Periodic Table Ionization Energy Chart
Periodic Table Ionization Energy Chart - Notice the general trend of increasing darkness (or ionization energy) as one moves to. This is the energy per mole necessary to remove electrons from gaseous atoms or atomic ions. As you go from left to right, you go from low ionization energy to high ionization energy. The energy required to remove an electron is the ionization energy. 1), in kj/mol, of selected elements. Web below is a full periodic table, with shading to demonstrate the periodic trend of ionization energy. Web on the periodic table, first ionization energy generally increases as you move left to right across a period. The tabular chart on the right is arranged by ionization energy. For chemistry students and teachers: This is due to increasing nuclear charge, which results in the outermost electron being more strongly bound to the nucleus. Web ionization energy chart of all the elements is given below. The first chemical element is cesium and the last one is helium. Web this list contains the 118 elements of chemistry. Web the periodic table of the elements (with ionization energies) 1. In physics and chemistry, ionization energy ( ie) is the minimum energy required to remove the most. Web an element's first ionization energy is the energy required to remove the outermost, or least bound, electron from a neutral atom of the element. Web these tables list values of molar ionization energies, measured in kj⋅mol −1. Web the ionization energy is a measure of the energy required to remove one electron from one mole of gaseous atoms or. So before i even look at a periodic table of elements, let's make sure. There are trends that match the structure of the periodic table. The first molar ionization energy applies to the neutral atoms. Because positive charge binds electrons more strongly, the second ionization energy of. Web the above image clearly shows you the periodic table with ionization energy. In physics and chemistry, ionization energy ( ie) is the minimum energy required to remove the most loosely bound electron of an isolated gaseous atom, positive ion, or molecule. Which group of elements has the highest ionization energies? Web explore how ionization energy changes with atomic number in the periodic table of elements via interactive plots. The first molar ionization. Web explore how ionization energy changes with atomic number in the periodic table of elements via interactive plots. Web ionization energy is the minimum energy required to remove a loosely bound electron of an atom or molecule in the gaseous state. Web predicted values are used for elements beyond 104. The tabular chart on the right is arranged by ionization. Web what trends do you see on the periodic table for ionization energy and what causes these trends? The table lists only the first ie in ev units. Download printable periodic table with element names, atomic mass, and numbers for quick reference and lab use. 1), in kj/mol, of selected elements. X (g) + energy x + (g) + e. To convert to kj/mol, multiply by 96.4869. Web this list contains the 118 elements of chemistry. How would you write a chemical equation representing the third ionization energy for lithium? Web an element's first ionization energy is the energy required to remove the outermost, or least bound, electron from a neutral atom of the element. The energy required to remove. X (g) + energy x + (g) + e −. Web so, this is high, high ionization energy, and that's the general trend across the periodic table. The darker the shading, the higher the ionization energy. As you can see on the graph, the noble gases have the highest ionization energies, and the alkali metals have the lowest ionization energies.. Web the 1st ionization energy of the element m is a measure of the energy required to remove one electron from one mole of the gaseous atoms m. Web periodic behavior is most evident for ionization energy (i), the energy required to remove an electron from a gaseous atom. Web the periodic table of the elements (with ionization energies) 1.. The table lists only the first ie in ev units. Nist reference table on ground states and ionization energies for the neutral atoms. Web so, this is high, high ionization energy, and that's the general trend across the periodic table. What does the ionization energy quantitatively measure about an atom? Web ionization energy chart of all the elements is given. Web for each atom, the column marked 1 is the first ionization energy to ionize the neutral atom, the column marked 2 is the second ionization energy to remove a second electron from the +1 ion, the column marked 3 is the third ionization energy to remove a third electron from the +2 ion, and so on. The energy required to remove an electron is the ionization energy. Web an element's first ionization energy is the energy required to remove the outermost, or least bound, electron from a neutral atom of the element. The table lists only the first ie in ev units. Web below is a full periodic table, with shading to demonstrate the periodic trend of ionization energy. Between groups 1 and 18, ionization potentials generally increase across a period. Notice the general trend of increasing darkness (or ionization energy) as one moves to. So before i even look at a periodic table of elements, let's make sure. X (g) + energy x + (g) + e −. Image showing periodicity of the chemical elements for ionization energy: Web periodic behavior is most evident for ionization energy (i), the energy required to remove an electron from a gaseous atom. In physics and chemistry, ionization energy ( ie) is the minimum energy required to remove the most loosely bound electron of an isolated gaseous atom, positive ion, or molecule. As you can see on the graph, the noble gases have the highest ionization energies, and the alkali metals have the lowest ionization energies. This version of the periodic table shows the first ionization energy of (ie: Nist reference table on ground states and ionization energies for the neutral atoms. This is the energy per mole necessary to remove electrons from gaseous atoms or atomic ions.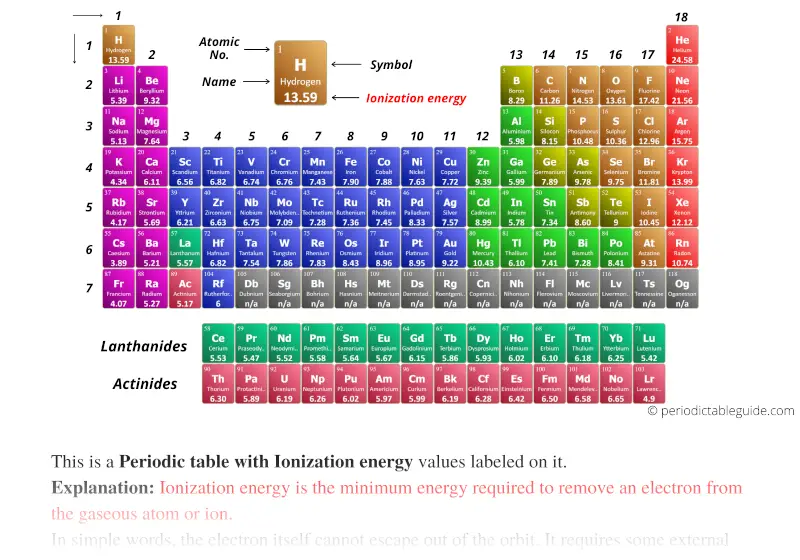
Periodic table with Ionization Energy Values (Labeled Image)

Ionization Energy Definition, Chart & Periodic Table Trend
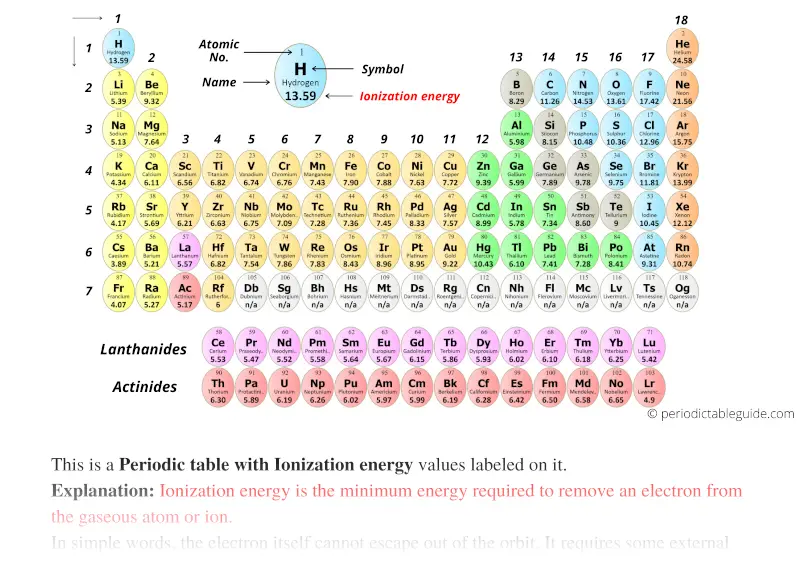
Periodic table with Ionization Energy Values (Labeled Image)
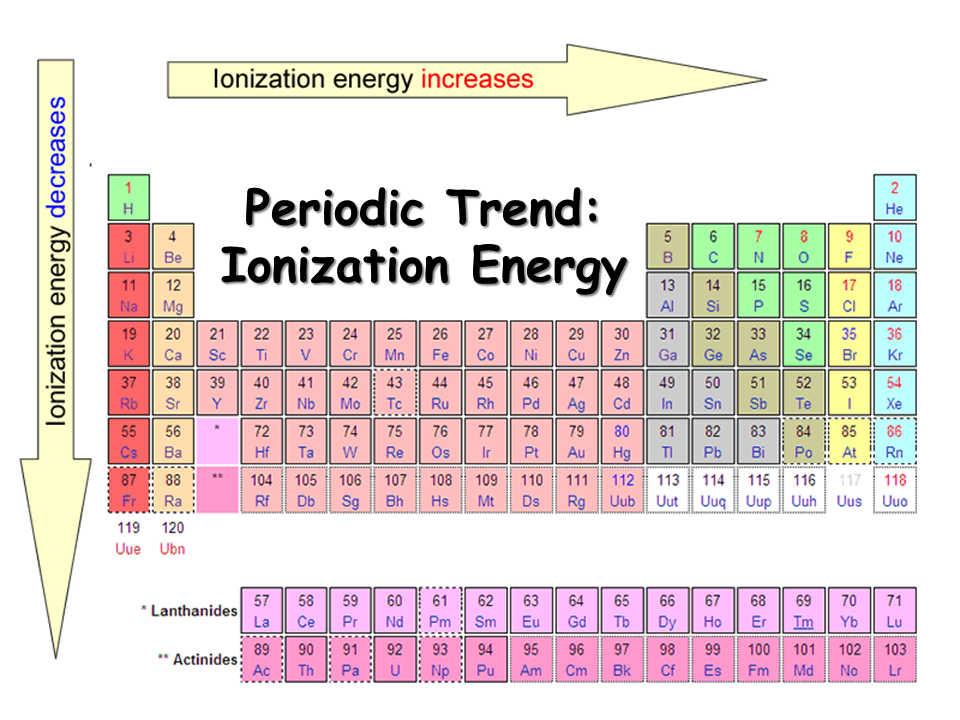
Ionization Enthalpy NEET Lab

What Is Ionization Energy? Definition and Trend

Periodic Variations in Element Properties Chemistry for Majors

Periodic Table Ionization Energy Chart
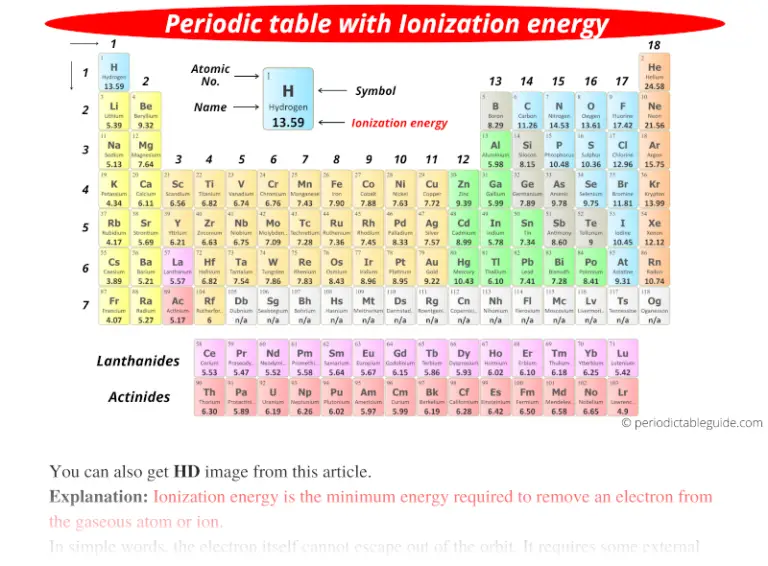
Periodic table with Ionization Energy Values (Labeled Image)
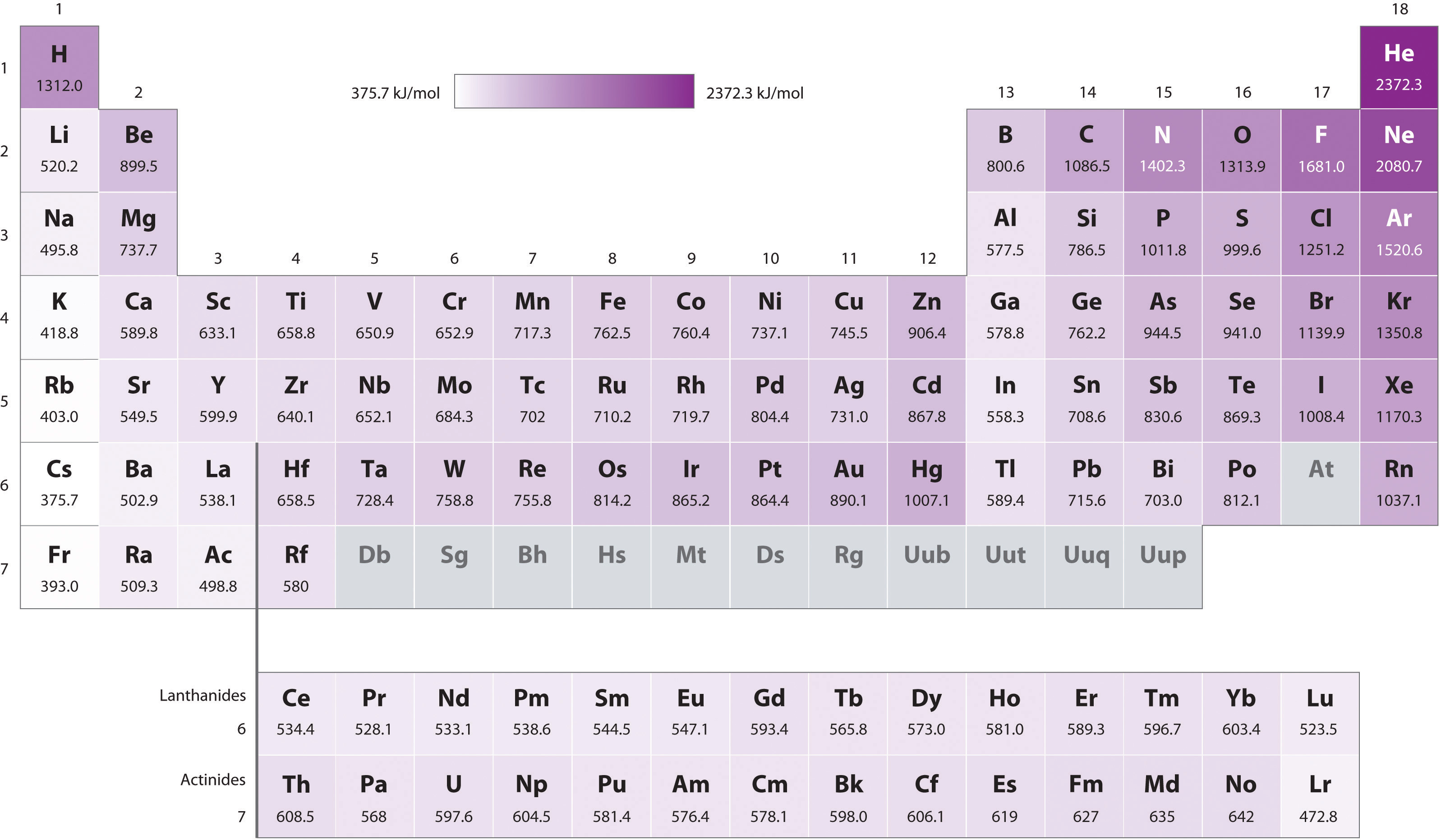
The Periodic Table and Periodic Trends
Periodic Trends in Ionization Energy Chemistry Socratic
To Convert To Kj/Mol, Multiply By 96.4869.
You Can Also Get The Hd Printable Periodic Table With Ionization Energy, From This Article Only.
1St In A Periodic Table Cityscape Style.
This Is Due To Increasing Nuclear Charge, Which Results In The Outermost Electron Being More Strongly Bound To The Nucleus.
Related Post: