Roadside Drainage Ditch Design
Roadside Drainage Ditch Design - Web roadside ditch management (rdm) stabilization is important to maintain proper water conveyance in ditches. Drainage & stormwater · bioengineering solutions · erosion control E main purpose of a roadside ditch is to protect the integrity of the road. The water from outlet ditches normally discharges to existing waterway. Design criteria for traversable drainage ditches are provided in the current. Web recommendations for ditch cross sections (front slope, bottom, depth, and back slope) can be found in the current edition of the roadside design guide. Web conndot drainage manual october 2000 11.6.4 roadside and median channels roadside channels are commonly used with uncurbed roadway sections to convey. Web methods and procedures are given for the hydraulic design of storm drainage systems. Web analyze a proposed roadside ditch at critical locations to verify that it will provide adequate hydraulic capacity to carry the peak rate of runoff that is expected to occur with the. If ditches are not stable, it can jeopardize the structure of the. Web proper drainage of water from the pavement is an important design step in pavement design either from the surface water or from the subsurface water. Roadside ditches convey runoff from roads and adjacent tributary areas. Web recommendations for ditch cross sections (front slope, bottom, depth, and back slope) can be found in the current edition of the roadside design. Web reshaping ditches can slow down water flow and reduce sediment movement. Web roadside ditches are generally located alongside uncurbed roadways with the primary purpose of conveying runoff away from the roadway. Web the design of the road drainage system is a major intervention in watershed management. If ditches are not stable, it can jeopardize the structure of the. Web. Web the design of the road drainage system is a major intervention in watershed management. If a road is equipped with a (proper) drainage system, the water along the roads will. Web outlet ditches are drainage structures that lead the water from the side ditches away from the road area. If the landscape design includes any changes in the highway. If the landscape design includes any changes in the highway drainage. Web proper drainage of water from the pavement is an important design step in pavement design either from the surface water or from the subsurface water. These structures, tested in arctic road. Design criteria for traversable drainage ditches are provided in the current. Web drainage ditches over which a. Design criteria for traversable drainage ditches are provided in the current. Design methods are presented for evaluating rainfall and runoff magnitude, pavement. Web reshaping ditches can slow down water flow and reduce sediment movement. Web roadside ditch management (rdm) stabilization is important to maintain proper water conveyance in ditches. The water from outlet ditches normally discharges to existing waterway. The water from outlet ditches normally discharges to existing waterway. Runof in roadside ditches directly contributes to stream flooding and stream. Design criteria for traversable drainage ditches are provided in the current. Web roadside ditch management (rdm) stabilization is important to maintain proper water conveyance in ditches. Drainage & stormwater · bioengineering solutions · erosion control Design criteria for traversable drainage ditches are provided in the current. Roadside ditches convey runoff from roads and adjacent tributary areas. If the landscape design includes any changes in the highway drainage. If a road is equipped with a (proper) drainage system, the water along the roads will. Web outlet ditches are drainage structures that lead the water from the. Roads are designed to drain rain and snowmelt away from the road, toward the. Runof in roadside ditches directly contributes to stream flooding and stream. Web methods and procedures are given for the hydraulic design of storm drainage systems. Web roadside ditches are generally located alongside uncurbed roadways with the primary purpose of conveying runoff away from the roadway. Web. Web the drainage section develops and updates policies, procedures, standards, specifications, and guidelines for these practice areas: Web the primary purpose for the roadside ditch is the control of surface drainage from the pavement and surrounding area. E main purpose of a roadside ditch is to protect the integrity of the road. Design criteria for traversable drainage ditches are provided. The water from outlet ditches normally discharges to existing waterway. Web the design of drainage ditches must give due consideration to the equipment and methods to be used for construction, and to the needs for and methods to be used in. Roadside ditches convey runoff from roads and adjacent tributary areas. Design criteria for traversable drainage ditches are provided in. Web roadside ditches are generally located alongside uncurbed roadways with the primary purpose of conveying runoff away from the roadway. Web the design of the road drainage system is a major intervention in watershed management. Web roadside ditch management (rdm) stabilization is important to maintain proper water conveyance in ditches. If ditches are not stable, it can jeopardize the structure of the. Roads are designed to drain rain and snowmelt away from the road, toward the. Drainage & stormwater · bioengineering solutions · erosion control Web recommendations for ditch cross sections (front slope, bottom, depth, and back slope) can be found in the current edition of the roadside design guide. Web roadside ditches are generally located alongside uncurbed roadways with the primary purpose of conveying runoff away from the roadway. Web methods and procedures are given for the hydraulic design of storm drainage systems. Design methods are presented for evaluating rainfall and runoff magnitude, pavement. Web the design of drainage ditches must give due consideration to the equipment and methods to be used for construction, and to the needs for and methods to be used in. Roadside ditches convey runoff from roads and adjacent tributary areas. Runof in roadside ditches directly contributes to stream flooding and stream. If a road is equipped with a (proper) drainage system, the water along the roads will. Web analyze a proposed roadside ditch at critical locations to verify that it will provide adequate hydraulic capacity to carry the peak rate of runoff that is expected to occur with the. Providing timely responses to inquiries from the.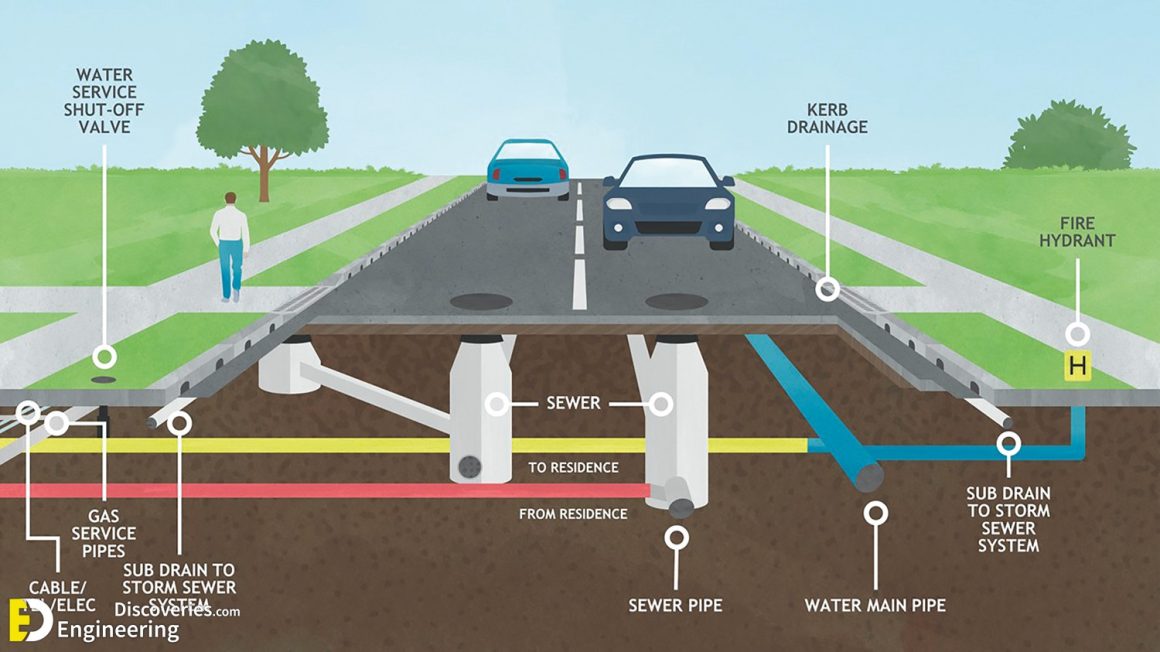
35+ Photos Of Highway Surface Drainage System Engineering Discoveries

18+ Best Drainage Ditch Landscaping Ideas & Designs For Your Yard

4. Components of road drainage system ROADEX Network

Highway Drainage System Information Engineering Discoveries
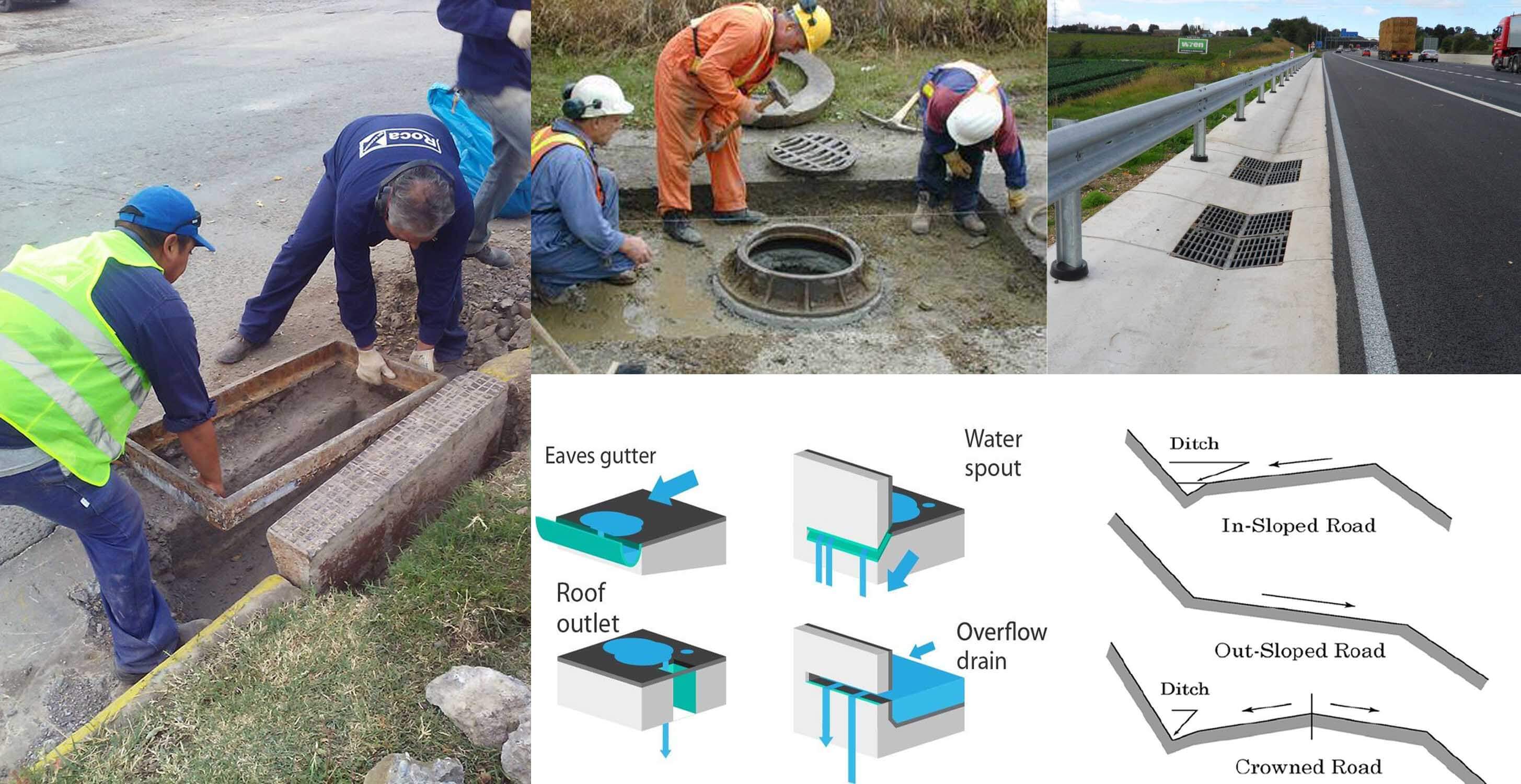
Highway Drainage System Information Engineering Discoveries

HIGHWAY DRAINAGE DESIGN OF LONGITUDINAL DRAIN YouTube

4. Components of road drainage system ROADEX Network

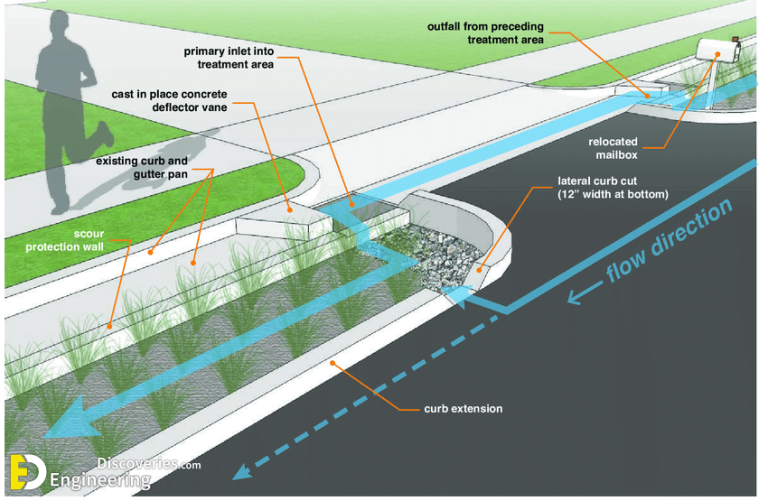
Types of Road Drainage systems & their features

GEOWEB Geocells Design & Build Highly Resistant Roadside Ditches

Roadside Drainage International Erosion Control Systems
If The Landscape Design Includes Any Changes In The Highway Drainage.
Web Sheet Ice On Side Ditches Can Be Prevented With Special Drainage Structures That Handle The Water Before It Reaches The Side Ditch.
Web Drainage Ditches Over Which A Motor Vehicle Can Safely Drive Are Called Traversable.
Web The District Roadway Design Engineer Should Be Consulted About Any Proposed Design Changes.
Related Post: