Everting Suture Pattern
Everting Suture Pattern - Web use synthetic absorbable suture materials. Examine the integrity of your anastomsis visually. Nffn patterns are appositional and bring tissue layers into direct contact with the same layer on the opposite side. Web for most tissue closure, appositional suture patterns are preferable, as they allow the best anatomical approximation of the disrupted tissue planes.inverting suture patterns have been traditionally described for the closure of hollow viscera. These patterns prevent leakage and minimize the risk of adhesions due to exposed suture. Web classify suture patterns based on their effect on tissue apposition. If an everting pattern is not used, the scales tend to roll in along the edge of the incision, and delay healing. Web mattress style sutures have an everting pattern and are usually applied as single interrupted sutures with the knot placed away from the wound edge. Web the use of a specific suture pattern may vary depending on the area being sutured, the length of the incision, the tension at the suture line, and the specific need for apposition, inversion, or eversion of the tissues. Web this video demonstrates the use of everting or quickert sutures to treat spastic entropion. Coeliotomy closure in larger lizards should be in 2 layers with the muscle closed by using a simple interrupted or continuous pattern with absorbable suture. These patterns prevent leakage and minimize the risk of adhesions due to exposed suture. Web mattress style sutures have an everting pattern and are usually applied as single interrupted sutures with the knot placed away. Web the use of a specific suture pattern may vary depending on the area being sutured, the length of the incision, the tension at the suture line, and the specific need for apposition, inversion, or eversion of the tissues. Always handle bowel wall using atraumatic technique. The author always uses a horizontal mattress pattern to close the skin of reptiles.. Web the skin should be closed using an everting suture pattern. As well as being able to perform the basic patterns, it important to be familiar with their basic properties so you will be able to decide when their use is appropriate. Web the use of a specific suture pattern may vary depending on the area being sutured, the length. Web classify suture patterns based on their effect on tissue apposition. As well as being able to perform the basic patterns, it important to be familiar with their basic properties so you will be able to decide when their use is appropriate. The procedure takes an average of 15 minutes to complete and requires only local anesthesia. ↑ mauriello jr. Web use synthetic absorbable suture materials. Web tension sutures redistribute tension across the edges of the wound, minimizing interruption of blood flow and necrosis. Web inverting patterns turn the cut edges inward and minimize exposed suture. Web methods a prospective single armed clinical trial of 62 eyelids in 57 patients undergoing everting suture correction of involutional entropion. Suture patterns can. Examine the integrity of your anastomsis visually. Reptile surgery is performed under general anesthesia, observing sterile technique, with appropriate monitoring and supportive care. Inner bite on each side of the incision is roughly equal to the thickness of the skin (ie. Web for most tissue closure, appositional suture patterns are preferable, as they allow the best anatomical approximation of the. Horizontal mattress sutures are placed so that the external suture material is. Perhaps the most vital component of the correct suture pattern is the surgical knot. Coeliotomy closure in larger lizards should be in 2 layers with the muscle closed by using a simple interrupted or continuous pattern with absorbable suture. Web classify suture patterns based on their effect on. Suture patterns can be broadly categorized as interrupted or continuous. Web the skin should be closed using an everting suture pattern. Everting sutures are sometimes useful to close skin because skin edges apposed with appositional sutures. Web methods a prospective single armed clinical trial of 62 eyelids in 57 patients undergoing everting suture correction of involutional entropion. The procedure takes. If an everting pattern is not used, the scales tend to roll in along the edge of the incision, and delay healing. These are used to close lumens in large animal species (intestines, bladders, uteri). Web methods a prospective single armed clinical trial of 62 eyelids in 57 patients undergoing everting suture correction of involutional entropion. Web the skin should. Coeliotomy closure in larger lizards should be in 2 layers with the muscle closed by using a simple interrupted or continuous pattern with absorbable suture. Examine the integrity of your anastomsis visually. Discuss the advantages and disadvantages of various suture patterns. Web tension sutures redistribute tension across the edges of the wound, minimizing interruption of blood flow and necrosis. Web. Web the use of a specific suture pattern may vary depending on the area being sutured, the length of the incision, the tension at the suture line, and the specific need for apposition, inversion, or eversion of the tissues. Web classify suture patterns based on their effect on tissue apposition. Suture patterns can be broadly categorized as interrupted or continuous. Web using the correct suture pattern will help to restore anatomical alignment of tissues, obliterate dead space, minimize tissue trauma and preserve blood supply to the tissues. Know when to apply these patterns in surgery. As well as being able to perform the basic patterns, it important to be familiar with their basic properties so you will be able to decide when their use is appropriate. Coeliotomy closure in larger lizards should be in 2 layers with the muscle closed by using a simple interrupted or continuous pattern with absorbable suture. Web inverting patterns turn the cut edges inward and minimize exposed suture. Examine the integrity of your anastomsis visually. Modified corncrib (inverted t) procedure with quickert suture for repair of involutional entropion. Perhaps the most vital component of the correct suture pattern is the surgical knot. Web the use of a specific suture pattern may vary depending on the area being sutured, the length of the incision, the tension at the suture line, and the specific need for apposition, inversion, or eversion of the tissues. Nffn patterns are appositional and bring tissue layers into direct contact with the same layer on the opposite side. Web to prevent dysecdysis after a skin incision heals, an everting suture pattern is used. Web a randomized controlled trial comparing everting sutures with everting sutures and a lateral tarsal strip for involutional entropion. Web the use of a specific suture pattern may vary depending on the area being sutured, the length of the incision, the tension at the suture line, and the specific need for apposition, inversion, or eversion of the tissues.
Common Suture Patterns and Suture Techniques EndoGynecology
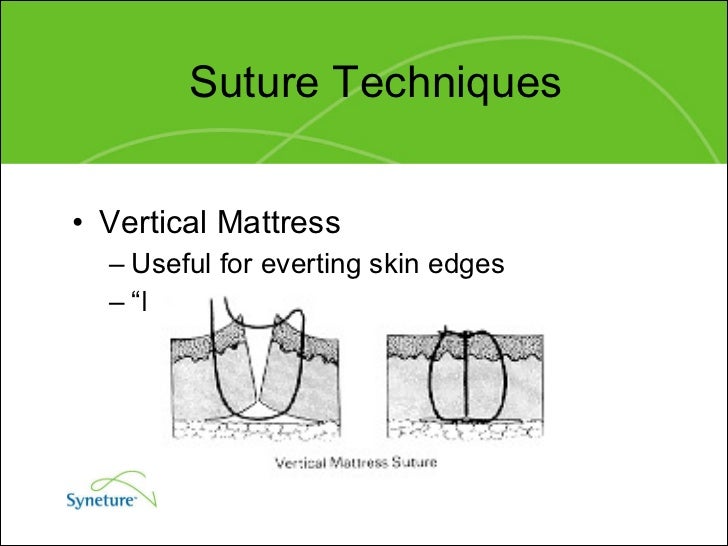
Suture

Common Everting Suture Patterns in Surgery YouTube
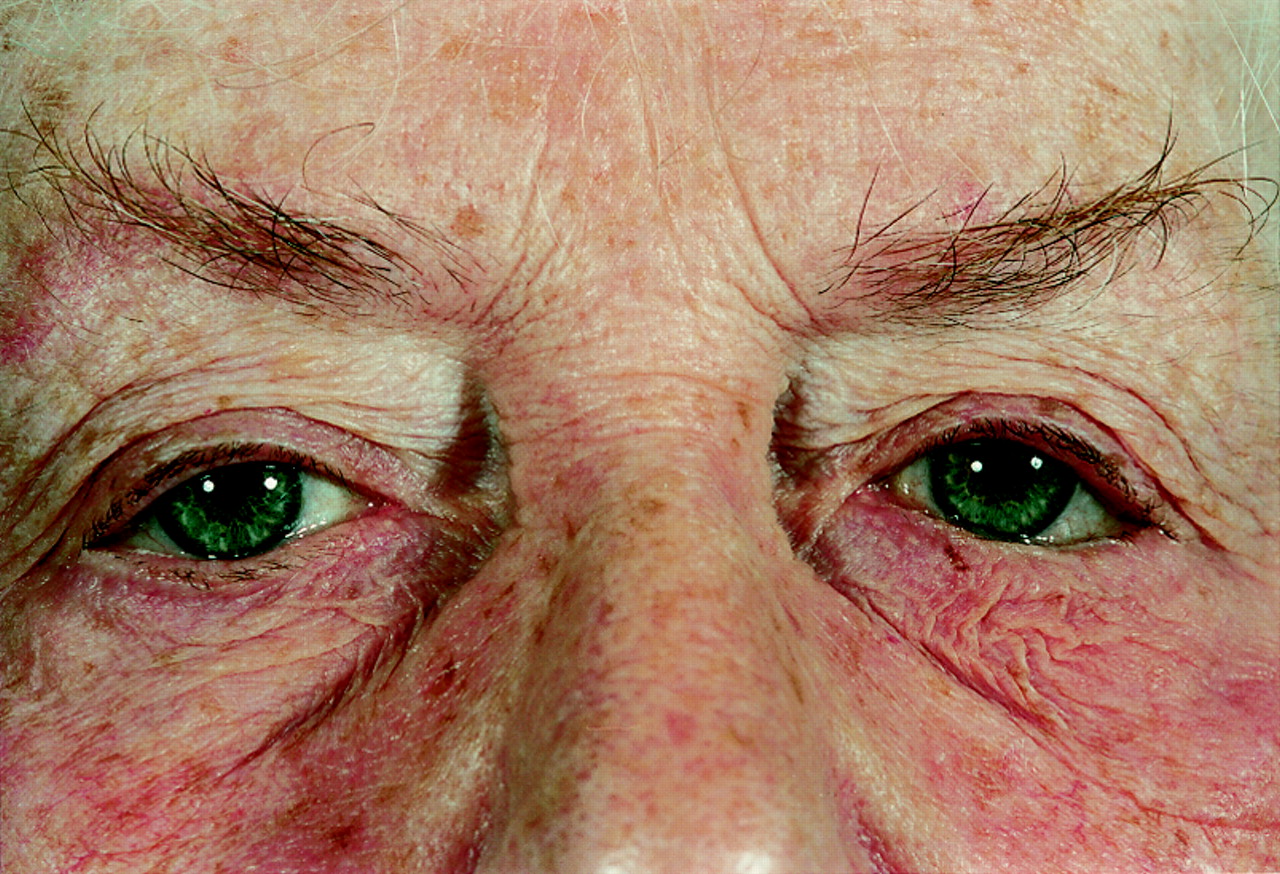
Everting suture correction of lower lid involutional entropion

A 10min novel technique for involutional entropion Miniincisional

Everting suture correction of lower lid involutional entropion

Demonstration of Three Everting Suture Patterns YouTube

(PDF) Suturing and Closure
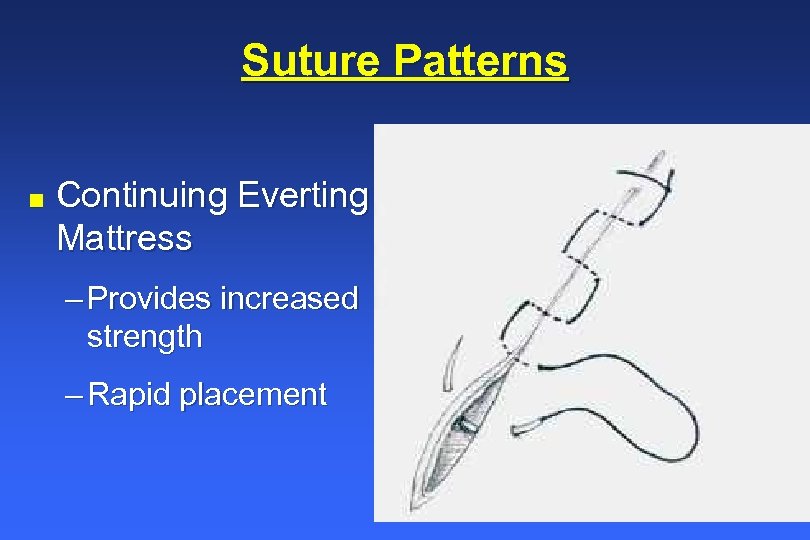
Wound Healing and Suture Knowledge ASR Certification Prep

Modified everting sutures an alternative treatment for mild to
These Patterns Prevent Leakage And Minimize The Risk Of Adhesions Due To Exposed Suture.
Web Use Synthetic Absorbable Suture Materials.
Web Mattress Style Sutures Have An Everting Pattern And Are Usually Applied As Single Interrupted Sutures With The Knot Placed Away From The Wound Edge.
Everting Sutures Are Sometimes Useful To Close Skin Because Skin Edges Apposed With Appositional Sutures.
Related Post: