Galvanic Action Chart
Galvanic Action Chart - We also provide other helpful methods for avoiding galvanic corrosion. Though the order of metals in a galvanic series remains the same in most conducting solutions, some. Web the galvanic corrosion table ranks metals from the most “active” to the least active. Web galvanic corrosion (also called bimetallic corrosion or dissimilar metal corrosion) is an electrochemical process in which one metal corrodes preferentially when it is in electrical contact with another, in the presence of an electrolyte. Web below is the galvanic corrosion chart, along with steps for using the chart properly to determine metal compatibility. Web read on to find out about what it is and how to use it to analyse the compatibility of joining metals. This chart is designed to assist in broadly assessing the risk of galvanic corrosion associated with a given metal coming into contact with another metal. The most active metals in the galvanic corrosion chart, like aluminum, zinc, or magnesium, are more likely to corrode when connected to. The closer together the material are on the chart to the right, the less galvanic action will occur. Web by knowing the relationships of the metals in the series, galvanic compatibility can be determined, preventing the possible harmful effects of galvanic corrosion. The following galvanic table lists metals in the order of their relative activity in seawater environment. The most active metals in the galvanic corrosion chart, like aluminum, zinc, or magnesium, are more likely to corrode when connected to. Galvanic series / galvanic table. Web view our galvanic series chart, pictures, definitions, and even a mnemonic device! Web the increased corrosion. Web below, we give a brief overview of galvanic corrosion and provide a galvanic corrosion chart to help fabricators and machinists avoid using the wrong metal combinations. Web electrolytic corrosion (electrolysis) occurs when dissimilar metals are in contact in the presence of an electrolyte, such as water (moisture) containing very small amounts of acid. Web however, you can completely avoid. Though the order of metals in a galvanic series remains the same in most conducting solutions, some. Web the increased corrosion of the anode is called “galvanic corrosion.” galvanic corrosion is sometimes used to extend the life of materials (i.e. Web a chart depicting the galvanic series for some common metals in a frequently encountered conducting solution, seawater, is included. Web below is the galvanic corrosion chart, along with steps for using the chart properly to determine metal compatibility. When two metals are submerged in an electrolyte, while also electrically connected by some external conductor, the less noble (base) will experience galvanic corrosion. We also provide other helpful methods for avoiding galvanic corrosion. By using the chart, contractors and homeowners. In this respect, one should understand how to read the following chart which lists all metals. The most active metals in the galvanic corrosion chart, like aluminum, zinc, or magnesium, are more likely to corrode when connected to. Most architects know enough about it to be dangerous, but what exactly causes this breakdown? Though the order of metals in a. You can also learn more about overcoming potentially compatibility issues between metals. Web below is a galvanic reaction chart for dissimilar metals. The most active metals in the galvanic corrosion chart, like aluminum, zinc, or magnesium, are more likely to corrode when connected to. Web galvanic corrosion (some times called dissimilar metal corrosion) is the process by which the materials. When two metals are submerged in an electrolyte, while also electrically connected by some external conductor, the less noble (base) will experience galvanic corrosion. So, for example, choosing zinc on zinc would have the lowest risk for corrosion. Web the increased corrosion of the anode is called “galvanic corrosion.” galvanic corrosion is sometimes used to extend the life of materials. To use the chart, align the metal to be assessed (for the risk of corrosion) in the left column with the contact metal listed in the. Web below, we give a brief overview of galvanic corrosion and provide a galvanic corrosion chart to help fabricators and machinists avoid using the wrong metal combinations. The below galvanic corrion chart or anodic. Web view this chart of galvanic compatibility. This chart is designed to assist in broadly assessing the risk of galvanic corrosion associated with a given metal coming into contact with another metal. The closer together the material are on the chart to the right, the less galvanic action will occur. The dissimilar metals set up a galvanic action which results. Web a chart depicting the galvanic series for some common metals in a frequently encountered conducting solution, seawater, is included in figure 1. The following galvanic table lists metals in the order of their relative activity in seawater environment. Web the increased corrosion of the anode is called “galvanic corrosion.” galvanic corrosion is sometimes used to extend the life of. Use this chart below to better understand what metals will work best together without potential for galvanic corrosion: This can help you in the selection of the best materials for your application where galvanic corrosion is a concern. When two metals are submerged in an electrolyte, while also electrically connected by some external conductor, the less noble (base) will experience galvanic corrosion. Web electrolytic corrosion (electrolysis) occurs when dissimilar metals are in contact in the presence of an electrolyte, such as water (moisture) containing very small amounts of acid. Web below, we give a brief overview of galvanic corrosion and provide a galvanic corrosion chart to help fabricators and machinists avoid using the wrong metal combinations. Web by knowing the relationships of the metals in the series, galvanic compatibility can be determined, preventing the possible harmful effects of galvanic corrosion. Web to minimize galvanic corrosion, select fasteners based on their material compatibility with the substrates. Zinc coatings on carbon steel and zinc anodes in water heaters), but, if it is not considered and the right conditions exist, it can lead to unexpected failures. Web the galvanic corrosion table ranks metals from the most “active” to the least active. Web view our galvanic series chart, pictures, definitions, and even a mnemonic device! Yet in today’s construction world it can be easy for a contractor to mix the wrong type of fastener with the wrong metal. You can also learn more about overcoming potentially compatibility issues between metals. Web below is the galvanic corrosion chart, along with steps for using the chart properly to determine metal compatibility. In this article, we'll look at an example to illustrate the use of the galvanic table. Web galvanic corrosion (also called bimetallic corrosion or dissimilar metal corrosion) is an electrochemical process in which one metal corrodes preferentially when it is in electrical contact with another, in the presence of an electrolyte. Below is a galvanic reaction chart for dissimilar metals.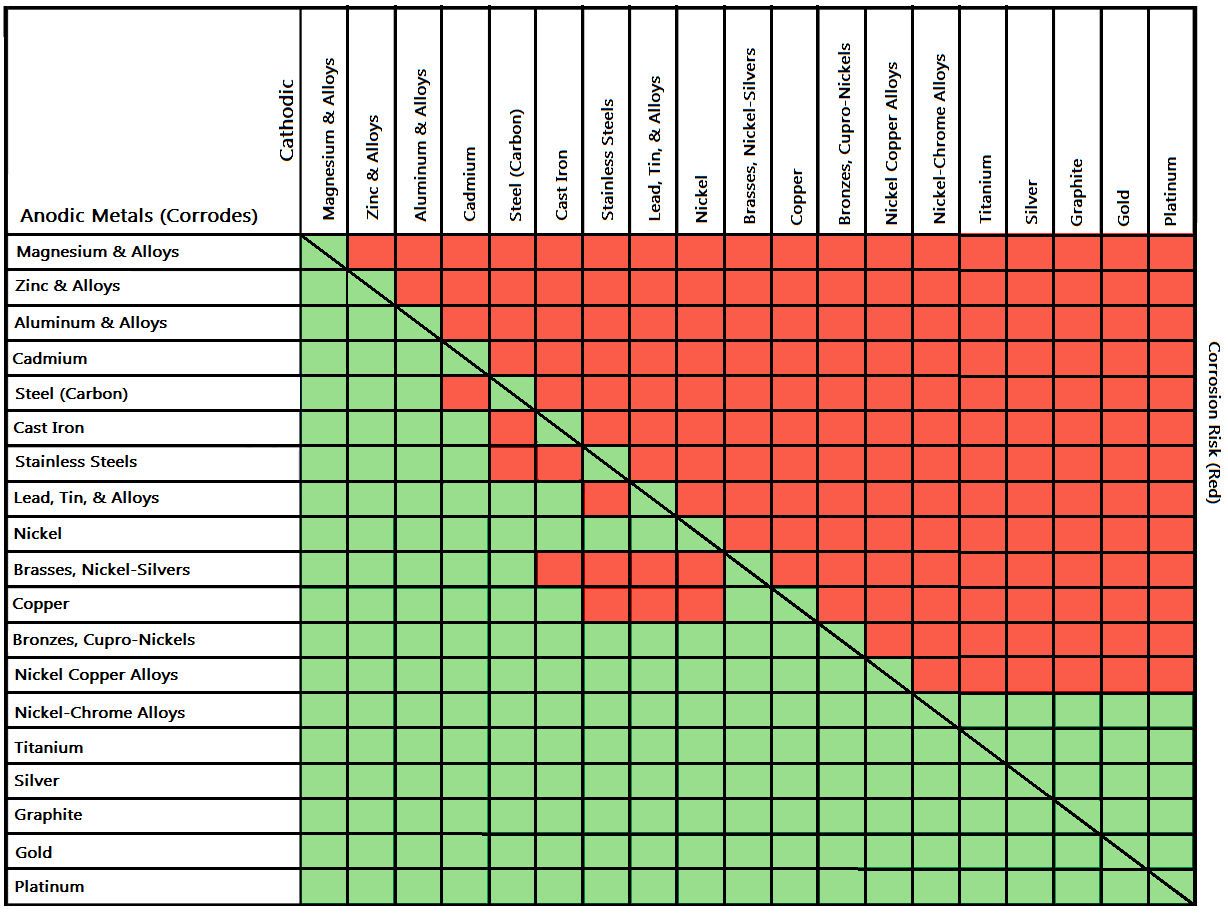
Stainless Steel Galvanic Corrosion Chart

Galvanic Reaction Chart All Points Fasteners
Galvanic Action Chart PDF
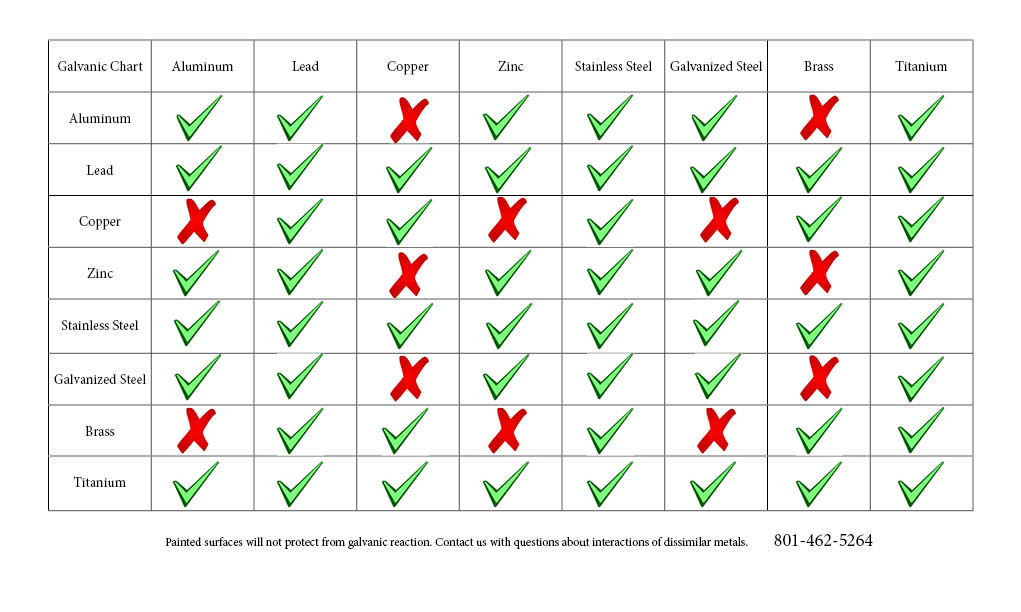
Galvanic Chart For Metals

Galvanic Corrosion Chart Metals
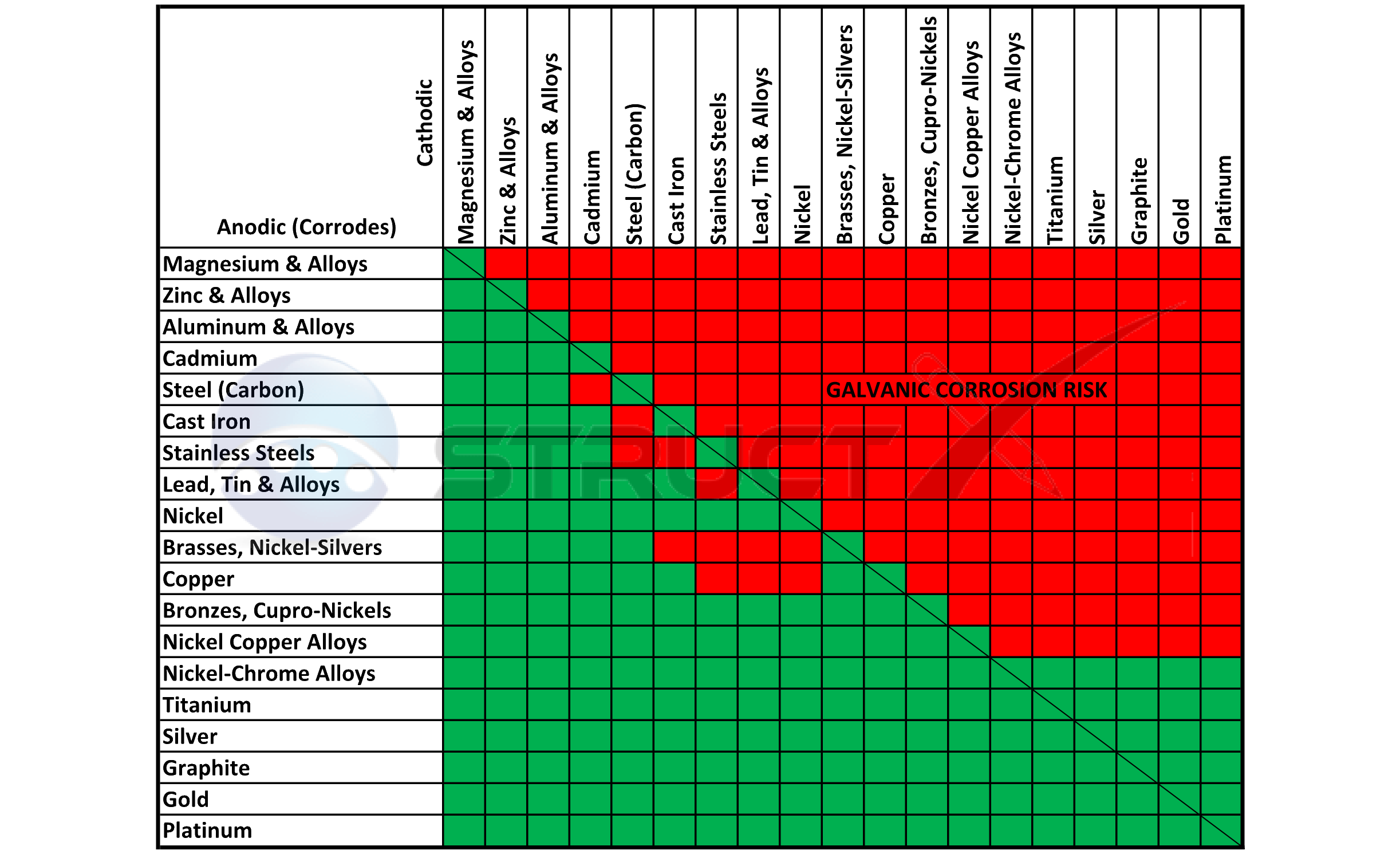
Galvanic Series (electrochemical series)
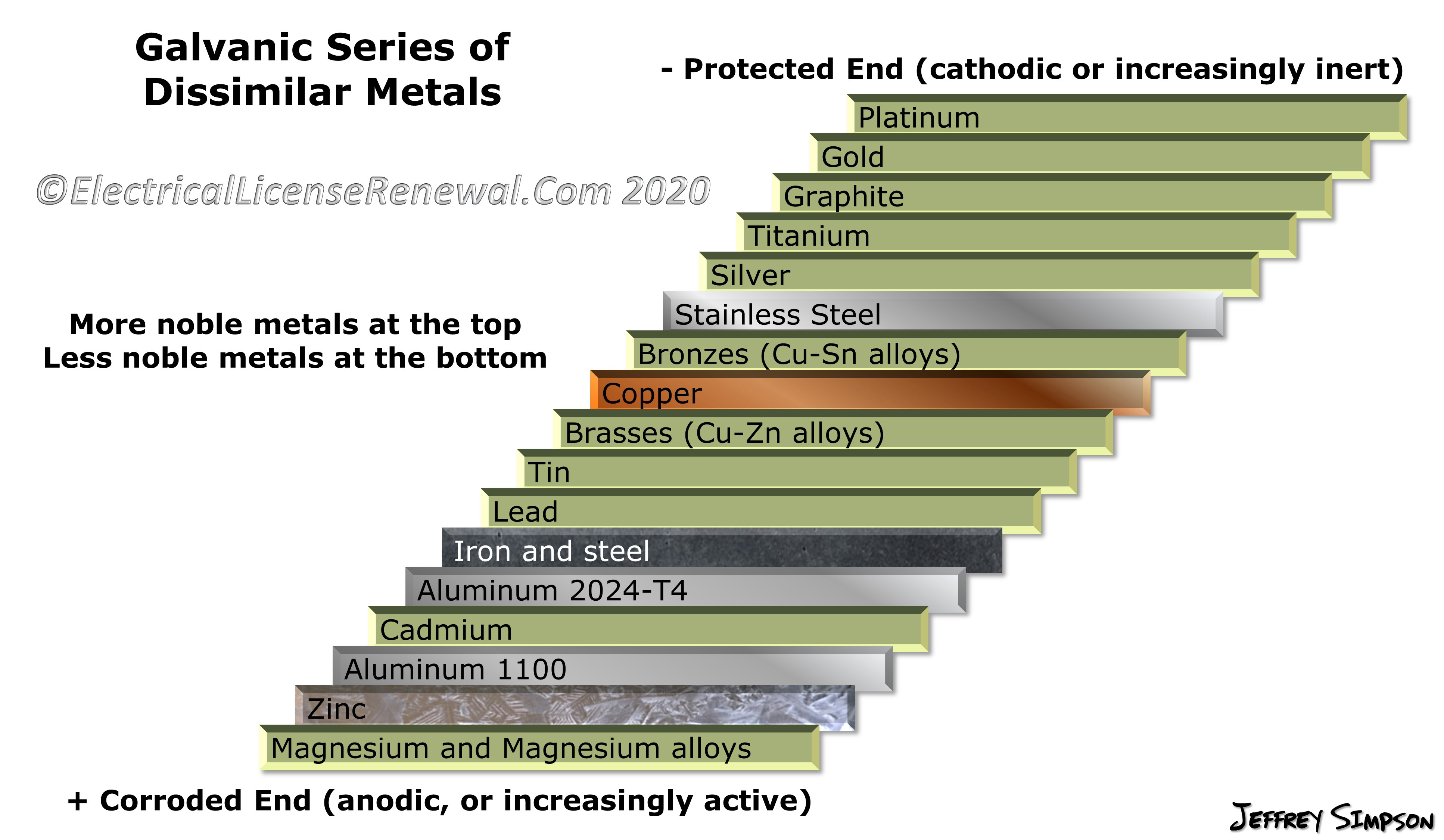
Galvanic Action Chart

Galvanic Action Corrosion Prevention Architect's Blog
![Galvanic Corrosion [with Chart] EngineerExcel](https://engineerexcel.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/03/galvanic-corrosion-chart.png)
Galvanic Corrosion [with Chart] EngineerExcel
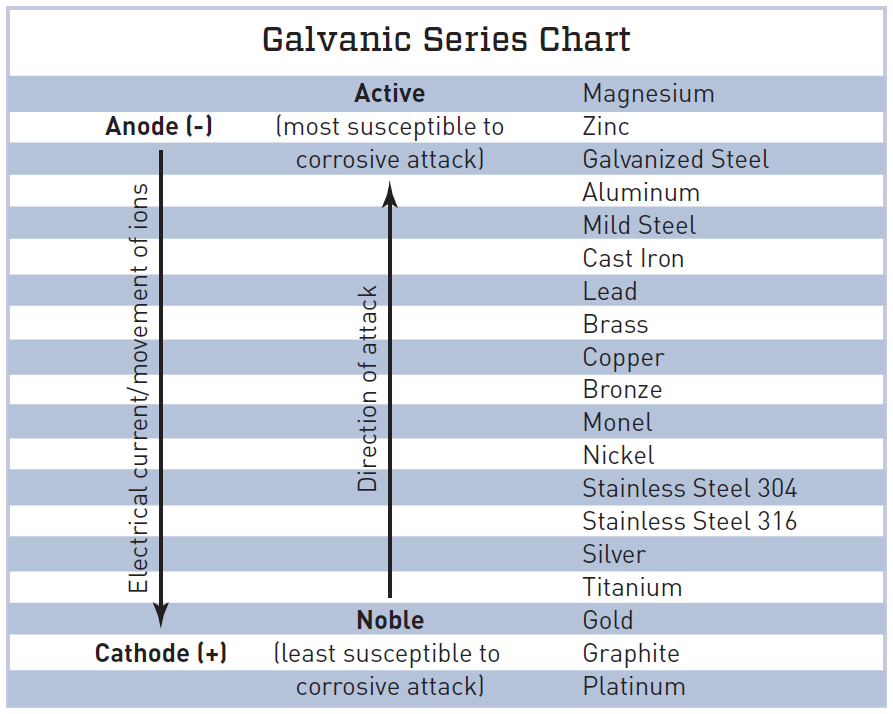
Galvanic Series Chart
The Dissimilar Metals Set Up A Galvanic Action Which Results In.
Web By Simply Choosing Metals That Avoid Galvanic Action There Will Never Be An Issue.
In This Respect, One Should Understand How To Read The Following Chart Which Lists All Metals.
The Most Active Metals In The Galvanic Corrosion Chart, Like Aluminum, Zinc, Or Magnesium, Are More Likely To Corrode When Connected To.
Related Post:
