Laser Wavelength Chart
Laser Wavelength Chart - Different laser technologies emit light at varied wavelengths, and the selection of wavelength depends on the specifics of the application and desired characteristics. Thin and thick lines, what do they mean? Web wavelength is inversely correlated with photon energy. Some lasers emit light in a very narrow spectrum of wavelengths. Web the chart below gives hazard distances for selected consumer laser types, and for various parameters such as the beam color, beam spread and power. Common commercial lasers with typical modes of operation and gain media, where cw stands for continuous wave. Web each laser wavelength is associated with a linewidth, which depends on several factors: Laser types with distinct laser lines are shown above the wavelength bar, while below are shown lasers that can emit in a wavelength range. Web wavelengths of commercially available lasers. Also, some frequently used wavelengths from sources with frequency doubling, frequency tripling or frequency quadrupling are listed. This article will examine laser wavelength, its factors, and how they vary. Web figure 1 shows 23 of the most common lasers and their wavelengths, modes of operation, and typical gain media. Web each laser wavelength is associated with a linewidth, which depends on several factors: Web wavelengths of commercially available lasers. Some lasers emit light in a very narrow. The gain bandwidth of the lasing medium and the design of the optical resonator, which may include elements to purposely narrow the linewidth, like filters or etalons. Different laser technologies emit light at varied wavelengths, and the selection of wavelength depends on the specifics of the application and desired characteristics. Web the co2 laser produces a beam of infrared light. In addition, text below the chart describes how divergence (beam spread), power and wavelength (color) affects these hazard distances. Web laser wavelength is the inverse of frequency (units: Also, some frequently used wavelengths from sources with frequency doubling, frequency tripling or frequency quadrupling are listed. Web wavelengths of commercially available lasers. Common commercial lasers with typical modes of operation and. Web wavelength is inversely correlated with photon energy. Web the co2 laser produces a beam of infrared light with the principal wavelength bands centering around 9.4 and 10.6 micrometers (as in figure3). The gain bandwidth of the lasing medium and the design of the optical resonator, which may include elements to purposely narrow the linewidth, like filters or etalons. Some. Also, some frequently used wavelengths from sources with frequency doubling, frequency tripling or frequency quadrupling are listed. Laser types with distinct laser lines are shown above the wavelength bar, while below are shown lasers that can emit in a wavelength range. Different laser technologies emit light at varied wavelengths, and the selection of wavelength depends on the specifics of the. Some lasers emit light in a very narrow spectrum of wavelengths. Web each laser wavelength is associated with a linewidth, which depends on several factors: The gain bandwidth of the lasing medium and the design of the optical resonator, which may include elements to purposely narrow the linewidth, like filters or etalons. Web wavelength is inversely correlated with photon energy.. Thin and thick lines, what do they mean? Different laser technologies emit light at varied wavelengths, and the selection of wavelength depends on the specifics of the application and desired characteristics. This article will examine laser wavelength, its factors, and how they vary. Web wavelength is inversely correlated with photon energy. Web each laser wavelength is associated with a linewidth,. Web figure 1 shows 23 of the most common lasers and their wavelengths, modes of operation, and typical gain media. Web laser wavelength is the inverse of frequency (units: Also, some frequently used wavelengths from sources with frequency doubling, frequency tripling or frequency quadrupling are listed. Some lasers emit light in a very narrow spectrum of wavelengths. Web the chart. Web the co2 laser produces a beam of infrared light with the principal wavelength bands centering around 9.4 and 10.6 micrometers (as in figure3). Also, some frequently used wavelengths from sources with frequency doubling, frequency tripling or frequency quadrupling are listed. Web wavelength is inversely correlated with photon energy. Different laser technologies emit light at varied wavelengths, and the selection. Thin and thick lines, what do they mean? In addition, text below the chart describes how divergence (beam spread), power and wavelength (color) affects these hazard distances. Web wavelength is inversely correlated with photon energy. Laser types with distinct laser lines are shown above the wavelength bar, while below are shown lasers that can emit in a wavelength range. The. Some lasers emit light in a very narrow spectrum of wavelengths. The gain bandwidth of the lasing medium and the design of the optical resonator, which may include elements to purposely narrow the linewidth, like filters or etalons. Web each laser wavelength is associated with a linewidth, which depends on several factors: Laser types with distinct laser lines are shown above the wavelength bar, while below are shown lasers that can emit in a wavelength range. In addition, text below the chart describes how divergence (beam spread), power and wavelength (color) affects these hazard distances. Web wavelength is inversely correlated with photon energy. Also, some frequently used wavelengths from sources with frequency doubling, frequency tripling or frequency quadrupling are listed. Common commercial lasers with typical modes of operation and gain media, where cw stands for continuous wave. Different laser technologies emit light at varied wavelengths, and the selection of wavelength depends on the specifics of the application and desired characteristics. Web wavelengths of commercially available lasers. Web the co2 laser produces a beam of infrared light with the principal wavelength bands centering around 9.4 and 10.6 micrometers (as in figure3). This article will examine laser wavelength, its factors, and how they vary.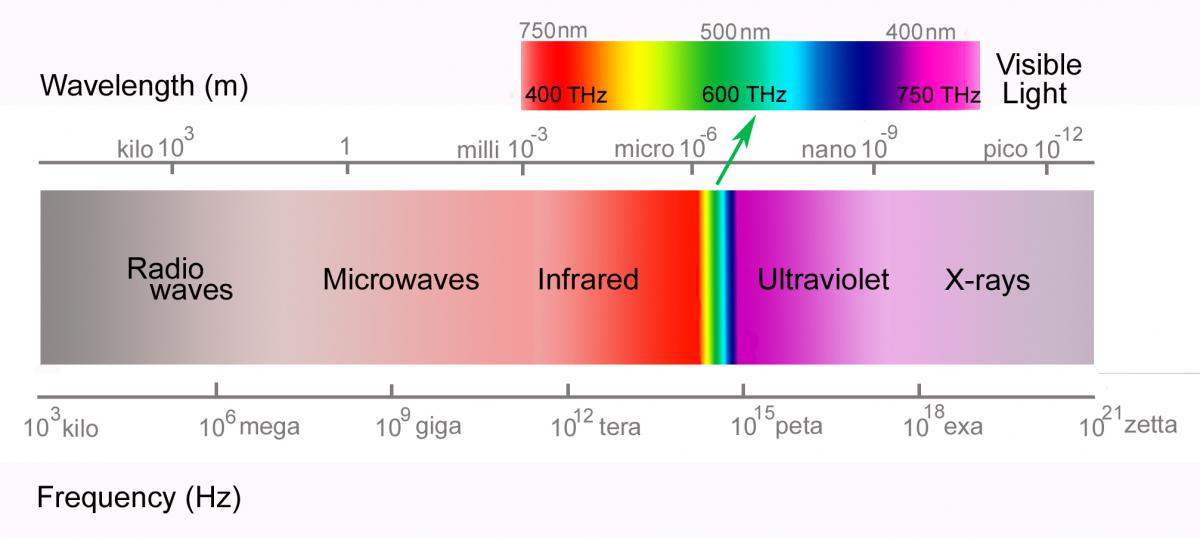
Fiber Lasers Everything You Need to Know Laserax

Lasers 101 Understanding Aesthetic Lasers «
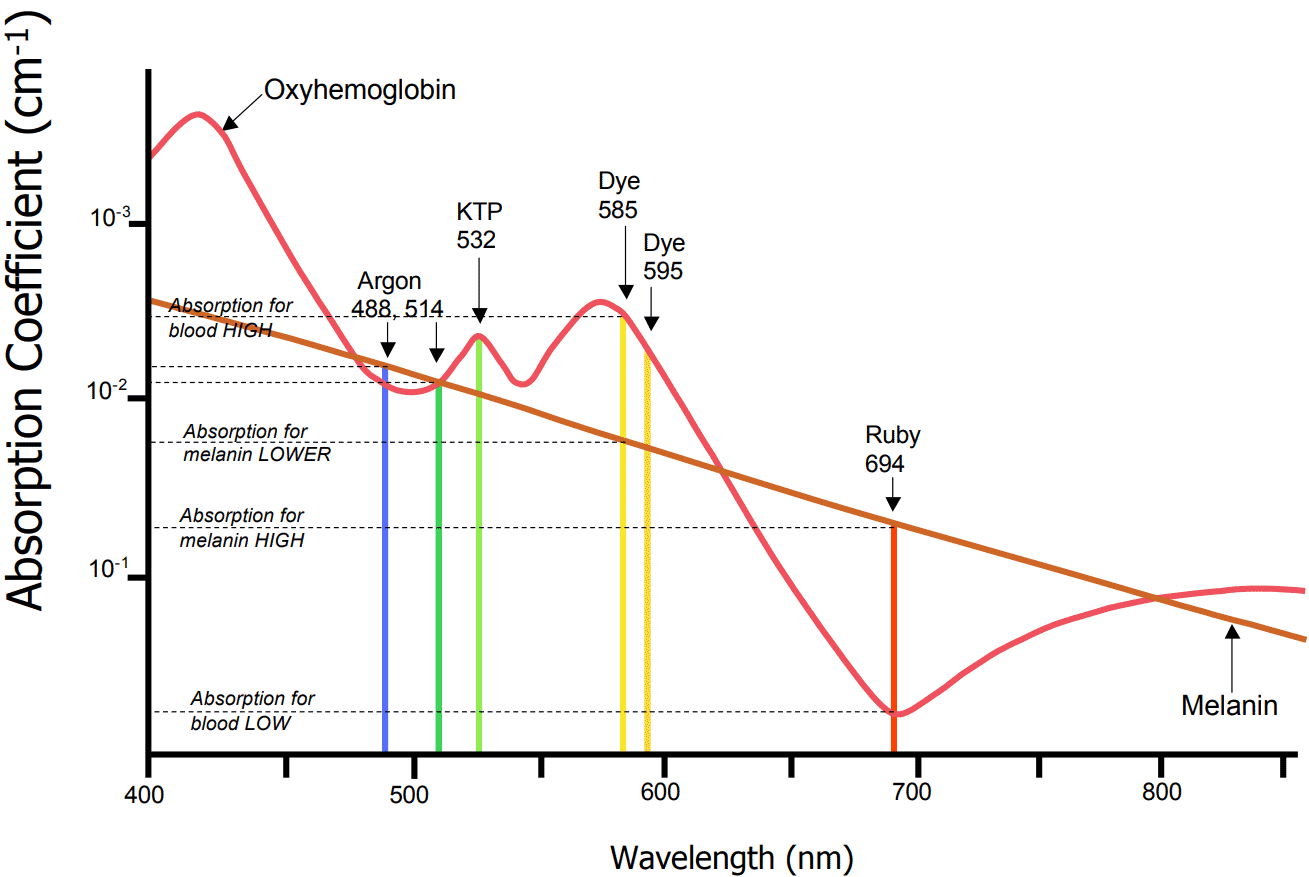
Rosacea Detailed Explanation Dr Nathan Holt

Answered Wavelength (m) 107 1011 109 105… bartleby

Pin on Astronomy Lasers

Visible Laser Beam Wavelength The Best Picture Of Beam
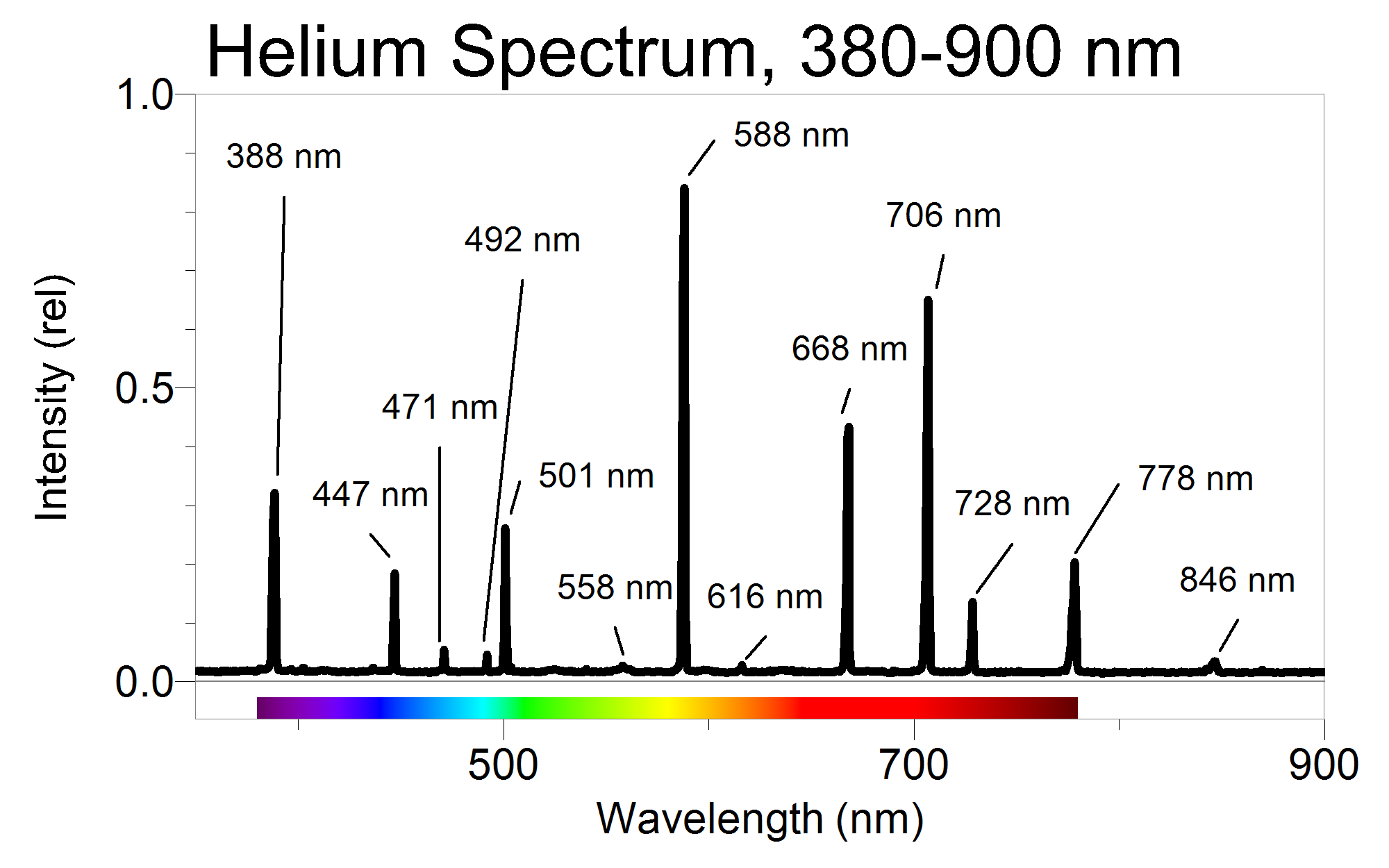
A Quantitative Investigation of the Helium Spectrum
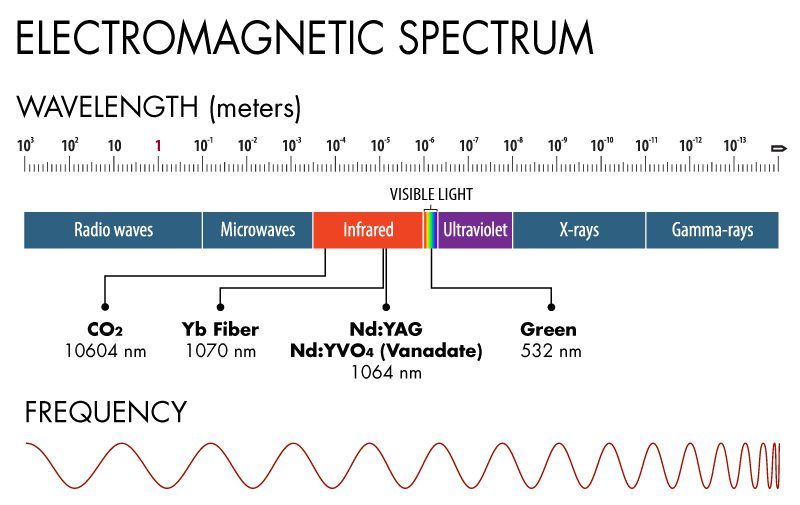
atrio Scetticismo comando fiber laser wavelength grafico congelato
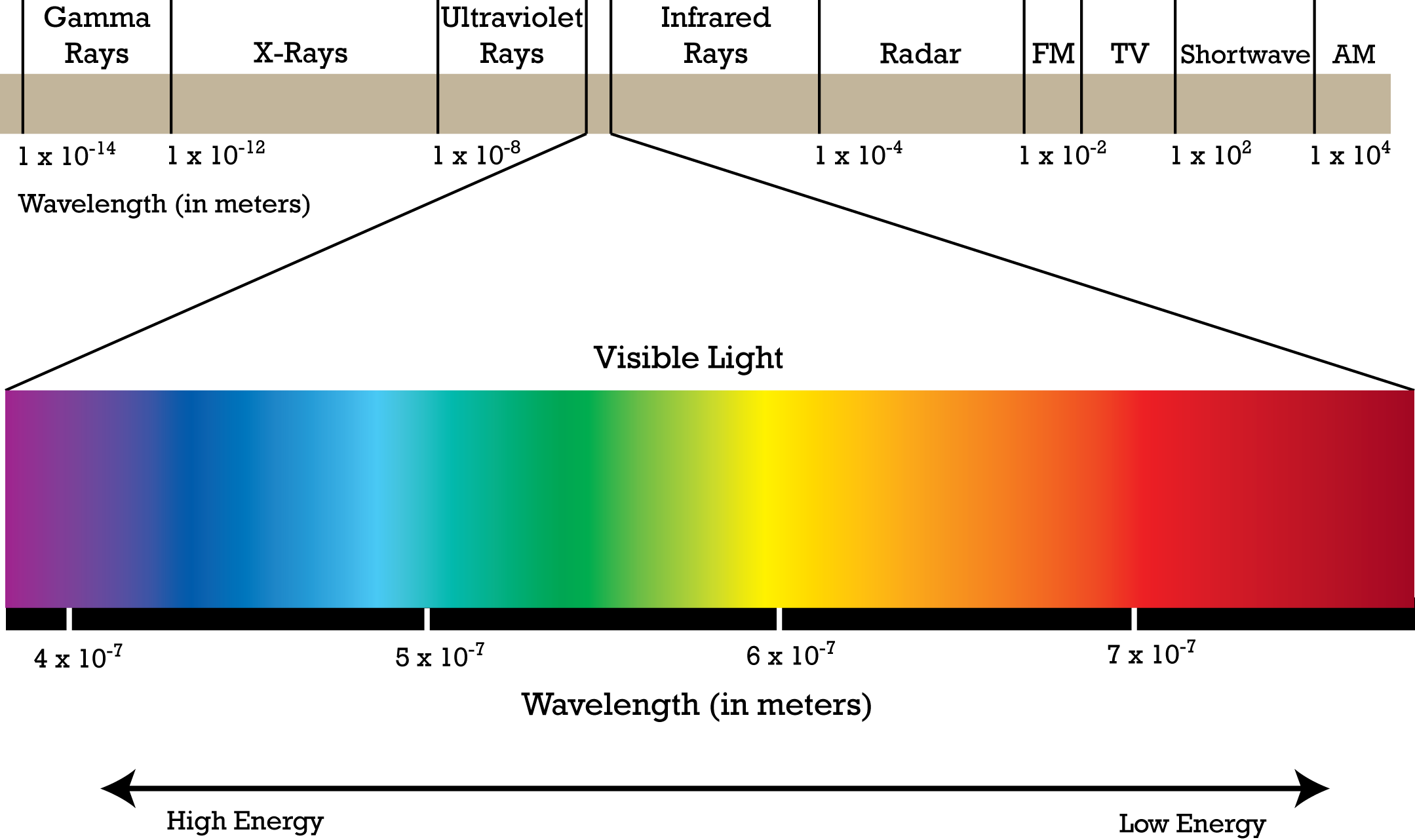
spectrum Communicating Science (14w112)
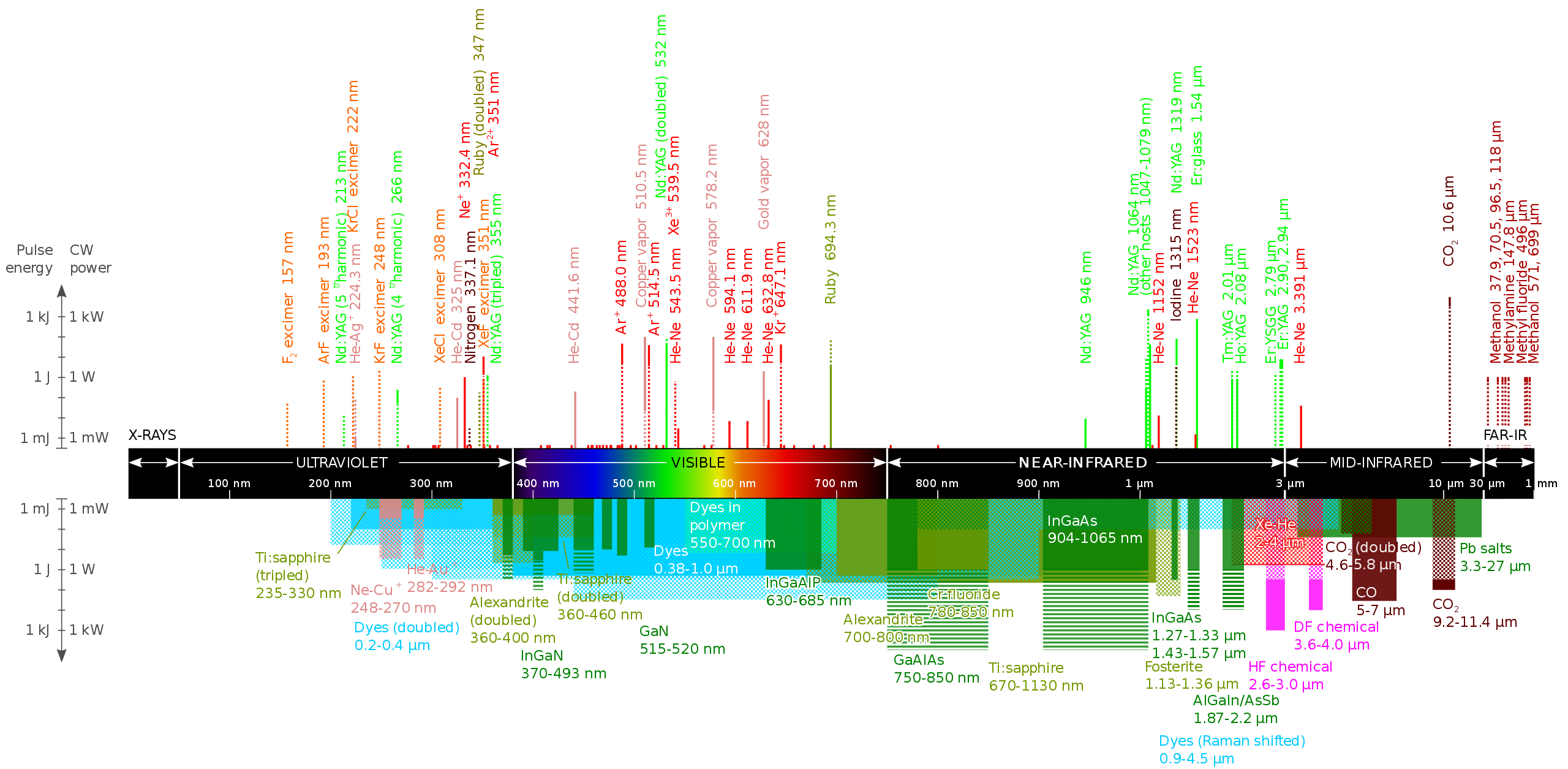
The laser wavelength chart explained
Web Figure 1 Shows 23 Of The Most Common Lasers And Their Wavelengths, Modes Of Operation, And Typical Gain Media.
Web Laser Wavelength Is The Inverse Of Frequency (Units:
Web The Chart Below Gives Hazard Distances For Selected Consumer Laser Types, And For Various Parameters Such As The Beam Color, Beam Spread And Power.
Thin And Thick Lines, What Do They Mean?
Related Post: