Red Blood Cell Morphology Chart
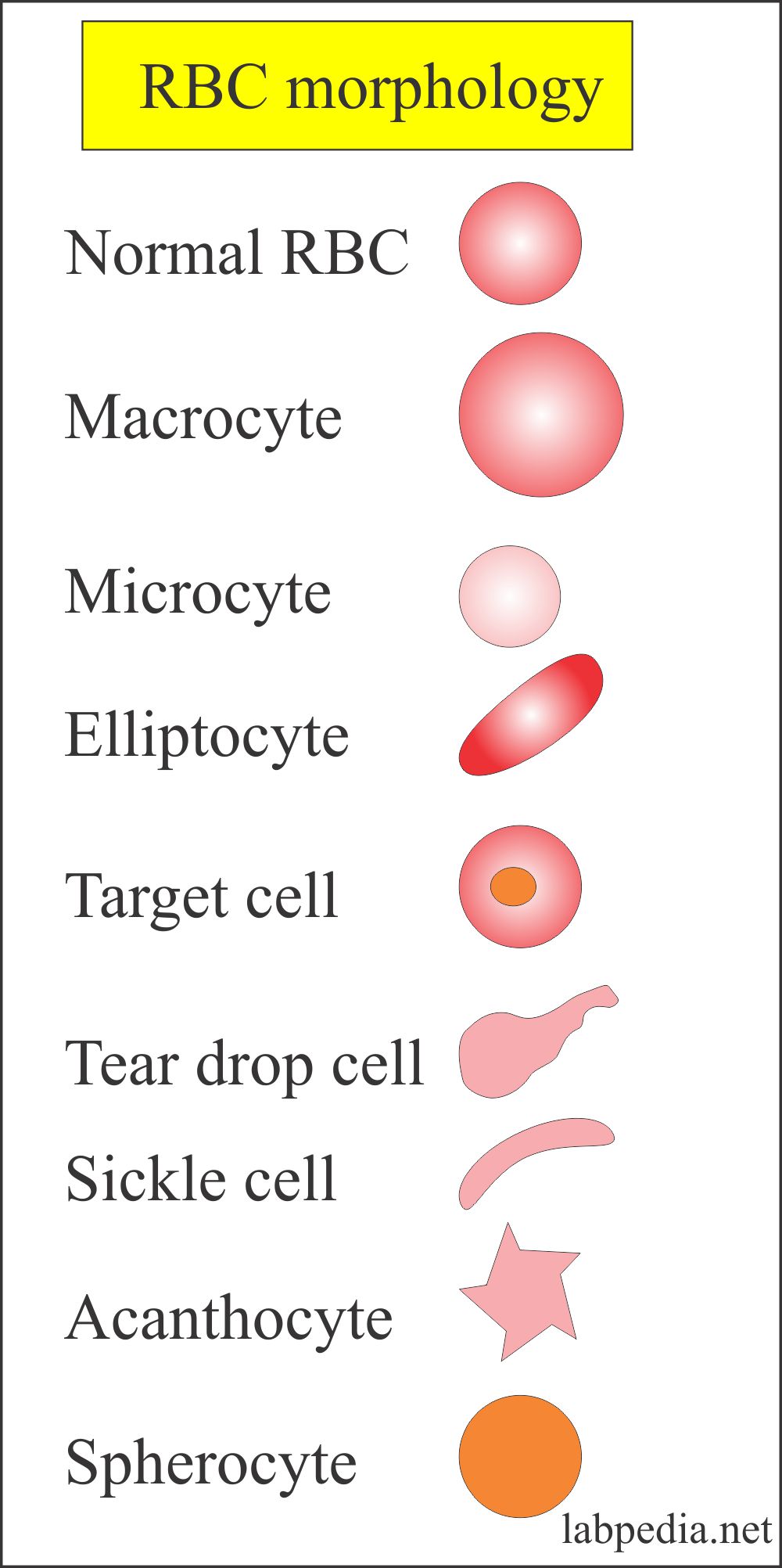
Red Blood Cell Morphology Chart - Their unique shape and composition allow for these specialized cells to carry out their essential functions. Web ‹ back to main atlas diagram of abnormal red blood cell morphologies in blood. All information (including use of the photographs and charts) is strictly for educational purpose and should not be used for any other purpose. There are also changes that occur in red blood cells that can give us clues as to underlying diseases. A decreased mcv indicates that there are a significant number of microcytes present. Below is a summary of terms used to describe red blood cell morphologic features, the meaning of the term and associated interpretation (the provided list of diseases is not exhaustive). Some of these changes can be pathologic in one context (or in one species) or physiologic in another. Rbc morphology may provide important diagnostic information regarding the underlying cause of anemia and systemic disease. White cells, red cells (erythrocytes) and platelets are counted per unit volume of whole blood. © 2012 please read the for more information. Web download table | red blood cell morphology grading chart from publication: All information (including use of the photographs and charts) is strictly for educational purpose and should not be used for any other purpose. Web how to spot abnormal red blood cells (rbc) morphology in the blood smear? Blood cell morphologic identification is a critical component of hematology laboratory. Rbc morphology may provide important diagnostic information regarding the underlying cause of anemia and systemic disease. Below is a summary of terms used to describe red blood cell morphologic features, the meaning of the term and associated interpretation (the provided list of diseases is not exhaustive). White cells, red cells (erythrocytes) and platelets are counted per unit volume of whole. Web the mean cell volume (mcv) indicates the average size of red blood cells present in the specimen. Dysmorphic rbcs (e.g., sickle cells, target cells) have an altered form and are often a sign of an underlying condition. Anisocytosis is divided into macrocytosis and microcytosis. Red blood cells sample for red blood cells takes blood in the edta. These include. Manual of hematology | | researchgate, the professional network for scientists. Web red blood cell and white blood cell morphology wall charts. Web the mean cell volume (mcv) indicates the average size of red blood cells present in the specimen. Web an overview of the common morphological changes in red blood cell and their clinicopathological significance. Web how to spot. Blood cell morphologic identification is a critical component of hematology laboratory practice, and is an important diagnostic aid. Web evaluation and interpretation of red blood cell (rbc) morphology is an important component of a complete blood count (cbc). Web download table | red blood cell morphology grading chart from publication: Their unique shape and composition allow for these specialized cells. A decreased mcv indicates that there are a significant number of microcytes present. Variation of size of rbc is called anisocytosis. Web red blood cell and white blood cell morphology wall charts. Web images of peripheral blood and/or bone marrow of blood disorders and normal hematopoiesis. Web how to spot abnormal red blood cells (rbc) morphology in the blood smear? Learn about different shapes (elliptical, sickle, etc.) and causes. White cells, red cells (erythrocytes) and platelets are counted per unit volume of whole blood. Manual of hematology | | researchgate, the professional network for scientists. Web variation in color. Anisocytosis is divided into macrocytosis and microcytosis. Nucleus of small lymphocyte is useful guide to the size of rbc. Web erythrocytes, or red blood cells , are the most common blood cells. Manual of hematology | | researchgate, the professional network for scientists. Web download table | red blood cell morphology grading chart from publication: A decreased mcv indicates that there are a significant number of microcytes. Nucleus of small lymphocyte is useful guide to the size of rbc. White cell count (leukocyte count) platelet count. Web images of peripheral blood and/or bone marrow of blood disorders and normal hematopoiesis. Web evaluation and interpretation of red blood cell (rbc) morphology is an important component of a complete blood count (cbc). An abnormal rbc test result is often. Web human cell growth and morphology were monitored microscopically. Rbc morphology may provide important diagnostic information regarding the underlying cause of anemia and systemic disease. Their unique shape and composition allow for these specialized cells to carry out their essential functions. Below is a summary of terms used to describe red blood cell morphologic features, the meaning of the term. Web images of peripheral blood and/or bone marrow of blood disorders and normal hematopoiesis. Blood cell morphologic identification is a critical component of hematology laboratory practice, and is an important diagnostic aid. Web evaluation and interpretation of red blood cell (rbc) morphology is an important component of a complete blood count (cbc). Some of these changes can be pathologic in one context (or in one species) or physiologic in another. Web a procedure in which a sample of blood is viewed under a microscope to count different circulating blood cells (red blood cells, white blood cells, platelets, etc.) and see whether the cells look normal. Web variation in color. In normal red blood cells, there is an area of central pallor that measures approximately 1/3 the diameter of the cell. • whole blood, uncentrifuged, anticoagulated with edta (purple or lavender cap) cell counts. Web the mean cell volume (mcv) indicates the average size of red blood cells present in the specimen. Their unique shape and composition allow for these specialized cells to carry out their essential functions. Rbc morphology may provide important diagnostic information regarding the underlying cause of anemia and systemic disease. Important preliminary findings include agglutination, polychromasia (reticulocytosis), target cells (liver disease or alcohol), and a dual population (mds or post transfusion). Rbc morphology may provide important diagnostic information regarding the underlying cause of anemia and systemic disease. Dysmorphic rbcs (e.g., sickle cells, target cells) have an altered form and are often a sign of an underlying condition. A teardrop cells accompanied by nrbcs can be reported even <4%. Red blood cell indices, colour, and size.
Variations in Red Blood Cell Morphology Size, Shape, Color and

Red Blood Cell Morphology Atlas Size variation, Hemoglobin GrepMed

Red Blood Cell Morphology Chart
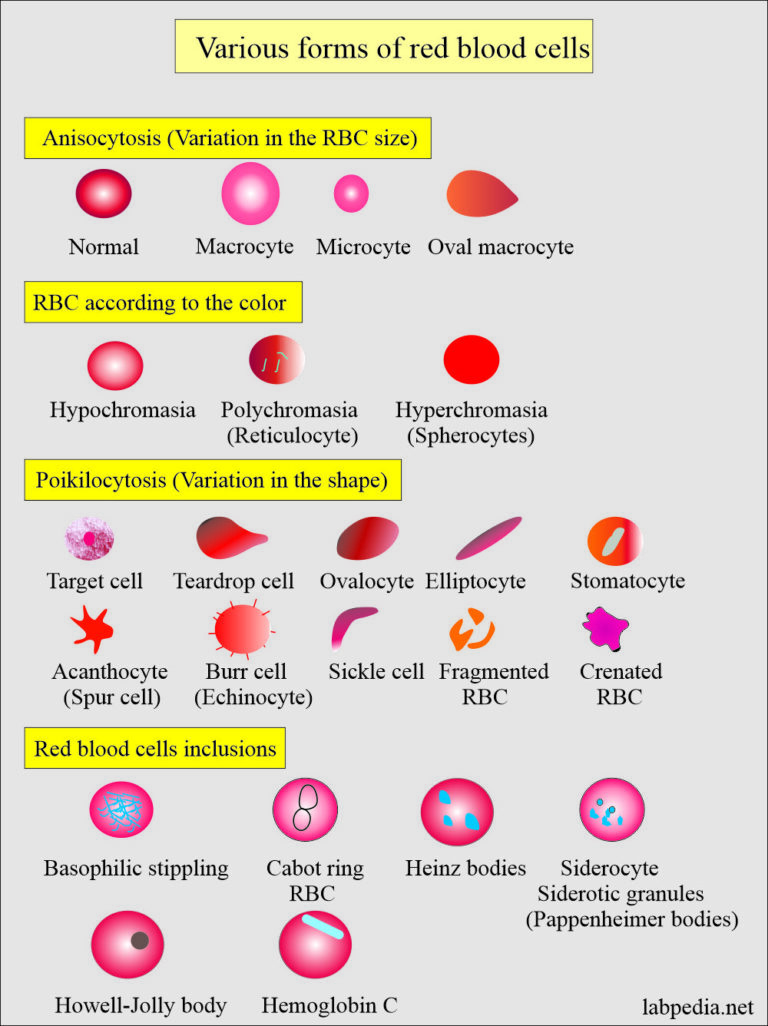
complete blood count, red blood cell morphology
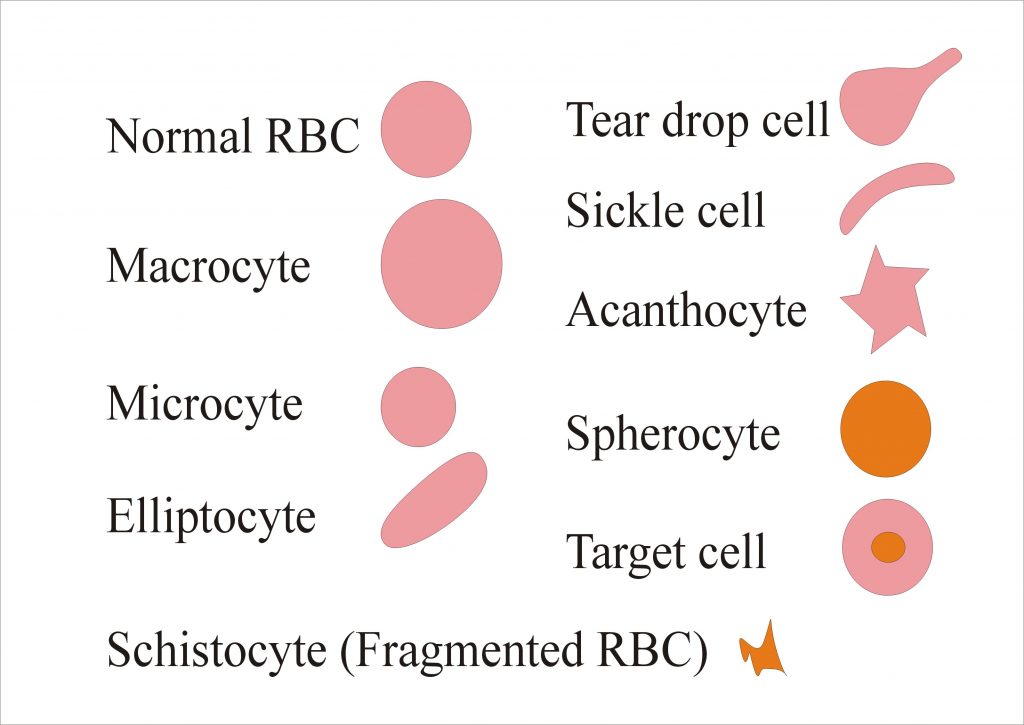
Red Blood Cell (RBC) Part 1 Morphology (Peripheral blood smear
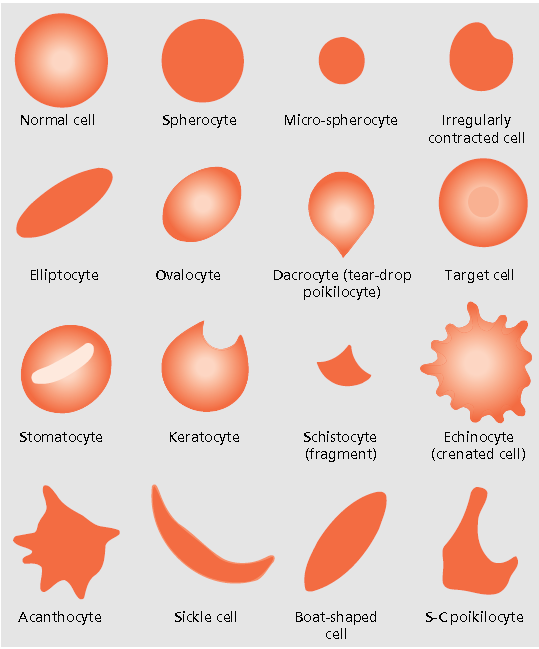
Medical Laboratory and Biomedical Science Blood Cell Morphology Guide
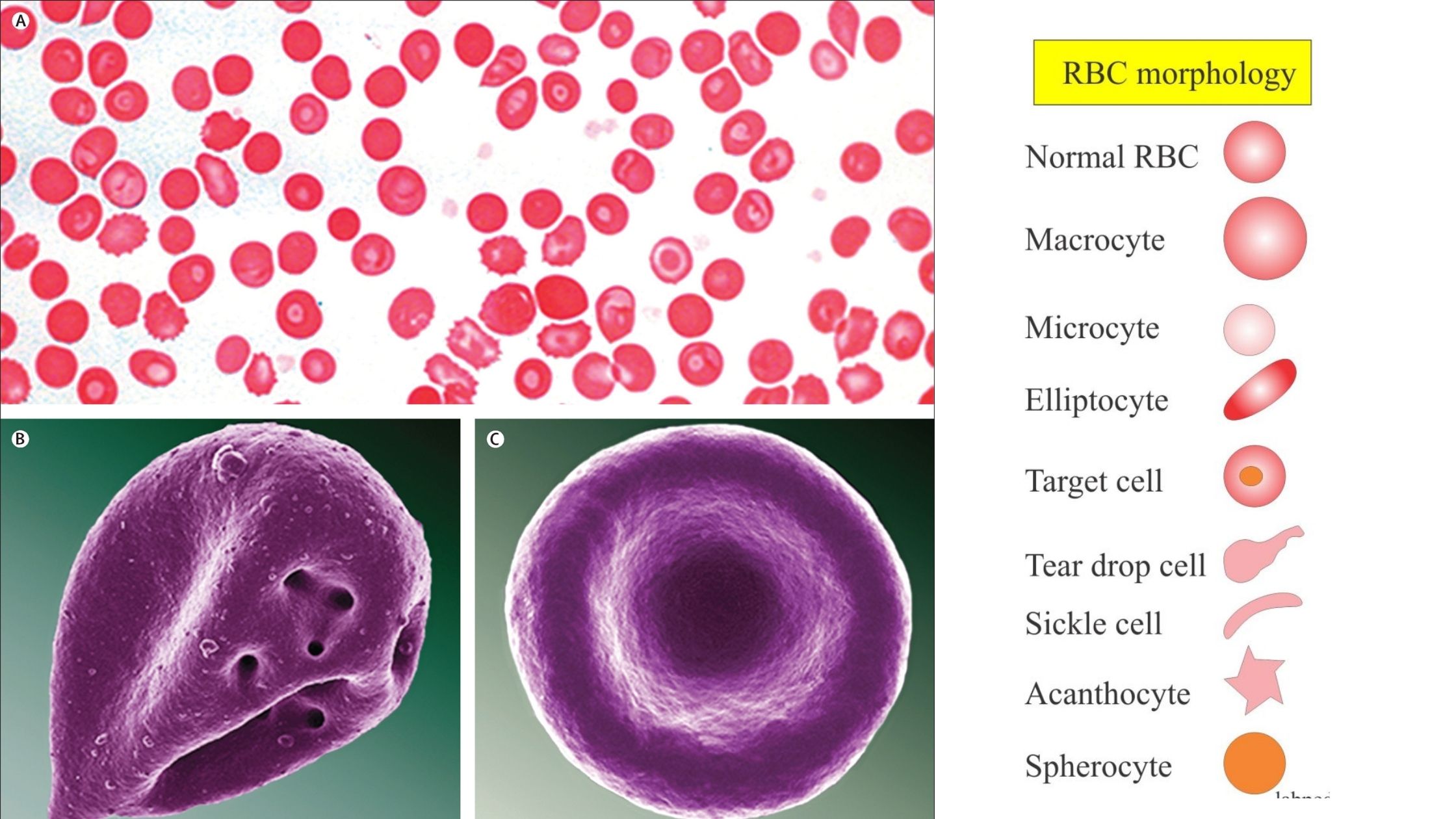
Red Blood Cell Morphology Size, Shape, Color and Inclusion Bodies

Pathologic Red Blood Cell (RBC) Morphologies and Associated GrepMed

RED BLOOD CELL MORPHOLOGY GRADING CHART Download Table
Red Blood Cell (RBC) Part 2 Peripheral blood smear, Normal Picture
© 2012 Please Read The For More Information.
Learn About Different Shapes (Elliptical, Sickle, Etc.) And Causes.
Web Human Cell Growth And Morphology Were Monitored Microscopically.
Web Download Table | Red Blood Cell Morphology Grading Chart From Publication:
Related Post: