Reinforcement Punishment Chart
Reinforcement Punishment Chart - Although the stickers themselves aren’t valuable, they can be exchanged for something that is. Reinforcement can be positive or negative, and punishment can also be positive or negative. It involves taking away something unpleasant in response to a stimulus. Behavior that is reinforced (rewarded) will likely be repeated, and behavior that is punished will occur less frequently. As a reminder, punishment is a consequence that immediately follows a behavior and decreases the future likelihood of the behavior. Reinforcement can be positive or negative, and punishment can also be positive or negative. Web reinforcement theory is a framework, also known as operant conditioning, detailed in the chart below: Web reinforcement in psychology involves increasing the likelihood of a behavior by introducing a stimulus, whereas punishment decreases the likelihood of a behavior by introducing a consequence. Positive reinforcement is the addition of a positive outcome to strengthen behavior. Both reinforcement and punishment can be positive or negative. Web thorndike (1898, 1911) and skinner have shown that reinforcement (also known as reward) strengthens a behavior, i.e., increases its frequency, whereas punishment weakens a behavior, i.e., decreases its frequency. Web reinforcement theory is a framework, also known as operant conditioning, detailed in the chart below: Reinforcement can be positive or negative, and punishment can also be positive or negative.. Positive reinforcement adds something to encourage behavior, while negative reinforcement removes something. Behavior that is reinforced (rewarded) will likely be repeated, and behavior that is punished will occur less frequently. Although the stickers themselves aren’t valuable, they can be exchanged for something that is. Reinforcement can also be distinguished as primary/secondary and intrinsic/extrinsic. Reinforcement strengthens a behavior, while punishment weakens. Both reinforcement and punishment can be positive or negative. Normally, we use “reinforce” in a speech to mean “emphasize,” while “punish” means “hurting.” Positive punishment introduces a consequence to deter behavior, and negative punishment takes something away. Web how it works. Web reinforcement theory is a framework, also known as operant conditioning, detailed in the chart below: Whether you are adding something to influence behavior (positive) or taking something away to influence behavior (negative). Web how it works. Reinforcement can also be distinguished as primary/secondary and intrinsic/extrinsic. Web the difference is that reinforcement aims to increase target behavior while punishment aims to decrease behavior. Ve a good understanding of reinforcement and punishment in terms of their impact. This means to review the broad processes and make sure they realize one process/procedure increa. On the contrary, punishment tends to decrease the changes of recurrence of the targeted behavior. Reinforcement aims to encourage a behavior, whereas punishment aims to reduce a behavior. Positive punishment involves taking away a desired stimulus to weaken a behavior. Positive reinforcement involves rewarding desired. What do the terms positive reinforcement and negative reinforcement really mean? Web reinforcement means you are increasing a behavior, and punishment means you are decreasing a behavior. Ve a good understanding of reinforcement and punishment in terms of their impact on behavior. Negative reinforcement is the removal of a negative outcome to strengthen a behavior. Reinforcement aims to encourage a. Web learn about the different types of reinforcement and punishment. Web this article encloses the difference between reinforcement and punishment, in a comprehensive manner. Web the difference is that reinforcement aims to increase target behavior while punishment aims to decrease behavior. Operant conditioning, or instrumental conditioning, is a theory of learning where behavior is influenced by its consequences. It focuses. Consistency and timing are crucial for effective positive reinforcement. Whether you are trying to encourage (reinforce) or discourage (punish) behavior. All reinforcers (positive or negative) increase the likelihood of a behavioral response. Reinforcement can also be distinguished as primary/secondary and intrinsic/extrinsic. It focuses on acknowledging and reinforcing actions through praise, rewards, or privileges. Reinforcement can be positive or negative, and punishment can also be positive or negative. Web it's split into two key consequences: Consistency and timing are crucial for effective positive reinforcement. Positive reinforcement involves rewarding desired behaviors to increase the likelihood of their repetition. All reinforcers (positive or negative) increase the likelihood of a behavioral response. Reinforcement aims to encourage a behavior, whereas punishment aims to reduce a behavior. Web it's split into two key consequences: Whether you are trying to encourage (reinforce) or discourage (punish) behavior. Web reinforcement means you are increasing a behavior, and punishment means you are decreasing a behavior. Reinforcement strengthens a behavior, while punishment weakens it. It involves taking away something unpleasant in response to a stimulus. Web for example, stickers on a chart are an example of token reinforcers. Reinforcement can be positive or negative, and punishment can also be positive or negative. Web reinforcement in psychology involves increasing the likelihood of a behavior by introducing a stimulus, whereas punishment decreases the likelihood of a behavior by introducing a consequence. In psychology, reinforcement refers to increasing the likelihood that a desired behavior will occur by. Positive reinforcement is the addition of a positive outcome to strengthen behavior. Reinforcement aims to encourage a behavior, whereas punishment aims to reduce a behavior. Consistency and timing are crucial for effective positive reinforcement. Reinforcement strengthens a behavior, while punishment weakens it. Web thorndike (1898, 1911) and skinner have shown that reinforcement (also known as reward) strengthens a behavior, i.e., increases its frequency, whereas punishment weakens a behavior, i.e., decreases its frequency. As with reinforcement, there are two types of punishment: Punishment, on the other hand, refers to any event that weakens or reduces the likelihood of a behavior. Positive reinforcement adds something to encourage behavior, while negative reinforcement removes something. Reinforcement can be positive or negative, and punishment can also be positive or negative. Web reinforcement means you are increasing a behavior, and punishment means you are decreasing a behavior. On the contrary, punishment tends to decrease the changes of recurrence of the targeted behavior.
Reinforcement/Punishment Diagram Quizlet

Positive/Negative Reinforcement/Punishment ABA Infographic by

Positive/Negative Reinforcement/Punishment ABA Infographic by
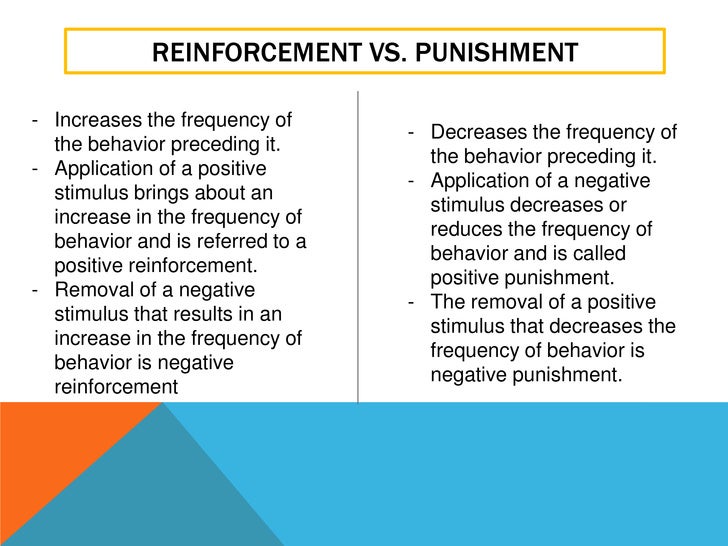
Reinforces & punishment 5

Printable Punishment Chart

Positive/Negative Reinforcement/Punishment Applied behavior analysis
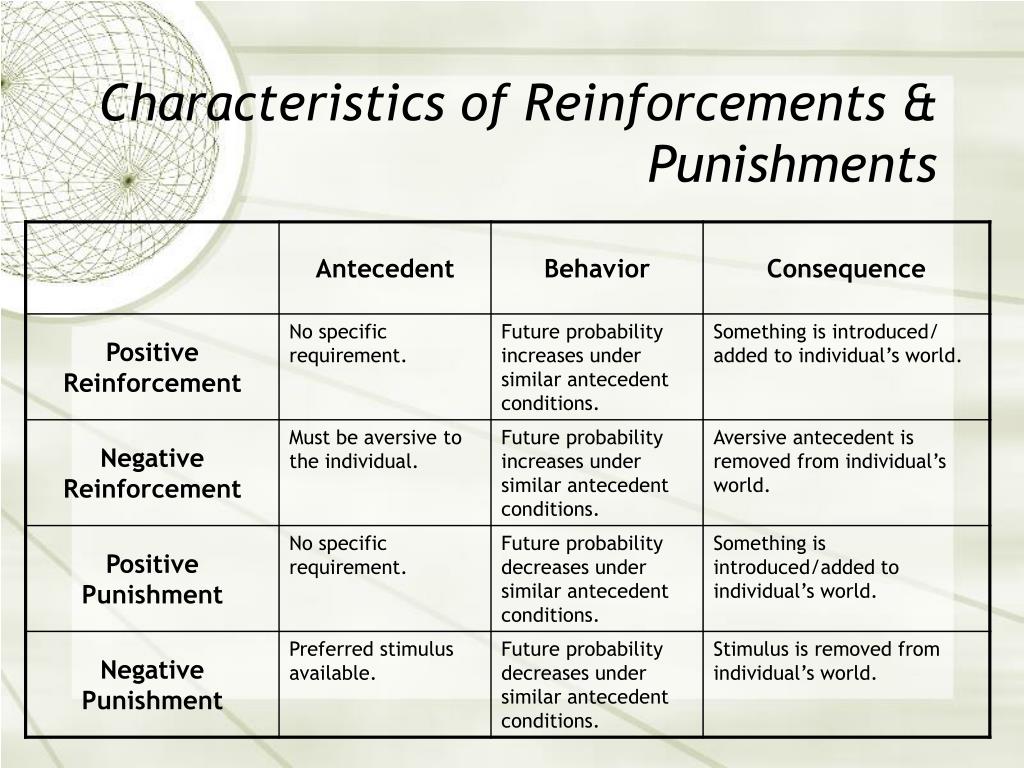
PPT Methods for Changing Target Behavior PowerPoint Presentation
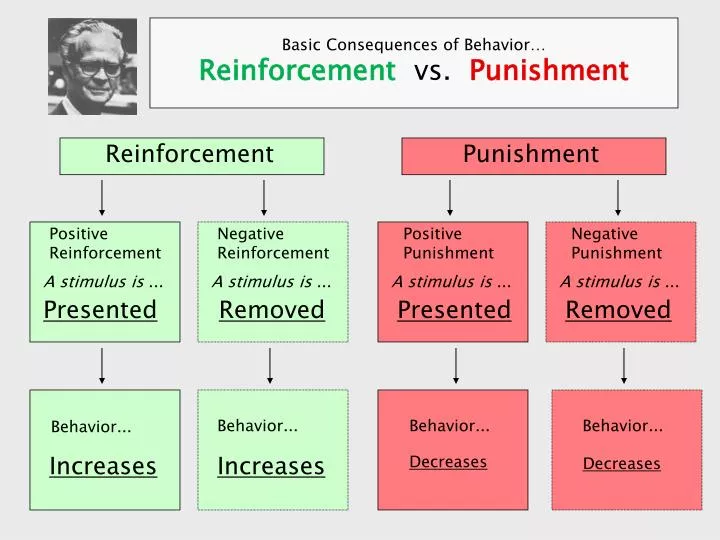
Reinforcement And Punishment Chart
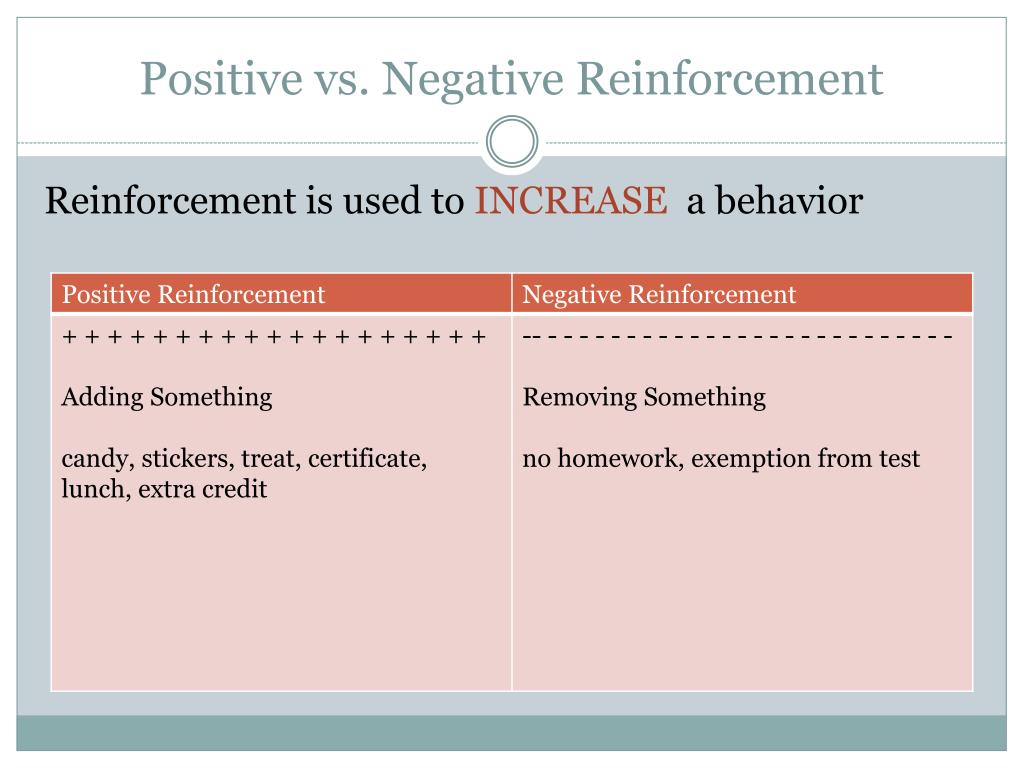
Positive And Negative Reinforcement Chart

Image result for consequence discipline charts Behavior analyst
Positive Punishment Introduces A Consequence To Deter Behavior, And Negative Punishment Takes Something Away.
To Increase Behavior To Decrease Behavior Reinforcer Punisher Something Is Removed Or Avoided Something Is Added Positive Reinforcement Negative Reinforcement Something Received Removed Positive Punishment Negative Punishment.
Negative Reinforcement Is The Removal Of A Negative Outcome To Strengthen A Behavior.
Reinforcement Can Also Be Distinguished As Primary/Secondary And Intrinsic/Extrinsic.
Related Post: