Ski Bindings Din Chart
Ski Bindings Din Chart - Setting din too high or too low; But what if you need to go beyond that? Web to choose a ski binding you first need to know the waist width of your skis to determine what size brakes you need. Manual calculation of din settings; Use the chart to find a recommended din range for your bindings. This chart is for information only. Only trained technicians should adjust din settings. Fill in the details to the best of your knowledge and we'll do the rest. Web based on your height, weight, age, boot sole length, and skier type, you will have a din setting that must fall within the advertised din range of the binding. Web din, which stands for deutsches institut für normung (german institute for standardization), is a standardized scale used to determine the release force of ski bindings. Web to choose a ski binding you first need to know the waist width of your skis to determine what size brakes you need. Din 7881 release bindings for alpine downhill skiing, adjustment scale for release values. Once you've established an accurate din range and brake width, you can look at additional binding features. Web want to work out the. A higher din number means that more force needs to be applied to the binding before it releases. If you're an average skier and find you need to set din more than 1 step above that recommended in this chart, examine your bindings for defects in adjustment, and examine your ski technique. Web set toe and heel release using din. Web the waist width of your skis will determine what size brakes you need, while your skiing ability, weight, height and boot sole length will determine the bindings' release force setting (din). Web the din setting is calculated based on your boot sole length, age, weight, height, and ability level when your bindings are mounted on your skis. Web settings. Web based on your height, weight, age, boot sole length, and skier type, you will have a din setting that must fall within the advertised din range of the binding. Only trained technicians should adjust din settings. Web set toe and heel release using din settings you choose. Common mistakes to avoid when setting your din. Weight (at the moment,. Web set toe and heel release using din settings you choose. Once you've established an accurate din range and brake width, you can look at additional binding features. Web to choose a ski binding you first need to know the waist width of your skis to determine what size brakes you need. If you're an average skier and find you. A lower setting, meanwhile, will release at a much lighter pressure. A higher din number means that more force needs to be applied to the binding before it releases. Web settings vary slightly by manufacturer but this chart should give you enough information to select which atomic, head, look, marker, rossignol, salomon, or tyrolia bindings to buy. Use our simple. Web based on your height, weight, age, boot sole length, and skier type, you will have a din setting that must fall within the advertised din range of the binding. Manual calculation of din settings; The din setting is the release value of a ski binding. Web the din setting is calculated based on your boot sole length, age, weight,. Web settings vary slightly by manufacturer but this chart should give you enough information to select which atomic, head, look, marker, rossignol, salomon, or tyrolia bindings to buy. When and why you should adjust your ski binding din settings A higher din setting means that more force is required to release the binding, while a lower din setting means that. When and why you should adjust your ski binding din settings Use our simple calculator to find out in seconds. You can use this ski binding din chart as a basic reference to find your setting. Setting din too high or too low; Weight (at the moment, it's important!) height; The din setting is the release value of a ski binding. It's easy to use & free! Fill in the details to the best of your knowledge and we'll do the rest. Web for a proper din setting chart, use you'll need to know: Web settings vary slightly by manufacturer but this chart should give you enough information to select. Web just fill in your ability level, weight, height, age, and boot sole length, and the calculator will provide you with an approximate din value. The higher the din, the higher the force required to release from your bindings. You can use this ski binding din chart as a basic reference to find your setting. The din setting is the release value of a ski binding. Please select the options honestly to find the din setting recommended for you. Web for a proper din setting chart, use you'll need to know: If you order skis and bindings at skatepro then you will naturally encounter our din calculator in the checkout. A higher din number means that more force needs to be applied to the binding before it releases. Using a din chart to calculate your settings; Web want to work out the din for your ski bindings? A common approach is to just grab the. Use our simple calculator to find out in seconds. Always have your bindings checked and adjusted by a professional. The information you need include: Web din settings are the standardized settings on your ski bindings that determine how easily your ski boots release from the bindings in the event of a fall. Stay safe & ski with secure bindings.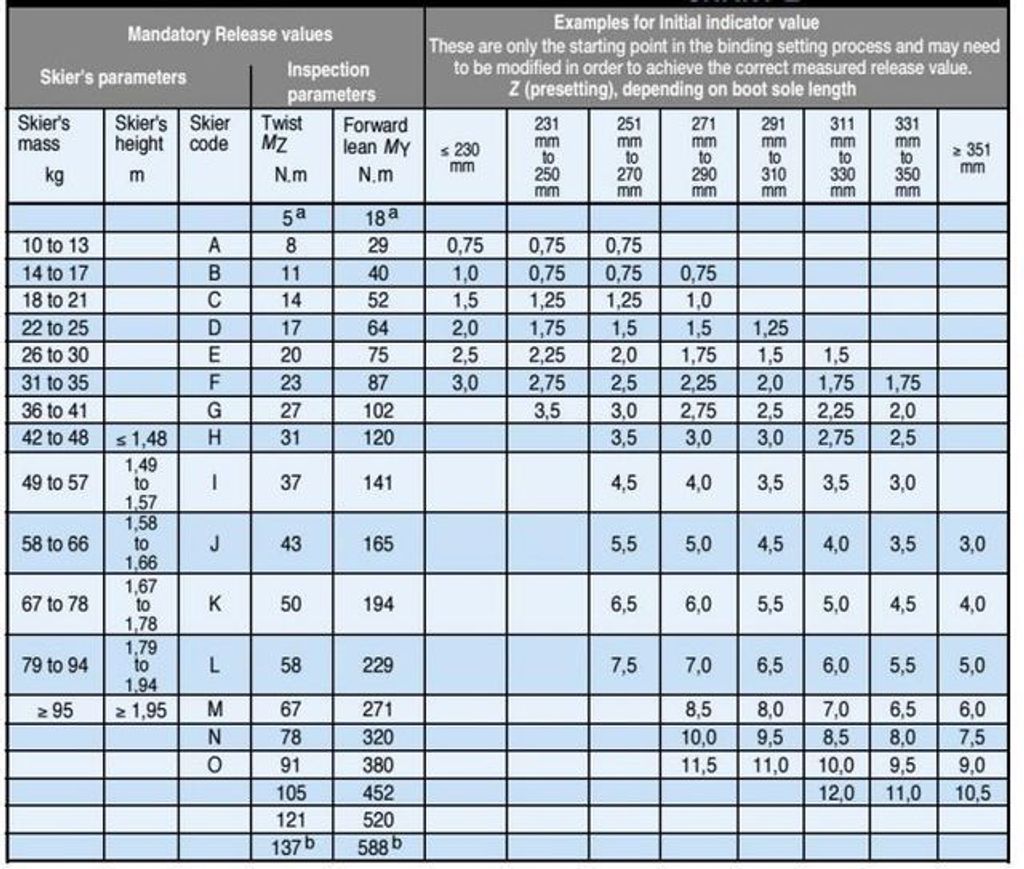
Ski Binding Din Chart
Rossignol Ski Binding Din Chart

Ski Binding DIN Settings Chart

Din Setting Chart

DIN Chart for ski binding release settings
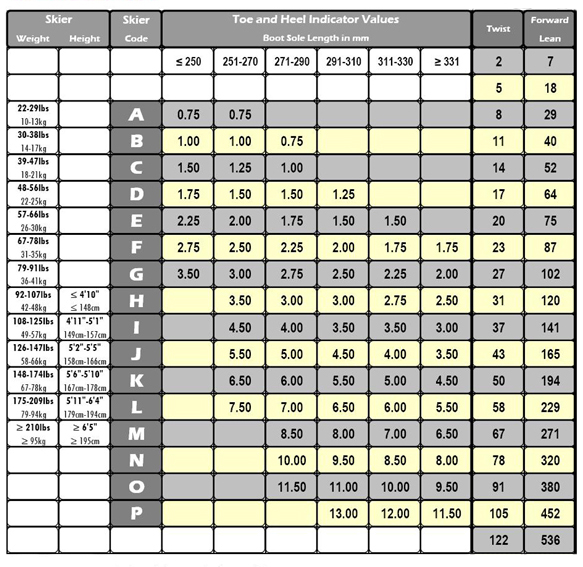
Downhill Ski Bindings DIN Chart Powder7 Ski Shop

Ski binding set up DIN and other help
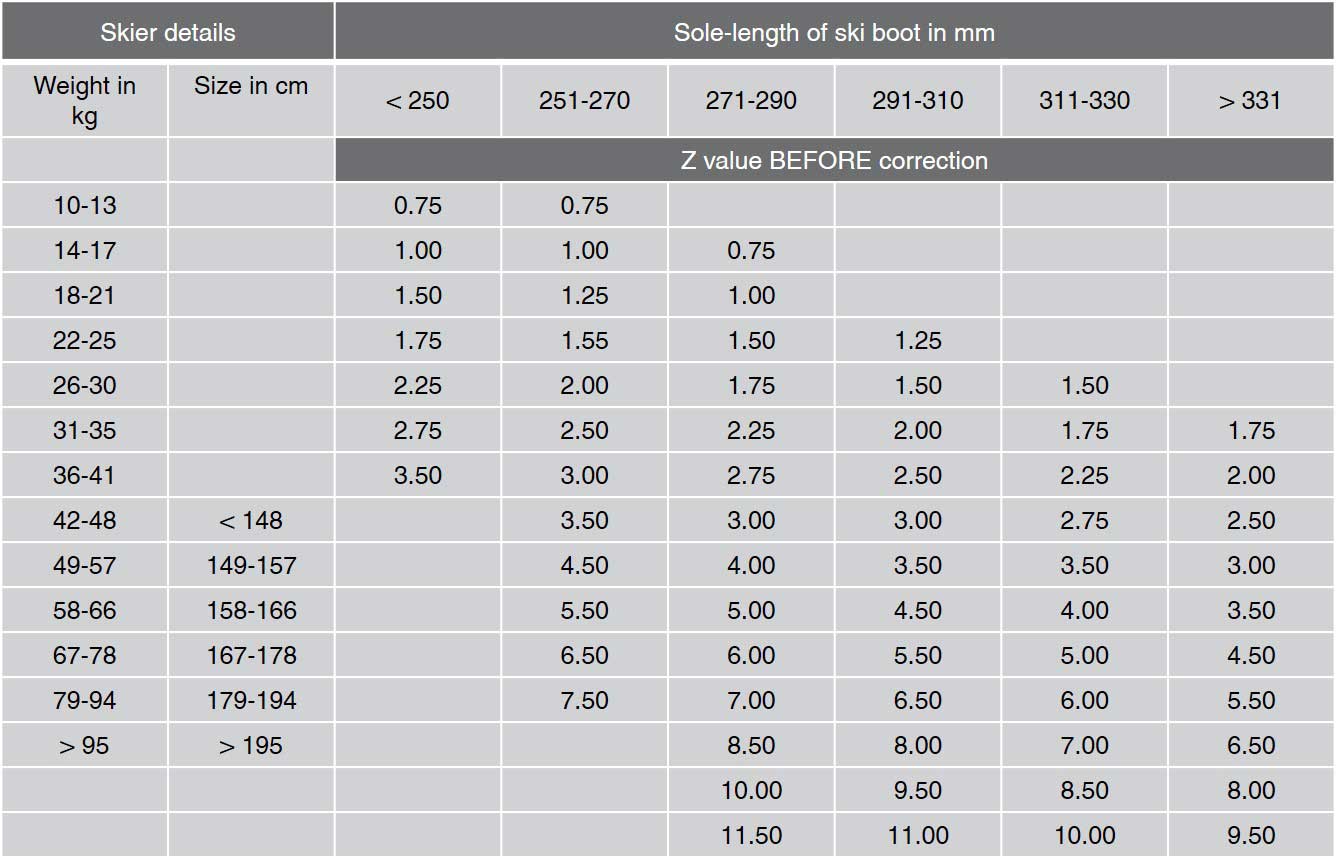
Din Chart For Ski Bindings

Ski Binding Sizing Chart
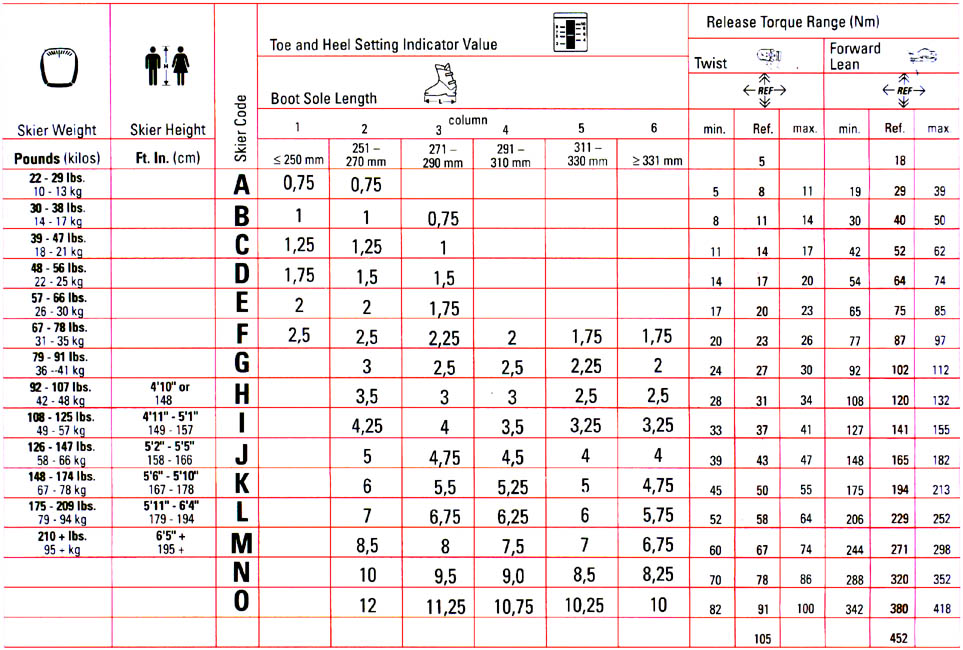
DIN Chart for ski binding release settings
Web Based On Your Height, Weight, Age, Boot Sole Length, And Skier Type, You Will Have A Din Setting That Must Fall Within The Advertised Din Range Of The Binding.
The Calculated Value Is For Reference Only.
You’ll Also Need To Know Your Din (Release Force) Setting Which Can Be Determined By Your Skiing Ability, Weight, Height, And Boot Sole Length.
Use The Chart To Find A Recommended Din Range For Your Bindings.
Related Post:
