Heart Chart
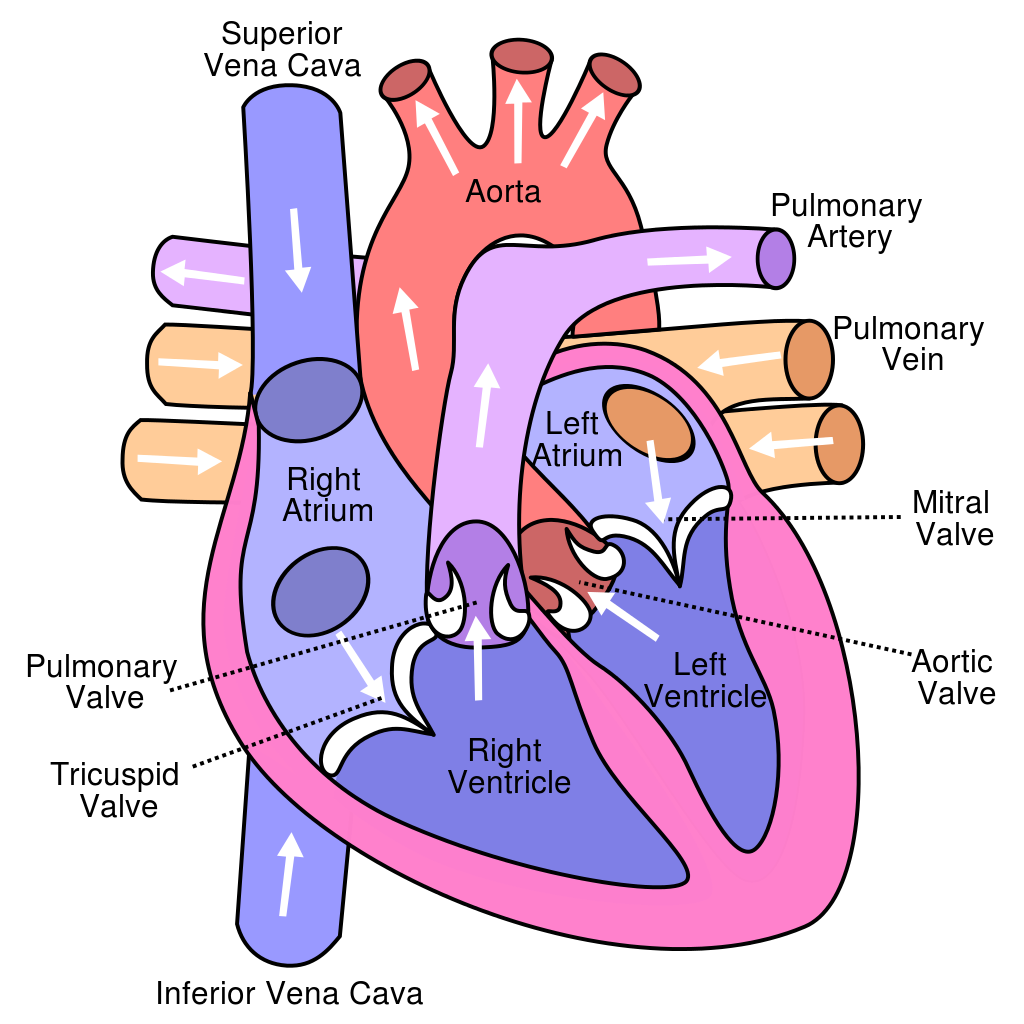
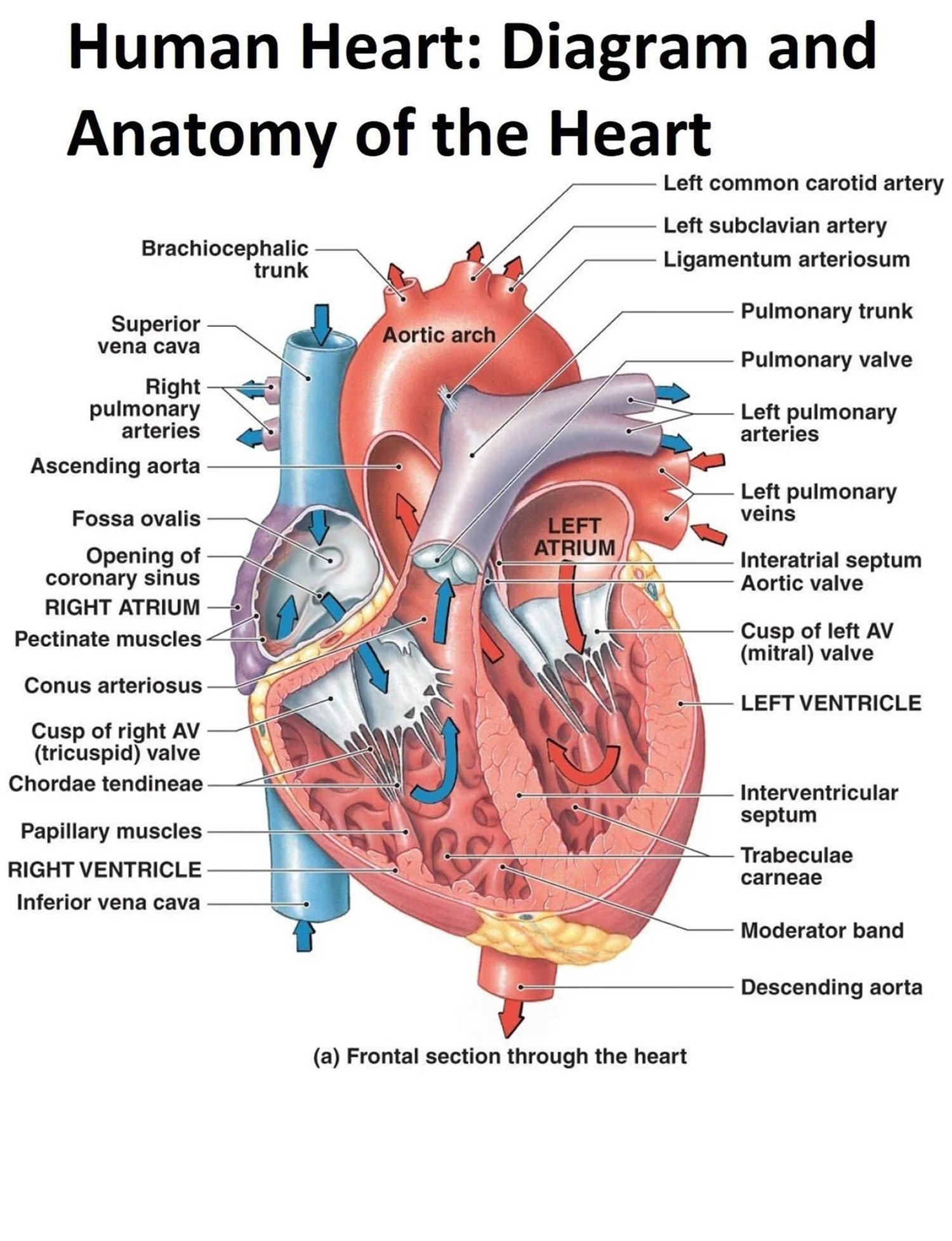
Heart Chart - Each contraction and relaxation is a heartbeat. Your heart contains four muscular sections that briefly hold blood before moving it.electrical impulses make your heart beat, moving blood through these chambers. It takes in deoxygenated blood through the veins and delivers it to the lungs for oxygenation before pumping it into the various arteries (which provide oxygen and nutrients to body tissues by transporting the blood throughout the body). Ventricular contractions, called systole, force blood out of the heart through the pulmonary and aortic valves.diastole occurs when blood flows from the atria to fill the ventricles. Web heart, organ that serves as a pump to circulate the blood.it may be a straight tube, as in spiders and annelid worms, or a somewhat more elaborate structure with one or more receiving chambers (atria) and a main pumping chamber (ventricle), as in mollusks. Muscle and tissue make up this powerhouse organ. It’s your circulatory system’s main organ. Web target heart rates chart; In fishes the heart is a folded tube, with three or four enlarged areas that correspond to the. Its pumping power also pushes blood through organs like the lungs to remove waste. This is a congenital (present at birth) heart defect where there is an abnormal opening in the septum (wall) between the atria (upper chambers) of the heart. It’s your circulatory system’s main organ. Asds can vary in size and may lead to abnormal blood flow between the atria, which can cause permanent damage to the lung blood vessels. Your heart. Web what is the heart? Web heart, organ that serves as a pump to circulate the blood.it may be a straight tube, as in spiders and annelid worms, or a somewhat more elaborate structure with one or more receiving chambers (atria) and a main pumping chamber (ventricle), as in mollusks. Web function and anatomy of the heart made easy using. Muscle and tissue make up this powerhouse organ. Web heart, organ that serves as a pump to circulate the blood.it may be a straight tube, as in spiders and annelid worms, or a somewhat more elaborate structure with one or more receiving chambers (atria) and a main pumping chamber (ventricle), as in mollusks. Ventricular contractions, called systole, force blood out. This is a congenital (present at birth) heart defect where there is an abnormal opening in the septum (wall) between the atria (upper chambers) of the heart. It takes in deoxygenated blood through the veins and delivers it to the lungs for oxygenation before pumping it into the various arteries (which provide oxygen and nutrients to body tissues by transporting. This is a congenital (present at birth) heart defect where there is an abnormal opening in the septum (wall) between the atria (upper chambers) of the heart. In fishes the heart is a folded tube, with three or four enlarged areas that correspond to the. Web target heart rates chart; Your heart contains four muscular sections that briefly hold blood. Includes an exercise, review worksheet, quiz, and model drawing of an anterior vi Web the heart is a muscular organ about the size of a closed fist that functions as the body's circulatory pump. It’s your circulatory system’s main organ. Muscle and tissue make up this powerhouse organ. Its pumping power also pushes blood through organs like the lungs to. Web what is the heart? Web the average heart beats between 60 and 90 times per minute, but this depends on a person’s cardiovascular health and activity level. Ventricular contractions, called systole, force blood out of the heart through the pulmonary and aortic valves.diastole occurs when blood flows from the atria to fill the ventricles. It’s your circulatory system’s main. Each contraction and relaxation is a heartbeat. Asds can vary in size and may lead to abnormal blood flow between the atria, which can cause permanent damage to the lung blood vessels. Web function and anatomy of the heart made easy using labeled diagrams of cardiac structures and blood flow through the atria, ventricles, valves, aorta, pulmonary arteries veins, superior. Web what is the heart? Web the cusps are pushed open to allow blood flow in one direction, and then closed to seal the orifices and prevent the backflow of blood. Its pumping power also pushes blood through organs like the lungs to remove waste. Asds can vary in size and may lead to abnormal blood flow between the atria,. Asds can vary in size and may lead to abnormal blood flow between the atria, which can cause permanent damage to the lung blood vessels. Web the heart is an amazing organ. This is a congenital (present at birth) heart defect where there is an abnormal opening in the septum (wall) between the atria (upper chambers) of the heart. The. It’s your circulatory system’s main organ. Web the heart is a muscular organ about the size of a closed fist that functions as the body's circulatory pump. Web the cusps are pushed open to allow blood flow in one direction, and then closed to seal the orifices and prevent the backflow of blood. Each contraction and relaxation is a heartbeat. Web the muscular wall of the heart powers contraction and dilation. Web the average heart beats between 60 and 90 times per minute, but this depends on a person’s cardiovascular health and activity level. Muscle and tissue make up this powerhouse organ. Includes an exercise, review worksheet, quiz, and model drawing of an anterior vi The more physically fit people are, the lower their resting. Web what is the heart? Web atrial septal defect (asd): Web heart, organ that serves as a pump to circulate the blood.it may be a straight tube, as in spiders and annelid worms, or a somewhat more elaborate structure with one or more receiving chambers (atria) and a main pumping chamber (ventricle), as in mollusks. This is a congenital (present at birth) heart defect where there is an abnormal opening in the septum (wall) between the atria (upper chambers) of the heart. It takes in deoxygenated blood through the veins and delivers it to the lungs for oxygenation before pumping it into the various arteries (which provide oxygen and nutrients to body tissues by transporting the blood throughout the body). Your heart contains four muscular sections that briefly hold blood before moving it.electrical impulses make your heart beat, moving blood through these chambers. Ventricular contractions, called systole, force blood out of the heart through the pulmonary and aortic valves.diastole occurs when blood flows from the atria to fill the ventricles.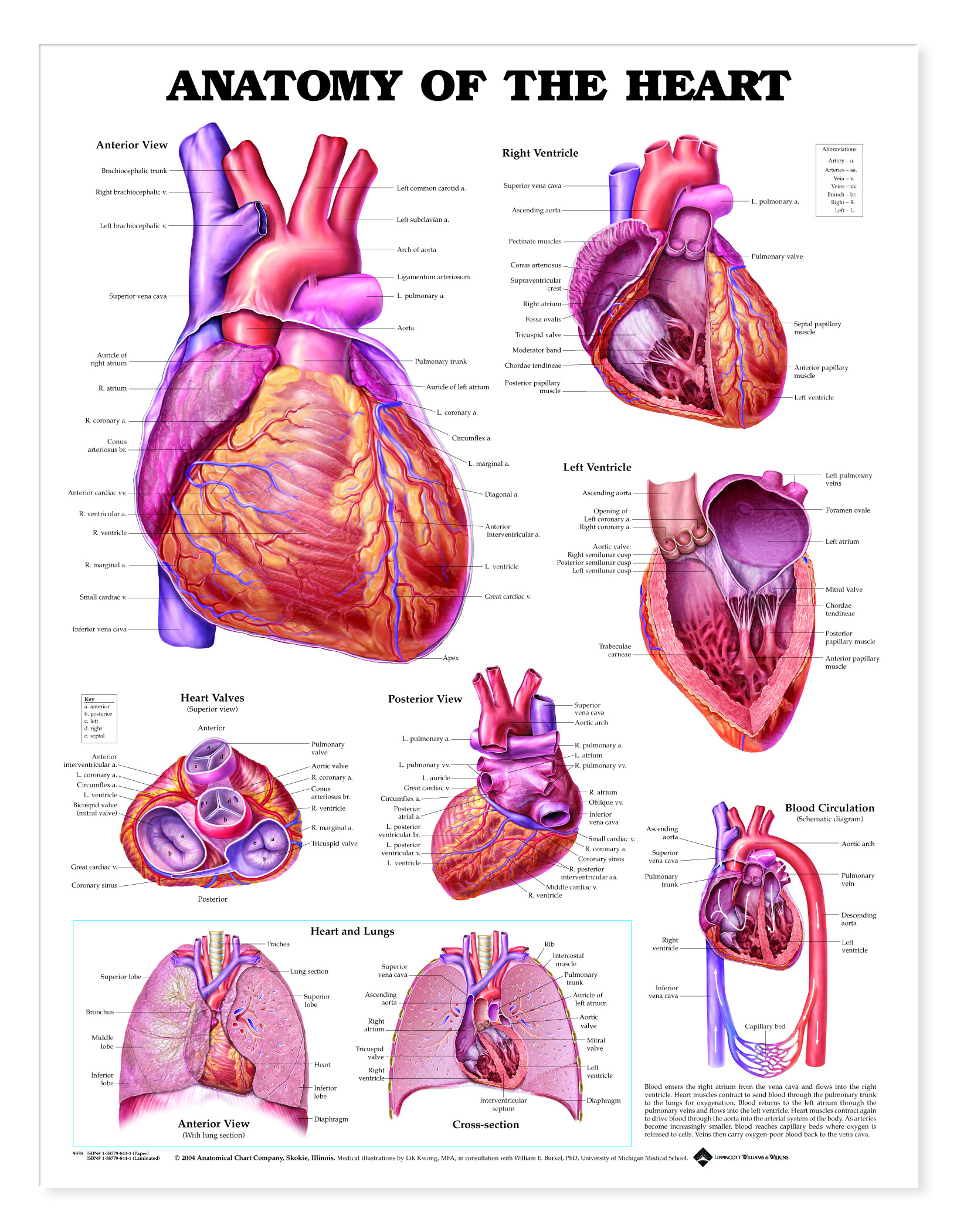
Anatomy of the Heart Charts 1944
Tips for How to Study the Cardiovascular System

Human Heart Anatomy Poster Etsy Heart anatomy, Medical anatomy
Heart Rate Chart Sample Templates at
The Human Heart Diagram Display Poster Diagram and Anatomy of the Heart

Heart Rate Chart And Rating Of Perceived Exertion Chart, 40 OFF

Human Heart Diagram Anatomy Diagram Educational Chart Mural Poster Images
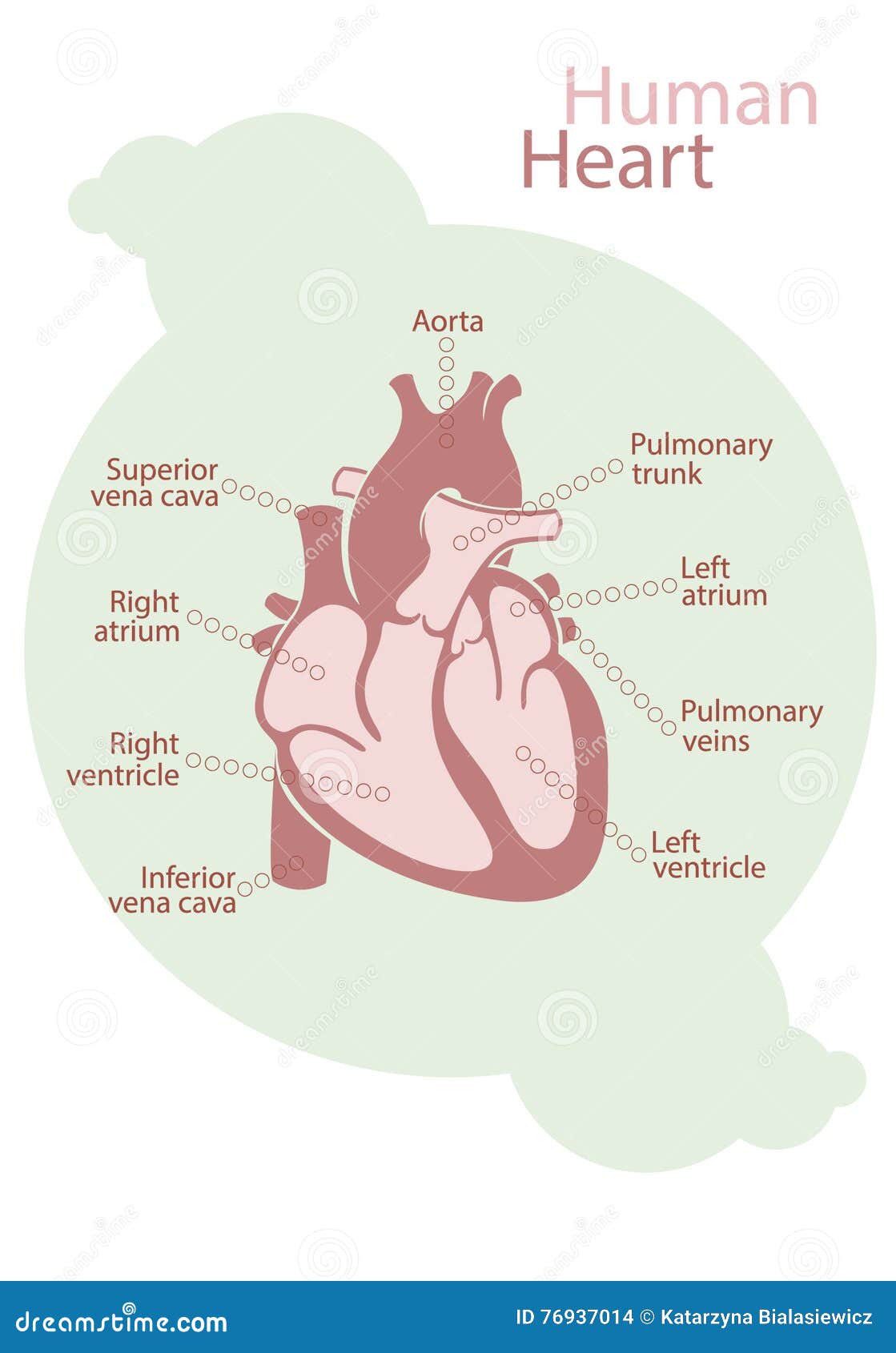
Chart of human heart stock illustration. Illustration of muscle 76937014

Flow Chart Of Blood Through Heart Flowchart Examples
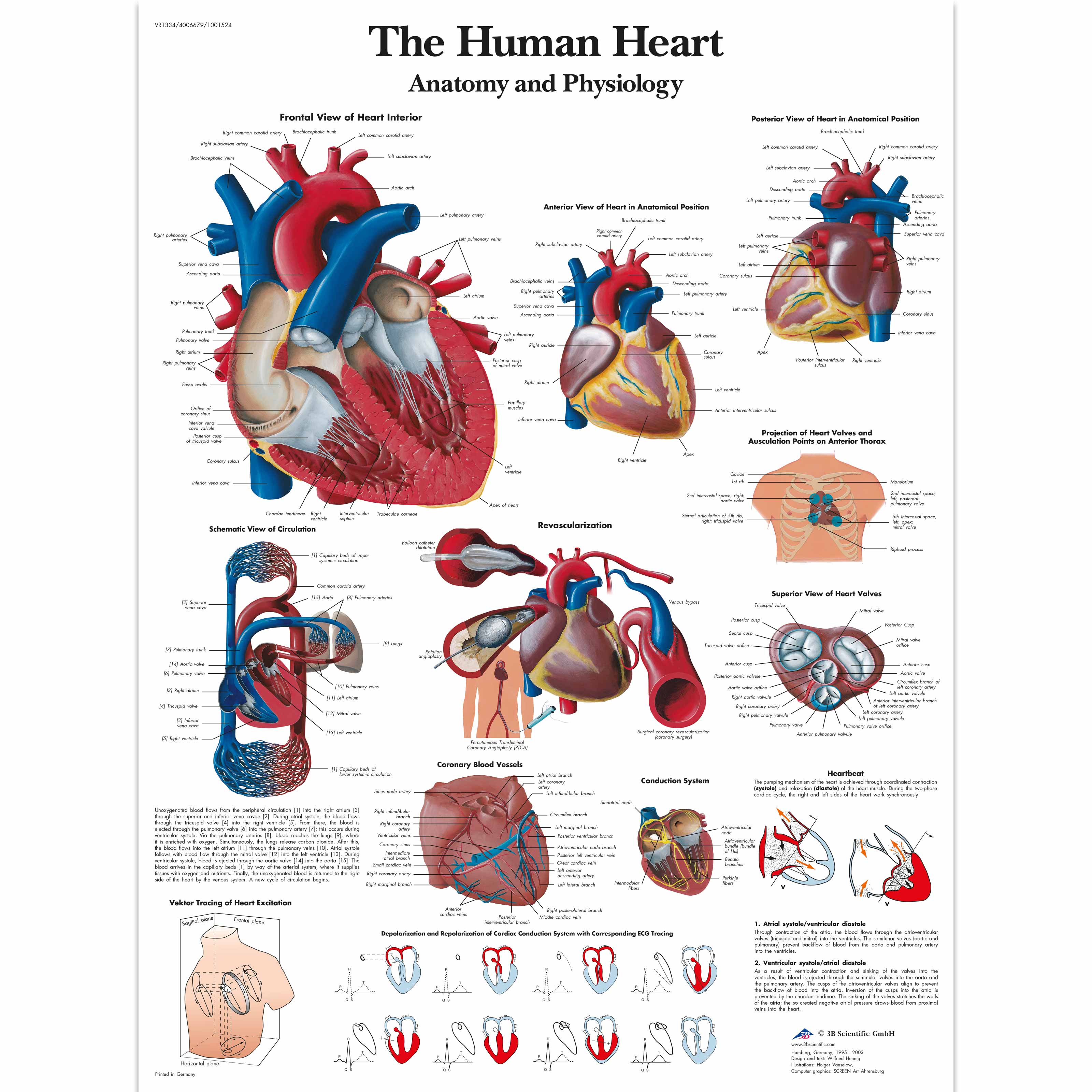
The Human Heart Chart Anatomy and Physiology 4006679 VR1334UU
Its Pumping Power Also Pushes Blood Through Organs Like The Lungs To Remove Waste.
Asds Can Vary In Size And May Lead To Abnormal Blood Flow Between The Atria, Which Can Cause Permanent Damage To The Lung Blood Vessels.
In Fishes The Heart Is A Folded Tube, With Three Or Four Enlarged Areas That Correspond To The.
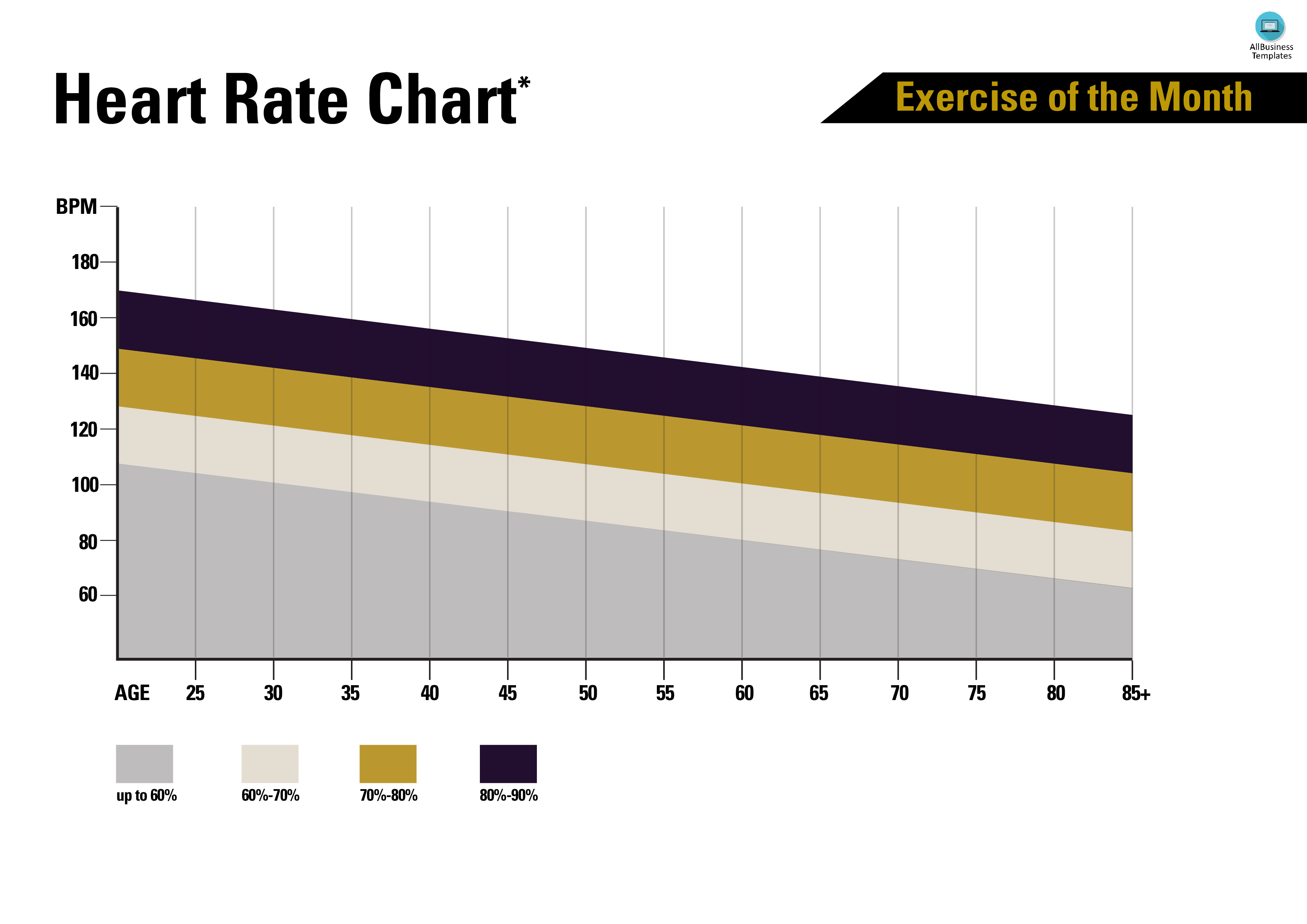
Web Target Heart Rates Chart;
Related Post: