Ionisation Energy Chart
Ionisation Energy Chart - There are exceptions to this periodic table. Web the periodic table of the elements (with ionization energies) 1. Web subsequent ionization energies of all elements have a general increasing trend because it becomes progressively harder to remove additional electrons. Learn the definition, trend on the periodic table, first & second ionization energies, see a chart and much more. Ionization energy is positive for neutral atoms, meaning that the ionization is an endothermic process. The energy required to remove an electron is the ionization energy. The ionization energy differs for each atom. Web what is ionization energy? Web values from crc are ionization energies given in the unit ev; Ionization energy is the energy required to remove an electron from an atom or ion. Also, learn first & second ionization energies. Ionization energy is always positive. The table lists only the first ie in ev units. Web x (g) + energy x + (g) + e −. The energy required to remove the outermost electron from an atom or a positive ion in its ground level. A high value of ionization energy shows a high attraction between the electron and the nucleus. Also, learn first & second ionization energies. Web subsequent ionization energies of all elements have a general increasing trend because it becomes progressively harder to remove additional electrons. Since going from right to left on the periodic table, the atomic radius increases, and the. On the periodic table, first ionization energy generally increases as you move left to right across a period. To convert to kj/mol, multiply by 96.4869. Web an element's first ionization energy is the energy required to remove the outermost, or least bound, electron from a neutral atom of the element. Ionization energy increases moving across a period and decreases moving. There are exceptions to this periodic table. Web ionization energy chart of all the elements is given below. The energy required to remove the outermost electron from an atom or a positive ion in its ground level. Web explore how ionization energy changes with atomic number in the periodic table of elements via interactive plots. Web an element's first ionization. Web subsequent ionization energies of all elements have a general increasing trend because it becomes progressively harder to remove additional electrons. Alkali metals alkaline earth metals. Web ionization energy is denoted by the symbols ie, ip, δh° and has units of kilojoule per mole ( (kj/mol) or electron volts (ev). Web what is ionization energy? The stronger an electron is. Web ionization energy is denoted by the symbols ie, ip, δh° and has units of kilojoule per mole ( (kj/mol) or electron volts (ev). The ionization energy differs for each atom. Web values from crc are ionization energies given in the unit ev; Where x is any atom or molecule, x + is the resultant ion when the original atom. The first molar ionization energy applies to the neutral atoms. Web what is ionization energy. Ionization energy is always positive. To convert to kj/mol, multiply by 96.4869. On the periodic table, first ionization energy generally decreases as you move down a group. Ionization is the process of removing an electron from a neutral atom (or compound). This is the energy per mole necessary to remove electrons from gaseous atoms or atomic ions. As described above, ionization energies are dependent upon the atomic radius. The energy required to remove an electron is the ionization energy. There are exceptions to this periodic table. Learn the definition, trend on the periodic table, first & second ionization energies, see a chart and much more. This is the energy per mole necessary to remove electrons from gaseous atoms or atomic ions. The ionization energy differs for each atom. On the periodic table, first ionization energy generally increases as you move left to right across a period.. The ionization energy differs for each atom. The first molar ionization energy applies to the neutral atoms. Since going from right to left on the periodic table, the atomic radius increases, and the ionization energy increases from left to right in the periods and up the groups. The first of these quantities is used in atomic physics, the second in. The ionization energy of the elements within a period. Web one is that when electrons start to fill p orbital the ionization energy goes down a little. Since going from right to left on the periodic table, the atomic radius increases, and the ionization energy increases from left to right in the periods and up the groups. Web the periodic table of the elements (with ionization energies) 1. Web explore how ionization energy changes with atomic number in the periodic table of elements via interactive plots. Web periodic table and trend of ionization energies. The table lists only the first ie in ev units. On the periodic table, first ionization energy generally increases as you move left to right across a period. Ionization energy is the energy required to remove an electron from an atom or ion. Nist reference table on ground states and ionization energies for the neutral atoms. Learn its chemical equation, values, trends across a period & down a group, & exception. This list contains the 118 elements of chemistry. A high value of ionization energy shows a high attraction between the electron and the nucleus. Web the ionization energy is a measure of the energy required to remove one electron from one mole of gaseous atoms or ions. Web values from crc are ionization energies given in the unit ev; First ionization energy, second ionization energy as well as third ionization energy of the elements are given in this chart.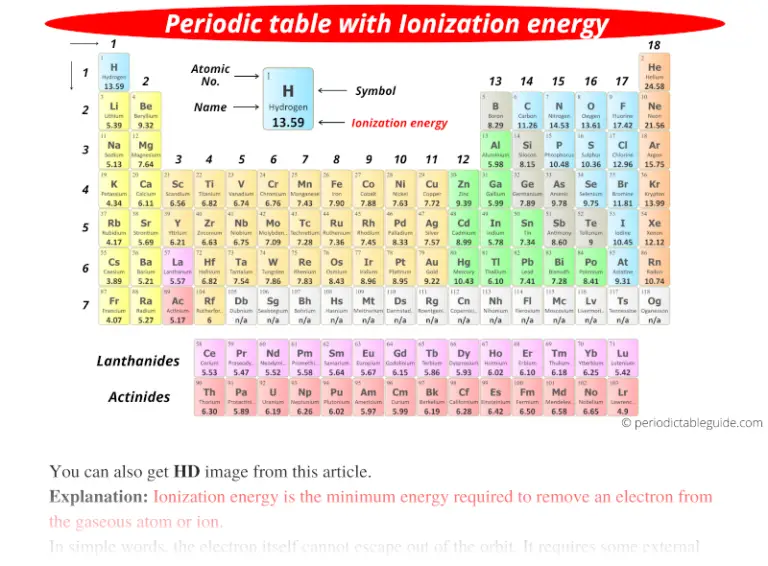
Periodic table with Ionization Energy Values (Labeled Image)

Pin by Cristina Baldacci on Chemistry Education Chemistry education
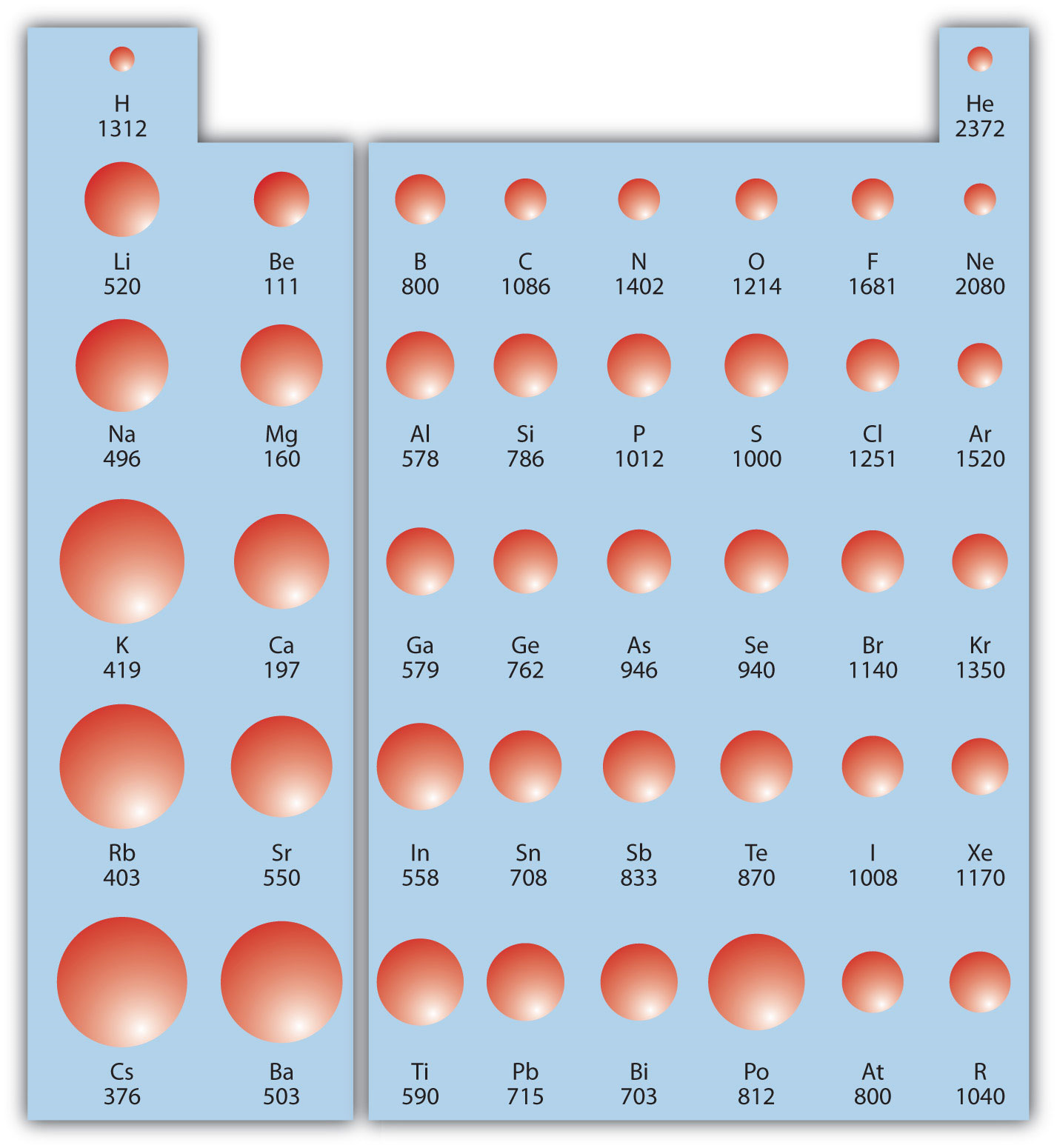
9.9 Periodic Trends Atomic Size, Ionization Energy, and Metallic

Ionization energy Definition & Facts Britannica
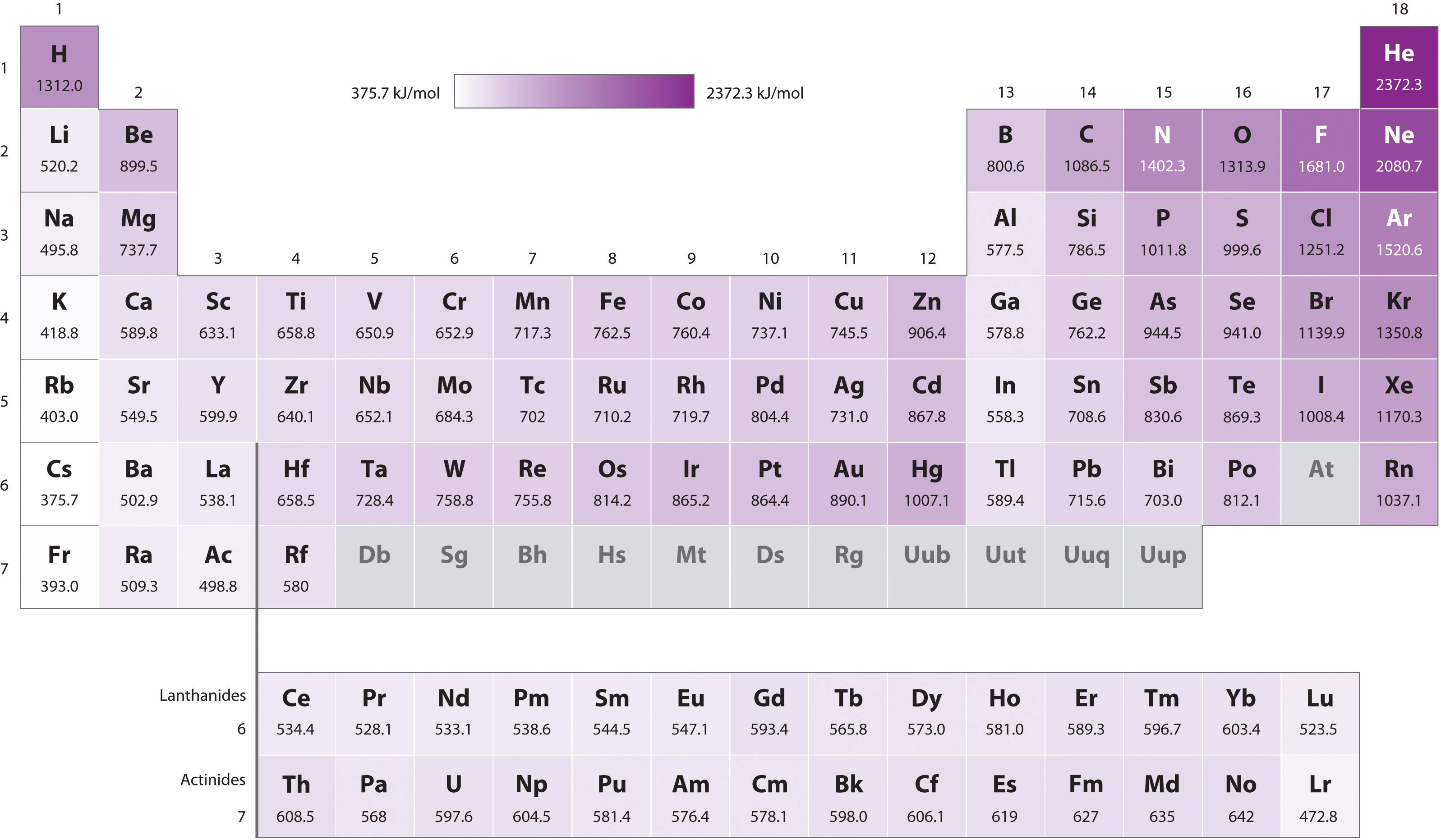
Periodic Table Ionization Energy Labeled
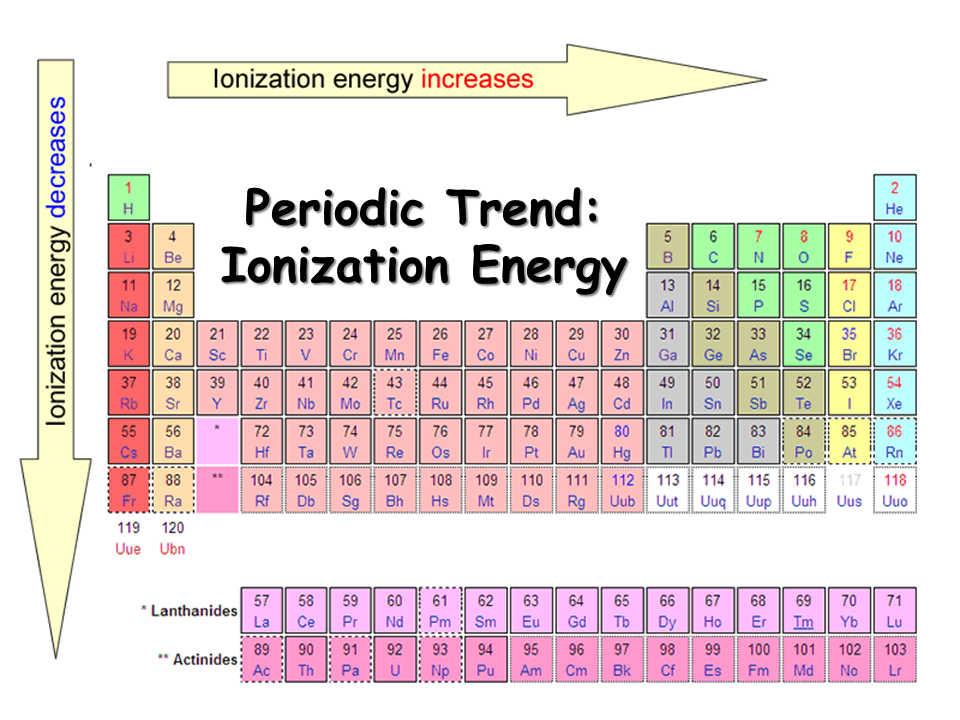
Ionization Enthalpy NEET Lab

Ionization Energy Definition, Chart & Periodic Table Trend
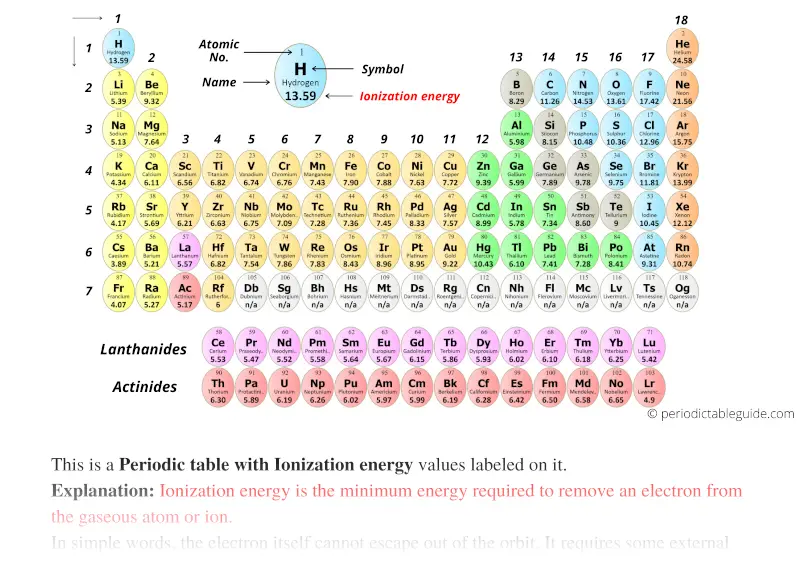
Periodic table with Ionization Energy Values (Labeled Image)

The Parts of the Periodic Table
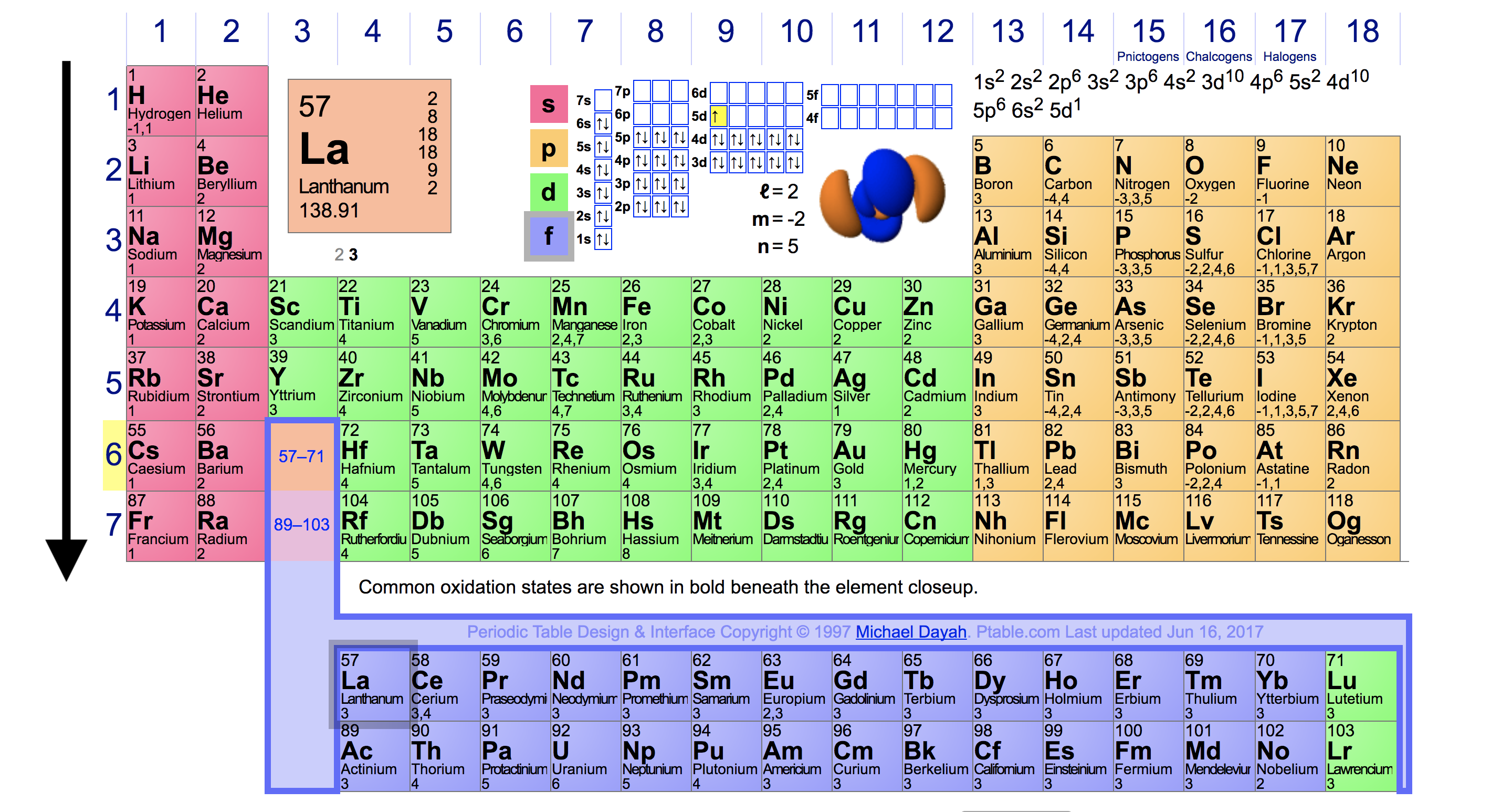
Periodic Trends in Ionization Energy Chemistry Socratic
The Ionization Energy Differs For Each Atom.
Web Ionization Energy Chart Of All The Elements Is Given Below.
Web Chemists Define The Ionization Energy (\(I\)) Of An Element As The Amount Of Energy Needed To Remove An Electron From The Gaseous Atom \(E\) In Its Ground State.
Web What Is Ionization Energy?
Related Post: