Reflection Coefficient From Smith Chart
Reflection Coefficient From Smith Chart - The smith chart is a polar plot of γ {\displaystyle \gamma } , therefore the magnitude of γ {\displaystyle \gamma } is given directly by the distance of a point to the center (with the edge of the smith. Web we now found the phase of the input reflection coefficient. You will recall from class that the input reflection coefficient to a transmission line of physical length l, г ü á, is given in terms of the load reflection coefficient г å by the expression г ü áг å a ? The smithplot function replaces the smithchart function. The reflection coefficient is completely determined by. Web this free online interactive smith chart tool is a calculator which can help you design matching networks and obtain maximum power transfer between your source and load. The reflection coefficient’s real and imaginary axis (the cartesian coordinates) is not shown on the actual smith chart. Web the reflection coefficient is just the ratio of the complex amplitude of a reflected wave to the amplitude of the incident wave. The most important application of smith chart is impedance matching. Web the smith chart • superimposes constant γ, r and x circles • we can quickly relate normalized line impedance to its corresponding reflection coefficient Web the horizontal line across the middle of the smith chart indicates pure resistance. Web the smith chart displays the complex reflection coefficient [equation 1, below], in polar form, for an arbitrary impedance (we'll call the impedance zl or the load impedance). Reflection coefficient and load (zl) are directly related: Web a smith chart is the polar plot of complex. Smith chart for reflection coefficient and load impedance: The normalized impedance is n 1(z)1 z(z) 1(z)1 γ γ γ γ + + == − − (2) the reflection coefficient and the. Web the most common view is to consider that the smith chart is a plot of the reflection coefficient at various stages in the circuit, i.e., γa, γb, γc,. Web the smith chart was invented by phillip smith in 1939 in order to provide an easily usable graphical representation of the complex reflection coefficient γ and reading of the associated complex terminating impedance. Basic facts and important points on the smith chart. To find the input reflection coefficient, we find the line that starts at the center of the. Web the smith chart was invented by phillip smith in 1939 in order to provide an easily usable graphical representation of the complex reflection coefficient γ and reading of the associated complex terminating impedance. Additionally the load, zl, is plotted and reactances, susceptances, or transmission lines transform the reflection coefficient from one stage to the next. This tool is javascript. Web a smith chart is the polar plot of complex reflection coefficient. O 1(z) z(z) z 1(z) γ γ ⎡ + ⎤ = ⎢ ⎥ ⎣ − ⎦ (1) where zo is the characteristic impedance of the system. Web there is a signal reflection with coefficient γ. Web the horizontal line across the middle of the smith chart indicates pure. Web the smith chart is a useful graphical tool to convert between impedances and reflection coefficients. Web the complex reflection coefficient (in the region | |, corresponding to passive loads) may be displayed graphically using a smith chart. The smith chart is a polar plot of γ {\displaystyle \gamma } , therefore the magnitude of γ {\displaystyle \gamma } is. The smith chart is a polar plot of γ {\displaystyle \gamma } , therefore the magnitude of γ {\displaystyle \gamma } is given directly by the distance of a point to the center (with the edge of the smith. To find the input reflection coefficient, we find the line that starts at the center of the smith chart and ends. Web the complex reflection coefficient (in the region | |, corresponding to passive loads) may be displayed graphically using a smith chart. Web the reflection coefficient is also known as s11 or return loss. Ý 6 ß 1 ; Web the horizontal line across the middle of the smith chart indicates pure resistance. A point on the unit circle indicate. You will recall from class that the input reflection coefficient to a transmission line of physical length l, г ü á, is given in terms of the load reflection coefficient г å by the expression г ü áг å a ? Web to achieve perfect matching, we want the antenna or load impedance to match the transmission line. To find. Web the smith chart • superimposes constant γ, r and x circles • we can quickly relate normalized line impedance to its corresponding reflection coefficient The smith chart is a polar plot of γ {\displaystyle \gamma } , therefore the magnitude of γ {\displaystyle \gamma } is given directly by the distance of a point to the center (with the. Web derivation of smith chart equations the relationship between impedance and reflection coefficient is given by: The most important application of smith chart is impedance matching. Web smith chart is used to represent the reflection coefficient graphically in polar coordinates. Or any device with a. Web the smith chart was invented by phillip smith in 1939 in order to provide an easily usable graphical representation of the complex reflection coefficient γ and reading of the associated complex terminating impedance. To find the input reflection coefficient, we find the line that starts at the center of the smith chart and ends on the , and then find the point where this line crosses the swr circle. Web the smith chart is a useful graphical tool to convert between impedances and reflection coefficients. Web a smith chart is the polar plot of complex reflection coefficient. O 1(z) z(z) z 1(z) γ γ ⎡ + ⎤ = ⎢ ⎥ ⎣ − ⎦ (1) where zo is the characteristic impedance of the system. In smith chart terms, we want to move the impedance zl towards the center of the smith chart, where the reflection coefficient is zero. The normalized impedance is n 1(z)1 z(z) 1(z)1 γ γ γ γ + + == − − (2) the reflection coefficient and the. Web a smith chart is commonly used to display the relationship between a reflection coefficient, typically s11 or s22, and a normalized impedance. Web the smith chart displays the complex reflection coefficient [equation 1, below], in polar form, for an arbitrary impedance (we'll call the impedance zl or the load impedance). Web this value is the conjugate of the lna's actual input reflection coefficient (with specified load), and is given by eq. Web as we discussed in class, the smith chart represents the complex plane of the reflection coefficient. Each point on the smith chart simultaneously represents both a value of z (bottom left), and the corresponding value of γ (bottom right), related by z= (1 + γ)/ (1 − γ).
The reflection coefficient in the Smith chart (&8 GHz; 12 GHz
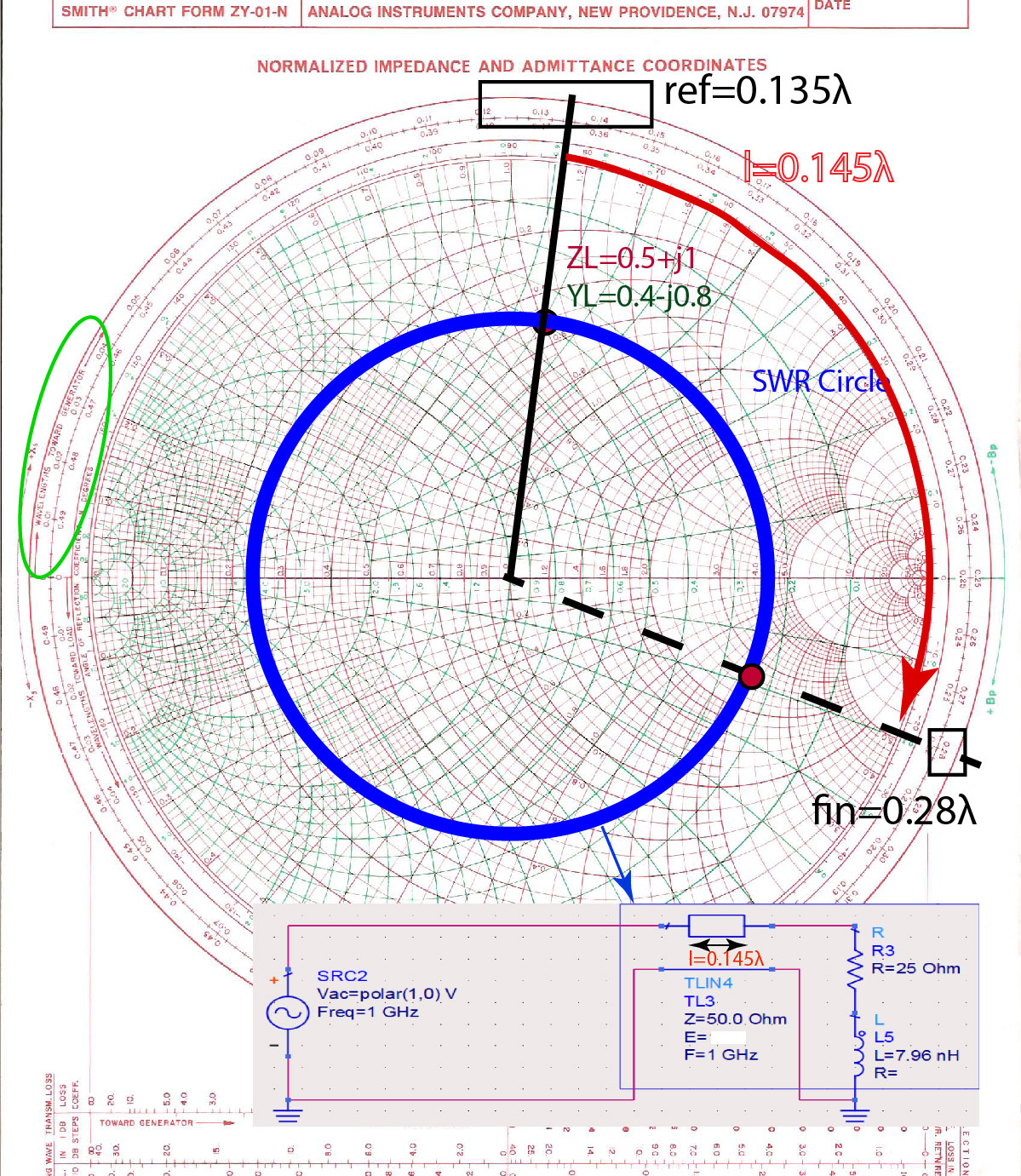
Input Reflection Coefficient and Impedance on Smith Chart Ximera

Smith chart reflection coefficient oplprice
Smith chart of the reflection coefficient. Download Scientific Diagram
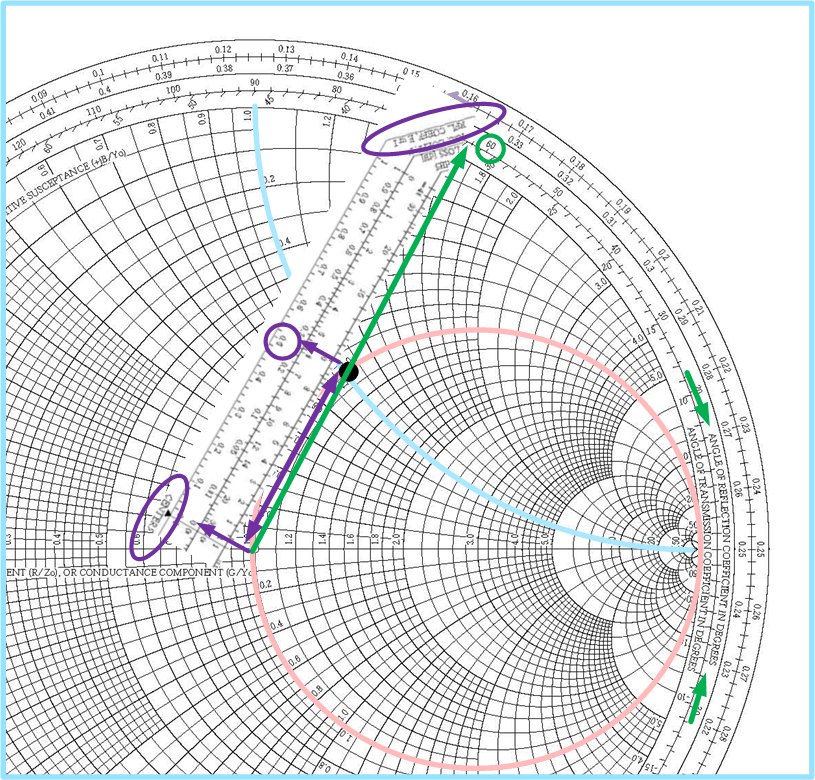
Impedance and Admittance on Smith Chart Ximera
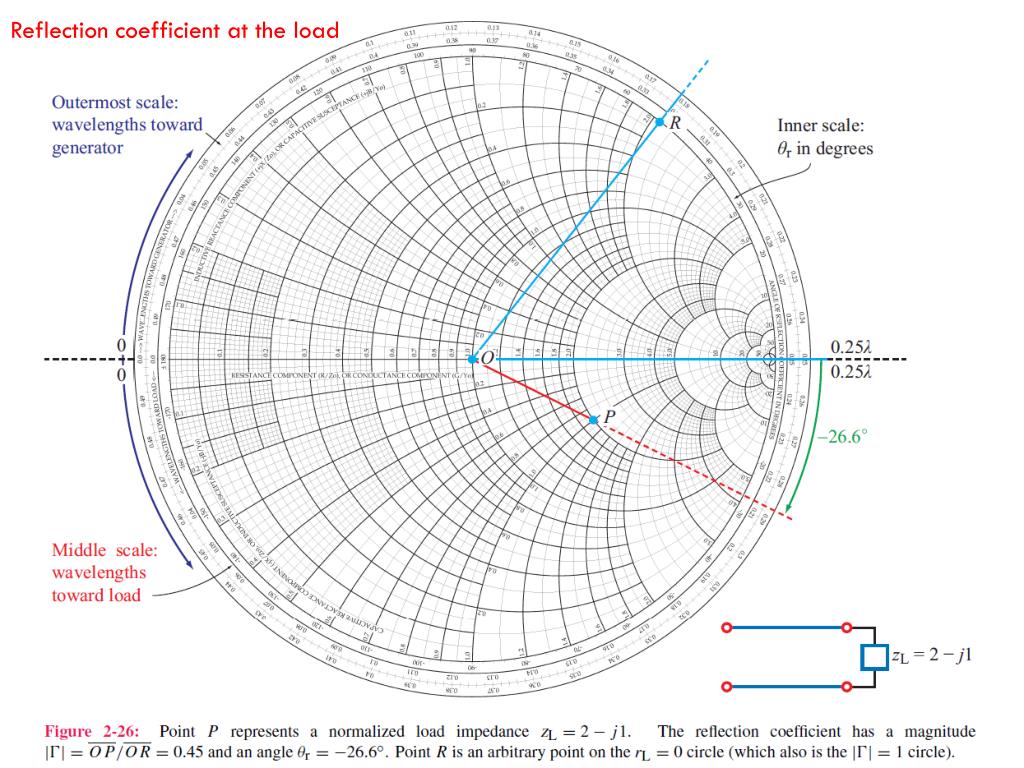
Smith chart reflection coefficient calculator manipodXX
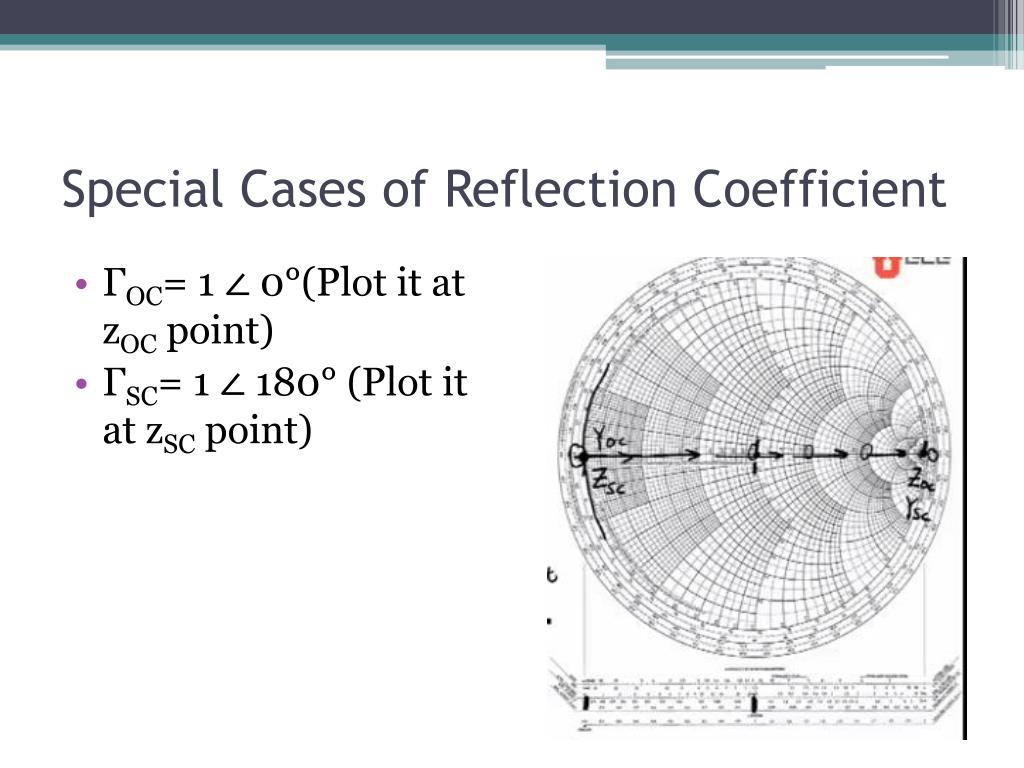
Smith chart reflection coefficient calculator qustbite

Smith chart representation of the reflection coefficient of port number

Reflection coefficient smith chart nanaxnational

Smith chart of the reflection coefficient í µí»¤ measured over a span
Web The Most Common View Is To Consider That The Smith Chart Is A Plot Of The Reflection Coefficient At Various Stages In The Circuit, I.e., Γa, Γb, Γc, Γd, And Γin.
You Will Recall From Class That The Input Reflection Coefficient To A Transmission Line Of Physical Length L, Г Ü Á, Is Given In Terms Of The Load Reflection Coefficient Г Å By The Expression Г Ü Áг Å A ?
The Reflection Coefficient’s Real And Imaginary Axis (The Cartesian Coordinates) Is Not Shown On The Actual Smith Chart.
This Is The Main Equation We'll Be Using, But There Will Be Some Quick Transformations To It.
Related Post: