Miranda V Arizona Drawing
Miranda V Arizona Drawing - Ernesto miranda was arrested after a victim identified him as her assailant. Arizona is the supreme court case where it was held that the custodial interrogation of an individual must be accompanied by an instruction that the person has the right to remain silent, any statements made can be used against the person, and that the individual has the right to counsel , either retained or appointed. The state of arizona retried & reconvicted miranda for both of his crimes in 1967. Arizona addressed four different cases involving custodial interrogations. Web the supreme court ruled that suspects must be informed of their rights, and therefore the evidence used to convict miranda was invalid. Sixth amendment right to an attorney. Web the case came out of phoenix, arizona, and was decided by the nation's highest court in 1966. Web the jury found miranda guilty. They asked the witness whether she could identify the person who committed the crime. But how do students know if they are in custody? The police brought miranda into custody, but they did not inform him of his right to remain silent or his right to an attorney. Arizona (1966) culminated in the famed “miranda rights” requirement during arrests. Web case summary of miranda v. Web • gain insight into the reasoning used by the supreme court in miranda v. The defendants offered incriminating. Bogart, georgia context & purpose this lesson introduces a unit that explores the judicial branch and how its design protects the supreme court’s In each of these cases, the defendant was questioned by police officers, detectives, or a prosecuting attorney in a room in which he was cut off from the outside world. 436 (1966), was a landmark decision of. Web the supreme court’s decision in miranda v. Arizona, the supreme court ruled that anyone accused of a crime must be warned about the right to remain silent and the right to an attorney. Web the supreme court ruled that suspects must be informed of their rights, and therefore the evidence used to convict miranda was invalid. Sixth amendment right. Web in the landmark case miranda v. Arizona (1966) culminated in the famed “miranda rights” requirement during arrests. A lesson plan using the time magazine archive database from ebsco lesson overview name: Supreme court on june 13, 1966, established the miranda warnings, a set of guidelines for police interrogations of criminal suspects in custody designed to ensure that suspects are. Miranda was not informed of his fifth amendment right to remain silent or right to have counsel present. Arizona, the supreme court established that police must inform anyone interrogated in police custody that they have the following constitutional rights: Arizona, the supreme court ruled that anyone accused of a crime must be warned about the right to remain silent and. Arizona, the supreme court ruled that anyone accused of a crime must be warned about the right to remain silent and the right to an attorney. Web the jury found miranda guilty. Evidence of each confession was used at trial. In each of these cases, the defendant was questioned by police officers, detectives, or a prosecuting attorney in a room. Arizona, legal case in which the u.s. Sixth amendment right to an attorney. The police brought miranda into custody, but they did not inform him of his right to remain silent or his right to an attorney. Arizona, the supreme court established that police must inform anyone interrogated in police custody that they have the following constitutional rights: They found. Web in the landmark case miranda v. Evidence of each confession was used at trial. Miranda was not informed of his fifth amendment right to remain silent or right to have counsel present. In each of these cases, the defendant was questioned by police officers, detectives, or a prosecuting attorney in a room in which he was cut off from. Arizona is the supreme court case where it was held that the custodial interrogation of an individual must be accompanied by an instruction that the person has the right to remain silent, any statements made can be used against the person, and that the individual has the right to counsel , either retained or appointed. Synopsis of rule of law.. A lesson plan using the time magazine archive database from ebsco lesson overview name: The supreme court’s decision in miranda v. But how do students know if they are in custody? Ernesto miranda was arrested after a victim identified him as her assailant. Synopsis of rule of law. The culminating activity is completing and discussing the worksheet comparing four circuit court cases to identify common factors that courts use to make that determination. Web the case came out of phoenix, arizona, and was decided by the nation's highest court in 1966. Supreme court case of miranda v. In each of these cases, the defendant was questioned by police officers, detectives, or a prosecuting attorney in a room in which he was cut off from the outside world. Synopsis of rule of law. But how do students know if they are in custody? Arizona, legal case in which the u.s. Web ernesto miranda was accused of a serious crime. The police brought miranda into custody, but they did not inform him of his right to remain silent or his right to an attorney. Web the jury found miranda guilty. Arizona, the supreme court ruled that anyone accused of a crime must be warned about the right to remain silent and the right to an attorney. Web miranda rights come into play when someone is in police custody. Arizona (1966) culminated in the famed “miranda rights” requirement during arrests. Ernesto miranda was arrested after a victim identified him as her assailant. Arizona (1966) the supreme court held that the custodial interrogation of an individual must be accompanied by an instruction that the person has the right to remain silent, any statements made can be used against the person, and that the individual has the right to counsel, either retained or appointed; Sixth amendment right to an attorney.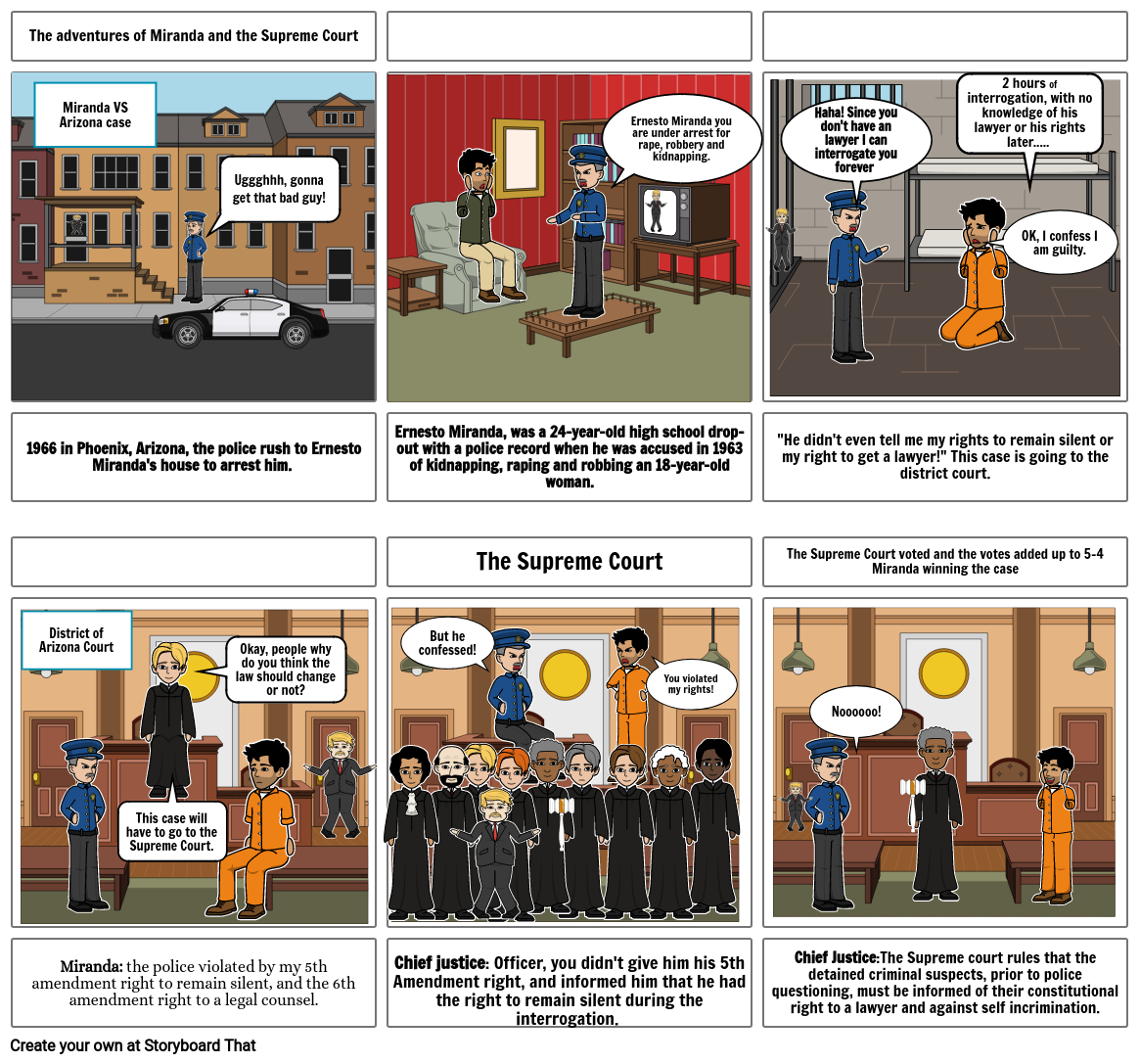
Miranda VS Arizona Storyboard von kraustar
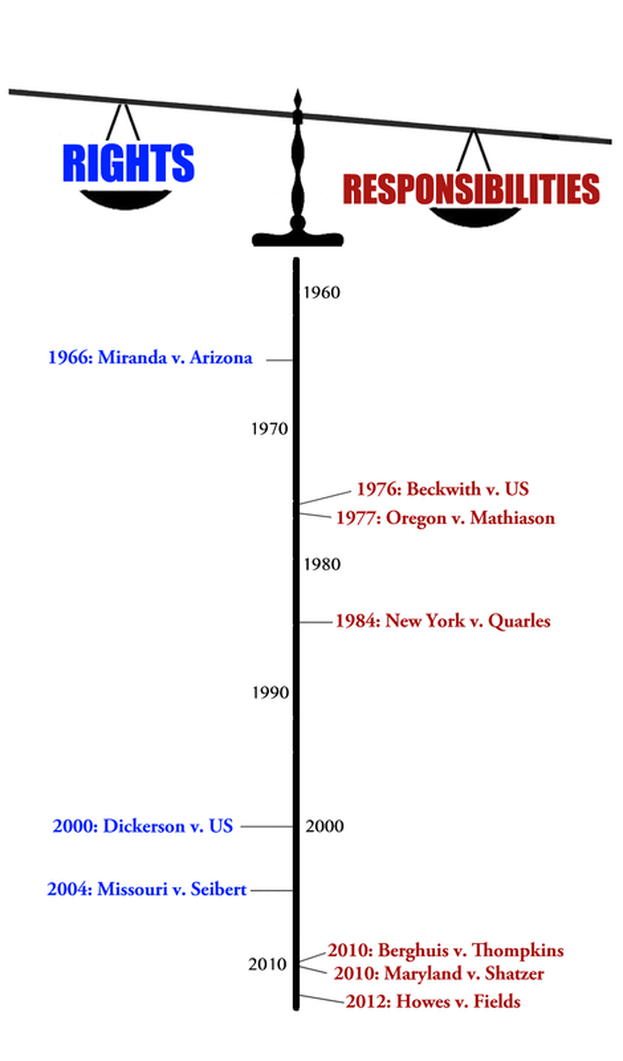
Miranda, Post 1966 Miranda v. Arizona Rebalancing Rights and

Miranda v. Arizona Summary, Facts & Significance Video & Lesson

Miranda v. Arizona Fifty Years of Silence Romano Law

Miranda v. Arizona Civil Rights or Civil Liberties Supreme Court Cases

Miranda vs. Arizona Case

Miranda, Post 1966 Miranda v. Arizona Rebalancing Rights and

Miranda V. Arizona Art Print United States Supreme Court Case Quote

Miranda v. Arizona (SCOTUSToons) YouTube
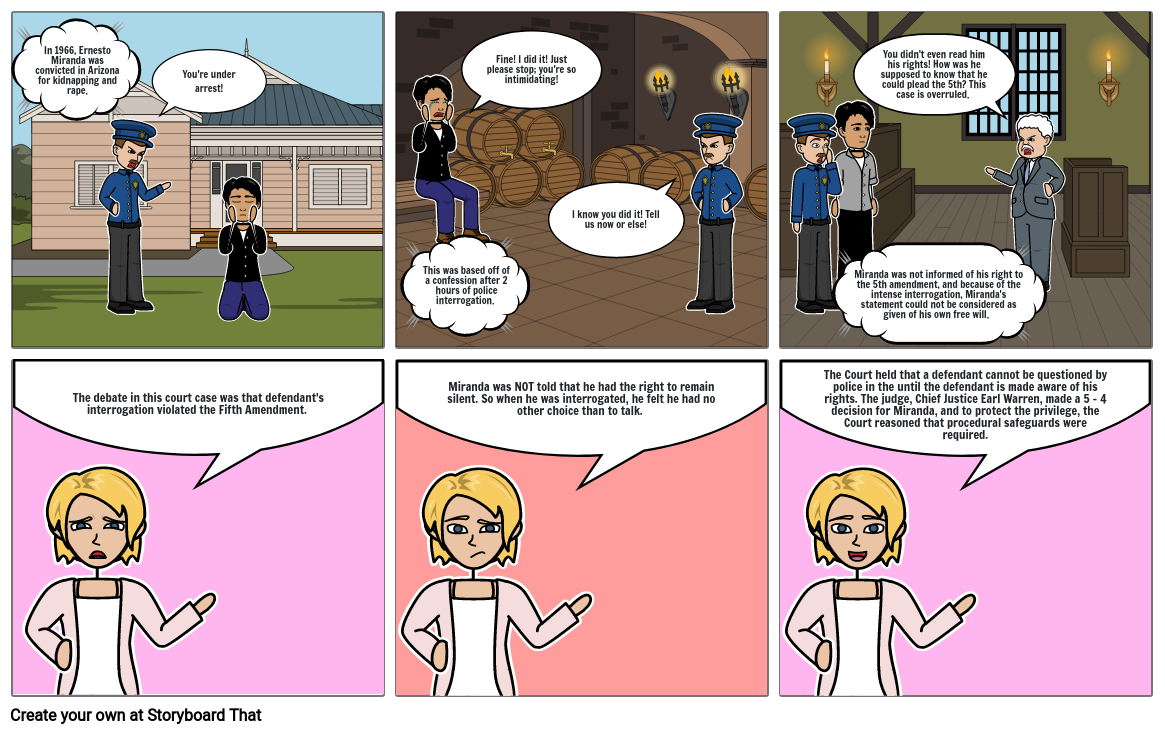
Miranda vs. Arizona Storyboard by 22ccf613
They Asked The Witness Whether She Could Identify The Person Who Committed The Crime.
Arizona, The Supreme Court Established That Police Must Inform Anyone Interrogated In Police Custody That They Have The Following Constitutional Rights:
Web The Supreme Court Ruled That Suspects Must Be Informed Of Their Rights, And Therefore The Evidence Used To Convict Miranda Was Invalid.
The Rights To Justice, An Online Presentation Of Historical Documents That Shed Light On The Arguments Around, And The.
Related Post: