Shoulder Joint Capsular Pattern
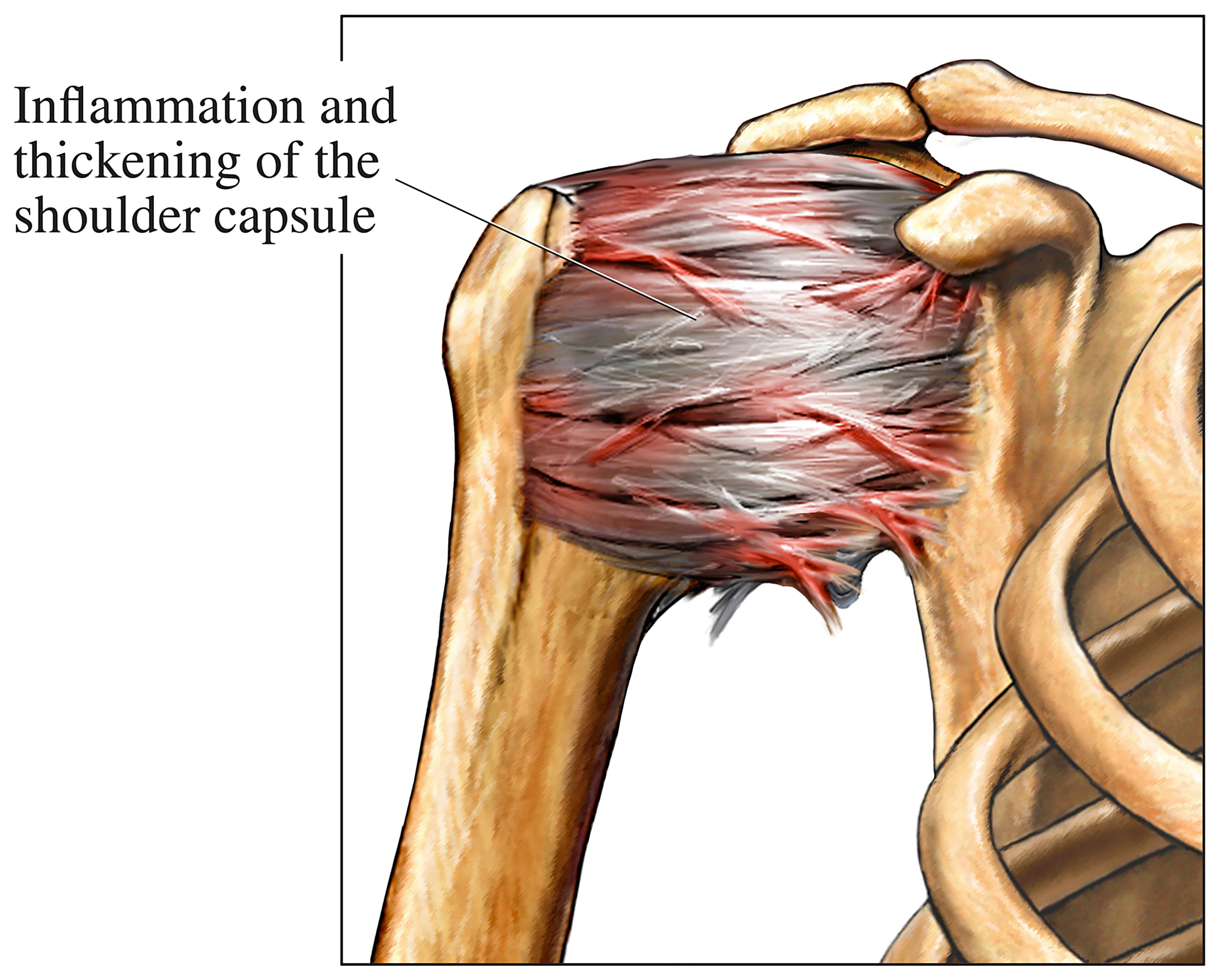
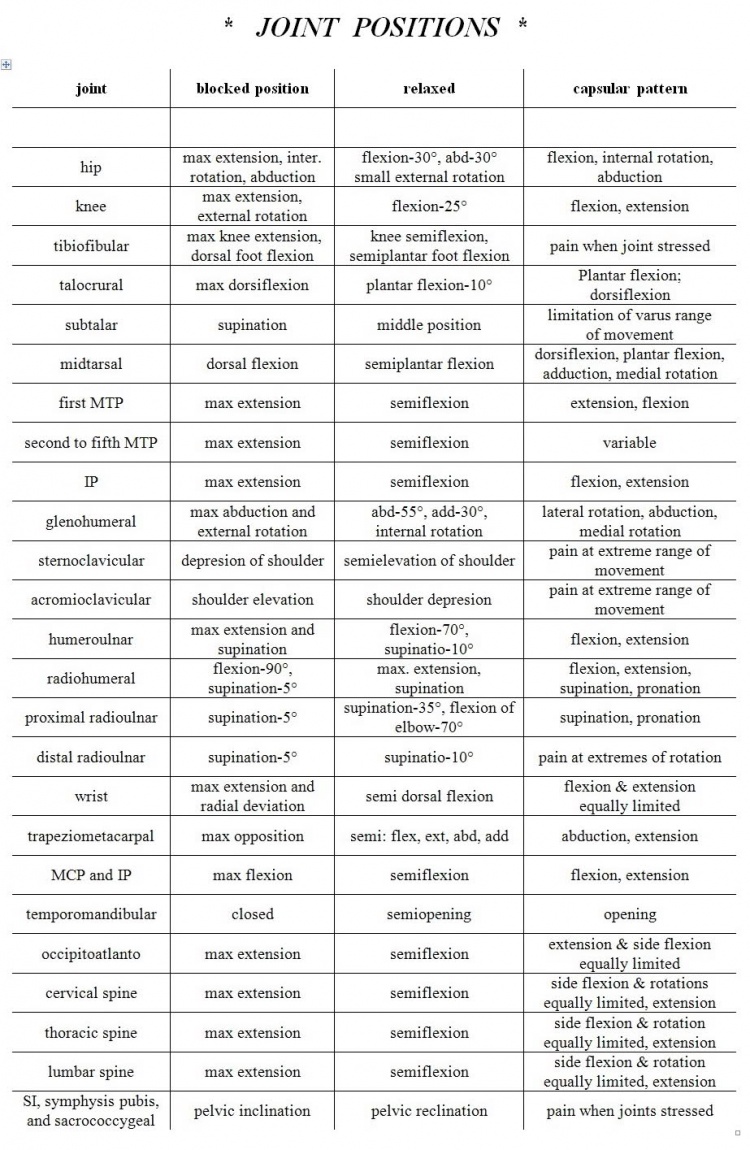
Shoulder Joint Capsular Pattern - In frozen shoulder, the shoulder capsule thickens and becomes stiff and tight. The capsular pattern is a combination of pain and/or limitation, which points in the direction of a joint problem. Web frozen shoulder occurs when the connective tissue enclosing the joint thickens and tightens. This joint is formed from the combination of the humeral head and the glenoid fossa of the scapula. Web a capsular pattern is therefore evident with most loss of external rotation followed by flexion/abduction and then internal rotation. Web the overall active and passive range of motion (rom) of the shoulder joint in the capsular pattern is reduced, with the largest changes in rom observed, in descending order, in external rotation, abduction, and internal rotation 12). Lateral rotation > elevation > medial rotation. Starts when range of movement at the joint begins to improve. Web in the shoulder, the capsular pattern dictates that motion restrictions occur first in lateral rotation, then in abduction, and third in medial rotation. This has been explained in shoulder mobilization. In frozen shoulder, the shoulder capsule thickens and becomes stiff and tight. Web the glenohumeral, or shoulder, joint is a synovial joint that attaches the upper limb to the axial skeleton. When we apply the concept of capsule constrained theory we need to understand the pathology site before mobilisation. Web the most common cause of bony shoulder stiffness is osteoarthritis. Review treatment and management options for patients with frozen shoulder/adhesive capsulitis. The hallmark signs of this condition are severe pain and being unable to move your shoulder — either on your own or with the help of someone else. At the completion of this chapter, the reader will be able to: A capsular pattern is a proportional motion restriction unique. Describe the diagnostic approach for evaluating adhesive capsulitis. Signs and symptoms typically begin slowly, then get worse. Describe the anatomy of the joints, ligaments, muscles, blood, and nerve supply that comprise the shoulder complex. Symptoms usually start slowly and get worse over time. A clinician should be aware about the joint limitation that exists but isn't capsular in nature. Web the glenohumeral, or shoulder, joint is a synovial joint that attaches the upper limb to the axial skeleton. Web patients with frozen shoulder commonly present with rom restrictions in a capsular pattern. Web the overall active and passive range of motion (rom) of the shoulder joint in the capsular pattern is reduced, with the largest changes in rom observed,. Signs and symptoms typically begin slowly, then get worse. A clinician should be aware about the joint limitation that exists but isn't capsular in nature. Thick bands of tissue — called adhesions — develop. Starts when range of movement at the joint begins to improve. Web the overall active and passive range of motion (rom) of the shoulder joint in. Web the glenohumeral joint capsule is an important passive stabiliser of the shoulder joint. Signs and symptoms typically begin slowly, then get worse. Web a beighton score was not calculated but based on symptomatic joint hypermobility she was diagnosed with shoulder microinstability and infraspinatus tendinopathy secondary to hsd. Web the common capsular pattern of limitation has historically been described as. Symptoms usually start slowly and get worse over time. A capsular pattern is a proportional motion restriction unique to every joint that indicates irritation of the entire joint. Each joint, under muscular control, has a specific capsular pattern. Capsular pattern in the shoulder is a limitation of certain passive movements : Frozen shoulder, also called adhesive capsulitis, involves stiffness and. Web the glenohumeral joint capsule is an important passive stabiliser of the shoulder joint. Starts when range of movement at the joint begins to improve. The shoulder joint has a capsular pattern where external rotation is more limited than abduction which is more limited than. Web shoulder joint mobilisation follows a definitive pattern based on the concave convex rule. Her. Web shoulder pain accompanied by a marked decrease in range of motion is the chief characteristic of adhesive capsulitis. The hallmark signs of this condition are severe pain and being unable to move your shoulder — either on your own or with the help of someone else. Pathology and pathogenesis of primary frozen shoulder. Starts when range of movement at. But within one to three years symptoms typically get better. Frozen shoulder, also called adhesive capsulitis, involves stiffness and pain in the shoulder joint. Web a capsular pattern is therefore evident with most loss of external rotation followed by flexion/abduction and then internal rotation. Web shoulder joint mobilisation follows a definitive pattern based on the concave convex rule. Web the. In frozen shoulder, the shoulder capsule thickens and becomes stiff and tight. The capsular pattern is a combination of pain and/or limitation, which points in the direction of a joint problem. Review treatment and management options for patients with frozen shoulder/adhesive capsulitis. On examination, this characteristically presents as stiffness with a hard end feel capsular pattern, although this is less. Web a beighton score was not calculated but based on symptomatic joint hypermobility she was diagnosed with shoulder microinstability and infraspinatus tendinopathy secondary to hsd. Web summarize the pathophysiology of frozen shoulder/adhesive capsulitis. A capsular pattern is a proportional motion restriction unique to every joint that indicates irritation of the entire joint. Starts when range of movement at the joint begins to improve. It provides most of the shoulder's extensibility anteriorly and inferiorly, and it “winds up” during abduction and external rotation. It is one of four joints that comprise the shoulder complex. Each joint, under muscular control, has a specific capsular pattern. Web the common capsular pattern of limitation has historically been described as diminishing motions with external shoulder rotation being the most limited, followed closely by shoulder flexion, and internal rotation. Web the most common cause of bony shoulder stiffness is osteoarthritis (oa) of the glenohumeral joint. This has been explained in shoulder mobilization. In the early stages of a capsular restriction you may only see limitations to external rotation. Web shoulder joint mobilisation follows a definitive pattern based on the concave convex rule.
Capsular pattern 1 Physical therapy, School work, Therapy
Adhesive Capsulitis of the Shoulder Therapists in Galway Therapists
Capsular and Noncapsular Patterns Physiopedia
Capsular pattern of the shoulder labquiz
Frozen Shoulder Adhesive Capsulitis OrthoInfo AAOS

capsular pattern shoulder YouTube

Mr Paul Jarrett Adhesive Capsulitis / Frozen Shoulder Murdoch
Capsular Ligament of the Shoulder Joint ClipArt ETC

27Physiocouk manchesterphysio Joint Capsular

Capsular pattern of the shoulder labquiz
The Hallmark Signs Of This Condition Are Severe Pain And Being Unable To Move Your Shoulder — Either On Your Own Or With The Help Of Someone Else.
A Clinician Should Be Aware About The Joint Limitation That Exists But Isn't Capsular In Nature.
Web The Glenohumeral Joint Capsule Is An Important Passive Stabiliser Of The Shoulder Joint.
For Example In The Shoulder Joint In Case Of Subacromial Bursitis, Abduction May Be Restricted But With Minimal Restriction In Rotation Component Of Joint.
Related Post: