Landing Pattern
Landing Pattern - Web when the aircraft reaches pattern altitude, put the nose on the horizon, allow it to get to pattern speed, adjust the pitch and power, and trim for level flight. Patterns exist to provide an orderly flow and to make your actions predictable to other pilots. Web 2 when entering any pattern, controlled or not, always do so with strobes and landing light(s) on, day or night. Most patterns for piston planes were 1,000 agl (or thereabouts) but many were 800 feet and some were even lower than that. Position the aircraft where the runway is approximately a half mile to one mile off the wingtip. The idea is to start a bit high in your final approach, give up altitude for airspeed, fly your poh recommended airspeed to your aiming point, power idle, a somewhat aggressive pitch “up”and typic. The exact nature of each airport traffic pattern is dependent on the runway in use, wind conditions (which determine the runway in use), obstructions, and other factors. Web so, what is “the pattern”? The direction and placement of the pattern, the altitude at which it is to be flown, and the procedures for entering and exiting the pattern may depend on local conditions. To safely stay out of the pattern, fly over the airport at an altitude that is at least 1,000 feet above traffic pattern altitude (not field elevation). That is why student pilots are typically taught this information early in their training. Most manufacturers have recommended pattern speeds, at least for final approach. Once you are on the ground, you are. Or even earlier, if you want. Web when necessary, the tower controller will issue clearances or other information for aircraft to generally follow the desired flight path. The idea is to start a bit high in your final approach, give up altitude for airspeed, fly your poh recommended airspeed to your aiming point, power idle, a somewhat aggressive pitch “up”and typic. Airport traffic patterns ensure that air traffic moves into and out of an airport safely. Since both are best seen from above, fly directly over the. It’s the path you will fly when leaving and returning to the airport, specifically the runway. These instructions assume you are approaching a towered airport for landing in a left traffic pattern, and the winds are. Web the standard traffic pattern consists of a downwind, base, and final leg. If the pilot will mentally enlarge the indicator for the runway. Web an airfield traffic pattern is a standard path followed by aircraft when taking off or landing while maintaining visual contact with the airfield. Once you are on the ground, you are. Web landing a plane is the most important part of a flight. Most patterns are flown in a rectangle. Web do you have a perfect landing every time? Airport traffic patterns ensure that air traffic moves into and out of an airport safely. The standard traffic pattern altitude is 1,000 feet above aerodrome elevation, with turbine aircraft maintaining 1,500 feet above aerodrome elevation. Before we get into the details, let's start by taking a quick look at the different legs of a traffic pattern: Pilots assume that other. Everyone is used to aircraft landing on the. But according to the aim, you should start monitoring your airport's ctaf frequency and make your first call when you're 10 miles out. These instructions assume you are approaching a towered airport for landing in a left traffic pattern, and the winds are. 1) make your first radio call 10 miles out.. It's the very first signature basketball shoe. Web so, what is “the pattern”? At an airport, the pattern (or circuit) is a standard path for coordinating air traffic. It’s the path you will fly when leaving and returning to the airport, specifically the runway. Since both are best seen from above, fly directly over the airport. Principal component analysis (pca) showed that 2 principal components can show the similarities and differences between different. Patterns exist to provide an orderly flow and to make your actions predictable to other pilots. Companies leveraging location analysis to understand customers can deepen their analysis by examining economic. It's the very first signature basketball shoe. The landing pattern represents a set. Web nfta deputy director of aviation russ stark said it's going to be an adjustment for those living near the airport because flight patterns are changing. Web an airfield traffic pattern is a standard path followed by aircraft when taking off or landing while maintaining visual contact with the airfield. Web an airfield traffic pattern helps to “direct traffic” over. Web 2 when entering any pattern, controlled or not, always do so with strobes and landing light(s) on, day or night. Everyone is used to aircraft landing on the. It's the very first signature basketball shoe. Web the standard traffic pattern is a rectangular pattern consisting of an upwind, crosswind, downwind, and final approach leg. Pilots assume that other pilots. Companies leveraging location analysis to understand customers can deepen their analysis by examining economic. The traffic pattern is comprised of several components which standardized flow of aircraft, at a. Web the standard traffic pattern consists of a downwind, base, and final leg. Web landing a plane is the most important part of a flight. The exact nature of each airport traffic pattern is dependent on the runway in use, wind conditions (which determine the runway in use), obstructions, and other factors. Web 2 when entering any pattern, controlled or not, always do so with strobes and landing light(s) on, day or night. The idea is to start a bit high in your final approach, give up altitude for airspeed, fly your poh recommended airspeed to your aiming point, power idle, a somewhat aggressive pitch “up”and typic. It is a steep approa. Web fly a flawless traffic pattern. Airport traffic patterns ensure that air traffic moves into and out of an airport safely. For executives and analysts seeking to understand the state of the consumer, economic clues—including data on credit card delinquencies and housing costs—provide helpful indicators. Before we get into the details, let's start by taking a quick look at the different legs of a traffic pattern: Most patterns for piston planes were 1,000 agl (or thereabouts) but many were 800 feet and some were even lower than that. For a typical trainer such as a cessna 172, a “standard” traffic pattern is flown to the left and at 1,000 feet above ground level (agl). It’s the path you will fly when leaving and returning to the airport, specifically the runway. Fly to a position that gives you a good look at the airport and the windsock.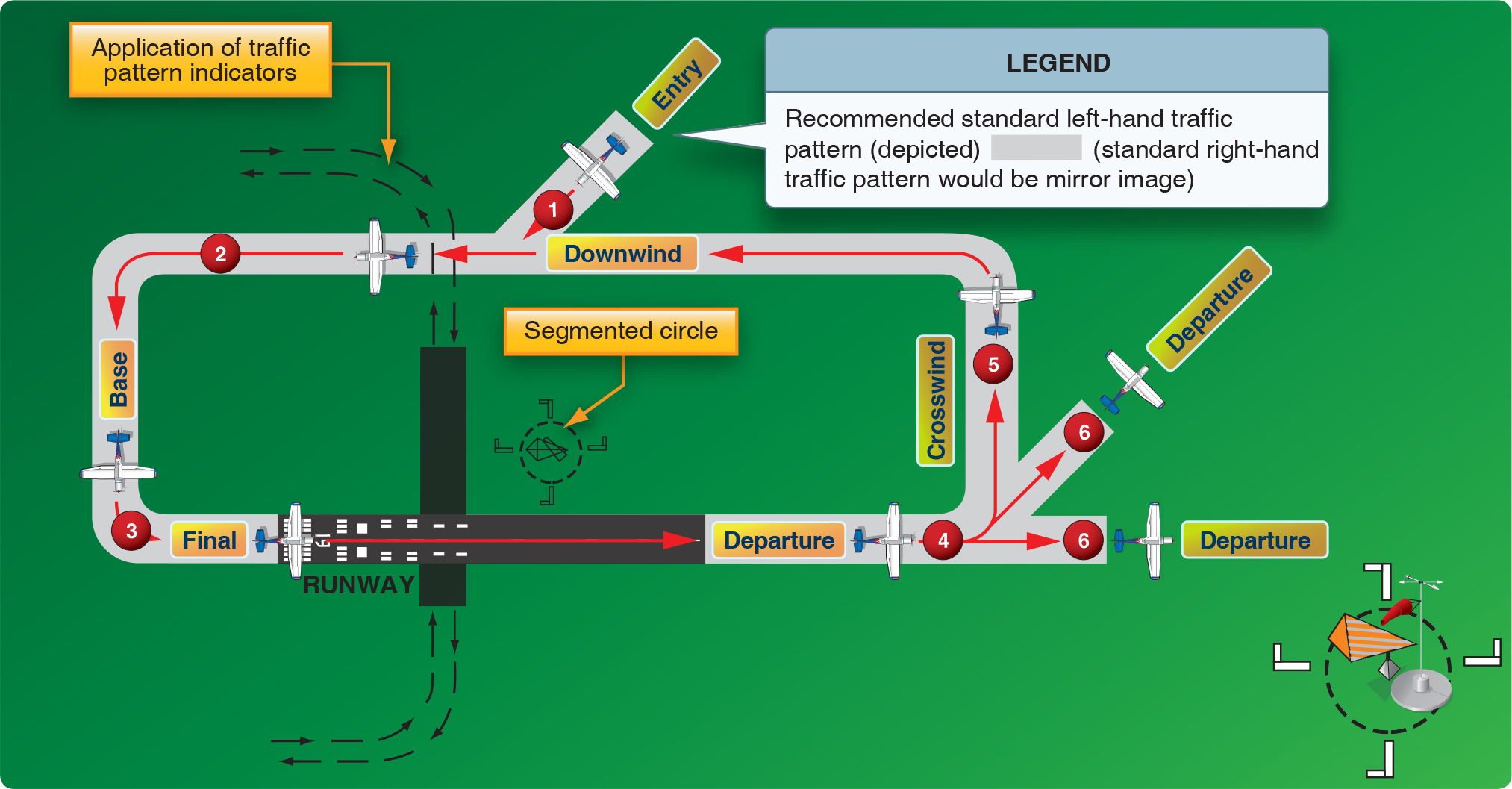
Procedures and Airport Operations Traffic Patterns Learn to Fly Blog

Pattern Work, Approach Landing, Ground School, Private Pilot, Darren

Chapter 7 of Airplane Flying Handbook Airport Trafic Patterns YouTube
Airport Operations

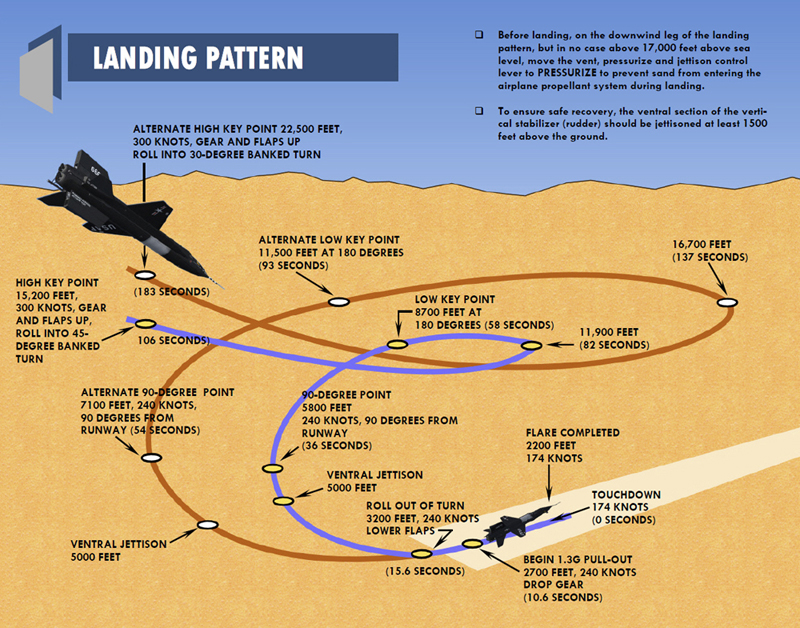
Baseline Landing Pattern Evergreen Soaring
Landing
Procedures and Airport Operations Traffic Patterns Learn to Fly Blog
/Traffic_patterns_depicted_in_FAA-H-8083-25-56a058ce3df78cafdaa1229b.jpg)
How to Fly a General Aviation Traffic Pattern

Landing Pattern Learning to fly the aircraft landing pattern
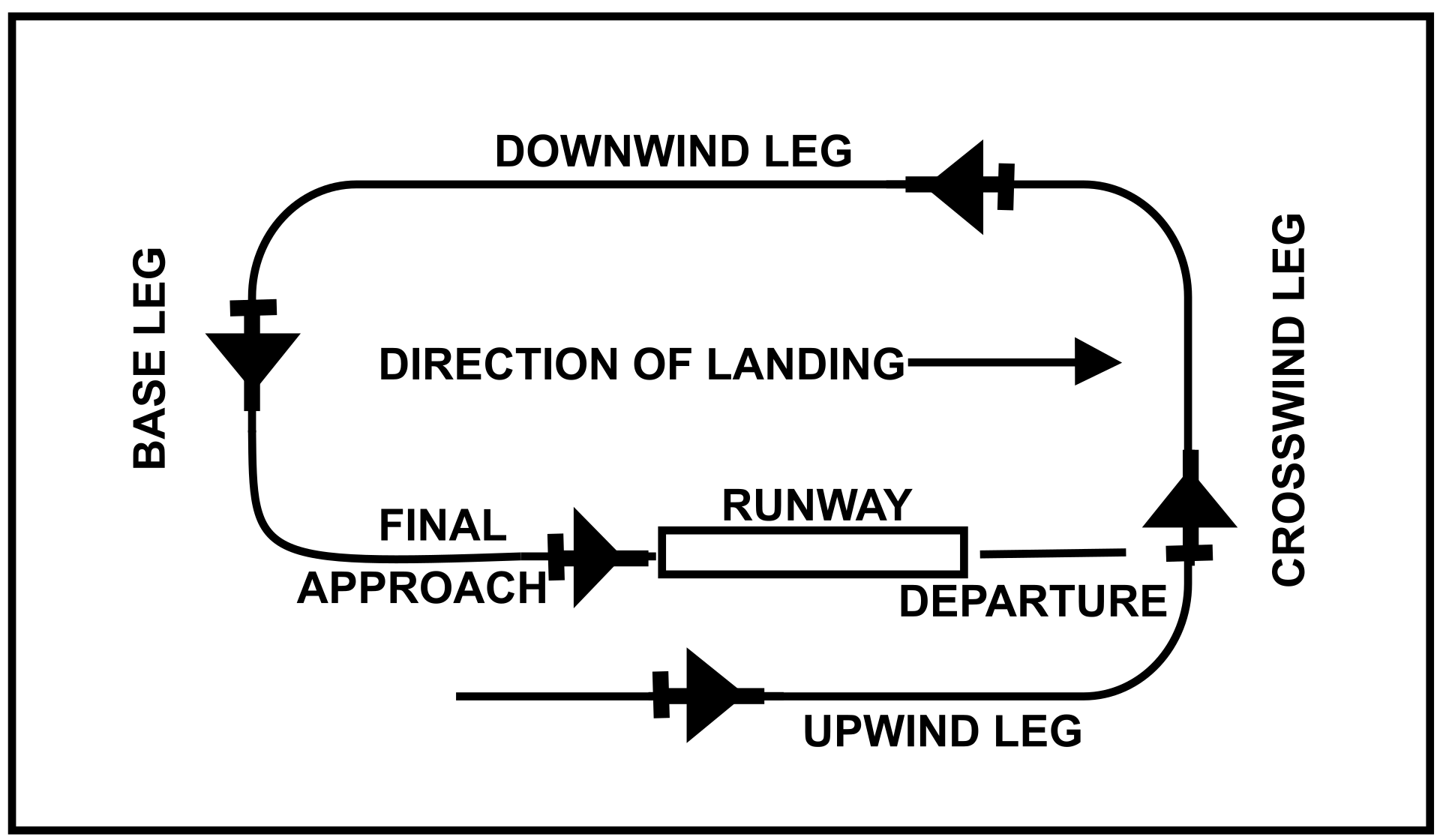
Everything You Should Know About the Airport Traffic Pattern
Web By Gary Sankary.
And If They Don't, The Faa Recommends 1.4 X V S0 For Base, And 1.3 X V S0 For Final.
Web When Approaching An Airport For Landing, The Traffic Pattern Should Be Entered At A 45° Angle To The Downwind Leg, Headed Toward A Point Abeam Of The Midpoint Of The Runway To Be Used For Landing.
That Is Why Student Pilots Are Typically Taught This Information Early In Their Training.
Related Post: