Macromolecules Chart
Macromolecules Chart - The molecule is the smallest unit of the substance that retains its. Carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids. Web biological macromolecules are large molecules, necessary for life, that are built from smaller organic molecules. There are four major classes of biological macromolecules. Web properties, structure, and function of biological macromolecules. Web macromolecules carbohydrates lipids structures & functions monomer name(s) monomer diagram(s) polymer(s) * not a true polymer… name of bond Web chemical structure of a polypeptide macromolecule. Protein shape and function are intricately linked; In some cases, it’s important to know which carbons on the two sugar rings are connected by a glycosidic bond. Explore their structures, functions, and how they are made and broken by. Each carbon atom in a. The molecule is the smallest unit of the substance that retains its. Primary, secondary, tertiary, and quaternary. Web learn the key terms, types, building blocks, functions, and examples of biological macromolecules such as carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids. Web macromolecule, any very large molecule, usually with a diameter ranging from about 100 to 10,000. Protein shape and function are intricately linked; “macromolecules are very large molecules that are formed by the polymerization of smaller molecules called monomers.”. In some cases, it’s important to know which carbons on the two sugar rings are connected by a glycosidic bond. Web proteins are organized at four levels: Each carbon atom in a. Carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids. Web learn about the four main classes of macromolecules: “macromolecules are very large molecules that are formed by the polymerization of smaller molecules called monomers.”. In some cases, it’s important to know which carbons on the two sugar rings are connected by a glycosidic bond. Web properties, structure, and function of biological macromolecules. A macromolecule is a very large molecule important to biological processes, such as a protein or nucleic acid. The molecule is the smallest unit of the substance that retains its. The image below depicts how the bacterial protein barnase undergoes. Web learn the key terms, types, building blocks, functions, and examples of biological macromolecules such as carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and. Web chemical structure of a polypeptide macromolecule. In some cases, it’s important to know which carbons on the two sugar rings are connected by a glycosidic bond. A macromolecule is a very large molecule important to biological processes, such as a protein or nucleic acid. Each carbon atom in a. Explore their structures, functions, and how they are made and. Each carbon atom in a. Web macromolecule, any very large molecule, usually with a diameter ranging from about 100 to 10,000 angstroms. Web learn the key terms, types, building blocks, functions, and examples of biological macromolecules such as carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids. Web biological macromolecules are large molecules, necessary for life, that are built from smaller organic molecules.. Web proteins are organized at four levels: Explore their structures, functions, and how they are made and broken by. Web macromolecule proteins monomer name and chemical composition and name of bond between adjacent monomers amino acids peptide bonds types of this macromolecule. Web chemical structure of a polypeptide macromolecule. Each carbon atom in a. A macromolecule is a very large molecule important to biological processes, such as a protein or nucleic acid. Web learn about the four main classes of macromolecules: Web macromolecule proteins monomer name and chemical composition and name of bond between adjacent monomers amino acids peptide bonds types of this macromolecule. Each carbon atom in a. In some cases, it’s important. In some cases, it’s important to know which carbons on the two sugar rings are connected by a glycosidic bond. Carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids. “macromolecules are very large molecules that are formed by the polymerization of smaller molecules called monomers.”. Web proteins are organized at four levels: Web properties, structure, and function of biological macromolecules. There are four major classes of biological macromolecules. Web carbohydrates are essential macromolecules that are classified into three subtypes: The molecule is the smallest unit of the substance that retains its. Web biological macromolecules are large molecules, necessary for life, that are built from smaller organic molecules. Primary, secondary, tertiary, and quaternary. Web properties, structure, and function of biological macromolecules. Web macromolecules carbohydrates lipids structures & functions monomer name(s) monomer diagram(s) polymer(s) * not a true polymer… name of bond In some cases, it’s important to know which carbons on the two sugar rings are connected by a glycosidic bond. The image below depicts how the bacterial protein barnase undergoes. Each carbon atom in a. Explore their structures, functions, and how they are made and broken by. Web learn the key terms, types, building blocks, functions, and examples of biological macromolecules such as carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids. Web learn about the four main classes of macromolecules: Web macromolecule proteins monomer name and chemical composition and name of bond between adjacent monomers amino acids peptide bonds types of this macromolecule. “macromolecules are very large molecules that are formed by the polymerization of smaller molecules called monomers.”. Web macromolecule, any very large molecule, usually with a diameter ranging from about 100 to 10,000 angstroms. There are four major classes of biological macromolecules. Web chemical structure of a polypeptide macromolecule. Web proteins are organized at four levels: Primary, secondary, tertiary, and quaternary. Protein shape and function are intricately linked;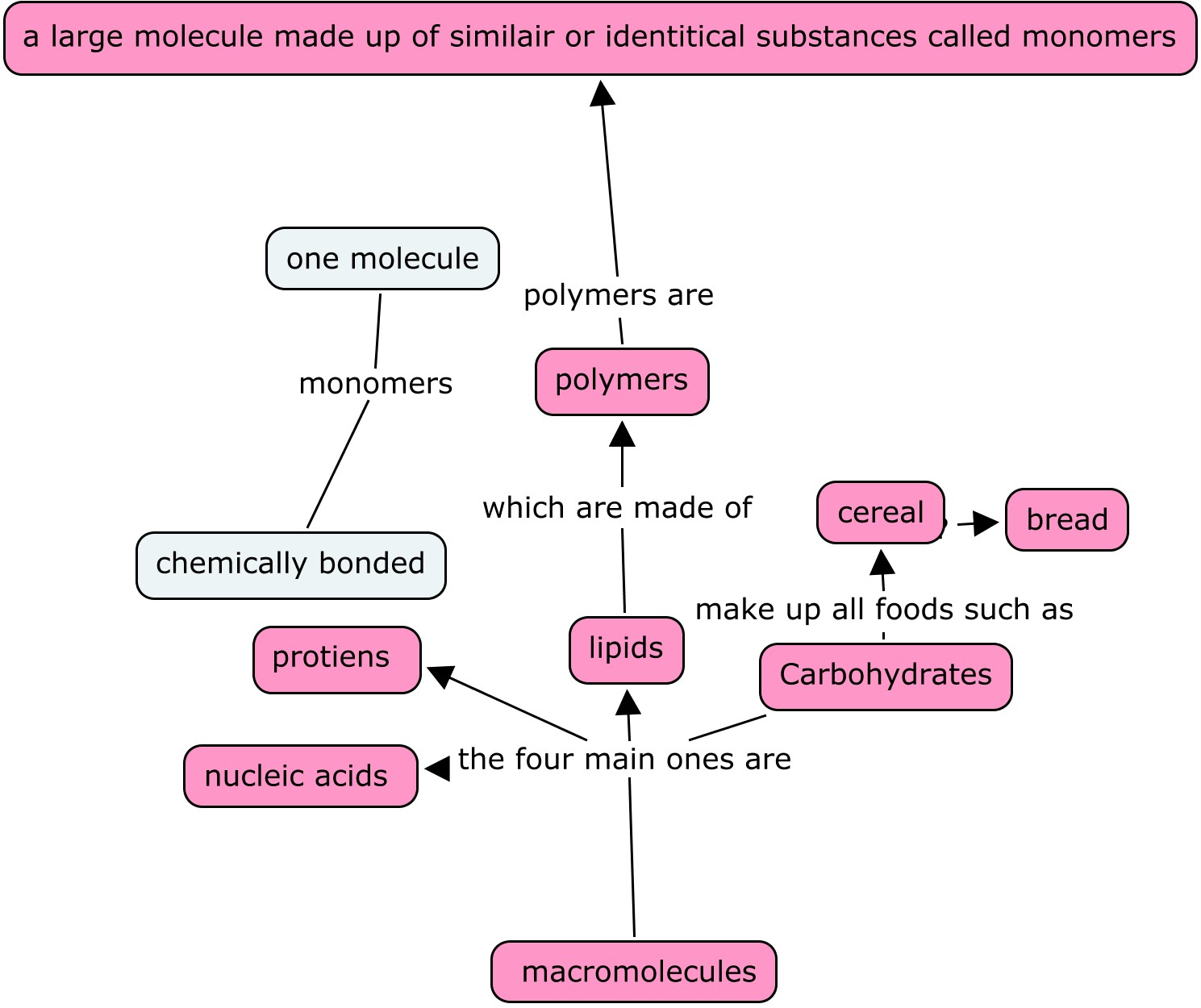
Biology by patricia m Macromolecules c map

simple diagram of macromolecules, proteins, carbohydrates, lipids, and
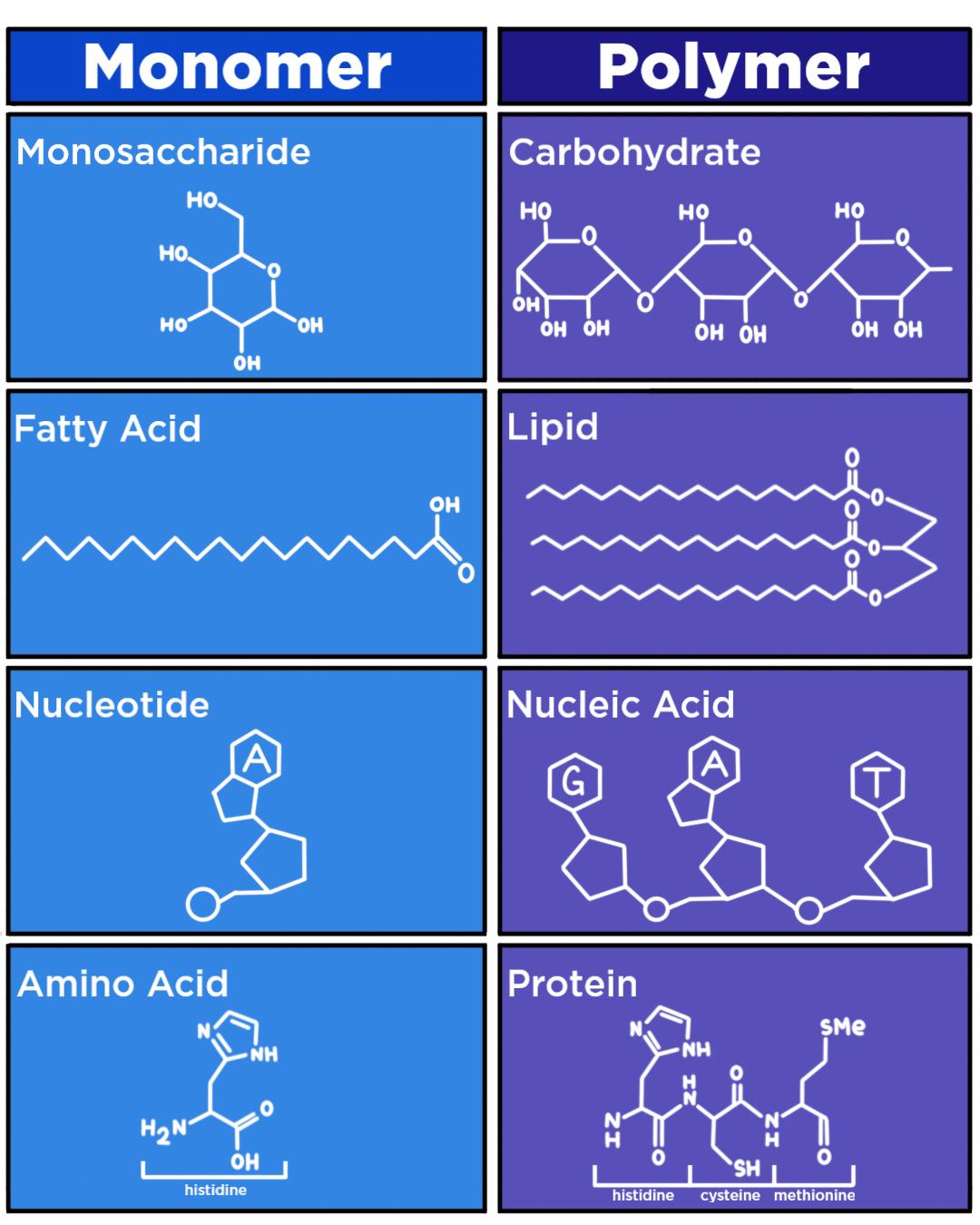
Macromolecules Monomers And Polymers Chart

Farah Bazzi Mrs. Bazzi`s Biology Classroom

October 2017 AP Biology

Pre IB/GT Biology 1 Macromolecules Chart Diagram Quizlet
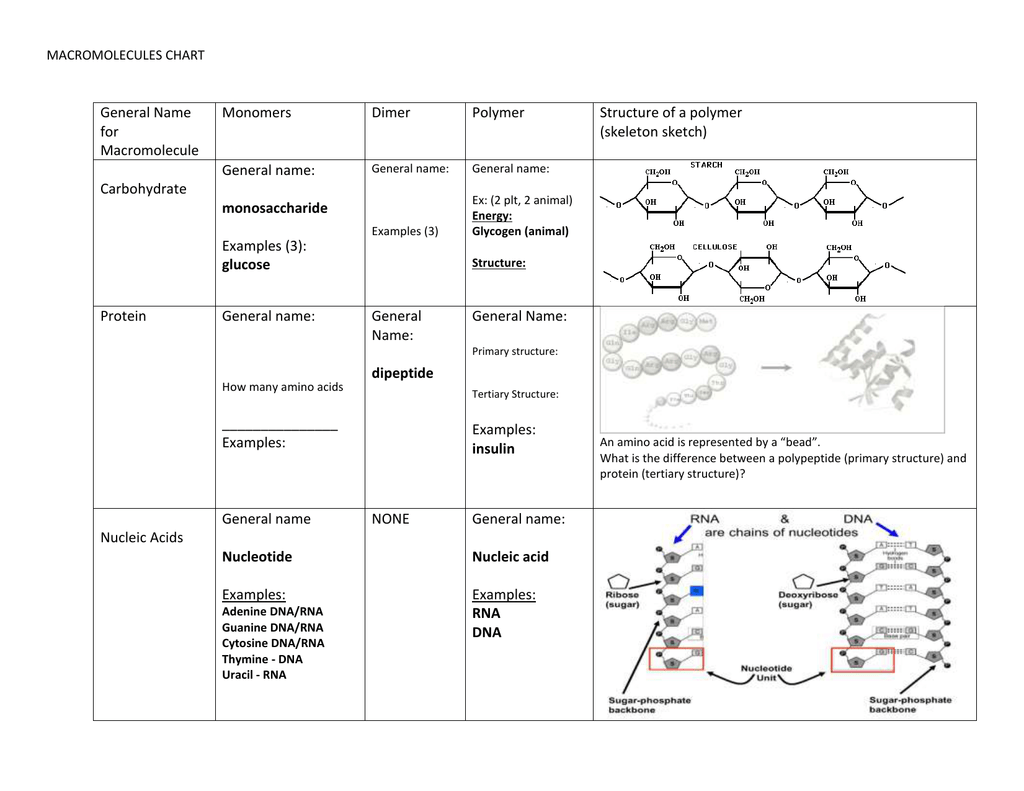
MACROMOLECULES CHART General Name for Macromolecule

2.3 Biologically Important Macromolecules Biology LibreTexts

Macromolecules Teaching biology, Biology lessons, Science biology
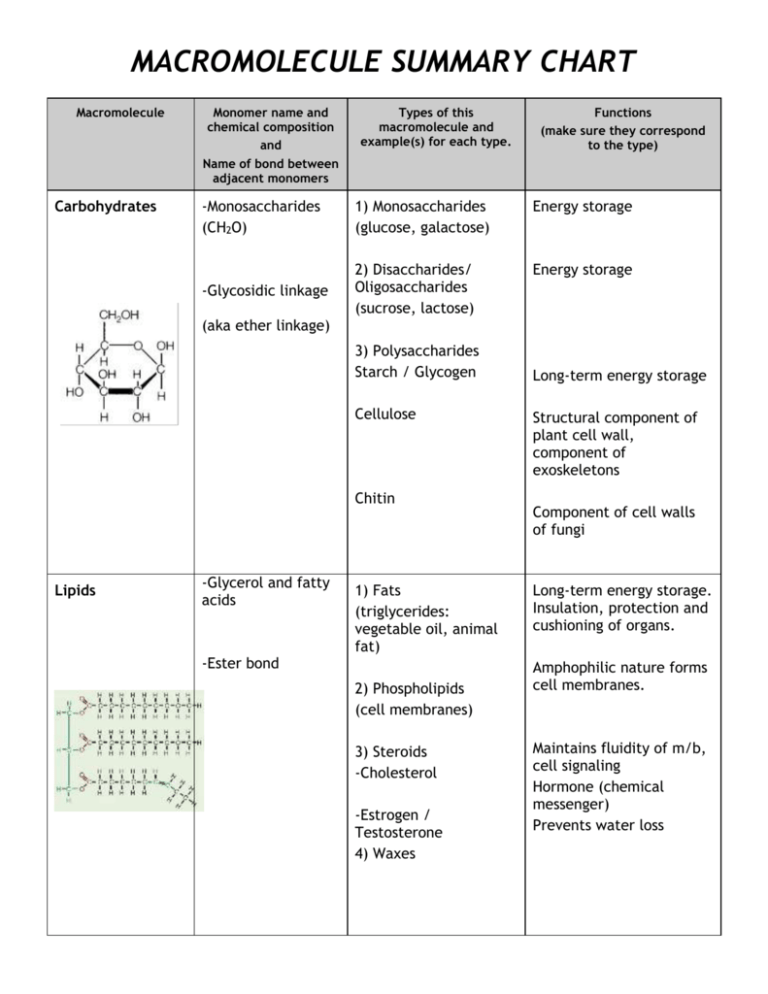
macromolecule summary chart
Web Carbohydrates Are Essential Macromolecules That Are Classified Into Three Subtypes:
A Macromolecule Is A Very Large Molecule Important To Biological Processes, Such As A Protein Or Nucleic Acid.
The Molecule Is The Smallest Unit Of The Substance That Retains Its.
Web Biological Macromolecules Are Large Molecules, Necessary For Life, That Are Built From Smaller Organic Molecules.
Related Post: