Piano Key Frequency Chart
Piano Key Frequency Chart - Web the frequencies of the piano keys are determined by their distance from the keyboard's center, with the closest keys having the highest frequencies and the farthest keys having the lowest frequencies. The a5 key is thus one octave higher than a4 since it has twice the frequency. For example, the a4 key has a frequency of 440 hz. Web in theory it is easy, to get the frequency of the note other than a4=440hz you just multiply/divide 440hz by the proper number. For example, to get a2, you divide by 4 and get a2=110hz. Middle c has a frequency of 261.626 hz. Here's a video of micro tuning. Here are some key highlights from the frequency list below: Web below you can find a list of frequencies of all the keys on a piano. The number beside each key is the fundamental frequency in units of cycles per seconds, or hertz. Middle c has a frequency of 261.626 hz. For example, the a4 key has a frequency of 440 hz. Click on a row to hear the note played. Web the frequencies of the piano keys are determined by their distance from the keyboard's center, with the closest keys having the highest frequencies and the farthest keys having the lowest frequencies.. Middle c has a frequency of 261.626 hz. Web on a piano, each adjacent key (color doesn't matter), from left to right, their frequencies forms a geometric sequence. The number beside each key is the fundamental frequency in units of cycles per seconds, or hertz. Here's a video of micro tuning. Note that a5 has a frequency of 880 hz. The number beside each key is the fundamental frequency in units of cycles per seconds, or hertz. Web below you can find a list of frequencies of all the keys on a piano. Web graph functions, plot points, visualize algebraic equations, add sliders, animate graphs, and more. For example, to get a2, you divide by 4 and get a2=110hz. The. The a5 key is thus one octave higher than a4 since it has twice the frequency. Middle c has a frequency of 261.626 hz. Web the frequencies of the piano keys are determined by their distance from the keyboard's center, with the closest keys having the highest frequencies and the farthest keys having the lowest frequencies. Here's a video of. Note that a5 has a frequency of 880 hz. Web in theory it is easy, to get the frequency of the note other than a4=440hz you just multiply/divide 440hz by the proper number. Web graph functions, plot points, visualize algebraic equations, add sliders, animate graphs, and more. The scaling factor is 2^(1/12)≈1.05946. Here are some key highlights from the frequency. Web in theory it is easy, to get the frequency of the note other than a4=440hz you just multiply/divide 440hz by the proper number. The highest note on a standard piano has a frequency of 4186.009 hz. Note that a5 has a frequency of 880 hz. The scaling factor is 2^(1/12)≈1.05946. Here's a video of micro tuning. Web on a piano, each adjacent key (color doesn't matter), from left to right, their frequencies forms a geometric sequence. The highest note on a standard piano has a frequency of 4186.009 hz. Middle c has a frequency of 261.626 hz. Here are some key highlights from the frequency list below: Web in theory it is easy, to get the. For example, to get a2, you divide by 4 and get a2=110hz. Web on a piano, each adjacent key (color doesn't matter), from left to right, their frequencies forms a geometric sequence. The scaling factor is 2^(1/12)≈1.05946. The number beside each key is the fundamental frequency in units of cycles per seconds, or hertz. The highest note on a standard. Web the frequencies of the piano keys are determined by their distance from the keyboard's center, with the closest keys having the highest frequencies and the farthest keys having the lowest frequencies. Web graph functions, plot points, visualize algebraic equations, add sliders, animate graphs, and more. The number beside each key is the fundamental frequency in units of cycles per. For example, the a4 key has a frequency of 440 hz. Here are some key highlights from the frequency list below: The scaling factor is 2^(1/12)≈1.05946. Middle c has a frequency of 261.626 hz. Note that a5 has a frequency of 880 hz. Web below you can find a list of frequencies of all the keys on a piano. Web on a piano, each adjacent key (color doesn't matter), from left to right, their frequencies forms a geometric sequence. Click on a row to hear the note played. For example, the a4 key has a frequency of 440 hz. Web in theory it is easy, to get the frequency of the note other than a4=440hz you just multiply/divide 440hz by the proper number. The a5 key is thus one octave higher than a4 since it has twice the frequency. For example, to get a2, you divide by 4 and get a2=110hz. Here are some key highlights from the frequency list below: Middle c has a frequency of 261.626 hz. The highest note on a standard piano has a frequency of 4186.009 hz. The number beside each key is the fundamental frequency in units of cycles per seconds, or hertz. Here's a video of micro tuning.
Piano Notes Chart
Complete Keyboard Frequencies PDF Pitch (Music) Piano
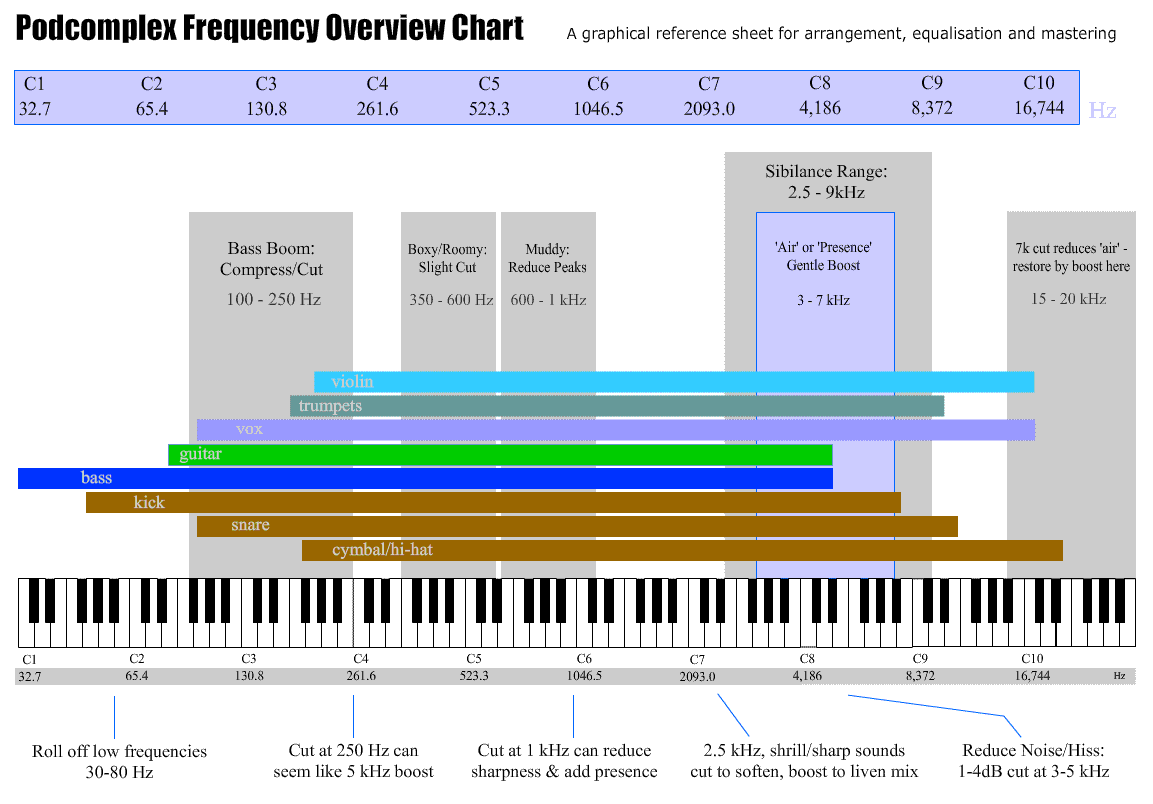
Keyboard Notes By Frequency (Part 2)

Piano Keys Frequency Chart

Piano Keys Frequency Chart
Piano Keys Frequency Chart
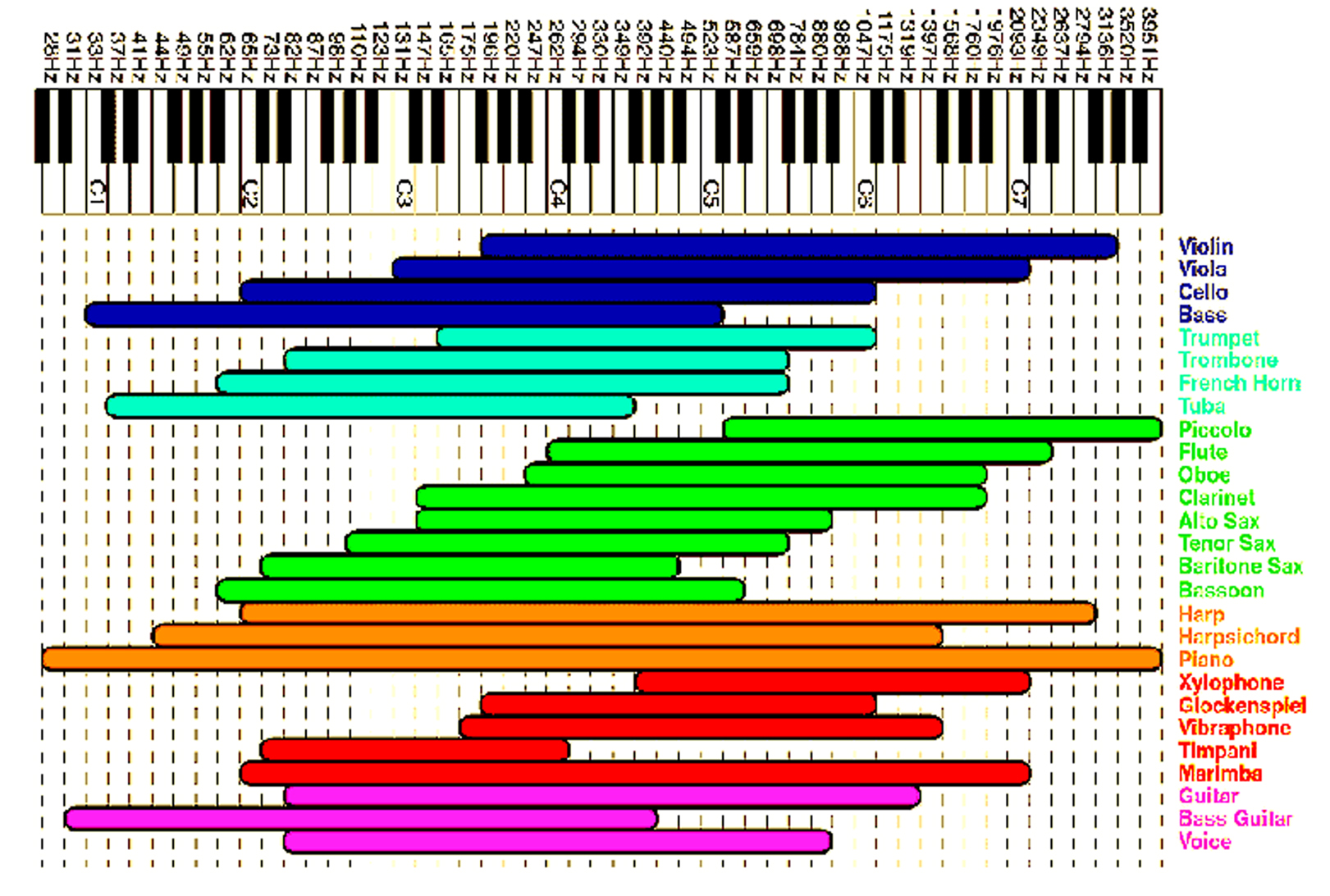
An easy guide to reading your audiogram with pictures and illustrations

frequency What are the true frequencies of the piano keys? Music

Learn major scales piano, treble clef, charts, pattern/formula, chords
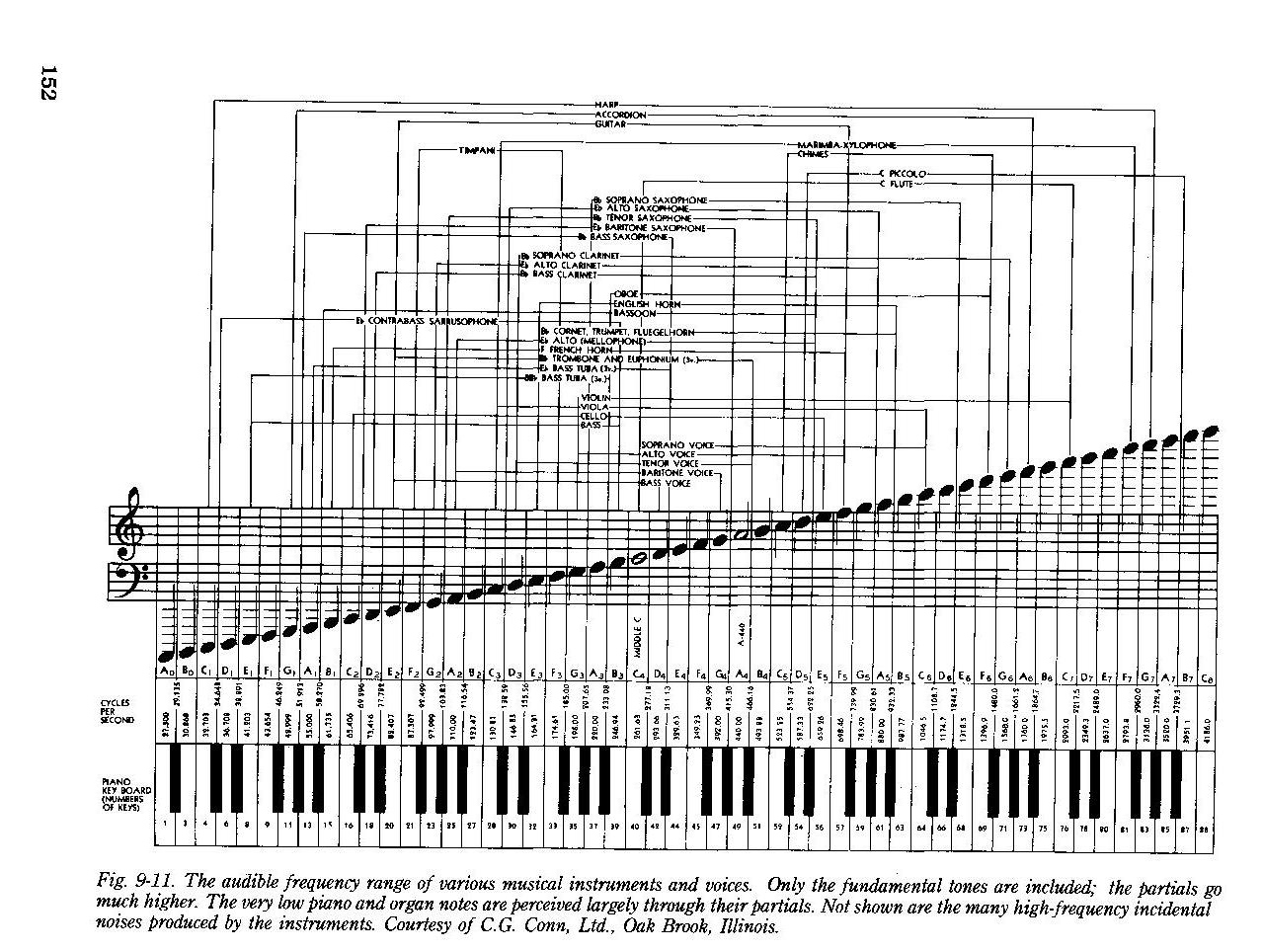
Piano Keys Frequency Chart
Note That A5 Has A Frequency Of 880 Hz.
Web The Frequencies Of The Piano Keys Are Determined By Their Distance From The Keyboard's Center, With The Closest Keys Having The Highest Frequencies And The Farthest Keys Having The Lowest Frequencies.
The Scaling Factor Is 2^(1/12)≈1.05946.
Web Graph Functions, Plot Points, Visualize Algebraic Equations, Add Sliders, Animate Graphs, And More.
Related Post:
