In An Ecg Pattern The P Wave Is Caused By
In An Ecg Pattern The P Wave Is Caused By - Web what causes the different p wave morphologies in an ecg tracing that shows wandering atrial pacemaker? Web early repolarization are characterized by the following ecg changes: The normal p wave is a low. The first 1/3 of the p wave corresponds to right atrial activation, the final 1/3 corresponds to left. The variable strength of the atrial contraction caused by each. Web the ecg changes associated with acute pulmonary embolism may be seen in any condition that causes acute pulmonary hypertension, including hypoxia causing. Web an ecg readout represents the pattern of electrical activity in the heart as a line of waves. It represents the electrical activity associated with atrial depolarization. Web normal p wave, shown in darker red diagram demonstrating features of a normal sinus rhythm electrocardiogram wave. The action potentials that initiate myocardiocyte depolarization. Web an ecg readout represents the pattern of electrical activity in the heart as a line of waves. Web the ecg has, as one could expect, low sensitivity but high specificity with respect to detecting atrial enlargement. The variable strength of the atrial contraction caused by each. Web the factors that determine p‐wave appearance include (1) the origin of the. Web the p wave represents the time during which the electrical impulse travels through the atria, causing depolarization and leading to their contraction. Web the three waves of the qrs complex represent ventricular depolarization. St segment elevations with concave st segment. The normal p wave is a low. Web the factors that determine p‐wave appearance include (1) the origin of. Web in an ecg pattern, the pq interval indicates how long it takes the cardiac impulse ti travel from the The first 1/3 of the p wave corresponds to right atrial activation, the final 1/3 corresponds to left. It is important to remember that the p wave represents the sequential activation of the right and left atria, and it is. The pr interval is assessed in order to determine whether impulse conduction from the atria to the. Left atrial enlargement is also referred to as p mitrale, and. The action potentials that initiate myocardiocyte depolarization. Web the p wave is the first deflection of the cardiac cycle seen on an ekg. The p wave on the ecg represents atrial. It is important to remember that the p wave represents the sequential activation of the right and left atria, and it is common to see notched or biphasic p waves of right and. Web the p wave is the first deflection of the cardiac cycle seen on an ekg. Web normal p wave, shown in darker red diagram demonstrating features. Web the p wave is the first deflection of the cardiac cycle seen on an ekg. Web the factors that determine p‐wave appearance include (1) the origin of the sinus rhythm that defines right atrial depolarization vector, (2) localization of left atrial. St segment elevations with concave st segment. Web the p wave represents the time during which the electrical. Web inverted p wave (ecg) an inverted p wave on an ecg is usually a sign of ectopic atrial rhythm. For the inexperienced, one of the most confusing aspects of ecg reading is the labeling of. Web in an ecg pattern, the pq interval indicates how long it takes the cardiac impulse ti travel from the Web the ecg has,. For the inexperienced, one of the most confusing aspects of ecg reading is the labeling of. Web normal p wave, shown in darker red diagram demonstrating features of a normal sinus rhythm electrocardiogram wave. It represents the electrical depolarization of the atria of the heart. Web what causes the different p wave morphologies in an ecg tracing that shows wandering. The first 1/3 of the p wave corresponds to right atrial activation, the final 1/3 corresponds to left. Web the p wave represents the time during which the electrical impulse travels through the atria, causing depolarization and leading to their contraction. It is important to remember that the p wave represents the sequential activation of the right and left atria,. Web the ecg has, as one could expect, low sensitivity but high specificity with respect to detecting atrial enlargement. The variable strength of the atrial contraction caused by each. The key points on those waves are labeled p, q, r, s, and t. It is important to remember that the p wave represents the sequential activation of the right and. Web the p wave is the first deflection of the cardiac cycle seen on an ekg. The first 1/3 of the p wave corresponds to right atrial activation, the final 1/3 corresponds to left. Web the right and left atrial waveforms summate to form the p wave. St segment elevations with concave st segment. For the inexperienced, one of the most confusing aspects of ecg reading is the labeling of. The action potentials that initiate myocardiocyte depolarization. Web the p wave and pr segment is an integral part of an electrocardiogram (ecg). The variable strength of the atrial contraction caused by each. The normal p wave is a low. It represents the electrical depolarization of the atria of the heart. Web early repolarization are characterized by the following ecg changes: Web the ecg changes associated with acute pulmonary embolism may be seen in any condition that causes acute pulmonary hypertension, including hypoxia causing. Web what causes the different p wave morphologies in an ecg tracing that shows wandering atrial pacemaker? The repolarization of the atria is usually not visible because. The p wave on the ecg represents atrial. Web the ecg has, as one could expect, low sensitivity but high specificity with respect to detecting atrial enlargement.
ECG interpretation Characteristics of the normal ECG (Pwave, QRS

Electrocardiograms (EKGs/ECGs) Evaluating P Waves Stepwards

Electrocardiograms (EKGs/ECGs) Evaluating P Waves Stepwards

P wave wikidoc

ECG interpretation Characteristics of the normal ECG (Pwave, QRS
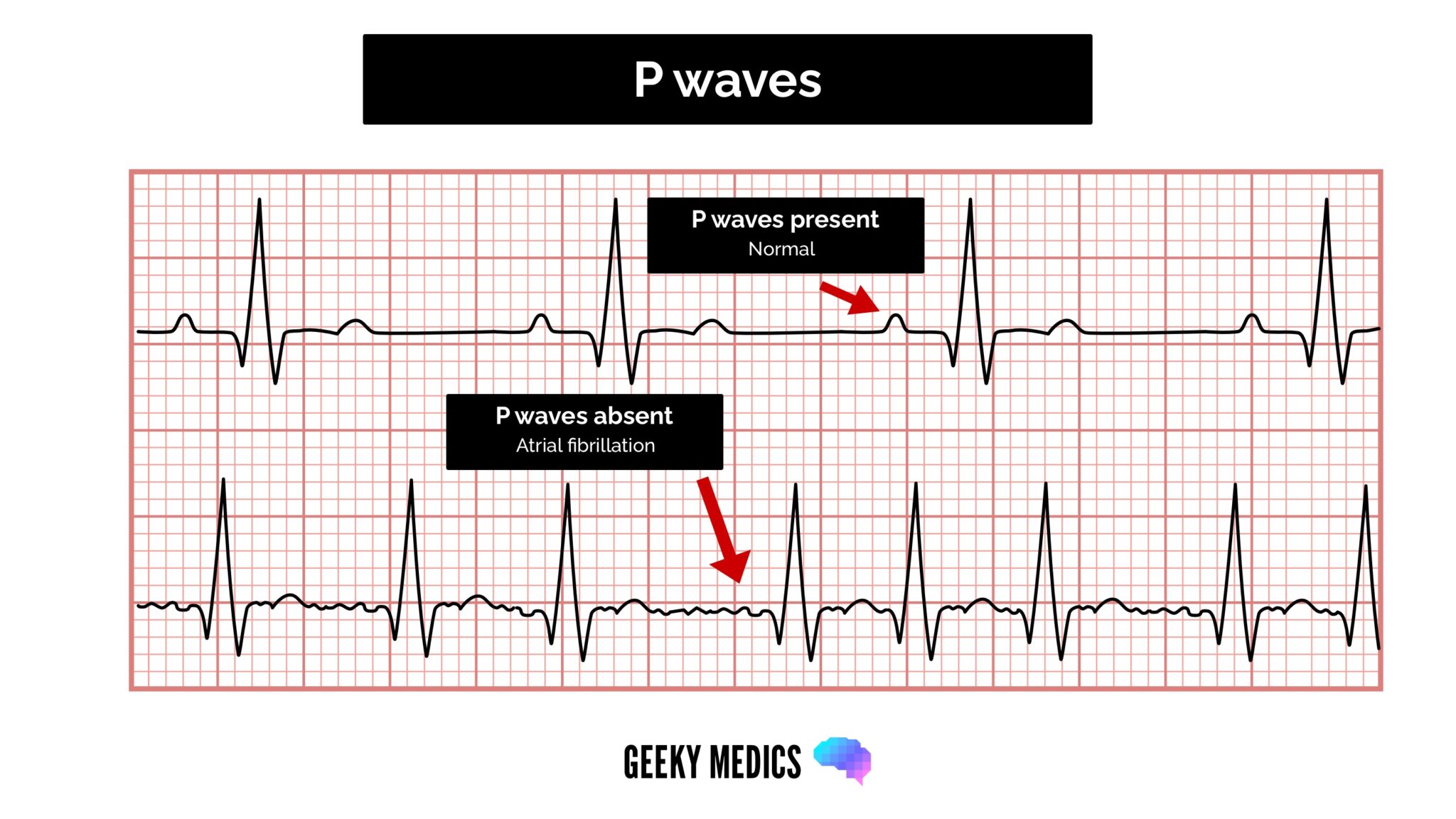
How to Read an ECG ECG Interpretation EKG Geeky Medics

ECG interpretation Characteristics of the normal ECG (Pwave, QRS

Understanding the Normal ECG PWave, QRS Complex, ST Segment, TWave
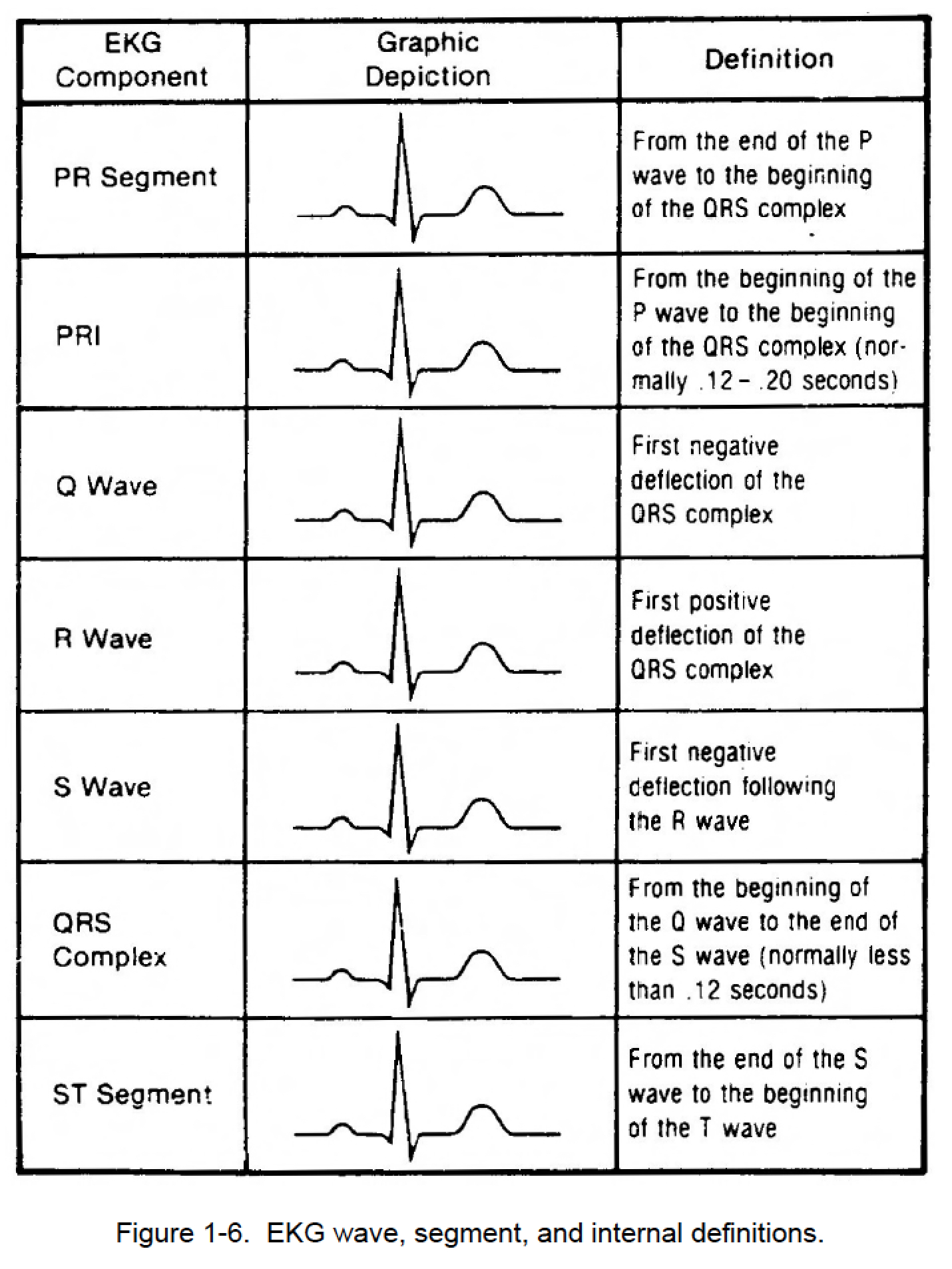
Figure 16. EKG wave, segment, and internal definitions Cardiac
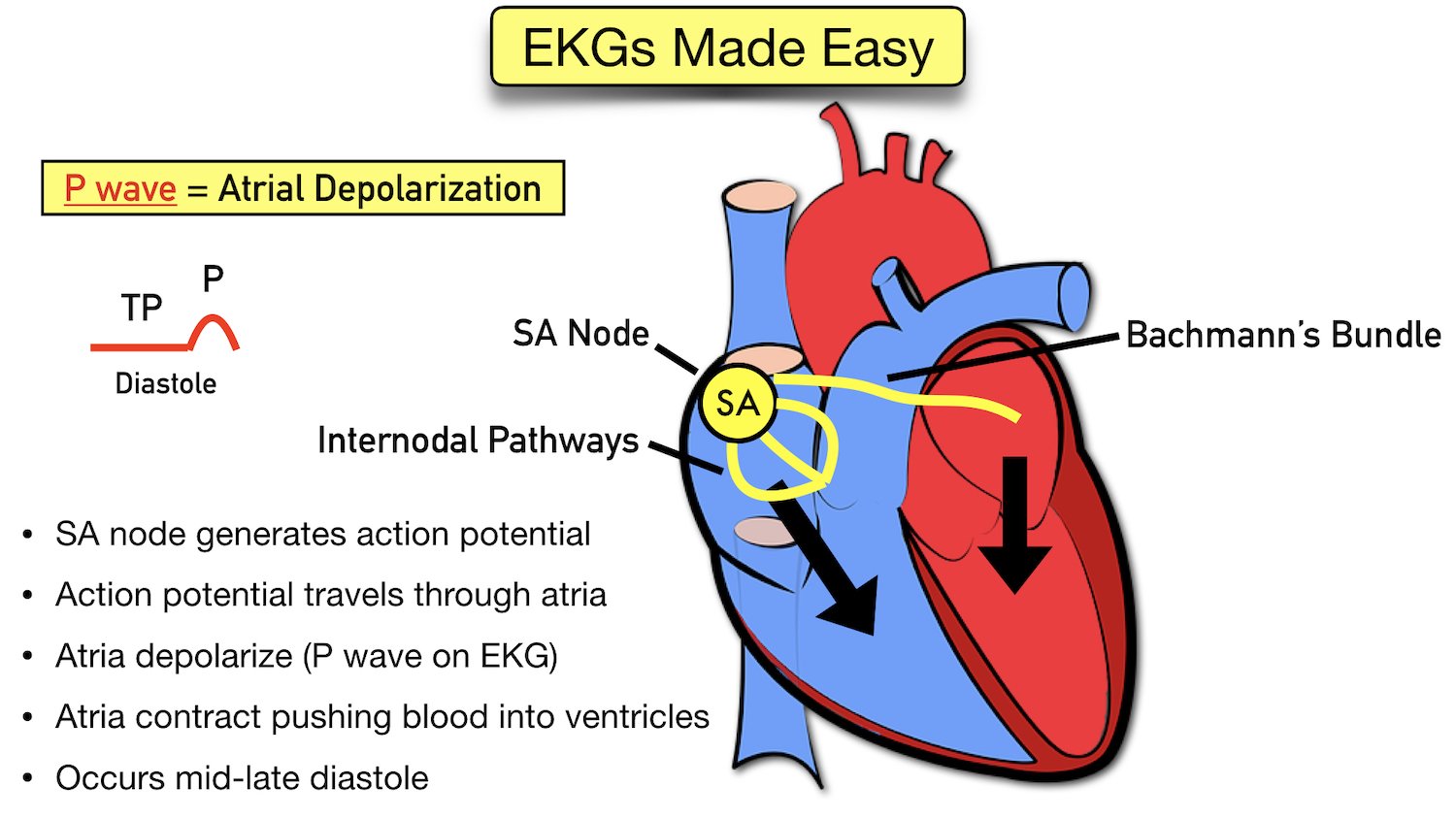
ECG Waveform Explained EKG Labeled Diagrams and Components — EZmed
Web In An Ecg Pattern, The Pq Interval Indicates How Long It Takes The Cardiac Impulse Ti Travel From The
Web The Three Waves Of The Qrs Complex Represent Ventricular Depolarization.
The Pr Interval Is Assessed In Order To Determine Whether Impulse Conduction From The Atria To The.
Web The P Wave Represents The Time During Which The Electrical Impulse Travels Through The Atria, Causing Depolarization And Leading To Their Contraction.
Related Post: