Nuclear Dot Pattern
Nuclear Dot Pattern - Web few nuclear dots pattern. Some, but not all labs will report a titre above 1:160 as positive. Web the nuclear dot pattern, observed in antinuclear antibody (ana) testing, is a distinctive immunofluorescence pattern characterized by discrete speckles or dots within the cell nucleus. Doctors may order an ana test if you have signs or symptoms of an autoimmune. Frequently, these dots are presented near the nucleolus and are known as coiled bodies or cajal bodies. This pattern emerges when specific autoantibodies in the patient's serum react with nuclear proteins, most notably sp100 and promyelocytic leukemia (pml) protein. Pleomorphic pattern is caused by antibodies to the proliferating cell nuclear antigen. For this test, we use a specific type of. Web the classical nuclear patterns are speckled, homogeneous, nucleolar and centromere. Web ana patterns can be associated with different autoimmune conditions. The level or titer and the pattern. If your child tests positive for anas, it may mean they have an autoimmune disease. Although lower amounts of these antibodies can be seen in the normal population as well, a spurt in titers is seen in patients of ctd. Web the numa pattern had the highest ana titers: We looked for mnd. We looked for mnd in 9189 sera belonging to 6240 patients stored for autoimmune diseases with prevalent cutaneous features. Web antibodies that attack healthy proteins within the cell nucleus are called antinuclear antibodies (anas). Web ana patterns can be associated with different autoimmune conditions. When active, usually a homogenous pattern on ana or less commonly speckled, rim, or nucleolar when. Web the results of the antinuclear antibody (ana) test, together with a health care provider's careful consideration of a patient's symptoms, physical findings, and other laboratory test results, may assist in the diagnosis of autoimmune disorders. Web is the ana pattern suggestive of a specific disease? Web testing of antinuclear antibodies (anas) by indirect immunofluorescence assay (iifa) provides valuable information. Some, but not all labs will report a titre above 1:160 as positive. An antinuclear antibody (ana) test looks for antinuclear antibodies in your child’s blood. Doctors may order an ana test if you have signs or symptoms of an autoimmune. Below is a summary of the patterns discussed: Web next, we asked if dissimilar cleavage patterns differ in the. Some, but not all labs will report a titre above 1:160 as positive. Doctors may order an ana test if you have signs or symptoms of an autoimmune. Web physicists introduce method for mechanical detection of individual nuclear decays. Graduate student jiaxiang wang works on the optical trap used for this work. We looked for mnd in 9189 sera belonging. Those dots represent a distinct pattern from the multiple nuclear dots pattern, despite being found in similar clinical conditions. Their positivity strongly suggests the diagnosis of primary biliary cirrhosis, irrespective of antimitochondrial antibody status. Frequently, these dots are presented near the nucleolus and are known as coiled bodies or cajal bodies. We looked for mnd in 9189 sera belonging to. Web antibodies that attack healthy proteins within the cell nucleus are called antinuclear antibodies (anas). An antinuclear antibody (ana) test looks for antinuclear antibodies in your child’s blood. These patterns can range from homogenous to speckled, and each carries its own significance in terms of potential autoimmune conditions. Web ana patterns can be associated with different autoimmune conditions. We looked. Doctors may order an ana test if you have signs or symptoms of an autoimmune. For this test, we use a specific type of. The level or titer and the pattern. An autoimmune disease causes your child’s immune system to attack their own cells, tissues and organs by mistake. Web next, we asked if dissimilar cleavage patterns differ in the. When active, usually a homogenous pattern on ana or less commonly speckled, rim, or nucleolar when present in high. Web antibodies that attack healthy proteins within the cell nucleus are called antinuclear antibodies (anas). Web the results of the antinuclear antibody (ana) test, together with a health care provider's careful consideration of a patient's symptoms, physical findings, and other laboratory. When active, usually a homogenous pattern on ana or less commonly speckled, rim, or nucleolar when present in high. Web the nuclear dot pattern, observed in antinuclear antibody (ana) testing, is a distinctive immunofluorescence pattern characterized by discrete speckles or dots within the cell nucleus. Some, but not all labs will report a titre above 1:160 as positive. Web next,. Their positivity strongly suggests the diagnosis of primary biliary cirrhosis, irrespective of antimitochondrial antibody status. Titres are reported in ratios, most often 1:40, 1:80, 1:160, 1:320, and 1:640. Graduate student jiaxiang wang works on the optical trap used for this work. At times, laboratories testing ana also report a “pattern”. The most frequent systemic autoimmune diseases were sjögren syndrome (ss) (18.1%), rheumatoid arthritis (ra) (13.8%), and systemic lupus erythematosus (sle) (11%). This pattern emerges when specific autoantibodies in the patient's serum react with nuclear proteins, most notably sp100 and promyelocytic leukemia (pml) protein. An autoimmune disease causes your child’s immune system to attack their own cells, tissues and organs by mistake. Web antibodies that attack healthy proteins within the cell nucleus are called antinuclear antibodies (anas). Web nuclear patterns include the distinct staining pattern of the nucleoplasm—speckled or homogeneous—and patterns attributed to specific nuclear subcomponents, i.e., centromere, nuclear dots, nucleolar, or nuclear envelope. Web the term antinuclear antibody (ana) describes a variety of autoantibodies that react with constituents of cell nuclei including dna, proteins and ribonucleoproteins 1,2. When active, usually a homogenous pattern on ana or less commonly speckled, rim, or nucleolar when present in high. Web the classical nuclear patterns are speckled, homogeneous, nucleolar and centromere. Some, but not all labs will report a titre above 1:160 as positive. Web the results of the antinuclear antibody (ana) test, together with a health care provider's careful consideration of a patient's symptoms, physical findings, and other laboratory test results, may assist in the diagnosis of autoimmune disorders. Although lower amounts of these antibodies can be seen in the normal population as well, a spurt in titers is seen in patients of ctd. Web ana are a specific class of autoantibodies that have the capability of binding and destroying certain structures within the nucleus of the cells [ 1 ].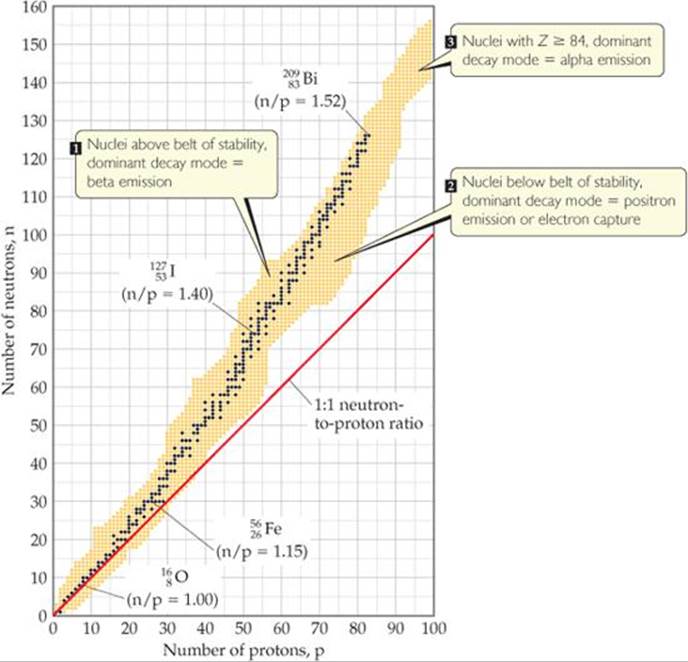
PATTERNS OF NUCLEAR STABILITY NUCLEAR CHEMISTRY CHEMISTRY THE

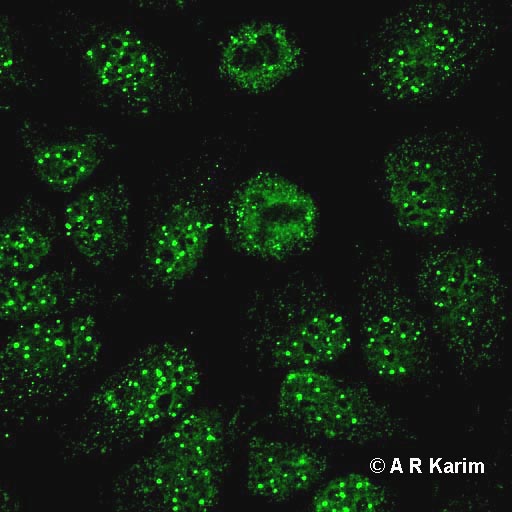
Less frequent and/or rare nuclear patterns. A. Multiple nuclear dots
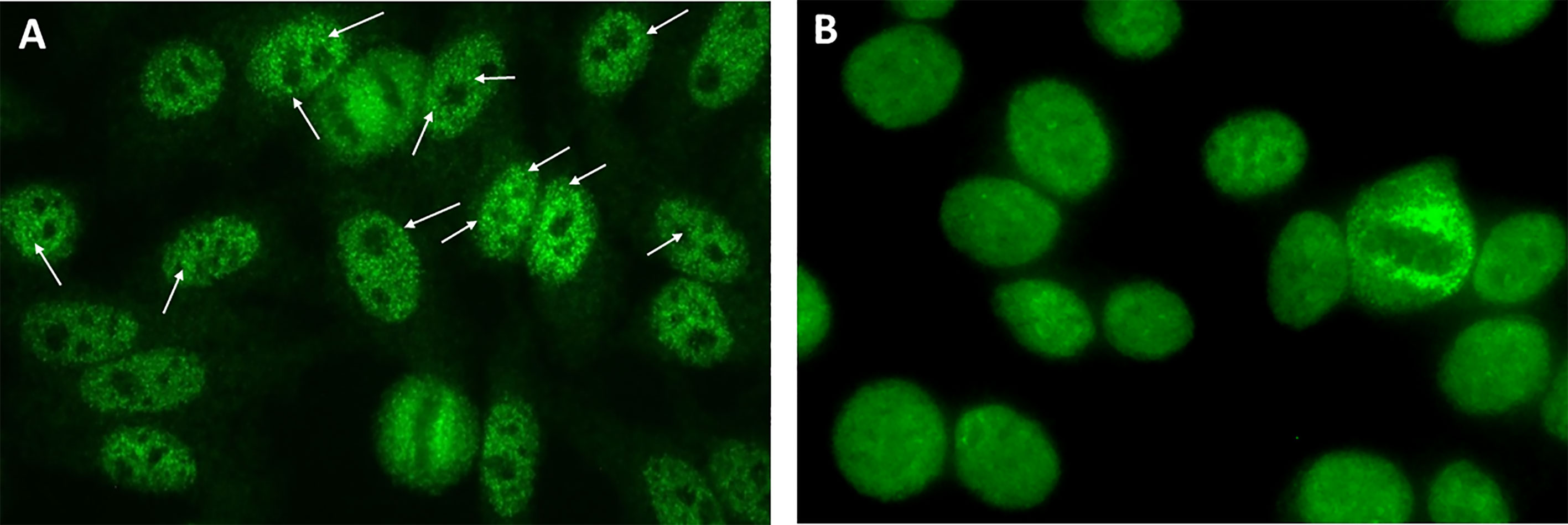
Frontiers Strong Association of the Myriad Discrete Speckled Nuclear

Ana Pattern Nuclear 7thongs

Positive Ana Speckled Pattern Chumado

Nuclear Dot Pattern Pattern.rjuuc.edu.np
Nuclear without mitotic staining University of Birmingham

Seamless nuclear pattern stock vector. Illustration of intricate

Puntos Nucleares Múltiples/ Membrana nuclear Lisa / Citoplasmático

Seamless nuclear pattern Royalty Free Vector Image
If Your Child Tests Positive For Anas, It May Mean They Have An Autoimmune Disease.
Pleomorphic Pattern Is Caused By Antibodies To The Proliferating Cell Nuclear Antigen.
We Looked For Mnd In 9189 Sera Belonging To 6240 Patients Stored For Autoimmune Diseases With Prevalent Cutaneous Features.
Web The Nuclear Dot Pattern, Observed In Antinuclear Antibody (Ana) Testing, Is A Distinctive Immunofluorescence Pattern Characterized By Discrete Speckles Or Dots Within The Cell Nucleus.
Related Post: