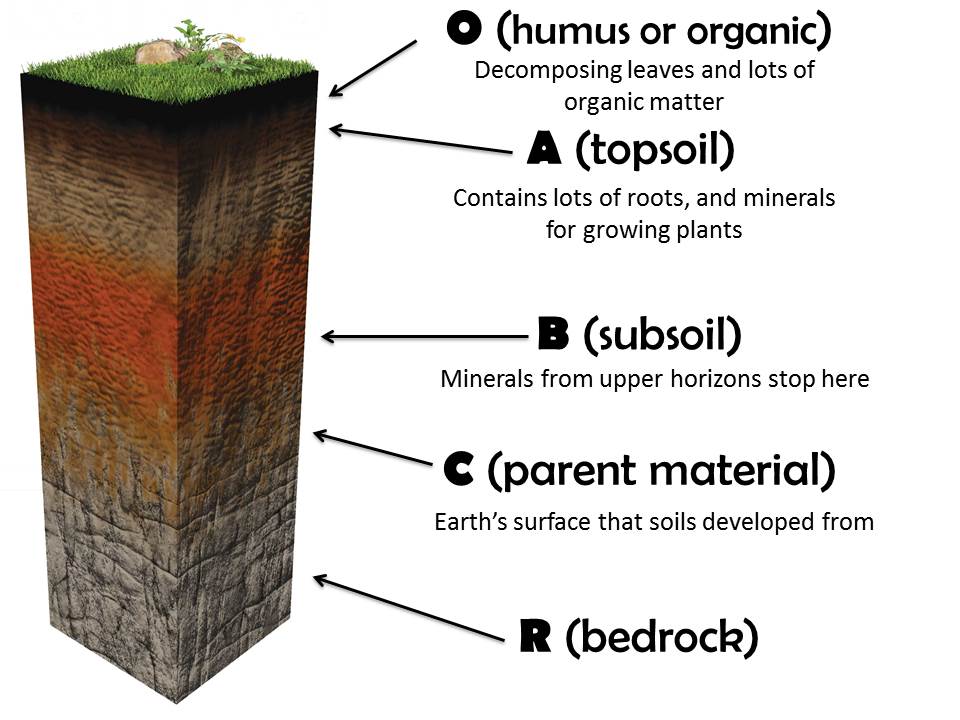
Science Teaching & Learning
8 Schematic representation of soil horizons, showing how development

The Significance of Soil Part II BlueSky Organics™
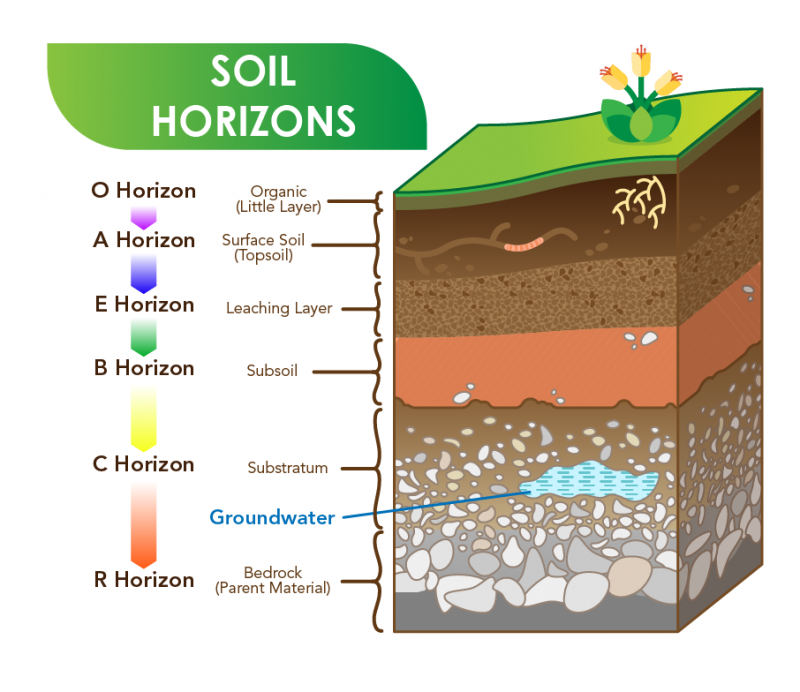
What is Soil? Let's Talk Science

soils (lesson 0088) TQA explorer

PPT Soil Formation and Weathering PowerPoint Presentation, free

Horizon Layers of Soil Soil Horizon Explanation With Examples
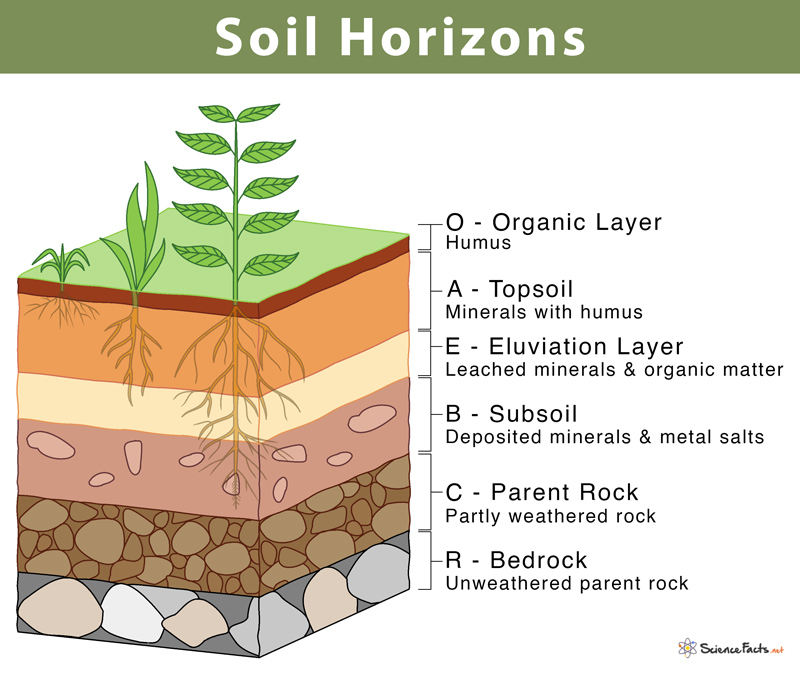
Soil Horizons Definition, Features, and Diagram

Learning Geology Soil Profiles And Soil Properties
Mostly Organic Matter Such As Decomposing Leaves.
Web Soil Description Methodology Was Developed By Soil Scientists Throughout The Entire Course Of The Soil Survey.
Web A Wiki Page That Provides Information On Soil Horizons And Their Significance In Soil Ecology.
Predict Potential Management Or Use Challenges Based Upon Given Horizon Sequence
Related Post: