Flight Level Chart
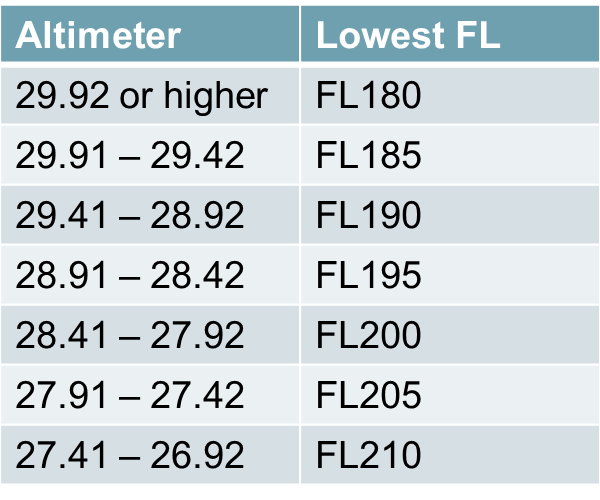
Flight Level Chart - These flight levels are dependent on the atmospheric pressure and vary according to the weather conditions. Web the basic aviation weather hazards—thunderstorms, icing, turbulence and reduced visibility—are present in the flight levels just as they are at lower altitudes. Web we will discuss this deeply in further articles where i talk about east bound levels, west bound levels, vfr flight levels and rvsm airspaces. Web since class a airspace is everywhere, sectional charts don’t depict it. To boston and on the west coast, the los angeles/san diego area. For example, 20,000 feet msl would be flight level 200 (fl200). Web the terminology “altitude ( or height) one thousand five hundred metres” is used by atc when assigning flight altitude values in metres based upon: The altimeter setting used is the isa pressure of 1013 hpa or (29.92 inhg). Web ifr enroute aeronautical planning charts index (an index graphic of the atlantic and pacific) north pacific route charts are designed for faa controllers to monitor transoceanic flights. Aircraft in class a airspace don’t use feet to express altitude. Below the transition level feet are used. Standard metric level is measured in metric meters. Web a flight level (fl) is a standard pressure altitude, expressed as three numbers. The actual height varies due flying at a constant pressure. Aircraft flying on flight levels all measure their altitude from the same pressure setting, 1013.2 hpa (or 29.92 inhg). A flight level (fl) is the vertical distance of an aircraft above the isobaric surface of 1013.25hpa (hecto pascal) or 29.92 in hg (inches of mercury). Seamless vfr sectional charts, terminal area charts, ifr enroute low charts, ifr enroute high charts, tfrs, adverse metars and tafs and aviation routes. Web ifr enroute aeronautical planning charts index (an index graphic of. Web flight planning with aviation & aeronautical charts on google maps. Ifr/vfr low altitude planning charts is designed for preflight and enroute flight planning for ifr/vfr flights. Seamless vfr sectional charts, terminal area charts, ifr enroute low charts, ifr enroute high charts, tfrs, adverse metars and tafs and aviation routes. Instead, they use flight levels. A flight level is pressure. Either, whether represented in feet or meters, is the distance at which an aircraft flies above the atmospheric level of standard pressure (pressure altitude). Only above the transition level (which depends on the local qnh but is typically 4000 feet above sea level) are flight levels used to indicate altitude; Web here's what you should know about the 10 types. For example, 20,000 feet msl would be flight level 200 (fl200). The altimeter setting used is the isa pressure of 1013 hpa or (29.92 inhg). Flight planning is easy on our large collection of aeronautical charts, including sectional charts, approach plates, ifr enroute charts, and helicopter route charts. At a flight level, every aircraft has the same altimeter setting; It. They just manifest themselves differently, thanks to colder ambient air temperatures, generally higher wind velocities and reduced pressure. Only above the transition level (which depends on the local qnh but is typically 4000 feet above sea level) are flight levels used to indicate altitude; Web ifr enroute low altitude charts provide aeronautical information for navigation under instrument flight rules below. Web ifr enroute aeronautical planning charts index (an index graphic of the atlantic and pacific) north pacific route charts are designed for faa controllers to monitor transoceanic flights. To boston and on the west coast, the los angeles/san diego area. Aircrafts fly at different altitudes as cleared by an air traffic controller and. Ifr/vfr low altitude planning charts is designed. Web pilots use several types of altitude for varying purposes, which include reading aeronautical charts, communicating with atc, and calculating aircraft performance. A flight level is pressure altitude expressed in hundreds of feet. Aircrafts fly at different altitudes as cleared by an air traffic controller and. They just manifest themselves differently, thanks to colder ambient air temperatures, generally higher wind. Only above the transition level (which depends on the local qnh but is typically 4000 feet above sea level) are flight levels used to indicate altitude; Web flight planning with aviation & aeronautical charts on google maps. The actual height varies due flying at a constant pressure. Let’s start with the simplest one. Web a flight level (fl) is a. Web enroute low altitude charts ifr enroute low altitude charts provide aeronautical information for navigation under instrument flight rules below 18,000 feet msl. Web since class a airspace is everywhere, sectional charts don’t depict it. Web we will discuss this deeply in further articles where i talk about east bound levels, west bound levels, vfr flight levels and rvsm airspaces.. Web this chart users' guide is an introduction to the federal aviation administration's ( faa) aeronautical charts and publications. The actual height varies due flying at a constant pressure. Let’s start with the simplest one. These flight levels are dependent on the atmospheric pressure and vary according to the weather conditions. They just manifest themselves differently, thanks to colder ambient air temperatures, generally higher wind velocities and reduced pressure. In this short guide, you’ll learn about the different altitude types and their significance. Web the terminology “altitude ( or height) one thousand five hundred metres” is used by atc when assigning flight altitude values in metres based upon: Web flight planning with aviation & aeronautical charts on google maps. Web enroute low altitude charts ifr enroute low altitude charts provide aeronautical information for navigation under instrument flight rules below 18,000 feet msl. Web make your flight plan at skyvector.com. Qnh for a flight below the transition level outside of the aerodrome control zone; To boston and on the west coast, the los angeles/san diego area. For example, 20,000 feet msl would be flight level 200 (fl200). Only above the transition level (which depends on the local qnh but is typically 4000 feet above sea level) are flight levels used to indicate altitude; A flight level is a standard nominal altitude in hundreds of feet. Web ifr enroute aeronautical planning charts index (an index graphic of the atlantic and pacific) north pacific route charts are designed for faa controllers to monitor transoceanic flights.
Flight Levels einführen Eine praxisnahe Anleitung in 8 Schritten
Understanding Airspace Part 1 Classes & VFR Charts Flykit Blog
Aircraft Altimeter
Was sind Flight Levels? Verstehen.Erkunden.Anwenden.
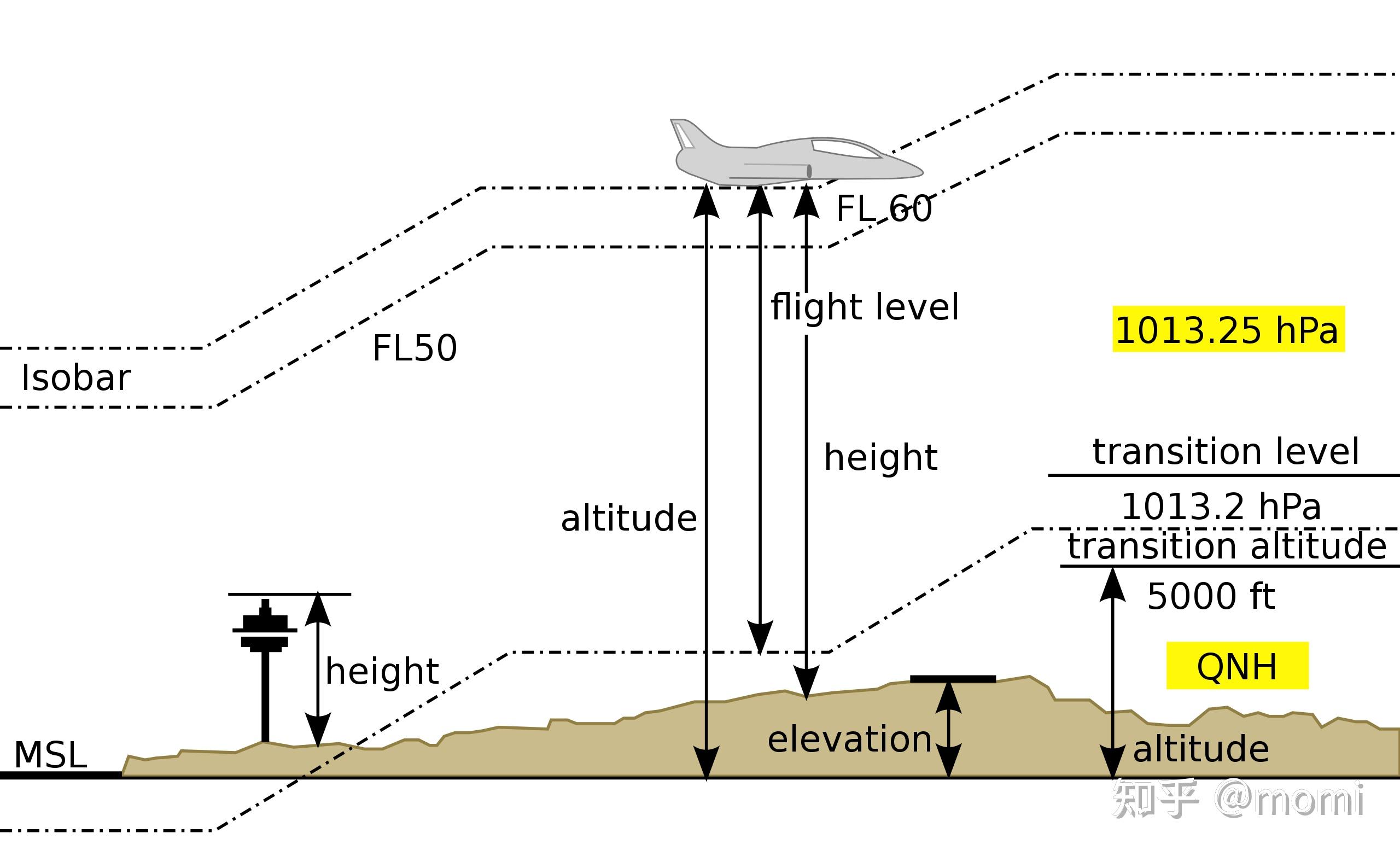
航空飞行高度elevation、height、altitude、flight level、QNE、QNH、QFE、AGL、MSL、正高

Instrument Flight Rules En Route Altitudes Learn to Fly
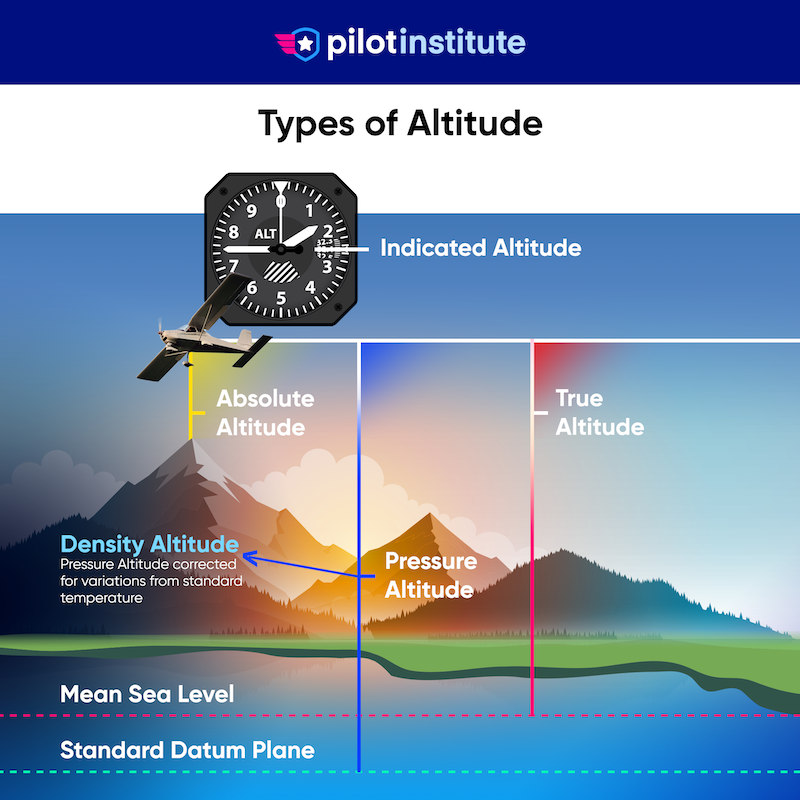
The 6 Types of Altitude in Aviation (Airplane Pilots) Pilot Institute
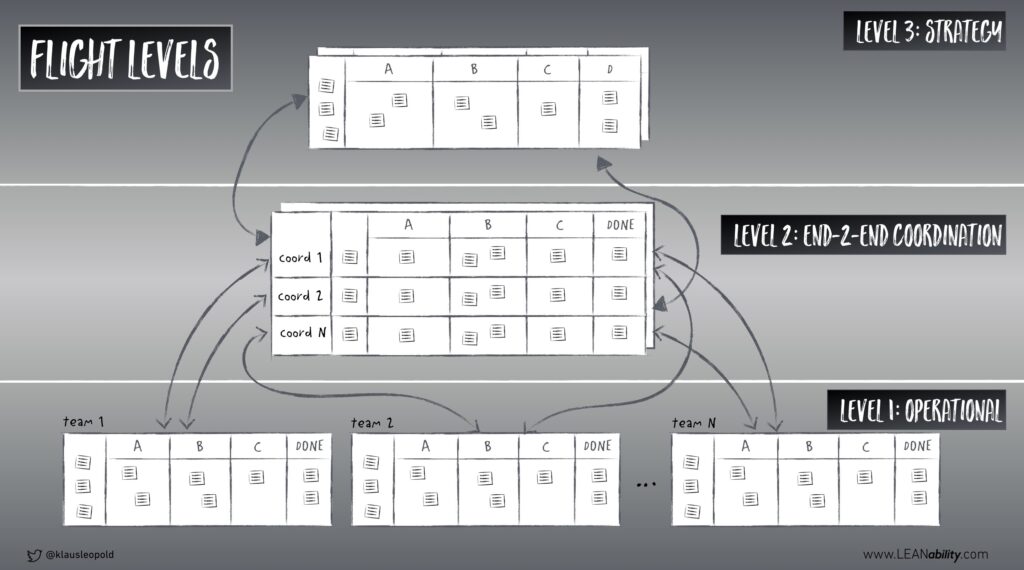
Flight Levels and Business Agility

Semicircular Cruising Level System (ICAO) Flight Crew Guide
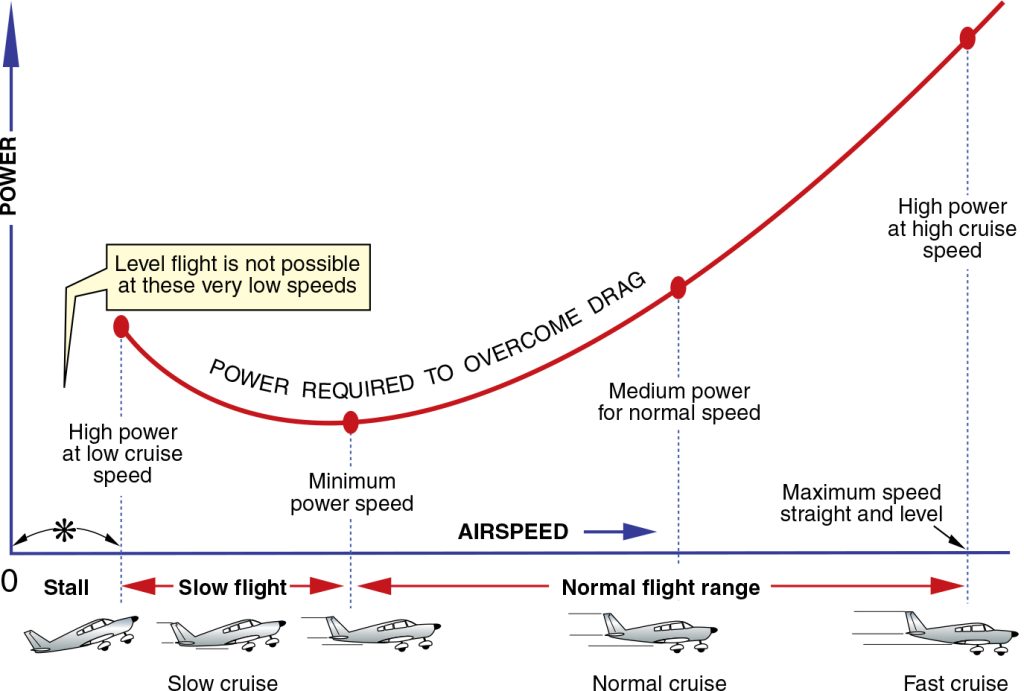
Aircraft Performance Changing Airspeed in StraightandLevel Flight
Web A Flight Level (Fl) Is A Standard Pressure Altitude, Expressed As Three Numbers.
Qfe For A Flight Within The The Aerodrome Control Zone.
Web Here's What You Should Know About The 10 Types Of Minimum Ifr Altitudes For Your Next Flight.
Aircraft Flying On Flight Levels All Measure Their Altitude From The Same Pressure Setting, 1013.2 Hpa (Or 29.92 Inhg).
Related Post: