Sinusoidal Pattern Ecg
Sinusoidal Pattern Ecg - An ecg is an essential investigation in the context of hyperkalaemia. The earliest manifestation of hyperkalaemia is an increase in t wave amplitude. Cardiovascular collapse and death are imminent. Tall tented t waves (early sign) prolonged pr interval; • treatment of hyperkalaemia includes emergency measures To address the clinical significance of sinusoidal heart rate (shr) pattern and review its occurrence, define its characteristics, and explain its physiopathology. The qrs complex duration is normal (0.08 sec) as is the morphology. Web at levels above 8.0 meq/l, we may see what looks like a bizarre idioventricular rhythm, or a sine wave pattern. This pattern usually appears when the serum potassium levels are well over 8.0 meq/l. Web sinus rhythm is the normal rhythm of the heart and no treatment is relevant. Web the sine wave pattern depicts worsening cardiac conduction delay caused by the elevated level of extracellular potassium. An ecg is an essential investigation in the context of hyperkalaemia. Web ecg features of normal sinus rhythm. Web sinus rhythm is present when the dominant pacemaker controlling impulse generation is the sinus node ( waveform 1 and waveform 2 ). Web. Web sinus rhythm is the normal rhythm of the heart and no treatment is relevant. Ed burns has compiled a very instructive. We describe the case of a patient who presented with hyperkalaemia and an electrocardiographic aspect consistent with a. The qrs complex duration is normal (0.08 sec) as is the morphology. Arrhythmias from the sinoatrial node are also discussed. Cardiovascular collapse and death are imminent. The combination of broadening qrs complexes and tall t waves produces a sine wave pattern on the ecg readout. Learn the definition, physiology, criteria for sinus rhythm, with emphasis on ecg interpretation. P waves upright in leads i and ii, inverted in avr. Ecg obtained after therapy for hyperkalemia was given and the potassium. This pattern usually appears when the serum potassium levels are well over 8.0 meq/l. Arrhythmias from the sinoatrial node are also discussed. Web ecg changes in hyperkalaemia. Ecg obtained after therapy for hyperkalemia was given and the potassium level corrected. In this setting, activation of the atria is from right to left, superior to inferior, and anterior to posterior. Fetal heart rate baseline undulating every 3 to 5 minutes for ≥ 20 minutes a ≥ 15 bpm above baseline rate, onset to peak < 30 seconds, lasts for at least 15 seconds ‡ Web ecg features of normal sinus rhythm. Arrhythmias from the sinoatrial node are also discussed. The physical examination was unremarkable, but oxygen saturation was. This sine. This sine wave pattern signals cardiac arrest is imminent. In this setting, activation of the atria is from right to left, superior to inferior, and anterior to posterior. Web hyperkalaemia is defined as a serum potassium level of > 5.2 mmol/l. Web at levels above 8.0 meq/l, we may see what looks like a bizarre idioventricular rhythm, or a sine. Ed burns has compiled a very instructive. Web the original ecg signals contain noise, primarily including baseline drift, powerline interference, and muscle artifacts. The combination of broadening qrs complexes and tall t waves produces a sine wave pattern on the ecg readout. Web ecg features of normal sinus rhythm. • treatment of hyperkalaemia includes emergency measures • treatment of hyperkalaemia includes emergency measures We describe the case of a patient who presented with hyperkalaemia and an electrocardiographic aspect consistent with a. Ed burns has compiled a very instructive. Tall tented t waves (early sign) prolonged pr interval; Web ecg changes in hyperkalaemia. The earliest manifestation of hyperkalaemia is an increase in t wave amplitude. This sine wave pattern signals cardiac arrest is imminent. To address the clinical significance of sinusoidal heart rate (shr) pattern and review its occurrence, define its characteristics, and explain its physiopathology. We describe the case of a patient who presented with hyperkalaemia and an electrocardiographic aspect consistent with. (see normal sinus rhythm and sinus arrhythmia.) Ed burns has compiled a very instructive. For a comprehensive discussion of hyperkalemia on the ecg with many examples of the different phases, go to life in the fast lane. Web ecg changes in hyperkalaemia. This sine wave pattern signals cardiac arrest is imminent. Web hyperkalaemia is defined as a serum potassium level of > 5.2 mmol/l. For a comprehensive discussion of hyperkalemia on the ecg with many examples of the different phases, go to life in the fast lane. In this setting, activation of the atria is from right to left, superior to inferior, and anterior to posterior. Cardiovascular collapse and death are imminent. Learn the definition, physiology, criteria for sinus rhythm, with emphasis on ecg interpretation. As k + levels rise further, the situation is becoming critical. This pattern usually appears when the serum potassium levels are well over 8.0 meq/l. Web sinus rhythm is present when the dominant pacemaker controlling impulse generation is the sinus node ( waveform 1 and waveform 2 ). Web the sine wave pattern depicts worsening cardiac conduction delay caused by the elevated level of extracellular potassium. An ecg is an essential investigation in the context of hyperkalaemia. Tall tented t waves (early sign) prolonged pr interval; Web sinus rhythm is the normal rhythm of the heart and no treatment is relevant. (see normal sinus rhythm and sinus arrhythmia.) Web high serum potassium can lead to alterations in the waveforms of the surface electrocardiogram (ecg) and cardiac death unless treated promptly. This sine wave pattern signals cardiac arrest is imminent. Web ecg features of normal sinus rhythm.
Sine Wave Hyperkalemia Ecg Changes
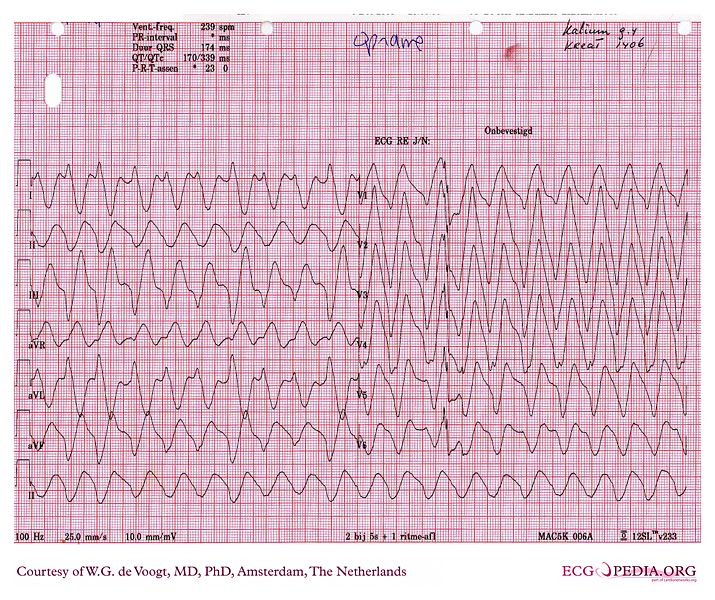
Sine wave pattern wikidoc
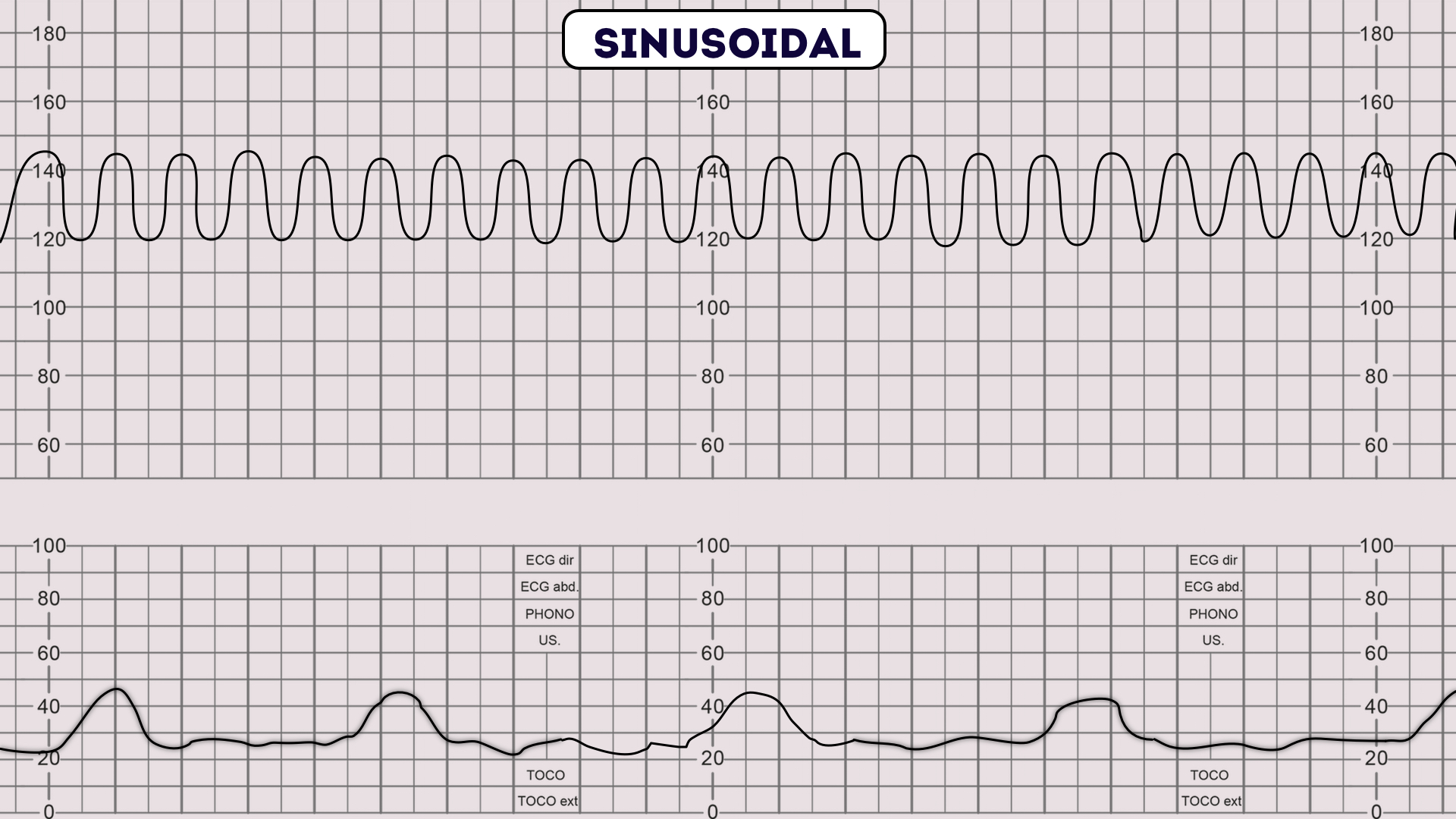
How to Read a CTG CTG Interpretation Geeky Medics

Sine Wave Pattern Ecg Images and Photos finder

ECG changes due to electrolyte imbalance (disorder) Cardiovascular

12 lead EKG showing sinewave done in the emergency room. Download

Understanding the EKG Signal Atrial Fibrillation Resources for Patients
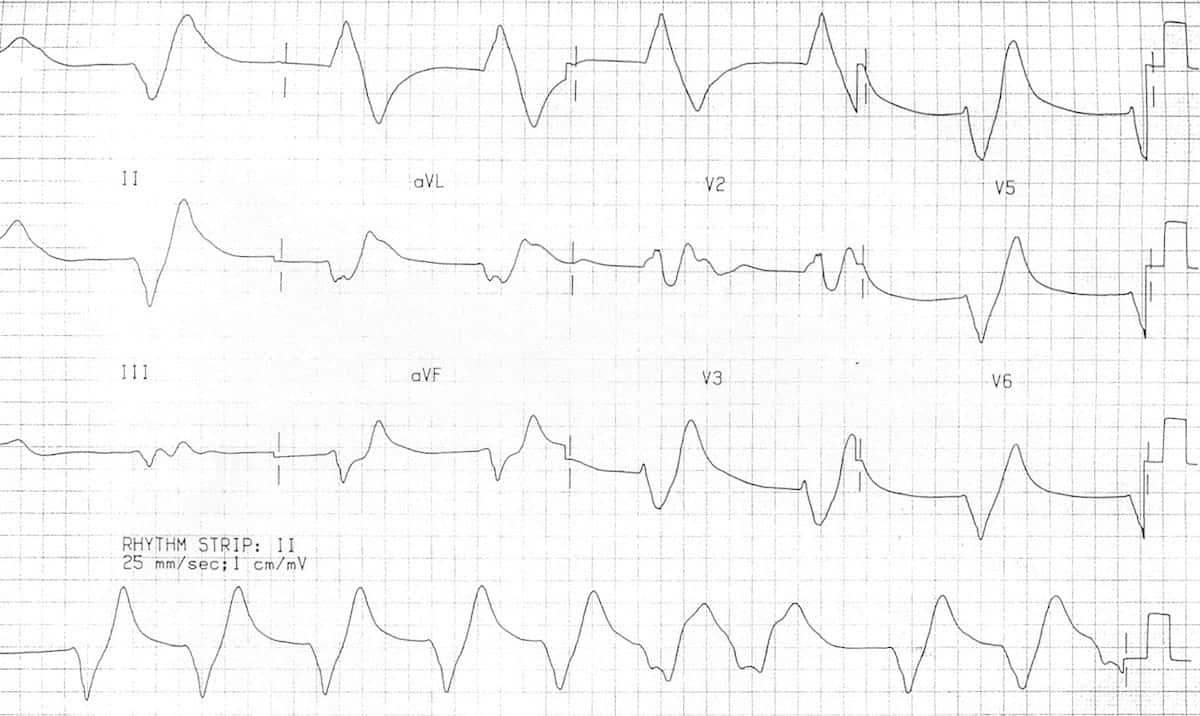
Hyperkalaemia ECG changes • LITFL • ECG Library

Ecg sinusoidal pulse lines frequency heartbeat Vector Image
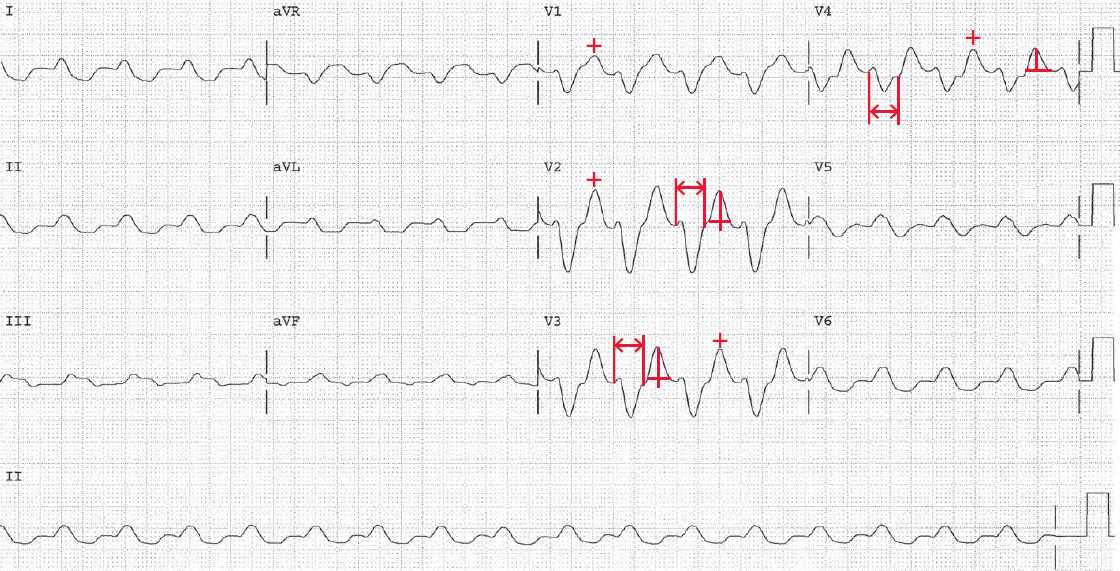
ECG Case 151 Hyperkalemia with Sine Wave Pattern Manual of Medicine
Web This Is The “Sine Wave” Rhythm Of Extreme Hyperkalemia.
The Pr Interval Remains Constant.
• Treatment Of Hyperkalaemia Includes Emergency Measures
Web Sine Wave Pattern In Hyperkalemia Is Attributed To Widening Of Qrs With St Elevation And Tented T Wave Merging Together With Loss Of P Wave And Prolongation Of Pr Interval (Ettinger Et Al., 1974).
Related Post: