Reticulonodular Pattern
Reticulonodular Pattern - It is characterised by the presence of perilymphatic and peribronchovascular. Web the chest radiograph revealed a diffuse, coarse reticulonodular pattern with no zonal predominance and short kerley b lines at the periphery of the mid and lower zones of. Web a typical example of predominantly reticulonodular pattern is sarcoidosis. Presence of viral epidemics in the community and seasonality of viral. Cxr (pa and lateral) shows bilateral and extensive reticular. Web the main radiological patterns are: Identifying and determining the cause of interstitial lung disease can be challenging. Web reticular interstitial pattern is one of the patterns of linear opacification in the lung. Web three principal patterns of reticulation may be seen. Web infection of the lower respiratory tract, acquired by way of the airways and confined to the lung parenchyma and airways, typically presents radiologically as one of. Web learn about the different types of interstitial patterns on chest radiographs, including reticulonodular, which is caused by overlap of reticular shadows or. Web interstitial lung disease is diagnosed radiographically when a reticular, nodular, or honeycomb pattern or any combination thereof is recognizable. Web infection of the lower respiratory tract, acquired by way of the airways and confined to the. These are interlobular septal thickening, honeycombing, and irregular reticulation. It is characterised by the presence of perilymphatic and peribronchovascular. Web diagnosis of viral pneumonia depends on clinical criteria, epidemiological factors (e.g. Web a typical example of predominantly reticulonodular pattern is sarcoidosis. Web learn about the different types of interstitial patterns on chest radiographs, including reticulonodular, which is caused by overlap. It can either mean a plain film or hrct/ct feature. Web nodular opacification is one of the broad patterns of pulmonary opacification that can be described on a chest radiograph or chest ct. These are interlobular septal thickening, honeycombing, and irregular reticulation. Identifying and determining the cause of interstitial lung disease can be challenging. Web reticular interstitial pattern is one. These are interlobular septal thickening, honeycombing, and irregular reticulation. Web a typical example of predominantly reticulonodular pattern is sarcoidosis. Web three principal patterns of reticulation may be seen. It can either mean a plain film or hrct/ct feature. Presence of viral epidemics in the community and seasonality of viral. This may be used to describe a regional pattern or a. Web infection of the lower respiratory tract, acquired by way of the airways and confined to the lung parenchyma and airways, typically presents radiologically as one of. Web the chest radiograph revealed a diffuse, coarse reticulonodular pattern with no zonal predominance and short kerley b lines at the periphery. Identifying and determining the cause of interstitial lung disease can be challenging. Cxr (pa and lateral) shows bilateral and extensive reticular. It can either mean a plain film or hrct/ct feature. A large number of disorders fall into this broad category. Web diagnosis of viral pneumonia depends on clinical criteria, epidemiological factors (e.g. A large number of disorders fall into this broad category. Web reticular interstitial pattern is one of the patterns of linear opacification in the lung. This may be used to describe a regional pattern or a. Web a typical example of predominantly reticulonodular pattern is sarcoidosis. Identifying and determining the cause of interstitial lung disease can be challenging. Cxr (pa and lateral) shows bilateral and extensive reticular. Diffuse, bilateral, reticulonodular infiltrates are often concerning for pulmonary infection, such as miliary tuberculosis (tb), or metastatic disease from. Web a typical example of predominantly reticulonodular pattern is sarcoidosis. Web three principal patterns of reticulation may be seen. Web learn about the different types of interstitial patterns on chest radiographs, including. It is characterised by the presence of perilymphatic and peribronchovascular. Web interstitial lung disease is diagnosed radiographically when a reticular, nodular, or honeycomb pattern or any combination thereof is recognizable. Web the main radiological patterns are: Web learn about the different types of interstitial patterns on chest radiographs, including reticulonodular, which is caused by overlap of reticular shadows or. To. Web nodular opacification is one of the broad patterns of pulmonary opacification that can be described on a chest radiograph or chest ct. Web the chest radiograph revealed a diffuse, coarse reticulonodular pattern with no zonal predominance and short kerley b lines at the periphery of the mid and lower zones of. Cxr (pa and lateral) shows bilateral and extensive. Web infection of the lower respiratory tract, acquired by way of the airways and confined to the lung parenchyma and airways, typically presents radiologically as one of. Web the main radiological patterns are: Presence of viral epidemics in the community and seasonality of viral. Identifying and determining the cause of interstitial lung disease can be challenging. This may be used to describe a regional pattern or a. A large number of disorders fall into this broad category. Cxr (pa and lateral) shows bilateral and extensive reticular. To recognize the radiological pattern of the disease, it is. It can either mean a plain film or hrct/ct feature. Web three principal patterns of reticulation may be seen. Web diagnosis of viral pneumonia depends on clinical criteria, epidemiological factors (e.g. Diffuse, bilateral, reticulonodular infiltrates are often concerning for pulmonary infection, such as miliary tuberculosis (tb), or metastatic disease from. Web reticular interstitial pattern is one of the patterns of linear opacification in the lung. Web learn about the different types of interstitial patterns on chest radiographs, including reticulonodular, which is caused by overlap of reticular shadows or. Web the chest radiograph revealed a diffuse, coarse reticulonodular pattern with no zonal predominance and short kerley b lines at the periphery of the mid and lower zones of. Web a typical example of predominantly reticulonodular pattern is sarcoidosis.
a) CXR in anteroposterior view shows bilateral reticular pattern with
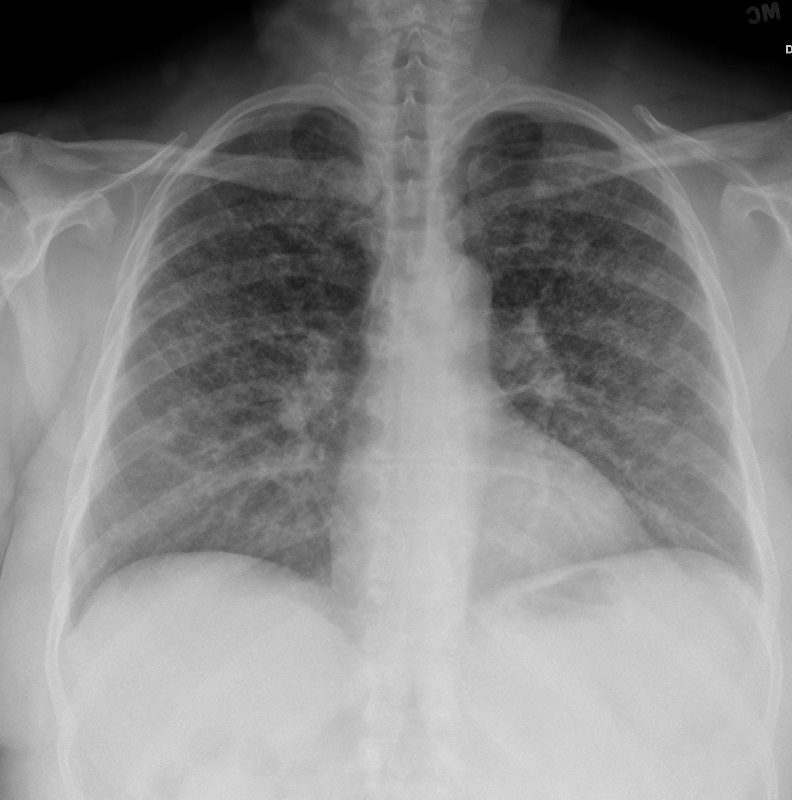
CXR Reticulonodular Pattern Lungs
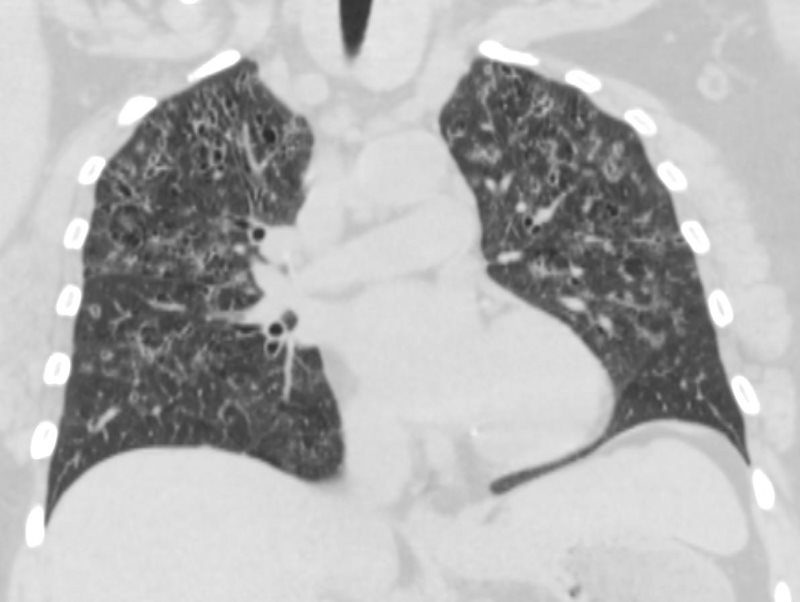
CXR Reticulonodular Pattern Lungs

SARCOIDOSIS There is a widespread, predominantly reticulonodular
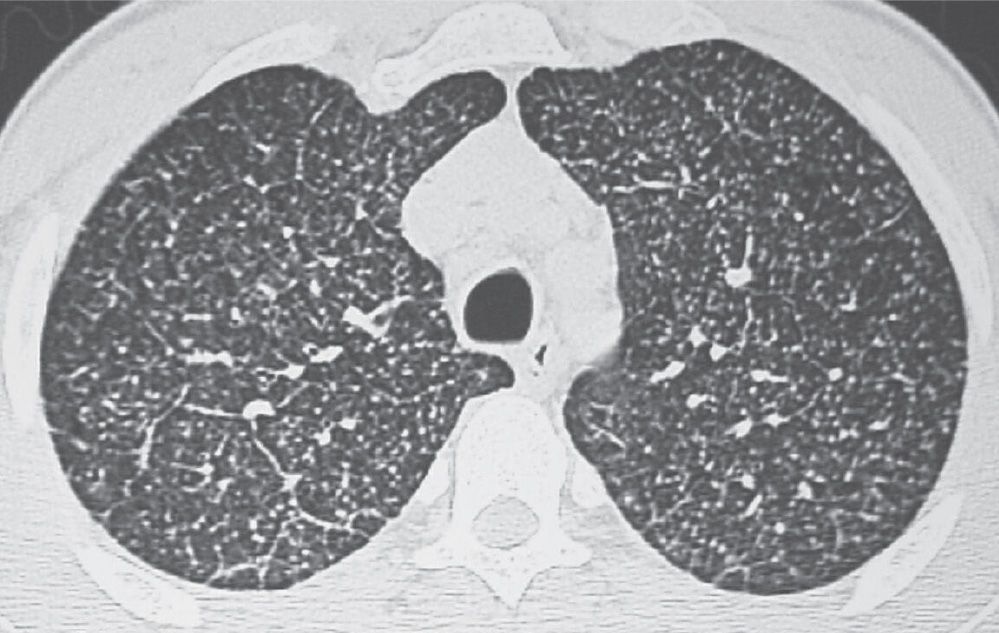
Interstitial Lung Disease Radiology Key
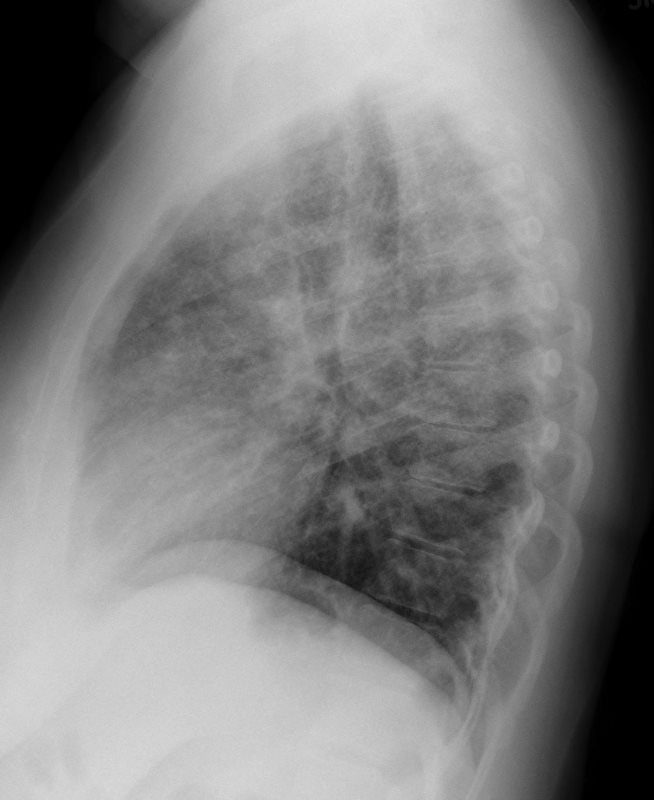
CXR Reticulonodular Pattern Lungs

Chest Xrays reticulonodular pattern with perihilar distribution

4 diffuse reticular or reticulonodular pattern

4 diffuse reticular or reticulonodular pattern
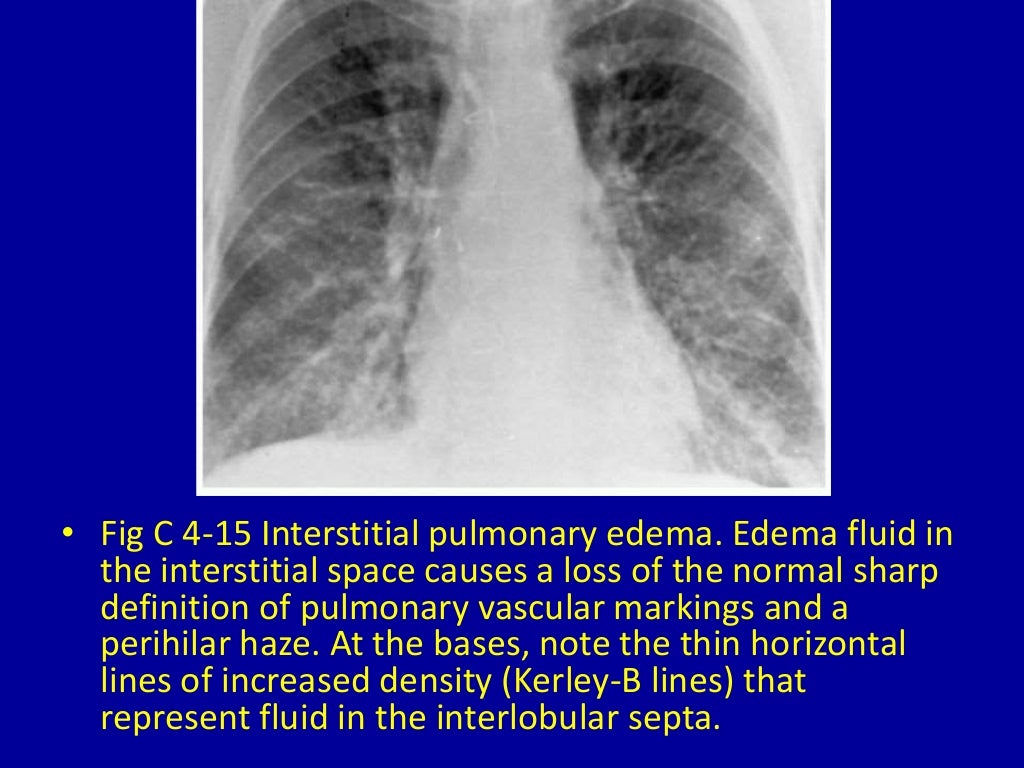
4 diffuse reticular or reticulonodular pattern
It Is Characterised By The Presence Of Perilymphatic And Peribronchovascular.
Web A Reticulonodular Interstitial Pattern Is An Imaging Descriptive Term That Can Be Used In Thoracic Radiographs Or Ct Scans When Are There Is An Overlap Of Reticular Shadows With Nodular Shadows.
Web Pattern Recognition Should Be Combined With Knowledge Of Clinical Factors In Order To Generate A Limited And Meaningful Differential Diagnosis [ Table 2 ].
These Are Interlobular Septal Thickening, Honeycombing, And Irregular Reticulation.
Related Post: