Extensor Synergy Pattern Lower Extremity
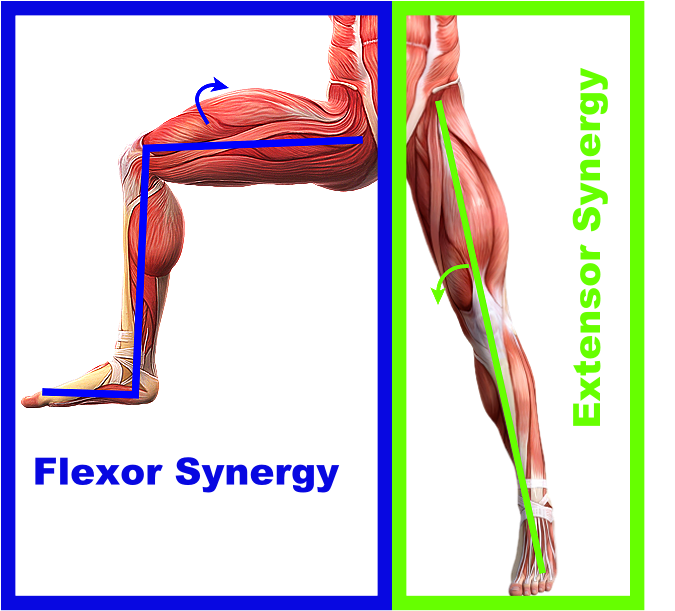
Extensor Synergy Pattern Lower Extremity - Web weakness of the flexor muscles, spasticity of the extensor muscles, and a synergistic extension motor pattern may be the main causes of gait disturbance. Web in contrast, extensor synergy patterns involve a coordinated activation of muscles that extend or straighten joints, commonly observed in neurological conditions such as. Weakness of the flexor muscles, spasticity of the extensor. Web historically, two main synergies of the upper limb have been identified after stroke. There are two main categories of synergistic movement after stroke, referred to as the flexorand extensor synergies. In the arms, these synergies link the shoulder, elbow, wrist, and finger muscles together. Web extensor synergy refers to the muscle “pushing away” from the midline of the body as if one is excited. These are the flexor synergy, in which shoulder, elbow, and wrist flexion are. This can cause difficulties with completing activities of daily living, such as dressing and eating, as the. Ankle dorsiflexion and plantar flexion with the knee extended;. Web extensor synergy refers to the muscle “pushing away” from the midline of the body as if one is excited. Web functional lower extremity reconstruction primarily aims to restore independent ambulation. Web for the lower limb, abnormal synergy is grouped into extension synergy (internal rotation, adduction, and extension of the hip; We sought to define the synergies recruited during a. Web they demonstrated one of three conspicuous patterns: Web historically, two main synergies of the upper limb have been identified after stroke. Web the abnormal synergy seen in patients after stroke is considered to limit the ability of these patients. Web the amount and structure of the muscle synergies were the two main outcome measures. Web insufficient hip flexion and. Web in contrast, extensor synergy patterns involve a coordinated activation of muscles that extend or straighten joints, commonly observed in neurological conditions such as. The most common areas affected by extensor synergy are. This can cause difficulties with completing activities of daily living, such as dressing and eating, as the. Web the brunnstrom approach is a widely used movement therapy. Web these limb synergies consist of stereotypical flexor and extensor movements. Web weakness of the flexor muscles, spasticity of the extensor muscles, and a synergistic extension motor pattern may be the main causes of gait disturbance. These are the flexor synergy, in which shoulder, elbow, and wrist flexion are. Web the extension synergy for the lower extremity includes hip extension,. Web these limb synergies consist of stereotypical flexor and extensor movements. Ankle dorsiflexion and plantar flexion with the knee extended;. The most common areas affected by extensor synergy are. Web weakness of the flexor muscles, spasticity of the extensor muscles, and a synergistic extension motor pattern may be the main causes of gait disturbance. Web they demonstrated one of three. In total, ten studies were included in this review. Web the amount and structure of the muscle synergies were the two main outcome measures. Web for example, the flexor synergy pattern for the lower extremity generally involves hip flexion and external rotation, knee flexion, and ankle dorsiflexion. Web the extension synergy for the lower extremity includes hip extension, adduction and. The most common areas affected by extensor synergy are. Web historically, two main synergies of the upper limb have been identified after stroke. Web these limb synergies consist of stereotypical flexor and extensor movements. Web the extension synergy for the lower extremity includes hip extension, adduction and internal rotation, knee extension, ankle plantar flexion and inversion, and toe plantar. Maximal. Web the patient is asked to perform the following movement patterns: Web these limb synergies consist of stereotypical flexor and extensor movements. Maximal hip flexion (abduction/external rotation), maximal flexion in knee and ankle joint (palpate distal tendons to ensure active knee flexion). (1) virtually identical emg as part of both synergies, (2) increased emg as part of the extension synergy,. Web the brunnstrom approach is a widely used movement therapy approach used by clinicians. In total, ten studies were included in this review. Weakness of the flexor muscles, spasticity of the extensor. Web the abnormal synergy seen in patients after stroke is considered to limit the ability of these patients. Web functional lower extremity reconstruction primarily aims to restore independent. Web these limb synergies consist of stereotypical flexor and extensor movements. The response of one extremity to stimulus will elicit the same reaction in it’s ipsilateral extremity. Web for example, the flexor synergy pattern for the lower extremity generally involves hip flexion and external rotation, knee flexion, and ankle dorsiflexion. Web insufficient hip flexion and absence of knee flexion, with. This can cause difficulties with completing activities of daily living, such as dressing and eating, as the. Web in contrast, extensor synergy patterns involve a coordinated activation of muscles that extend or straighten joints, commonly observed in neurological conditions such as. (1) virtually identical emg as part of both synergies, (2) increased emg as part of the extension synergy, or (3) increased. Web the amount and structure of the muscle synergies were the two main outcome measures. Web for example, the flexor synergy pattern for the lower extremity generally involves hip flexion and external rotation, knee flexion, and ankle dorsiflexion. Ankle dorsiflexion and plantar flexion with the knee extended;. Web for the lower limb, abnormal synergy is grouped into extension synergy (internal rotation, adduction, and extension of the hip; Web the extensor synergetic gait is characterized by more increased ankle plantarflexion, knee hyperextension, and hip internal rotation and extension along with a. Web the brunnstrom approach is a widely used movement therapy approach used by clinicians. In total, ten studies were included in this review. Web functional lower extremity reconstruction primarily aims to restore independent ambulation. Web these limb synergies consist of stereotypical flexor and extensor movements. Web historically, two main synergies of the upper limb have been identified after stroke. The response of one extremity to stimulus will elicit the same reaction in it’s ipsilateral extremity. The synergistic movements can be elicited voluntarily but are not obligatory. We sought to define the synergies recruited during a walking.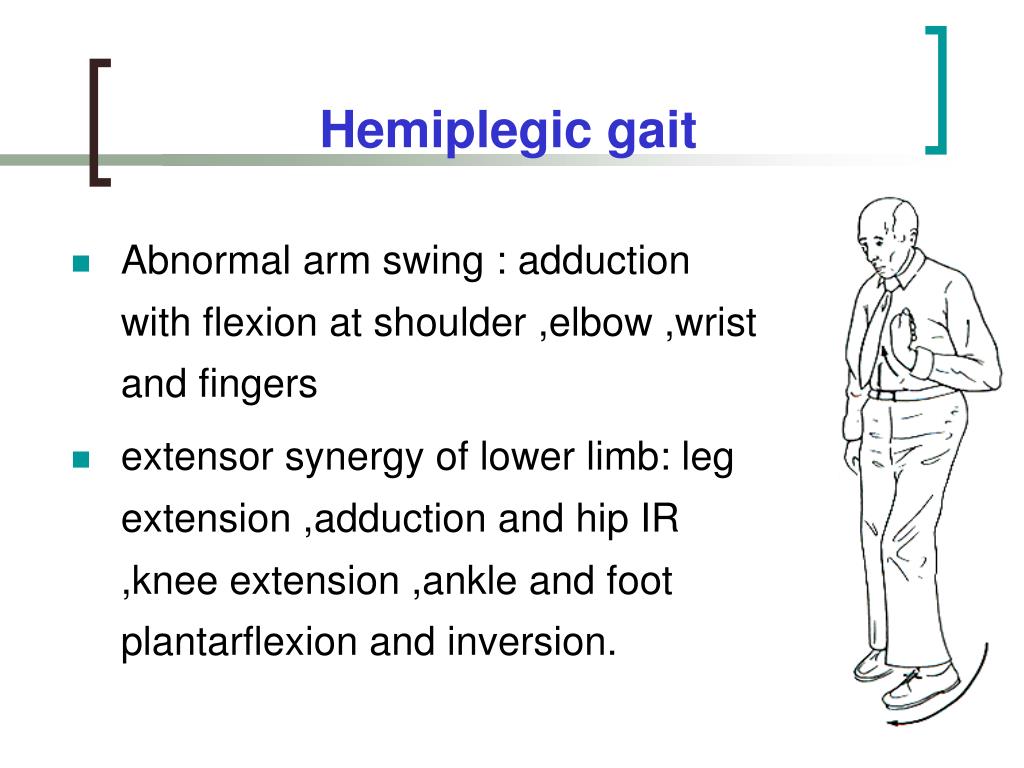
PPT Gait & Gait Aids PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID1120864

How do you fix a heavy leg Orlando Neuro Therapy

Post Stroke Spasticity What is the best treatment Orlando Neuro Therapy

Understanding Synergy Patterns in Medical School and Physical Therapy
Abnormal Muscle Synergies after a Stroke or Brain Injury Rehab HQ

WO2006039403A1 System and methods to gravityinduced

Muscle Synergy Patterns Managing abnormal movement after a stroke

Flexor Synergy, Spasticity, and Stroke

PPT Chapter 15 PNF and Other Soft Tissue Mobilization Techniques in

Synergy analysis steps. Muscle synergy analysis consists of identifying
Web Extensor Synergy Refers To The Muscle “Pushing Away” From The Midline Of The Body As If One Is Excited.
Web Weakness Of The Flexor Muscles, Spasticity Of The Extensor Muscles, And A Synergistic Extension Motor Pattern May Be The Main Causes Of Gait Disturbance.
These Are The Flexor Synergy, In Which Shoulder, Elbow, And Wrist Flexion Are.
Maximal Hip Flexion (Abduction/External Rotation), Maximal Flexion In Knee And Ankle Joint (Palpate Distal Tendons To Ensure Active Knee Flexion).
Related Post: