Monomers And Polymers Chart
Monomers And Polymers Chart - In chemistry, a hydrocarbon is any compound entirely composed of hydrogen and carbon molecules. Web terms in this set (10) study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like monosaccharide, polysaccharide, nucleotide and more. Look at the image below to familiarize yourself with monomer and polymer structure. Web concept 5.1 most macromolecules are polymers, built from monomers. Web most macromolecules are made from single subunits, or building blocks, called monomers. Web in biology, macromolecules refer to large organic molecules that form by polymerization, a process that joins smaller units called monomers via covalent bonds. Biological macromolecules play a critical role in cell structure and function. Web a monomer is a low molecular weight hydrocarbon molecule. Typically, the building blocks are organic molecules held together via covalent bonds. 6 minutes, 7 seconds read. For example, a carbohydrate is a polymer that is made. Look at the image below to familiarize yourself with monomer and polymer structure. The monomers combine with each other using covalent bonds to form larger molecules. Addition polymerization and condensation polymerization. Biological macromolecules play a critical role in cell structure and function. A molecule that is a building block for larger molecules (polymers). Web polymers are long molecules composed of chains of units called monomers. Web a monomer is a low molecular weight hydrocarbon molecule. Use the chart to identify the chemicals that appear in every type of monomer. Addition polymerization and condensation polymerization. A molecule from which a polymer is made is. Typically, the building blocks are organic molecules held together via covalent bonds. Web in biology, macromolecules refer to large organic molecules that form by polymerization, a process that joins smaller units called monomers via covalent bonds. Most (but not all) biological macromolecules are polymers,. A large molecule made of repeating subunits. Web the most important difference between monomers and polymers is that polymers are made of monomers. Web terms in this set (10) study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like monosaccharide, polysaccharide, nucleotide and more. 6 minutes, 7 seconds read. Web a monosaccharide is the monomer that makes up a polysaccharide. When monomers link together, what do they usually. Web monomers and polymers. Web most macromolecules are made from single subunits, or building blocks, called monomers. A molecule from which a polymer is made is. For example, a carbohydrate is a polymer that is made. Web terms in this set (10) study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like monosaccharide, polysaccharide, nucleotide and more. Most (but not all) biological macromolecules are polymers,. Biological macromolecules play a critical role in cell structure and function. The monomers combine with each other using covalent bonds to form larger molecules. When monomers link together, what do they usually. Addition polymerization and condensation polymerization. For example, a carbohydrate is a polymer that is made. The inverse — monomers being made of polymers. Use the chart to identify the chemicals that appear in every type of monomer. Web concept 5.1 most macromolecules are polymers, built from monomers. The monomers combine with each other using covalent bonds to form larger molecules. Web a monomer is a low molecular weight hydrocarbon molecule. Web how would you explain the relationship between monomers and polymers, using polysaccharides as an example? The monomers combine with each other using covalent bonds to form larger molecules. Addition polymerization and condensation polymerization. The monomers combine with each other using covalent bonds to form larger molecules. A large molecule made of repeating subunits (monomers). Web the monomers for each biological macromolecule are composed of the basic chemical formula. When monomers link together, what do they usually. The inverse — monomers being made of polymers. 6 minutes, 7 seconds read. Most (but not all) biological macromolecules are polymers,. Web monomers and polymers. Covalent bonds) study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like monomer (subunit) of carbohydrates, function of. Typically, the building blocks are organic molecules held together via covalent bonds. Web a monomer is a low molecular weight hydrocarbon molecule. Web there are two general types of polymerization reactions: When monomers link together, what do they usually. Monomers and polymers are both important types of molecules found in nature and used in a variety of industries. Web monomers are repetitive units that form a larger compound. Web a monomer is a low molecular weight hydrocarbon molecule. Web polymers are long molecules composed of chains of units called monomers. The monomers combine with each other using covalent bonds to form larger molecules. Addition polymerization and condensation polymerization. A molecule that is a building block for larger molecules (polymers). The monomers combine with each other using covalent. Web the monomers for each biological macromolecule are composed of the basic chemical formula. A large molecule made of repeating subunits (monomers). Look at the image below to familiarize yourself with monomer and polymer structure. A molecule from which a polymer is made is. Web terms in this set (10) study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like monosaccharide, polysaccharide, nucleotide and more. The monomers combine with each other using covalent bonds to form larger molecules.
16.7 Polymers Chemistry LibreTexts
PPT CELL BIOLOGY (C) 2015 PowerPoint Presentation, free download
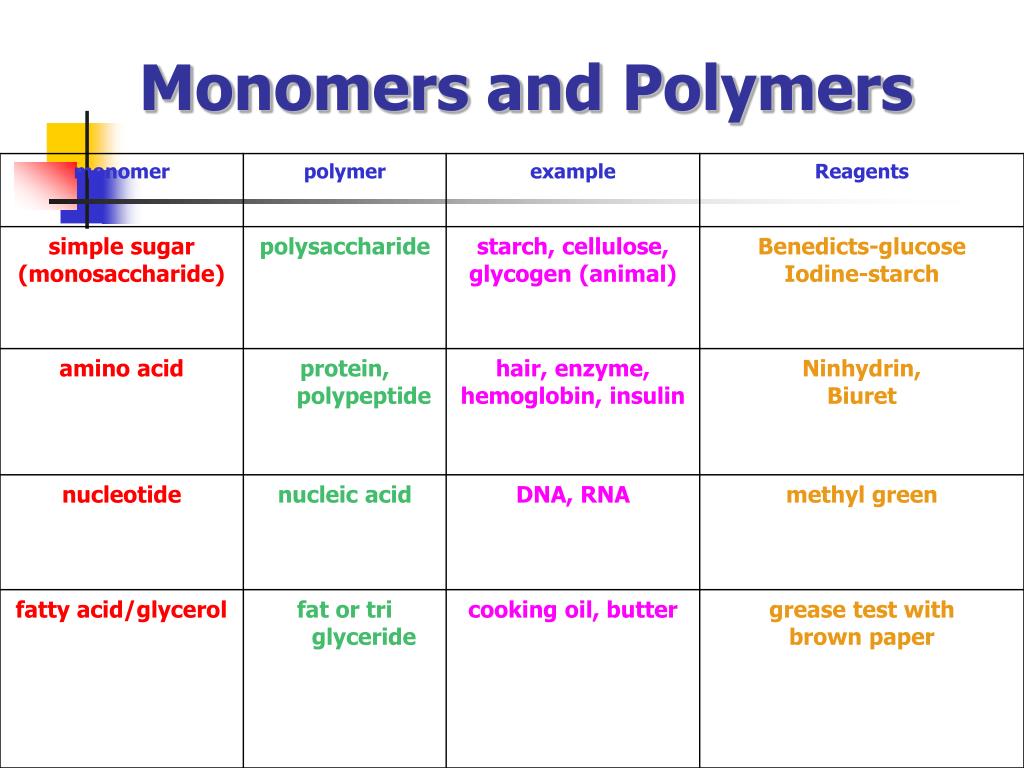
Macromolecules Monomers And Polymers Chart
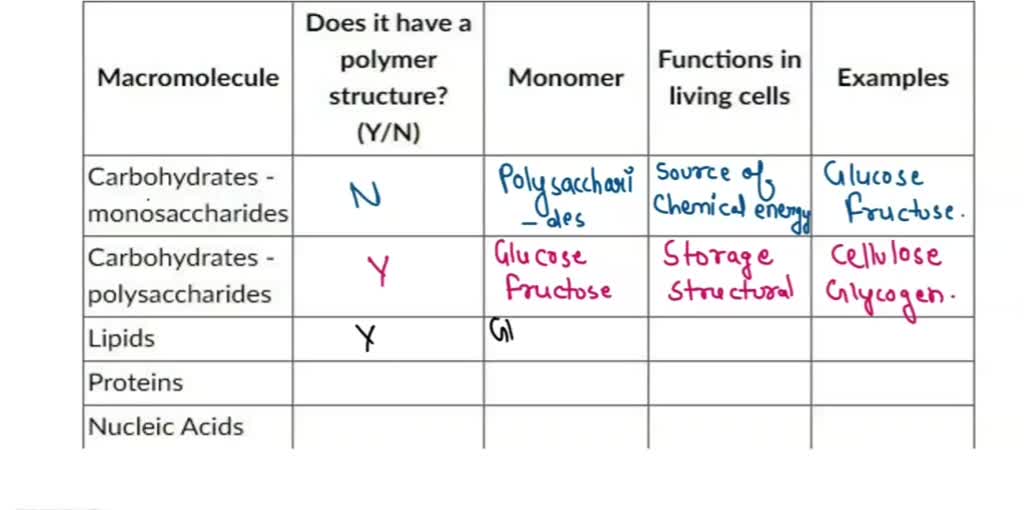
Polymers And Monomers Chart
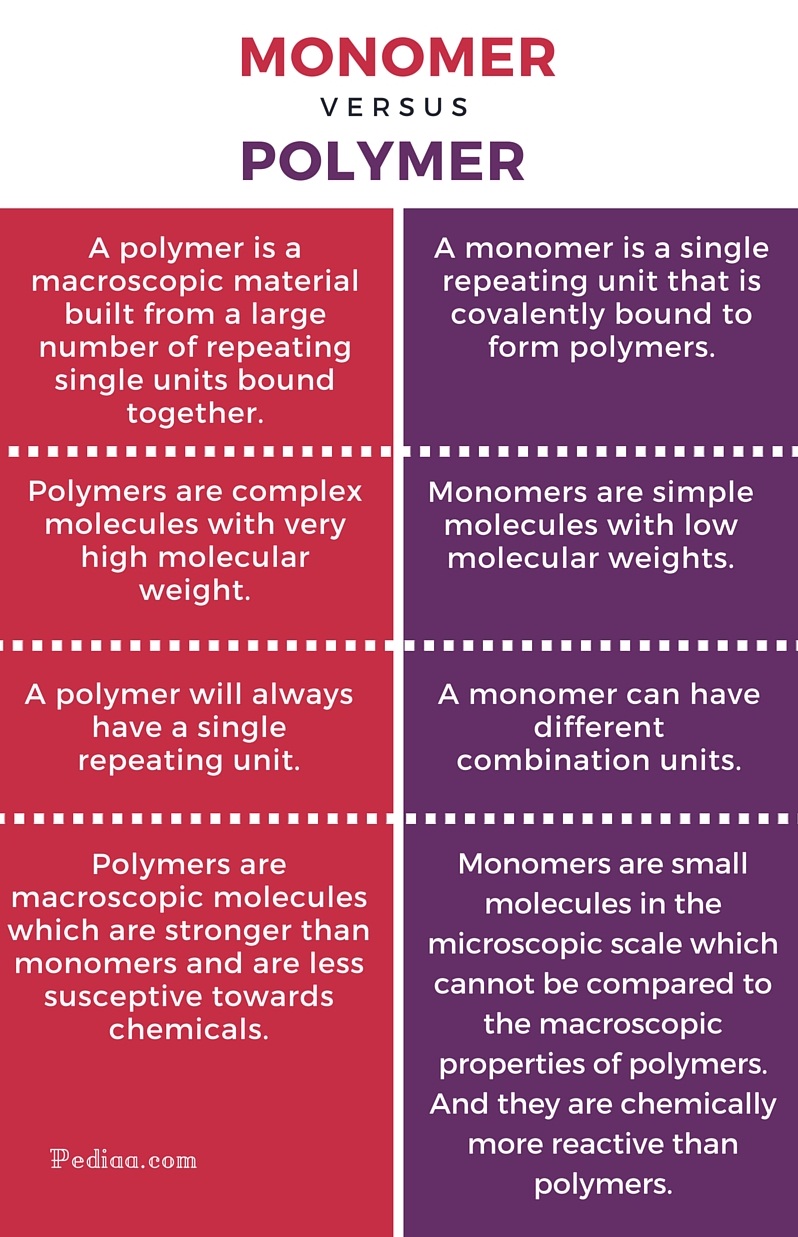
Difference Between Monomer and Polymer

Macromolecules Monomers And Polymers Chart
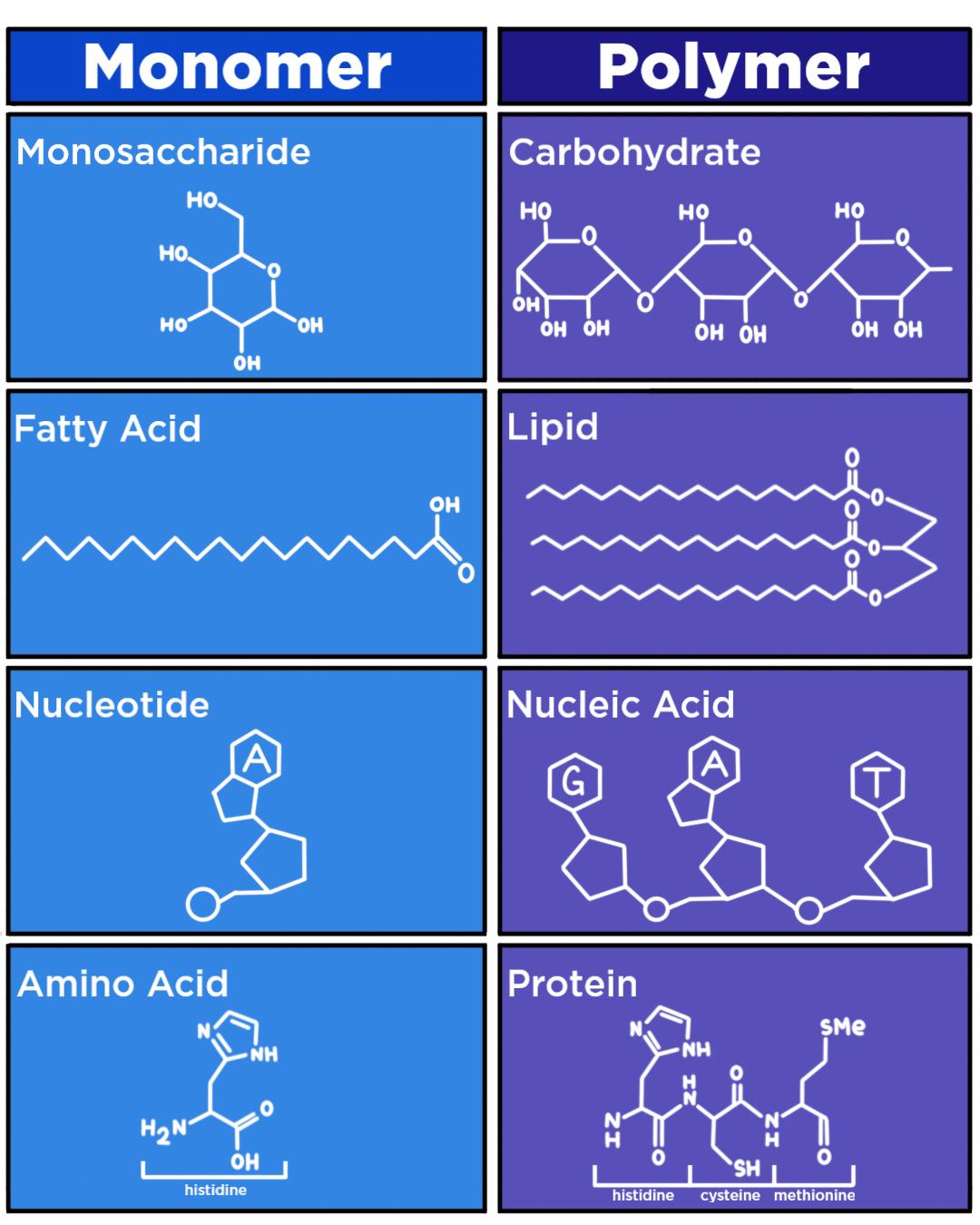
Macromolecules Monomers And Polymers Chart

Polymers Basicmedical Key
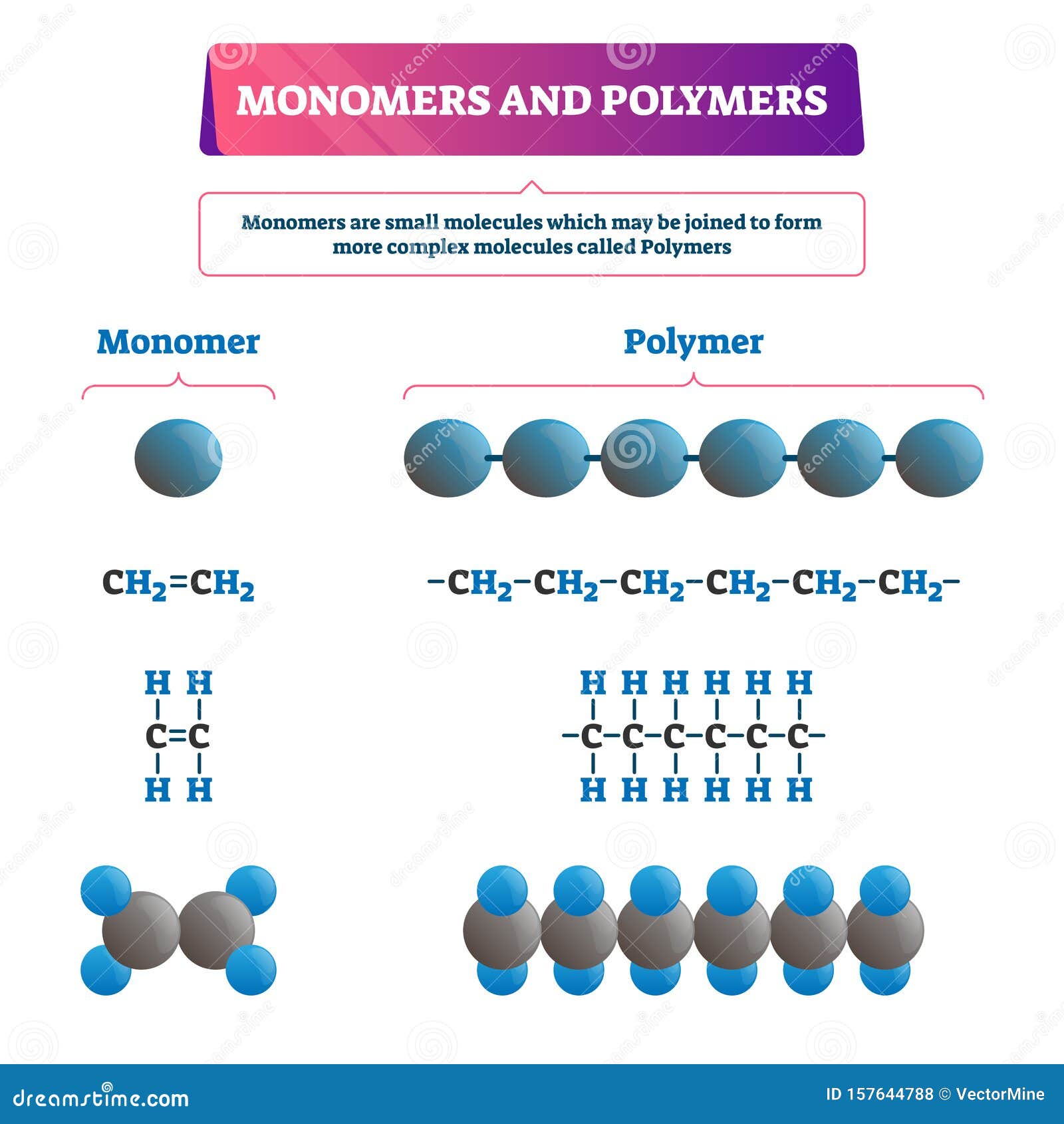
Monomer or Polymer Vector Illustration. Labeled Chemical Educational

What are the MONOMERS of each POLYMER? ppt download
Use The Chart To Identify The Chemicals That Appear In Every Type Of Monomer.
Covalent Bonds) Study With Quizlet And Memorize Flashcards Containing Terms Like Monomer (Subunit) Of Carbohydrates, Function Of.
Several Important Biological Polymers Include Proteins, Starch, Cellulose,.
Web In Biology, Macromolecules Refer To Large Organic Molecules That Form By Polymerization, A Process That Joins Smaller Units Called Monomers Via Covalent Bonds.
Related Post: