Radius Of Elements Chart
Radius Of Elements Chart - Over 4,400 nuclide decay modes; Because of these two trends, the largest atoms are found in the lower left corner of the periodic table, and the smallest are found in the upper right corner (figure 8.2.4 8.2. As there are no physical existence of orbital in atoms, it is difficult to measure the atomic radius. Atomic radii can be obtained from quantum mechanical calculations or. The element names in 10 different languages; Web the atomic radius of a particular element is an important characteristic as it helps us to understand many properties of atoms and how they react. Atom size values are calculated from atomic radius data. Cubic density @ 293 k: 700.0 °c (973.15 k, 1292.0 °f) boiling point: Web the following table shows empirically measured covalent radii for the elements, as published by j. Because of these two trends, the largest atoms are found in the lower left corner of the periodic table, and the smallest are found in the upper right corner (figure 8.2.4 8.2. Over 4,400 nuclide decay modes; On the periodic table, atomic radius generally decreases as you move from left to right across a period (due to increasing nuclear charge). Web the following table shows empirically measured covalent radii for the elements, as published by j. Image showing periodicity of the chemical elements for atomic radii (clementi) in a. Web the periodic table currently has 118 chemical elements (sn: Up to 40 properties (chemical & physical); As there are no physical existence of orbital in atoms, it is difficult to. Pdf without crop marks | pdf with crop marks. Web there is a correlation between the atomic radii as determined from these calculations and the radii of maximum charge density in the outermost shell of the atom. Web atomic radius of all the elements are mentioned in the chart below. The element names in 10 different languages; Web the periodic. Cubic density @ 293 k: Web how atomic radius is defined, and trends across a period and down a group. 1737.0 °c (2010.15 k, 3158.6 °f) number of protons/electrons: Atomic radius is the distance from the atom’s nucleus to the outermost electron orbital, and a lot of trends in the periodic table rely on this property due to its relationship. On the periodic table, atomic radius generally decreases as you move from left to right across a period (due to increasing nuclear charge) and increases as you move down a group (due to the increasing number of electron shells). Web the atomic radius of a particular element is an important characteristic as it helps us to understand many properties of. Web the periodic table contains nist’s latest critically evaluated data for atomic properties of the elements. Web get the atomic radius and ionic radius definitions, learn the difference between them, and explore their periodic table trend. Web the following table shows empirically measured covalent radii for the elements, as published by j. Visualize trends, 3d orbitals, isotopes, and mix compounds.. Web you can edit the radius of atoms of that element type using the radius field r [å] . As there are no physical existence of orbital in atoms, it is difficult to measure the atomic radius. Web the periodic table of the elements (including atomic radius) 1. Going across a period, the main group elements tend to decrease in. Web there is a correlation between the atomic radii as determined from these calculations and the radii of maximum charge density in the outermost shell of the atom. The values are in picometers (pm or 1×10 −12 m), with an accuracy of about 5 pm. Because of these two trends, the largest atoms are found in the lower left corner. Editing the radii for all oxygen atoms in a structure, using crystalmaker's atoms inspector. Going down a group, the main group elements tend to increase in atomic radius due to increased. Web explore how atomic radius changes with atomic number in the periodic table of elements via interactive plots. Atoms are not all the same size. Web the periodic table. Pdf without crop marks | pdf with crop marks. You can edit the colours and/or radii for specific crystal sites, by. The atomic radius of an atom is useful to understand as it helps to understand many properties of atoms and how they react. Cubic density @ 293 k: Atom size values are calculated from atomic radius data. Atoms are not all the same size. Web explore how atomic radius changes with atomic number in the periodic table of elements via interactive plots. The relative size of the atoms follows a set of trends on the periodic table. Web the atomic radius of a chemical element is the distance from the center of the nucleus to the outermost shell of an electron. Visualize trends, 3d orbitals, isotopes, and mix compounds. It assumes that you understand electronic structures for simple atoms written in s, p, d notation. Web the periodic table currently has 118 chemical elements (sn: Each atom’s size is relative to the largest element, cesium. Web the atomic radius of a particular element is an important characteristic as it helps us to understand many properties of atoms and how they react. Pdf without crop marks | pdf with crop marks. Look up chemical element names, symbols, atomic masses and other properties, visualize trends, or even test your elements knowledge by playing a periodic table game! Image showing periodicity of the chemical elements for atomic radii (clementi) in a. Web interactive periodic table showing names, electrons, and oxidation states. Web atomic radius chart for elements. Over 4,400 nuclide decay modes; That’s a variety, or isotope, of calcium with 28.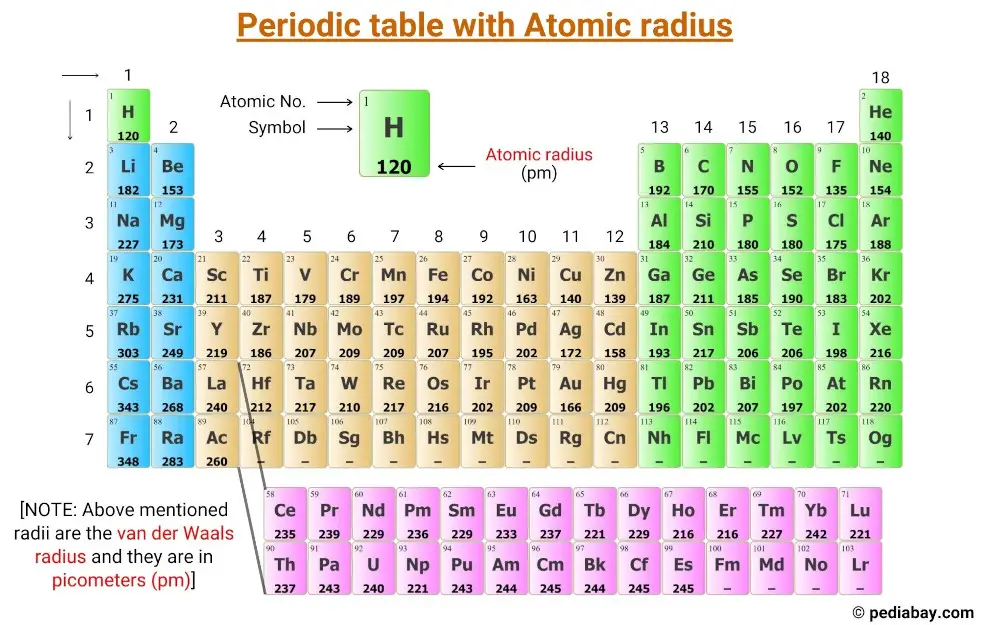
Atomic Radius of Elements (With Periodic table Chart) Pediabay
.png)
Periodic Table Of The Elements Atomic Radius vrogue.co
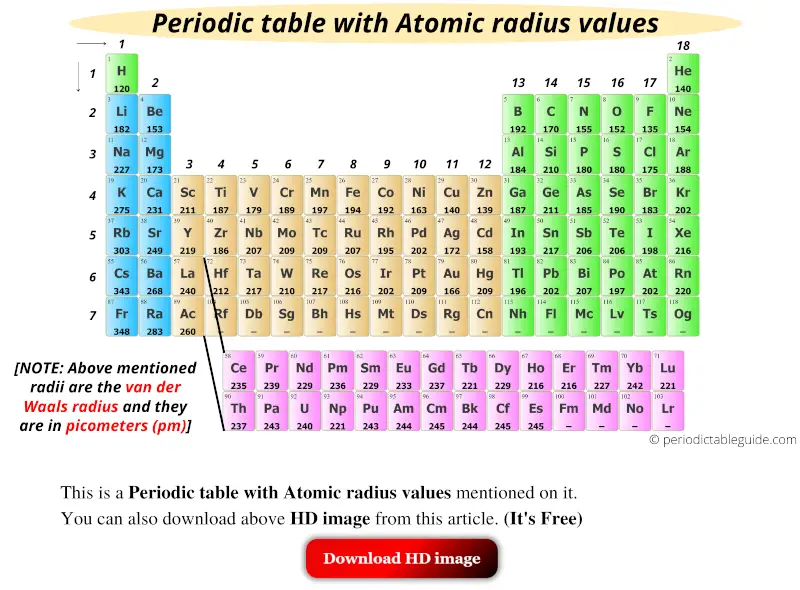
Get the Periodic table with Atomic radius values (Img+Chart)
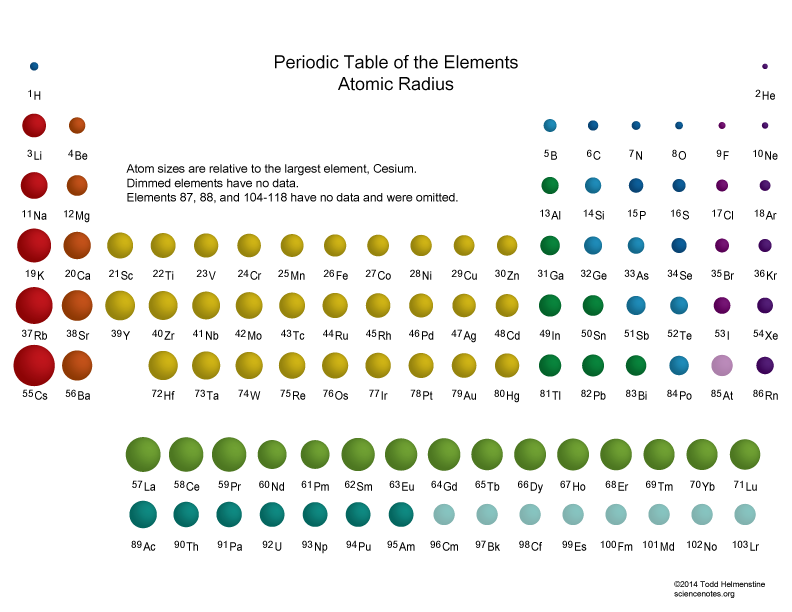
Atomic Radius Trends of the Periodic Table

Atoms
Periodic Table Atomic Radius Periodic Table Timeline
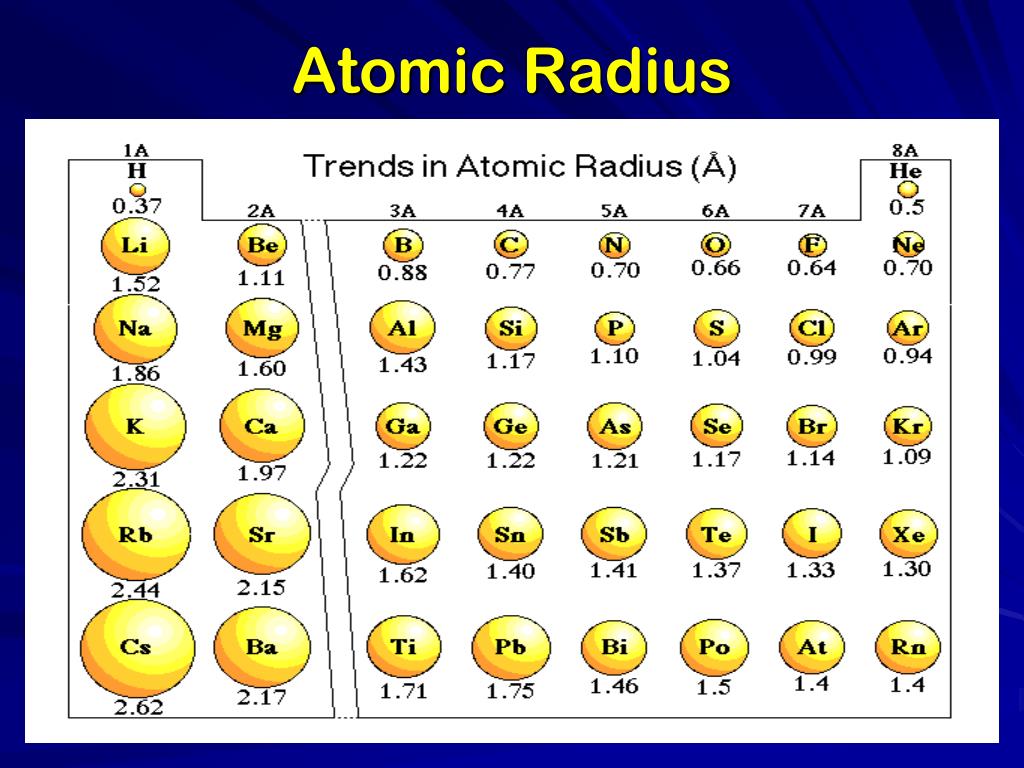
Atomic Radius Periodic Table Chart

Atomic Radius and Ionic Radius

Elements, Atomic Radii and the Periodic Radii

Atomic Radius of Elements
You Can Edit The Colours And/Or Radii For Specific Crystal Sites, By.
Going Down A Group, The Main Group Elements Tend To Increase In Atomic Radius Due To Increased.
Web Get The Atomic Radius And Ionic Radius Definitions, Learn The Difference Between Them, And Explore Their Periodic Table Trend.
Atomic Radius Is The Distance From The Atom’s Nucleus To The Outermost Electron Orbital, And A Lot Of Trends In The Periodic Table Rely On This Property Due To Its Relationship To Other Atomic.
Related Post: