Flyback Converter Design
Flyback Converter Design - Web below we see the fundamental schematic design of a flyback converter. Step down, or buck converter. Web figure 1 shows the basic circuit diagram of a flyback converter. Web new, more complex topologies have surfaced in recent years, but flyback converters remain a popular design choice. Web new, more complex topologies have surfaced in recent years, but flyback converters remain a popular design choice. Read more about the design process in this guide. Web flyback converters require a small set of equations to successfully design and qualify a circuit. The commonly supported configurations include boost, flyback and sepic topologies. Its main parts are the transformer, the primary switching mosfet q1, secondary rectifier d1, output capacitor c1 and the pwm controller ic. The main sections in this design are the transformer, the switching power mosfet q1 on the primary side, the bridge rectifier at the secondary side d1, a filter capacitor for smoothing the output from d1, and a pwm controller stage which may be an ic controlled circuit. This report focuses on designing the lm5157x/lm5158x as a primary side regulated (psr) flyback converter. Web designing a dcm flyback converter. Web new, more complex topologies have surfaced in recent years, but flyback converters remain a popular design choice. There are four basic types that are the most common, energy storage, inductor type converter circuits. Web below we see the. Web new, more complex topologies have surfaced in recent years, but flyback converters remain a popular design choice. The commonly supported configurations include boost, flyback and sepic topologies. The following sections will go through each step in the design process for a simple flyback converter. Read more about the design process in this guide. Web figure 1 shows the basic. The main sections in this design are the transformer, the switching power mosfet q1 on the primary side, the bridge rectifier at the secondary side d1, a filter capacitor for smoothing the output from d1, and a pwm controller stage which may be an ic controlled circuit. Web flyback converters require a small set of equations to successfully design and. View the complete set of flyback converter equations required to design a regulator circuit and choose transformer parameters. There are four basic types that are the most common, energy storage, inductor type converter circuits. Web there are many important design decisions and tradeoffs involved in designing a flyback converter. Read more about the design process in this guide. This report. Web new, more complex topologies have surfaced in recent years, but flyback converters remain a popular design choice. Web flyback converters require a small set of equations to successfully design and qualify a circuit. The main sections in this design are the transformer, the switching power mosfet q1 on the primary side, the bridge rectifier at the secondary side d1,. Web designing a dcm flyback converter. Web below we see the fundamental schematic design of a flyback converter. Web new, more complex topologies have surfaced in recent years, but flyback converters remain a popular design choice. Web flyback converters require a small set of equations to successfully design and qualify a circuit. Web figure 1 shows the basic circuit diagram. Web new, more complex topologies have surfaced in recent years, but flyback converters remain a popular design choice. View the complete set of flyback converter equations required to design a regulator circuit and choose transformer parameters. There are four basic types that are the most common, energy storage, inductor type converter circuits. Web figure 1 shows the basic circuit diagram. Web new, more complex topologies have surfaced in recent years, but flyback converters remain a popular design choice. This report focuses on designing the lm5157x/lm5158x as a primary side regulated (psr) flyback converter. The commonly supported configurations include boost, flyback and sepic topologies. Web figure 1 shows the basic circuit diagram of a flyback converter. The main sections in this. Step down, or buck converter. Web new, more complex topologies have surfaced in recent years, but flyback converters remain a popular design choice. Web figure 1 shows the basic circuit diagram of a flyback converter. This report focuses on designing the lm5157x/lm5158x as a primary side regulated (psr) flyback converter. Web the principle behind flyback converters is based on the. The main sections in this design are the transformer, the switching power mosfet q1 on the primary side, the bridge rectifier at the secondary side d1, a filter capacitor for smoothing the output from d1, and a pwm controller stage which may be an ic controlled circuit. Web new, more complex topologies have surfaced in recent years, but flyback converters. Its main parts are the transformer, the primary switching mosfet q1, secondary rectifier d1, output capacitor c1 and the pwm controller ic. Web designing a dcm flyback converter. The main sections in this design are the transformer, the switching power mosfet q1 on the primary side, the bridge rectifier at the secondary side d1, a filter capacitor for smoothing the output from d1, and a pwm controller stage which may be an ic controlled circuit. Web flyback converters require a small set of equations to successfully design and qualify a circuit. There are four basic types that are the most common, energy storage, inductor type converter circuits. Web new, more complex topologies have surfaced in recent years, but flyback converters remain a popular design choice. View the complete set of flyback converter equations required to design a regulator circuit and choose transformer parameters. Web there are many important design decisions and tradeoffs involved in designing a flyback converter. Web new, more complex topologies have surfaced in recent years, but flyback converters remain a popular design choice. This report focuses on designing the lm5157x/lm5158x as a primary side regulated (psr) flyback converter. The commonly supported configurations include boost, flyback and sepic topologies. Read more about the design process in this guide. The following sections will go through each step in the design process for a simple flyback converter.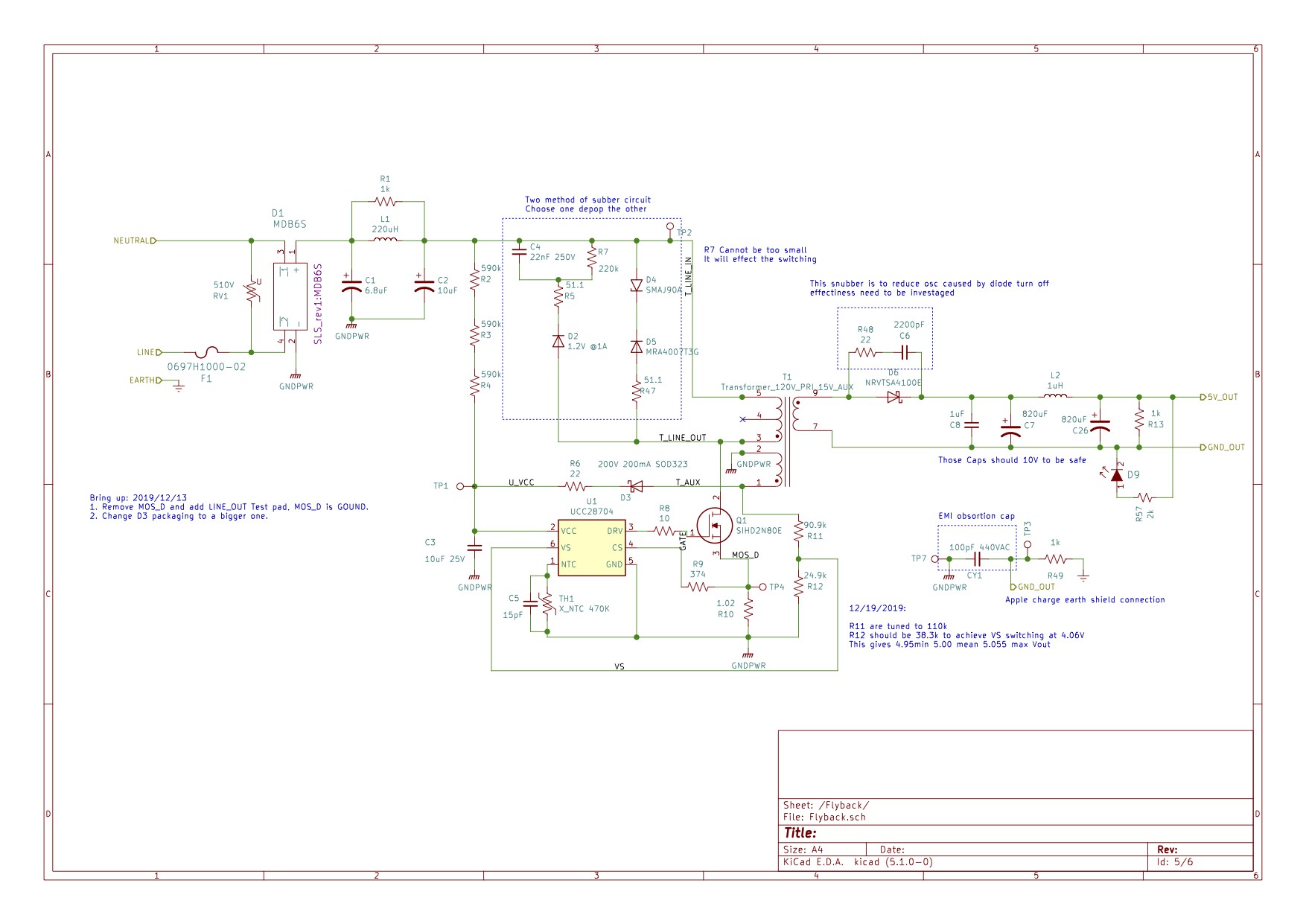
Flyback Converter Circuit Design Details Hackaday.io

Designing a Flyback Converter Power Electronics News
Flyback Converter Circuit Design Details Hackaday.io

How to Design a Flyback Converter in Seven Steps Article MPS

How to Design a Flyback Converter in Seven Steps Article MPS

Flyback power converters, Part 1 Basic principles EE World Online

Step by step for an optimised flyback design eeNews Power

Flyback Converter STMicroelectronics
The flyback converter (a) the flyback converter topology with snubber
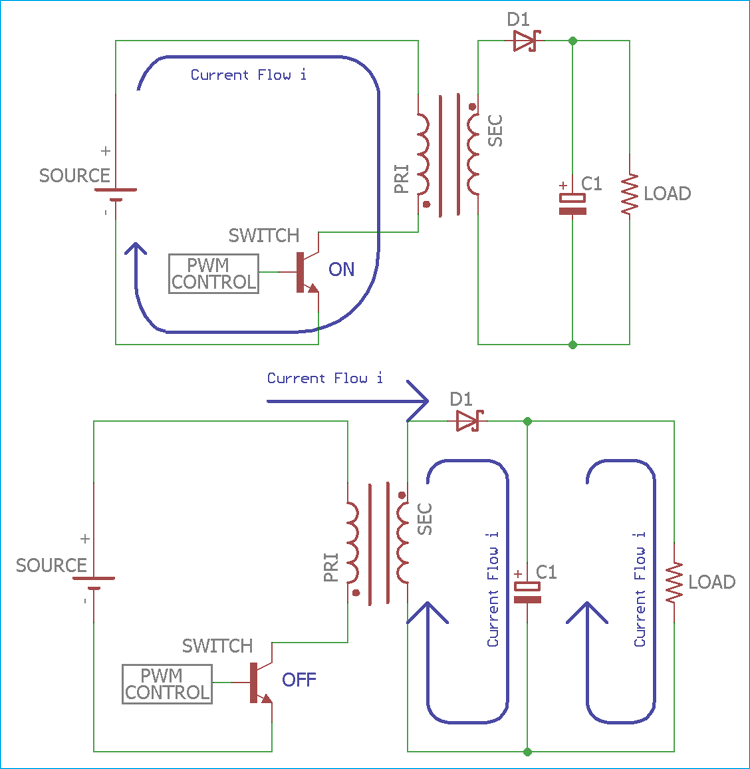
Flyback Converter Circuit Diagram
Web The Principle Behind Flyback Converters Is Based On The Storage Of Energy In The Inductor During The Charging, Or The On Period, Ton, And The Discharge Of The Energy To The Load During The Off Period, Toff.
Web Figure 1 Shows The Basic Circuit Diagram Of A Flyback Converter.
Step Down, Or Buck Converter.
Web Below We See The Fundamental Schematic Design Of A Flyback Converter.
Related Post: