Monomer Polymer Chart
Monomer Polymer Chart - An oligomer is a molecule that consists of a few monomer units. Look at the image below to familiarize yourself with monomer and polymer structure. Web learn about monomers and polymers. It is the smallest unit in a polymer, which is often a macromolecule with. Web polymers are long chain, giant organic molecules are assembled from many smaller molecules called monomers. Web chemistry classifies monomers by type, and two broad classes based on the type of polymer they form. Unit 4 elements of life. Web an immense variety of polymers can be built from a small number of monomers. When monomers link together, what do they usually. Web how would you explain the relationship between monomers and polymers, using polysaccharides as an example? Unit 5 energy and enzymes. Web monomers are repetitive units that form a larger compound. Typically, the building blocks are organic molecules held together via. If you think of a. The monomers combine with each other using covalent bonds to form larger molecules. Web an immense variety of polymers can be built from a small number of monomers. Web many natural materials—such as proteins, cellulose and starch, and complex silicate minerals—are polymers. Each vinyl chloride monomer molecule contributes a ch 2 group joined to a chcl unit by a single. Web polymers range from synthetic polymers to natural biopolymers such as dna and. Web polymers range from synthetic polymers to natural biopolymers such as dna and proteins. Unit 5 energy and enzymes. The monomers combine with each other using covalent bonds to form larger molecules. Unit 6 structure of a cell. Web unit 1 intro to biology. Web unit 1 intro to biology. Web many natural materials—such as proteins, cellulose and starch, and complex silicate minerals—are polymers. Web polymers range from synthetic polymers to natural biopolymers such as dna and proteins. Most (but not all) biological macromolecules are polymers,. Web most macromolecules are made from single subunits, or building blocks, called monomers. Unit 5 energy and enzymes. The monomers combine with each other using covalent bonds to form larger molecules. The monomers combine with each other using covalent bonds to form larger molecules. Unit 6 structure of a cell. Most large biological molecules are polymers, long chains made up of repeating molecular subunits, or building blocks, called monomers. If you think of a. The monomers combine with each other using covalent bonds to form larger molecules. Web unit 1 intro to biology. Web monomers are repetitive units that form a larger compound. For example, an amino acid acts as the building blocks for proteins. Polymers consist of many repeating monomer. The monomers combine with each other using covalent bonds to form larger molecules. Each vinyl chloride monomer molecule contributes a ch 2 group joined to a chcl unit by a single. Each cell has thousands of different kinds of macromolecules. Web in biology, macromolecules refer to large organic molecules that form by polymerization, a. The monomers combine with each other using covalent bonds to form larger molecules. Web chemistry classifies monomers by type, and two broad classes based on the type of polymer they form. Each vinyl chloride monomer molecule contributes a ch 2 group joined to a chcl unit by a single. Artificial fibers, films, plastics, semisolid resins, and. Polymers consist of many. Most (but not all) biological macromolecules are polymers,. Web a molecule from which a polymer is made is called a monomer. Web polymers range from synthetic polymers to natural biopolymers such as dna and proteins. If you think of a. Web a monomer is a type of molecule that has the ability to chemically bond with other molecules in a. Web study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like monomer (subunit) of carbohydrates, function of carbohydrates, polymer formed from simple sugars and more. Look at the image below to familiarize yourself with monomer and polymer structure. Web how would you explain the relationship between monomers and polymers, using polysaccharides as an example? Web learn about monomers and polymers. Web. Typically, the building blocks are organic molecules held together via. Web how would you explain the relationship between monomers and polymers, using polysaccharides as an example? Look at the image below to familiarize yourself with monomer and polymer structure. Web dna and rna are polymers (in the case of dna, often very long polymers), and are made up of monomers known as nucleotides. For example, an amino acid acts as the building blocks for proteins. Each vinyl chloride monomer molecule contributes a ch 2 group joined to a chcl unit by a single. Web monomers are repetitive units that form a larger compound. Web chemistry classifies monomers by type, and two broad classes based on the type of polymer they form. When monomers link together, what do they usually. Web polymers are long molecules composed of chains of units called monomers. Web most macromolecules are made from single subunits, or building blocks, called monomers. Web most macromolecules are made from single subunits, or building blocks, called monomers. Web many natural materials—such as proteins, cellulose and starch, and complex silicate minerals—are polymers. Unit 2 water, acids, and bases. If you think of a. A molecule that is a building block for larger molecules (polymers).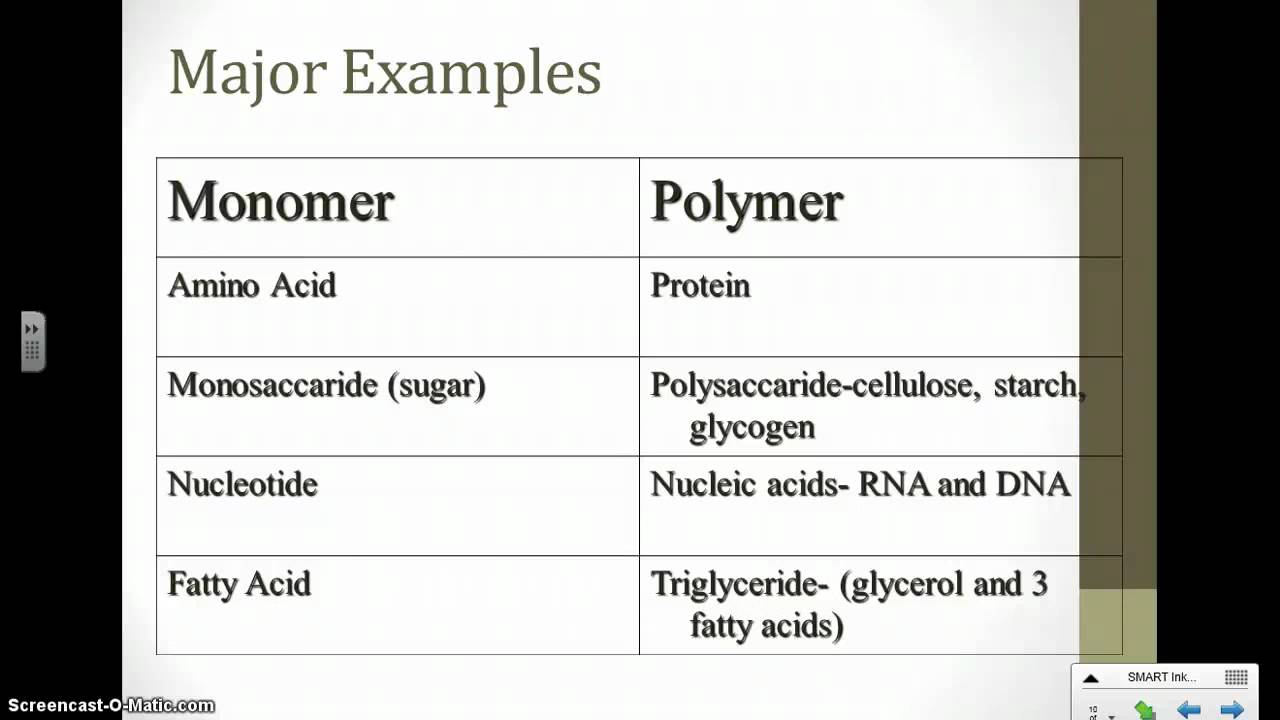
Monomers And Polymers Chart
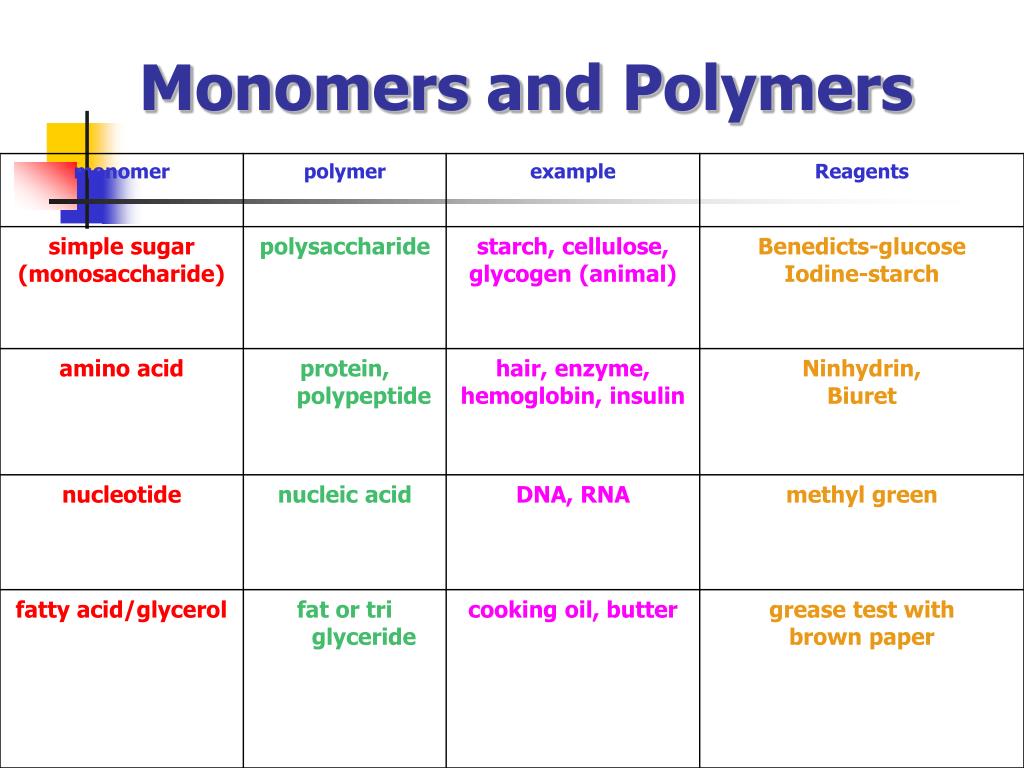
PPT CELL BIOLOGY (C) 2015 PowerPoint Presentation, free download

Names and structures of the main polymers and their groups described

Polymers Basicmedical Key

Monomers And Polymers Chart A Visual Reference of Charts Chart Master

Polymers And Monomers Chart

Polymers And Monomers Chart
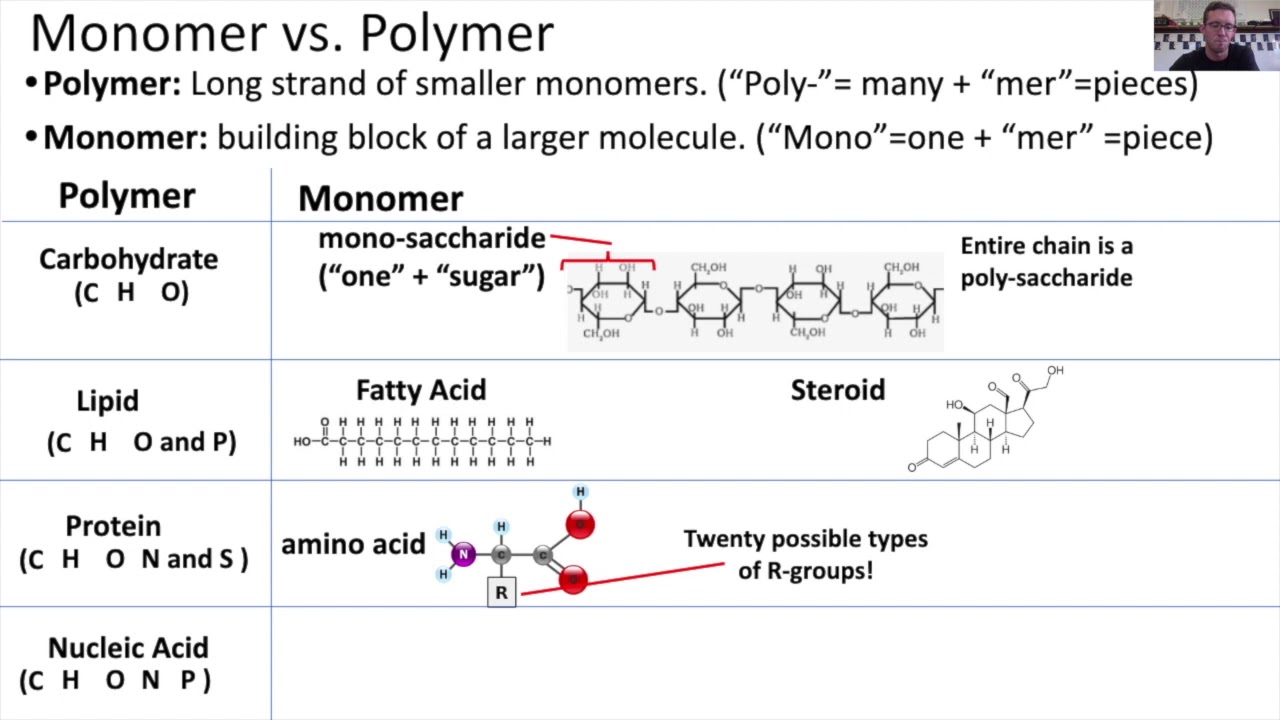
Monomers vs. Polymers YouTube
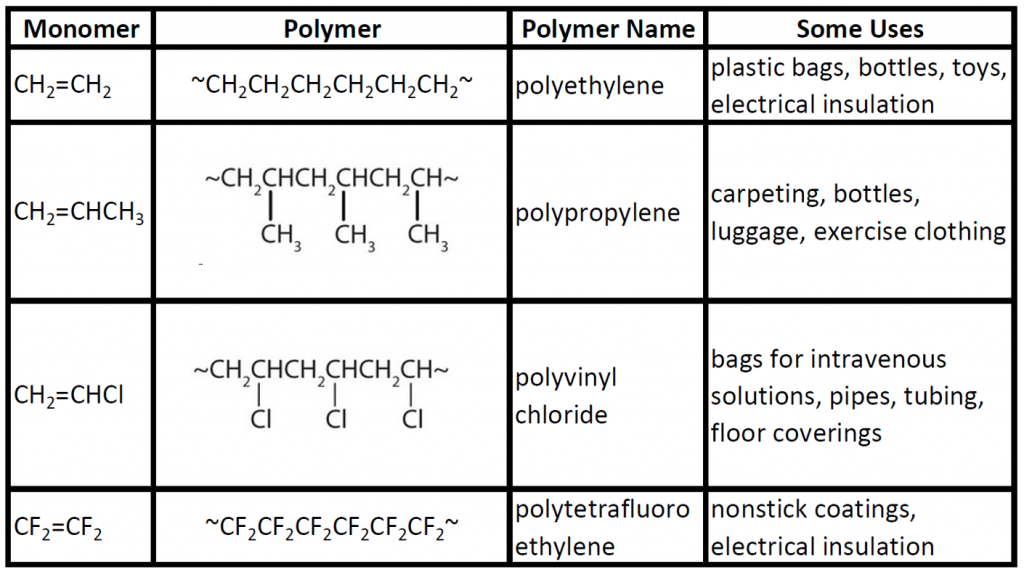
Polymers And Monomers Chart

Polymers And Monomers Chart
An Oligomer Is A Molecule That Consists Of A Few Monomer Units.
Web In Biology, Macromolecules Refer To Large Organic Molecules That Form By Polymerization, A Process That Joins Smaller Units Called Monomers Via Covalent Bonds.
Web A Monomer Is A Type Of Molecule That Has The Ability To Chemically Bond With Other Molecules In A Long Chain;
Web Unit 1 Intro To Biology.
Related Post: