Metamorphic Chart
Metamorphic Chart - Some examples of metamorphic rocks are gneiss, slate, marble, schist, and quartzite. Web metamorphic rock, any rock that results from the alteration of preexisting rocks in response to changing conditions, such as variations in temperature, pressure, and mechanical stress, and the addition or subtraction of chemical components. These rocks change forms via the rock cycle. Web metamorphic rocks are rocks that have undergone a profound transformation in mineral composition, texture, and sometimes even chemical structure without melting. Web metamorphic is the first studio album by south korean girl group stayc. Chart (2024) peak position south korean albums : Describe what a contact aureole is and how contact metamorphism affects surrounding rock. Describe the temperature and pressure conditions of the metamorphic environment. Web what’s something you’re listening to? Web the major types of metamorphic rocks are detailed here, which include regional, contact and mechanical metamorphism. The classification of metamorphic rocks is based on the minerals that are present and the temperature and pressure at which these minerals form. Web metamorphic grade refers to the range of metamorphic change a rock undergoes, progressing from low (little metamorphic change) grade to high (significant metamorphic change) grade. Web even rocks, a seemingly constant substance, can change into a. Igneous rocks form when molten rock (magma or lava) cools and solidifies. Web what’s something you’re listening to? Web metamorphic grade is a general term we use to describe the temperature at which metamorphism occurs. Describe what recrystallization is and how it affects mineral crystals. Web metamorphic grade refers to the range of metamorphic change a rock undergoes, progressing from. Web metamorphic rocks represent one of the three major classes of rocks, the others being igneous and sedimentary. Describe what recrystallization is and how it affects mineral crystals. Visual guide to rock types: Igneous rocks form when molten rock (magma or lava) cools and solidifies. Identify and describe the three principal metamorphic agents. Web metamorphic rock, any rock that results from the alteration of preexisting rocks in response to changing conditions, such as variations in temperature, pressure, and mechanical stress, and the addition or subtraction of chemical components. In the rock cycle, there are three different types of. Web explain the relationships among slate, phyllite, schist, and gneiss in terms of metamorphic grade.. Each class has its unique formation processes, characteristics, and significance in earth’s geology. Rocks that undergo a change to form a new rock are referred to as metamorphic rocks. Those that are foliated because they have formed in an environment with either directed pressure or shear stress, and those that are not foliated because they have formed in an environment. Describe the temperature and pressure conditions of the metamorphic environment. You identified many of these minerals in previous labs. Specimen # mineral name specimen # Web metamorphic rocks are rocks that have undergone a profound transformation in mineral composition, texture, and sometimes even chemical structure without melting. Web even rocks, a seemingly constant substance, can change into a new type. These rocks change forms via the rock cycle. Sedimentary rocks originate when particles settle out of water or air, or by precipitation of minerals from water. Web explain the relationships among slate, phyllite, schist, and gneiss in terms of metamorphic grade. Visual guide to rock types: Web even rocks, a seemingly constant substance, can change into a new type of. Describe the temperature and pressure conditions of the metamorphic environment. They come in various colors and often contain glittery mica. Region date format label south korea july 1, 2024. Web metamorphic rocks (changed rocks) are made when existing rocks are subjected to high temperatures and high pressures for long periods of time. Igneous rocks form when molten rock (magma or. Metamorphism (meta = change, morph = form) happens when molten rock intrudes other rocks and bakes the contact zone where the molten rock touches the preexisting rock. Metamorphic grade is important, not just because different kinds of rocks and minerals form at different temperatures, but because temperature affects chemical reaction rates. Web even rocks, a seemingly constant substance, can change. Chart (2024) peak position south korean albums : Web what’s something you’re listening to? The classification of metamorphic rocks is based on the minerals that are present and the temperature and pressure at which these minerals form. You identified many of these minerals in previous labs. Web metamorphic rock, any rock that results from the alteration of preexisting rocks in. Region date format label south korea july 1, 2024. By the end of this chapter, students will be able to: My choice would be stayc’s “cheeky icy thang,” without a doubt. Web explain the relationships among slate, phyllite, schist, and gneiss in terms of metamorphic grade. Describe what a contact aureole is and how contact metamorphism affects surrounding rock. Web metamorphic rocks represent one of the three major classes of rocks, the others being igneous and sedimentary. Some examples of metamorphic rocks are gneiss, slate, marble, schist, and quartzite. Next, check the rock's grain size and hardness. Web metamorphic grade refers to the range of metamorphic change a rock undergoes, progressing from low (little metamorphic change) grade to high (significant metamorphic change) grade. Web the three major types are igneous, sedimentary, and metamorphic rocks. Web metamorphic rocks are rocks that have undergone a profound transformation in mineral composition, texture, and sometimes even chemical structure without melting. Identify and describe the three principal metamorphic agents. Specimen # mineral name specimen # Rocks that undergo a change to form a new rock are referred to as metamorphic rocks. Sedimentary rocks originate when particles settle out of water or air, or by precipitation of minerals from water. Web the study of metamorphic rocks (now exposed at the earth's surface following erosion and uplift) provides information about the temperatures and pressures that occur at great depths within the earth's crust.
Overview of Metamorphic Rocks Laboratory Manual for Earth Science

Rock Collection and ID Chart 18 Rocks Igneous, Metamorphic
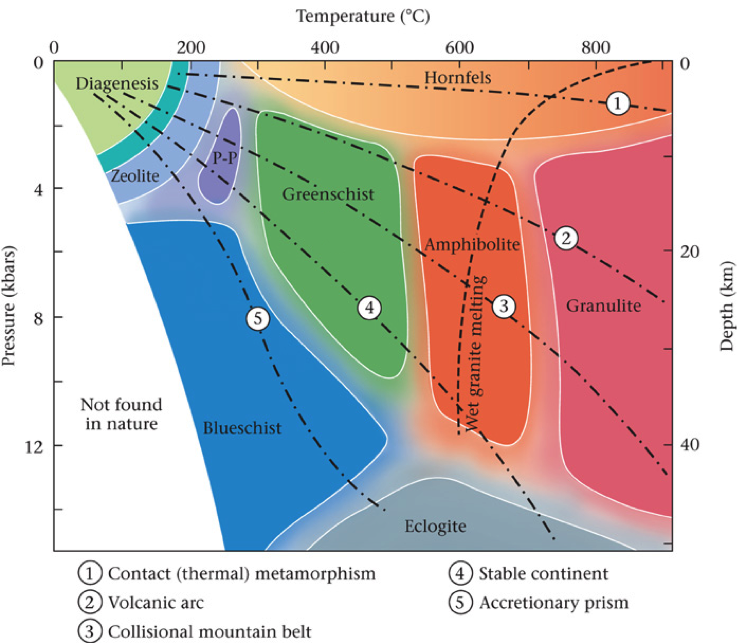
Metamorphic rocks, minerals, grade, and facies Lucky Sci

Regional Metamorphism Rocks, minerals, Geology humor, Geology

American Educational Identifying Metamorphic Rock Chart Amazon.in

Regional Metamorphism

Metamorphic Rock Chart Diagram Quizlet

Metamorphic Rock Identification Chart Pdf
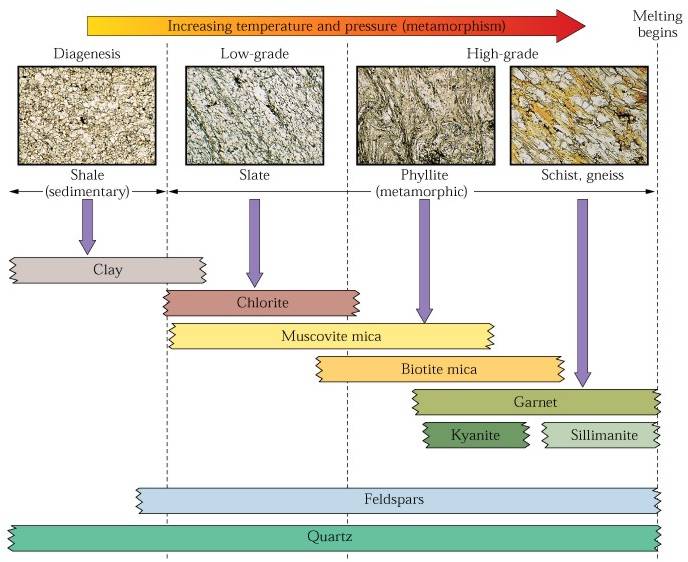
Metamorphic rocks, minerals, grade, and facies Lucky Sci

Metamorphic Rock Chart Flinn Scientific
Explain How Metamorphic Facies Relate To Plate Tectonic Processes.
In The Rock Cycle, There Are Three Different Types Of.
Visual Guide To Rock Types:
Web The Major Types Of Metamorphic Rocks Are Detailed Here, Which Include Regional, Contact And Mechanical Metamorphism.
Related Post: