Laser Wavelengths Chart
Laser Wavelengths Chart - Thousands of kinds of laser are known, but most of them are used only for specialized research. In detector applications, it is beneficial to use filtering to increase your snr and perhaps utilize a lens to limit field of view. For example, the minimum optical density at the 1.06 ?m nd:yag laser wavelength for a 10 second direct intrabeam exposure to the 100 watt maximum laser output can be. Click on a laser to see its applications and find suppliers, when available. The visible colors from shortest to longest wavelength are: Web photonics media presents a look at the major commercial laser lines, the wavelengths they produce, and their many applications. Web the photonics spectrum reference chart. Web for visual applications, the closer to 550nm (green) the laser wavelength is, the brighter it will appear. Blue violet (405nm), blue (445nm, 460nm), pure blue (473nm), green (532nm), yellow (589nm) and red. Also, some frequently used wavelengths from sources with frequency doubling, frequency tripling or frequency quadrupling are listed. Click on a laser to see its applications and find suppliers, when available. Web the wavelength of a laser is its most fundamental characteristic, determining its properties, material interactions, and applications. Web the most common unit used in expressing a laser's wavelength is a nanometer (nm). Web the first chart shows the visible light spectrum and associated wavelengths in nanometers.. The visible colors from shortest to longest wavelength are: Web this is a list of laser types, their operational wavelengths, and their applications. Blue violet (405nm), blue (445nm, 460nm), pure blue (473nm), green (532nm), yellow (589nm) and red. Web the wavelength of a laser is its most fundamental characteristic, determining its properties, material interactions, and applications. Use the filters to. Web why it is impossible to engrave or cut with lasers of wavelength more than 300 nm. Web the most common unit used in expressing a laser's wavelength is a nanometer (nm). In detector applications, it is beneficial to use filtering to increase your snr and perhaps utilize a lens to limit field of view. There are one billion nanometers. The gain bandwidth of the lasing medium and the design of the optical resonator, which may include elements to purposely narrow the linewidth, like filters or etalons. Web the most common unit used in expressing a laser's wavelength is a nanometer (nm). All the lasers with thin lines (i.e. Also, some frequently used wavelengths from sources with frequency doubling, frequency. For example, the minimum optical density at the 1.06 ?m nd:yag laser wavelength for a 10 second direct intrabeam exposure to the 100 watt maximum laser output can be. Web based upon the worst case exposure conditions outlined above, one can determine the optical density recommended to provide adequate eye protection for this laser. Web as for laser hair removal,. Web the first chart shows the visible light spectrum and associated wavelengths in nanometers. Web photonics media presents a look at the major commercial laser lines, the wavelengths they produce, and their many applications. Web discover the different types of lasers commonly used in various fields, from industrial applications to medical treatments. The gain bandwidth of the lasing medium and. Web discover the different types of lasers commonly used in various fields, from industrial applications to medical treatments. Blue violet (405nm), blue (445nm, 460nm), pure blue (473nm), green (532nm), yellow (589nm) and red. Web for visual applications, the closer to 550nm (green) the laser wavelength is, the brighter it will appear. Web chapters cover classification of lasers, evaluation of laserbeam. Web as for laser hair removal, as the name suggests, it's only used for hair removal. Use the filters to narrow your search by application or laser type. Instead of the light pulses used in the ipl method, it uses the light of the laser and only one wavelength on a. Blue violet (405nm), blue (445nm, 460nm), pure blue (473nm),. Web each laser wavelength is associated with a linewidth, which depends on several factors: The top half of the chart) are in that category. Web discover the different types of lasers commonly used in various fields, from industrial applications to medical treatments. Web part of photonics media's celebration of the 50th anniversary of the laser, this chart lists the major. The gain bandwidth of the lasing medium and the design of the optical resonator, which may include elements to purposely narrow the linewidth, like filters or etalons. Web chapters cover classification of lasers, evaluation of laserbeam ignition potential, laser beam ignition, fire safety requirements for laser equipment, flammable gases, reactive gases, ignitable liquids used in laser systems, operations and administration,. Web part of photonics media's celebration of the 50th anniversary of the laser, this chart lists the major types of commercial lasers available in wavelengths from 1 nm to 1 mm, broken down by type and application. Web laser wavelength chart shows the colors of visible light spectrum and associated wavelength in nanometers: Web photonics media presents a look at the major commercial laser lines, the wavelengths they produce, and their many applications. Click on a laser to see its applications and find suppliers, when available. The visible colors from shortest to longest wavelength are: Web the chart below gives hazard distances for selected consumer laser types, and for various parameters such as the beam color, beam spread and power. Web this is a list of laser types, their operational wavelengths, and their applications. Web chapters cover classification of lasers, evaluation of laserbeam ignition potential, laser beam ignition, fire safety requirements for laser equipment, flammable gases, reactive gases, ignitable liquids used in laser systems, operations and administration, and emergency preparedness. Printed on 60lb stock and folded. The gain bandwidth of the lasing medium and the design of the optical resonator, which may include elements to purposely narrow the linewidth, like filters or etalons. Web the most common unit used in expressing a laser's wavelength is a nanometer (nm). Some lasers emit light in a very narrow spectrum of wavelengths. Use the filters to narrow your search by application or laser type. Web each laser wavelength is associated with a linewidth, which depends on several factors: The top half of the chart) are in that category. Wavelength determines the color, beam visibility of laser pointer.
(Electronics) Laser Wavelength Chart The Old Map Gallery
![Typical types of lasers and corresponding wavelengths [69]. Download](https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Carl_Magnus/publication/328190911/figure/fig25/AS:680108046163971@1539161802872/Typical-types-of-lasers-and-corresponding-wavelengths-69.png)
Typical types of lasers and corresponding wavelengths [69]. Download
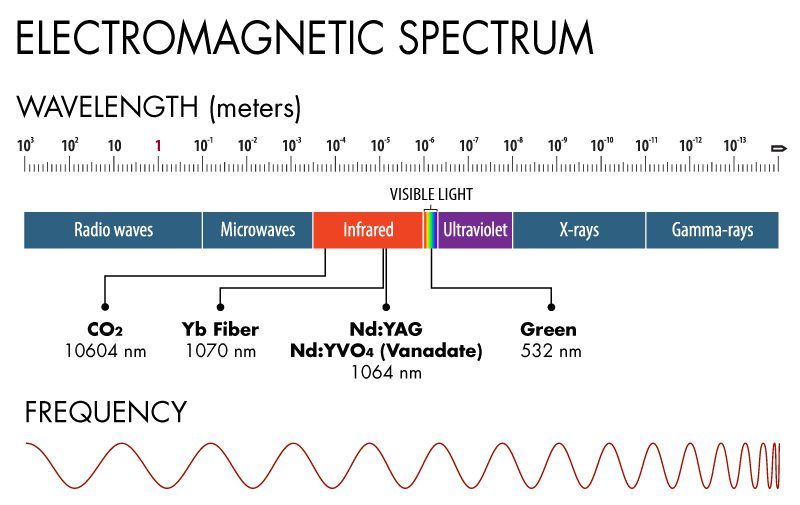
Laser Wavelengths for Specific Materials Pannier Marking Systems
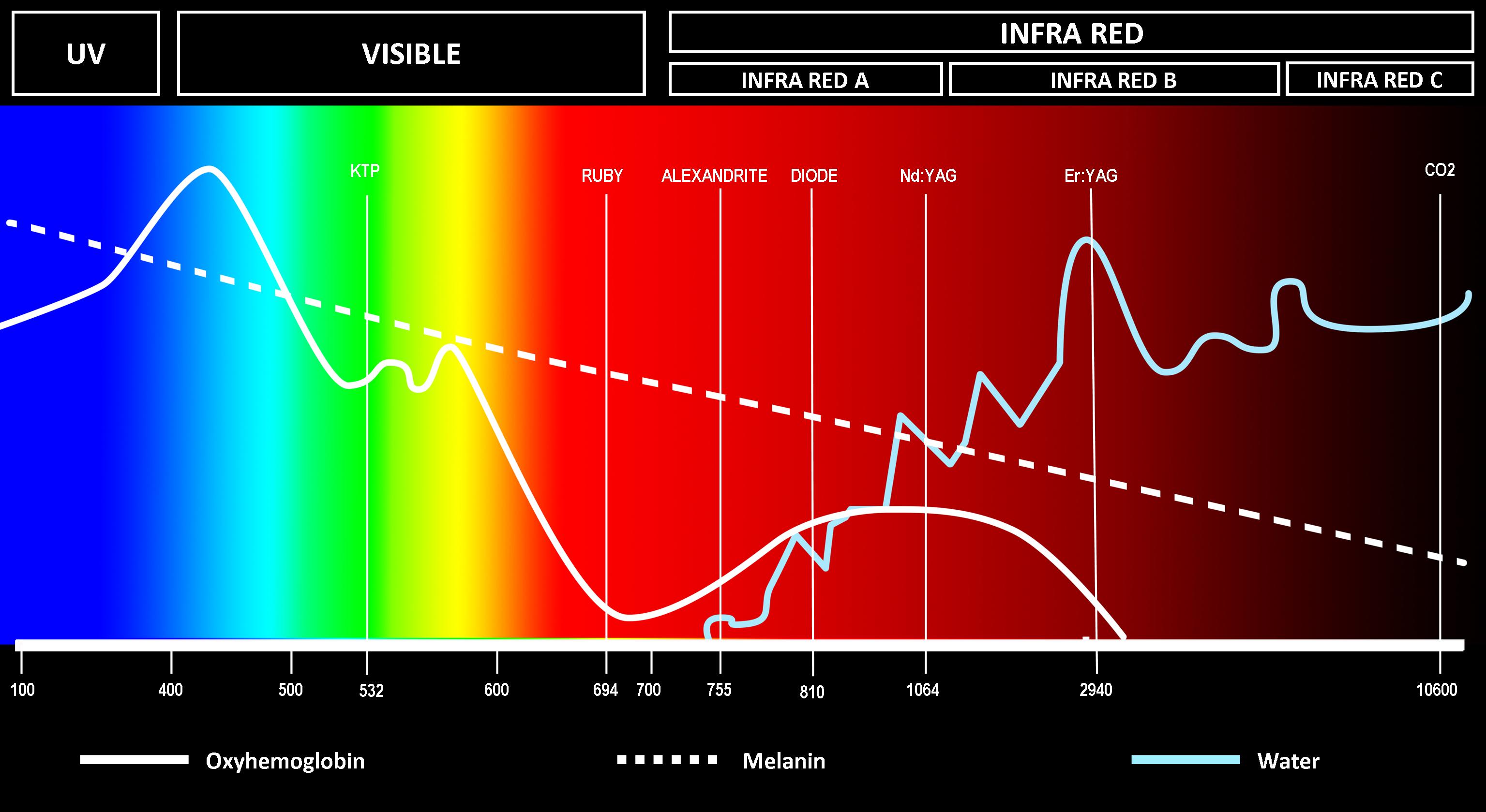
Laser Spectrum Chart
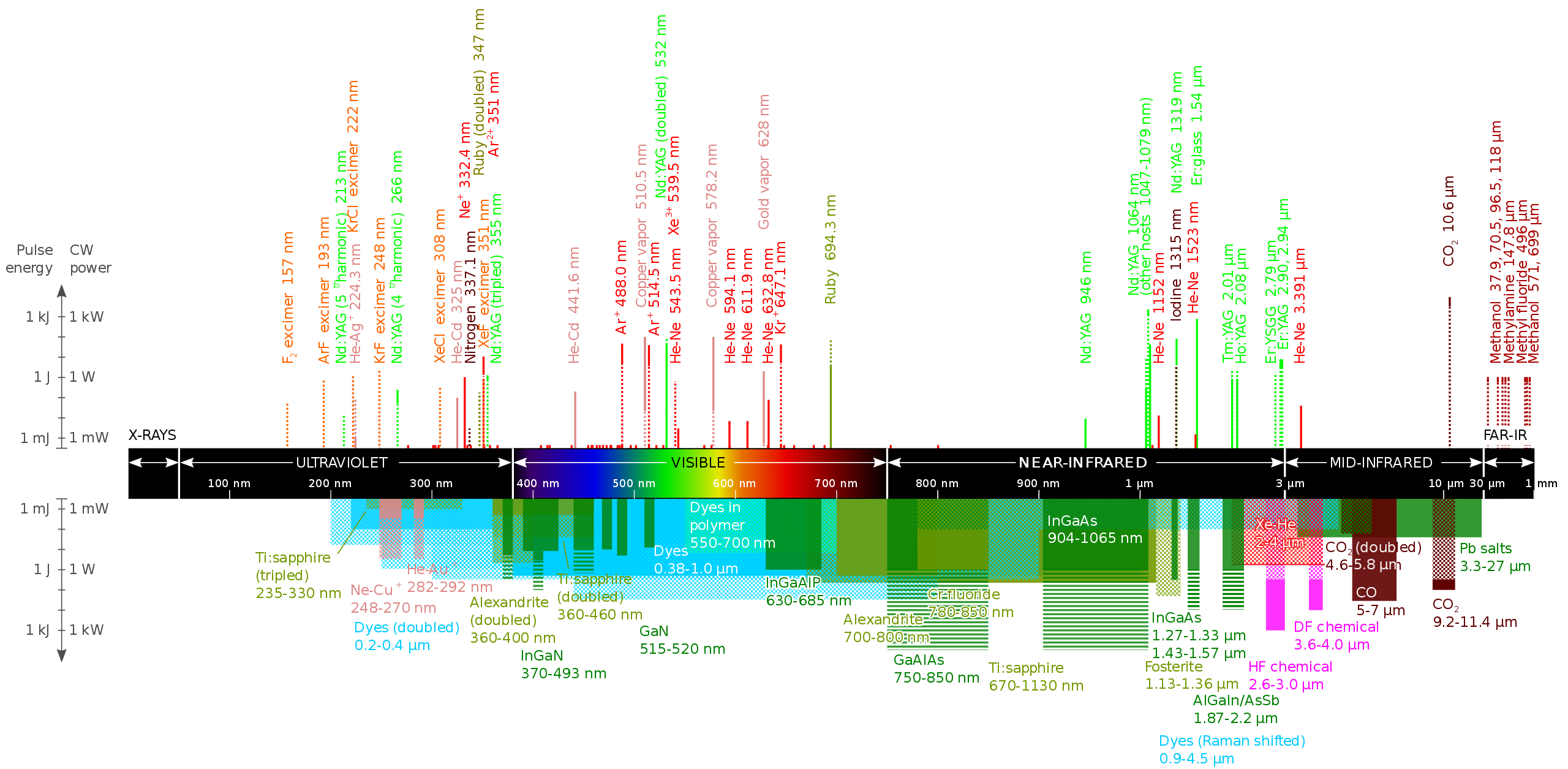
The laser wavelength chart explained

Laser Spectrum Chart
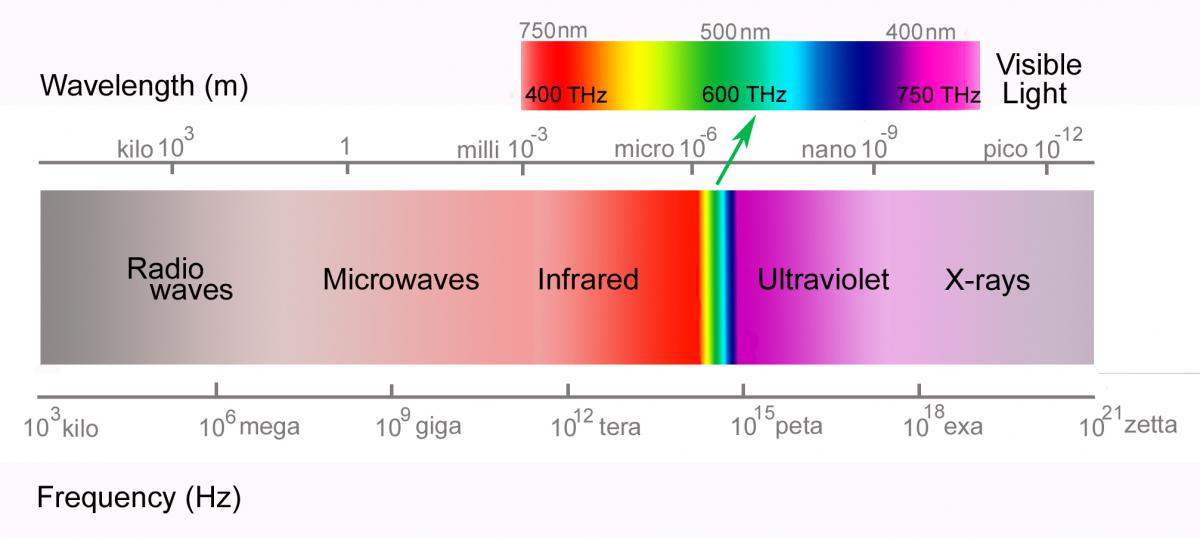
Fiber Lasers Everything You Need to Know Laserax

Laser Spectrum Chart

Chart of the laser wavelengths and pulse durations applied for
Skywise's Lasers & Optics Reference Area
Web The Co2 Laser Produces A Beam Of Infrared Light With The Principal Wavelength Bands Centering Around 9.4 And 10.6 Micrometers (As In Figure3).
In Addition, Text Below The Chart Describes How Divergence (Beam Spread), Power And Wavelength (Color) Affects These Hazard Distances.
Web The Wavelength Of A Laser Is Its Most Fundamental Characteristic, Determining Its Properties, Material Interactions, And Applications.
Laser Wavelength Is The Inverse Of Frequency (Units:
Related Post: