Residual Sugar In Wine Chart
Residual Sugar In Wine Chart - Below 1% sweetness, wines are considered dry. Typically, wines with less than 10 g/l are considered dry. Let’s look at the varying styles of wine and their residual sugar levels. So for example, a wine with 10. According to wine folly, the sugar in grapes is a blend of glucose and. Web the sweetness level of a wine is measured by the amount of residual sugar it contains. The abbreviation for this is g/l. A wine that has higher acidity will taste more ‘dry’ than a wine with less acidity. Many dry wines have none at all. Web learn how to identify and talk about the sweetness in wine with this chart and guide. The style of wine and decisions made by the winemaker can influence the. It’s measured in grams per liter. Web when reading a tech sheet: Typically, wines with less than 10 g/l are considered dry. So, technically, the less alcohol a wine has, the sweeter the wine is. Below 1% sweetness, wines are considered dry. Web learn how to measure residual sugar (rs) in wine, aka the sugar that remains after fermentation. Web residual sugar is the amount of unconverted grape sugars — measured in grams/liter (g/l). It is important to note that the sweetness of wine is not a measure of sugar content, but rather the amount. Several producers of new zealand sauvignon blanc will leave a couple. Risk of refermentation in the bottle. According to wine folly, the sugar in grapes is a blend of glucose and. So, technically, the less alcohol a wine has, the sweeter the wine is. The sweetness in a wine comes from residual sugar (rs), which is the sugar remaining in. Web the sweetness level of a wine is measured by the amount of residual sugar it contains. Web learn how to measure residual sugar in wine using different techniques and tools. We break down calories and carbohydrates, and how to watch your sugar intake. Web residual sugar (rs for short) refers to any natural grape sugars that are leftover after. Typically, wines with less than 10 g/l are considered dry. The style of wine and decisions made by the winemaker can influence the. Web residual sugar (rs) is the sugar left unfermented in a wine. Residual sugars are the grape sugars left over after fermentation in winemaking. Wines above 5% sweetness are. According to wine folly, the sugar in grapes is a blend of glucose and. Risk of refermentation in the bottle. The style of wine and decisions made by the winemaker can influence the. Web learn how to identify and talk about the sweetness in wine with this chart and guide. Find out why residual sugar is important for winemaking and. Web learn how to measure residual sugar (rs) in wine, aka the sugar that remains after fermentation. Explore the different levels of residual sugar in various wine styles and how to pair. Wines above 5% sweetness are. Below 1% sweetness, wines are considered dry. Several producers of new zealand sauvignon blanc will leave a couple. Web vintners measure residual sugar in wine in grams per liter. Risk of refermentation in the bottle. It is an important factor in determining. Explore the different levels of residual sugar in various wine styles and how to pair. Web residual sugar (rs) is the sugar left unfermented in a wine. If fermentable sugars (~0.5% or greater) and yeast remain in your wine, a second. Find out why residual sugar is important for winemaking and how to adjust it. A wine that has higher acidity will taste more ‘dry’ than a wine with less acidity. So, technically, the less alcohol a wine has, the sweeter the wine is. Below 1% sweetness,. Wines above 5% sweetness are. So, technically, the less alcohol a wine has, the sweeter the wine is. Web the sweetness level of a wine is measured by the amount of residual sugar it contains. Several producers of new zealand sauvignon blanc will leave a couple. This stands for residual sugar and is the measure of sweetness in wine. Web residual sugar is a term commonly used in the wine industry to describe the amount of sugar that remains in the wine after fermentation. Web the sweetness level is frequently indicated on wine labels. Web learn how residual sugar impacts the taste, texture, and balance of wine. A wine that has higher acidity will taste more ‘dry’ than a wine with less acidity. Below 1% sweetness, wines are considered dry. The style of wine and decisions made by the winemaker can influence the. Web learn how to identify and talk about the sweetness in wine with this chart and guide. Web learn how to measure residual sugar in wine using different techniques and tools. Web residual sugar (rs) is the natural grape sugar leftovers in a wine after the fermentation finishes. Web here’s how much sugar is in red and white wines, by the glass and bottle. Find out why residual sugar is important for winemaking and how to adjust it. Learn how rs affects sweetness, labelling and stability, and see a chart of rs levels for different wine. It’s measured in grams per liter. Web residual sugar (or rs) is from natural grape sugars leftover in a wine after the alcoholic fermentation finishes. If fermentable sugars (~0.5% or greater) and yeast remain in your wine, a second. Wines above 5% sweetness are.
UNCORKED Wine's residual sugar determines sweetness, dryness

You're So Sweet All About Residual Sugar in Wine At Home

Residual Sugar in Wine Chart
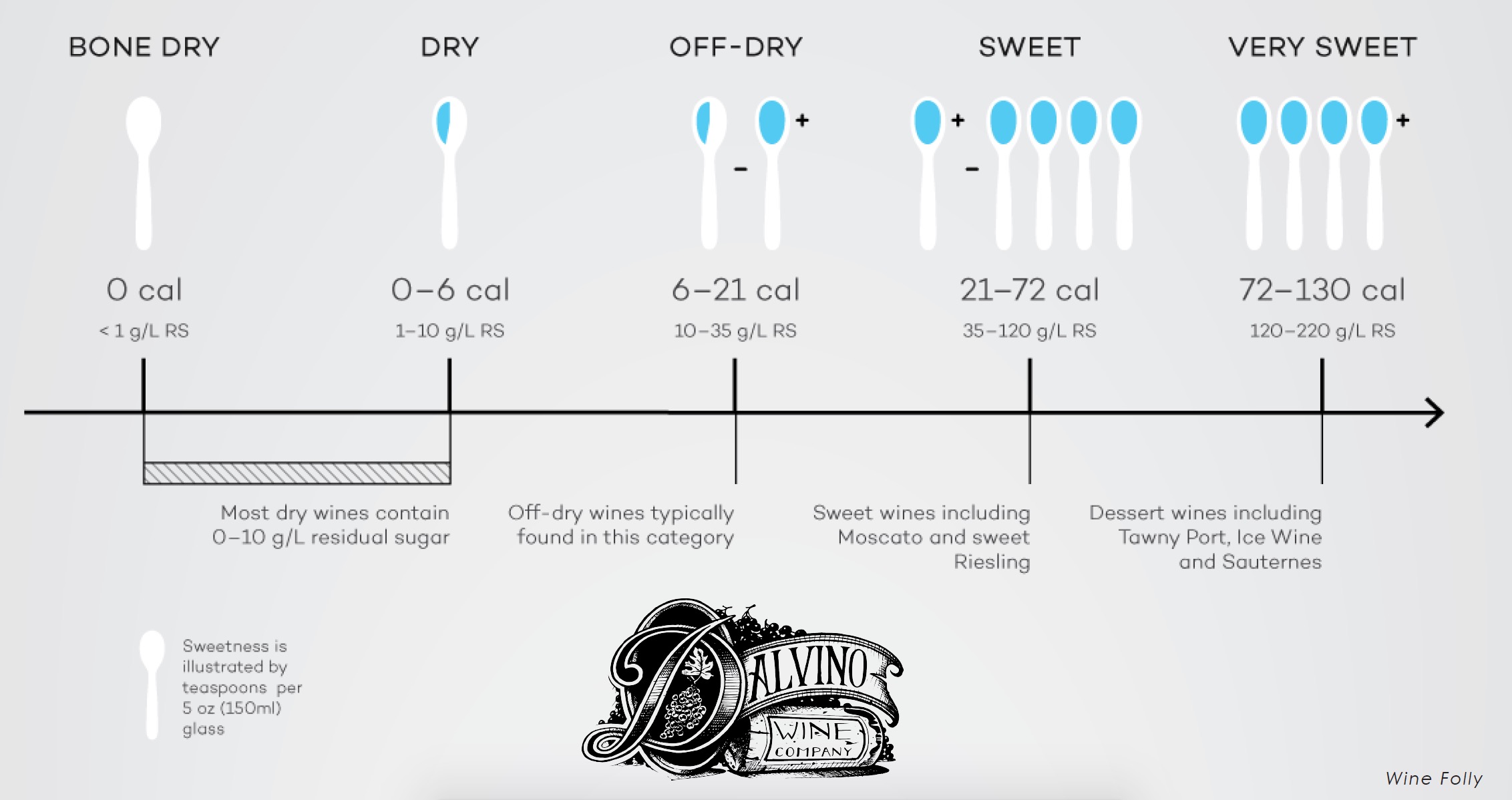
Residual Sugar in Wine and How it's Measured Dalvino Wine Company

Wine sweetness charts Boulogne Wine Blog
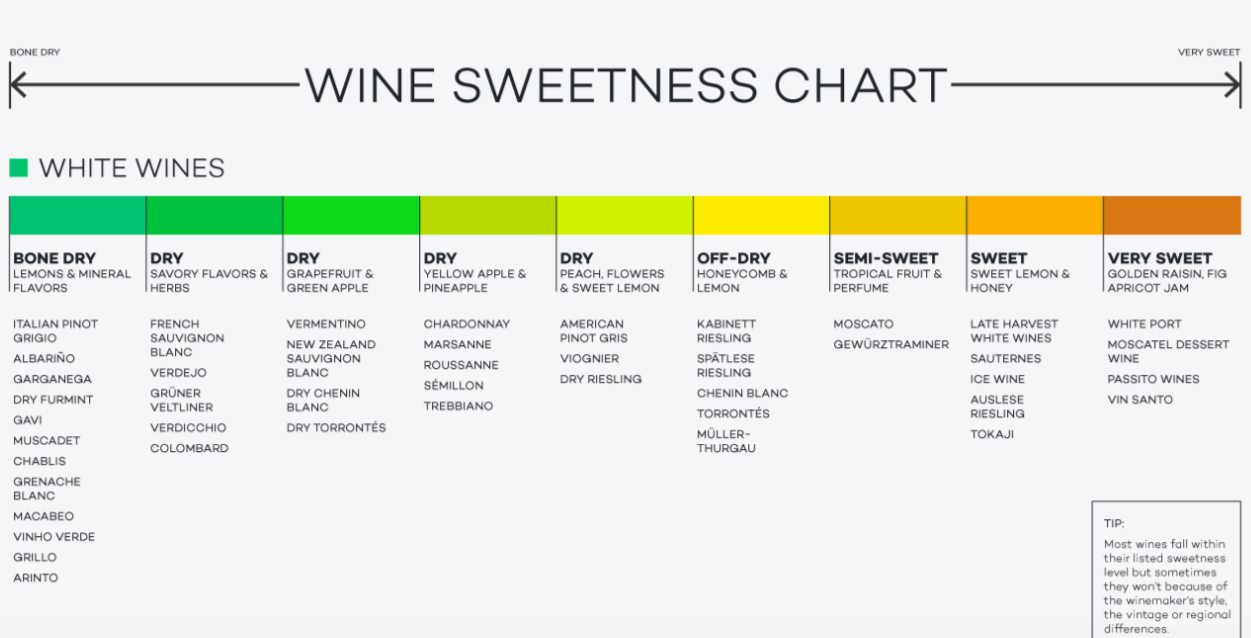
Residual Sugar and Cheap Wines

Residual Sugar In Wine Chart
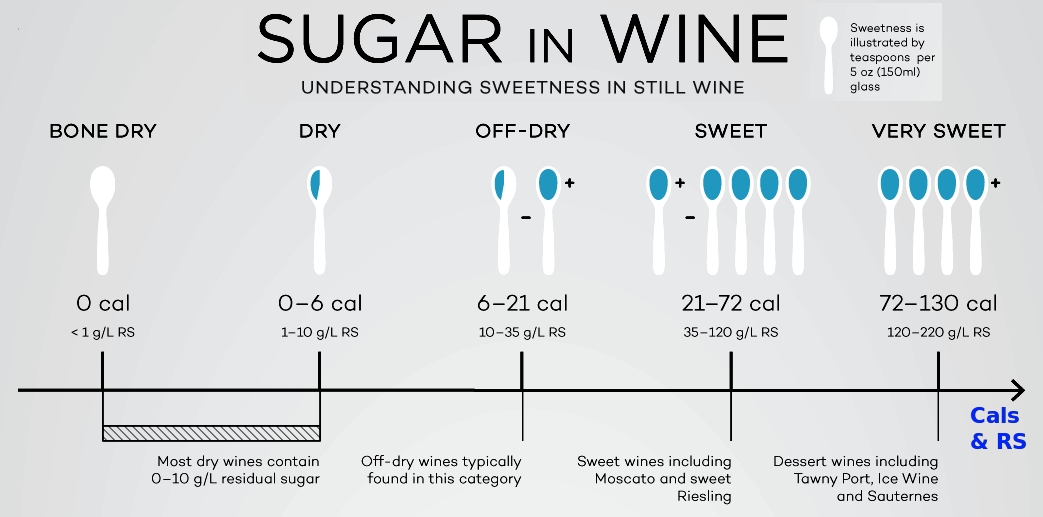
Residual Sugar in Wine Sweetness Chart and Calories in Wine Summary
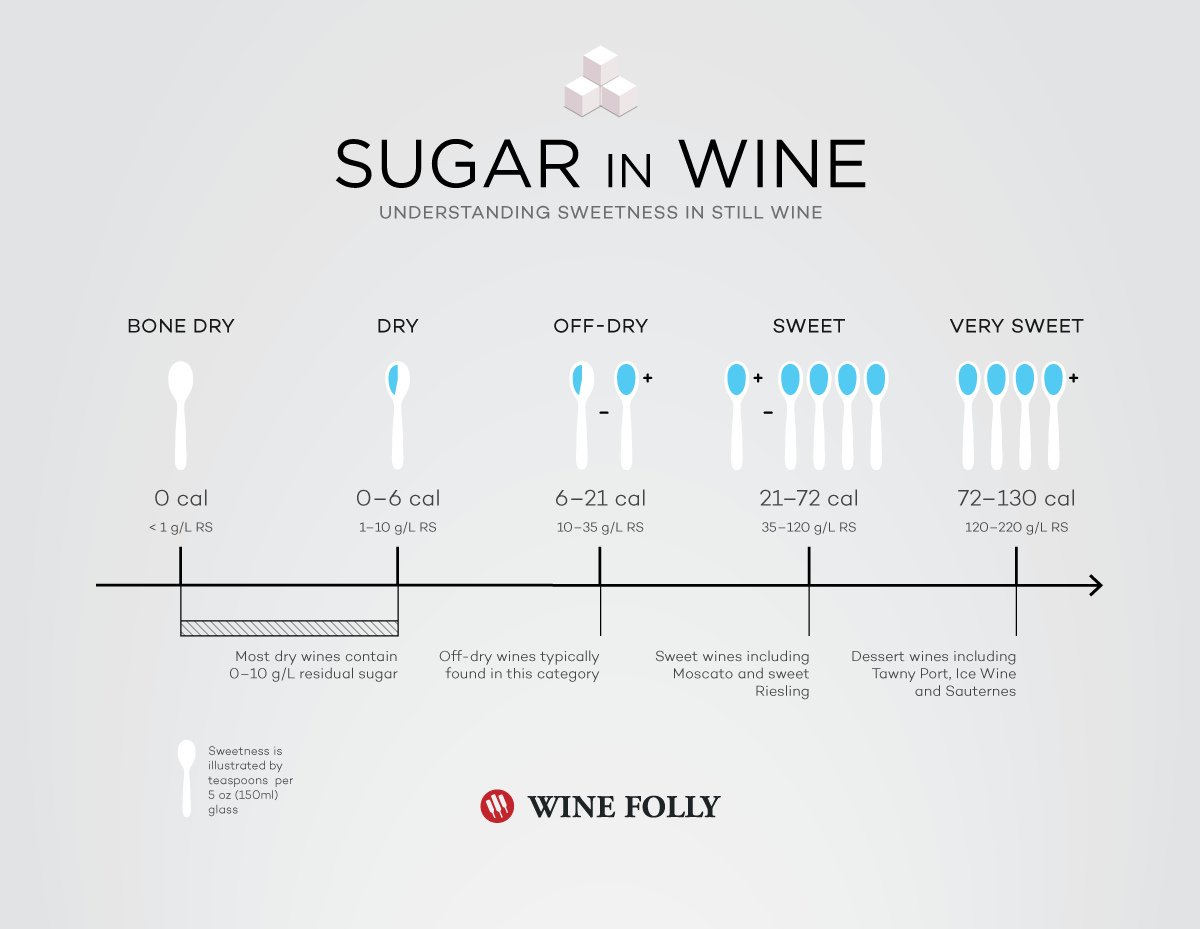
Sugar in Wine Chart (Calories and Carbs) Wine Folly

Residual Sugar WINE DECODED
Web When Reading A Tech Sheet:
Many Dry Wines Have None At All.
It Is An Important Factor In Determining.
Web Residual Sugar Is The Amount Of Unconverted Grape Sugars — Measured In Grams/Liter (G/L).
Related Post: