Enzyme Drawing
Enzyme Drawing - We will see that enzymes employ various chemical strategies to increase the rates of reactions, in addition to physical ones like reactant proximity and the introduction of strain. Web enzymes ( / ˈɛnzaɪmz /) are proteins that act as biological catalysts by accelerating chemical reactions. In this science activity you will investigate one of these enzymes, called catalase, to find out how it helps to protect your body from cell damage. The combination is called the enzyme/substrate complex. The active site is where substrates bind to the enzyme. Web in this activity, you will explore enzyme structure and function using schematic models in the (enzymes in action kit) that will help you to visualize the concepts and terminology. Some situations have more than one substrate molecule that the enzyme will change. Enzymes have an active site that provides a unique chemical environment, made up of certain amino acid r groups (residues). The area in which bonds of the reactant(s) are broken is known as the active site. Web in this section, we will explore chemical and physical factors that speed up reactions, and begin to relate these effects to reactions catalyzed by enzymes. Enzymes have an active site that provides a unique chemical environment, made up of certain amino acid r groups (residues). The active site of an enzyme recognizes, confines, and orients the substrate in a particular direction. Web enzymes ( / ˈɛnzaɪmz /) are proteins that act as biological catalysts by accelerating chemical reactions. The combination is called the enzyme/substrate complex.. The enzyme and the substrate are in the same area. Web get editable icons and illustrations of enzymes. They provide a lot of useful information, but they can also be pretty confusing the first time you see them. Web the functionality of an enzyme is determined by the shape of the enzyme. Web to describe the interaction between an enzyme. Web an enzymes is a protein that facilitates a cellular metabolic process by lowering activation energy (ea) levels in order to catalyze the chemical reactions between biomolecules. The combination is called the enzyme/substrate complex. Enzymes are proteins, having primary, secondary, tertiary and in certain cases, even quaternary structures. Web enzymes are biological catalysts (also known as biocatalysts) that speed up. Web the functionality of an enzyme is determined by the shape of the enzyme. This will also help you to draw the structure and diagram of enzymes. Web in this section, we will explore chemical and physical factors that speed up reactions, and begin to relate these effects to reactions catalyzed by enzymes. The area in which bonds of the. Elevated cardiac enzymes after a heart attack are a sign of serious heart damage. Web the functionality of an enzyme is determined by the shape of the enzyme. Web in this activity, you will explore enzyme structure and function using schematic models in the (enzymes in action kit) that will help you to visualize the concepts and terminology. Web an. Web get editable icons and illustrations of enzymes. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different molecules known as products. Enzymes are proteins consisting of one or more polypeptide chains. This will also help you to draw the structure and diagram of enzymes. Web enzymes are biological catalysts that accelerate. Web the functionality of an enzyme is determined by the shape of the enzyme. The sequence of amino acids specifies the structure, which in turn identifies the catalytic activity of the enzyme. Web in this article we will discuss about the structure of enzymes. Web enzymes are biological catalysts that speed up reactions. By making it easier for the reaction. If you do not have access to the kit, the images and videos provided will help you work through the activity. Web thanks to these amino acids, an enzyme's active site is uniquely suited to bind to a particular target—the enzyme's substrate or substrates—and help them undergo a chemical reaction. Some enzymes reduce the activation energy to such low levels. Graphs like the one shown below (graphing reaction rate as a function of substrate concentration) are often used to display information about enzyme kinetics. They provide a lot of useful information, but they can also be pretty confusing the first time you see them. Web enzymes can be described at four levels: Create professional science figures in minutes with biorender. Elevated cardiac enzymes after a heart attack are a sign of serious heart damage. The reactants of enzyme catalyzed reactions are called substrates. Web an enzyme marker is a blood test to measure enzymes, proteins in your blood that can indicate tissue damage or disease. The primary structure of an enzyme is the linear sequence of amino acids in its. Enzymes are very, very specific. Then they view a graph showing energy changes with and without an enzyme, revealing how enzymes lower activation energy. You can use these templates in combination with chemical structures and reaction schemes to show how an experiment is performed or. Web the functionality of an enzyme is determined by the shape of the enzyme. The combination is called the enzyme/substrate complex. If you do not have access to the kit, the images and videos provided will help you work through the activity. Web four steps of enzyme action 1. High levels of cpk isoenzymes may indicate a muscle disease, while elevated liver enzymes suggest liver damage. The active site of an enzyme recognizes, confines, and orients the substrate in a particular direction. They provide a lot of useful information, but they can also be pretty confusing the first time you see them. The active site is where substrates bind to the enzyme. Some situations have more than one substrate molecule that the enzyme will change. Web in this article we will discuss about the structure of enzymes. The area in which bonds of the reactant(s) are broken is known as the active site. Enzymes are proteins, having primary, secondary, tertiary and in certain cases, even quaternary structures. Enzymes have an active site that provides a unique chemical environment, made up of certain amino acid r groups (residues)./what-is-enzyme-structure-and-function-375555_v4-6f22f82931824e76b1c31401230deac8.png)
Structure and Function of an Enzyme

Enzymes Functions Definition Classification
Enzyme Illustrations, RoyaltyFree Vector Graphics & Clip Art iStock

Enzymes Cells Vector Illustration Closeup View Medicals Molecular
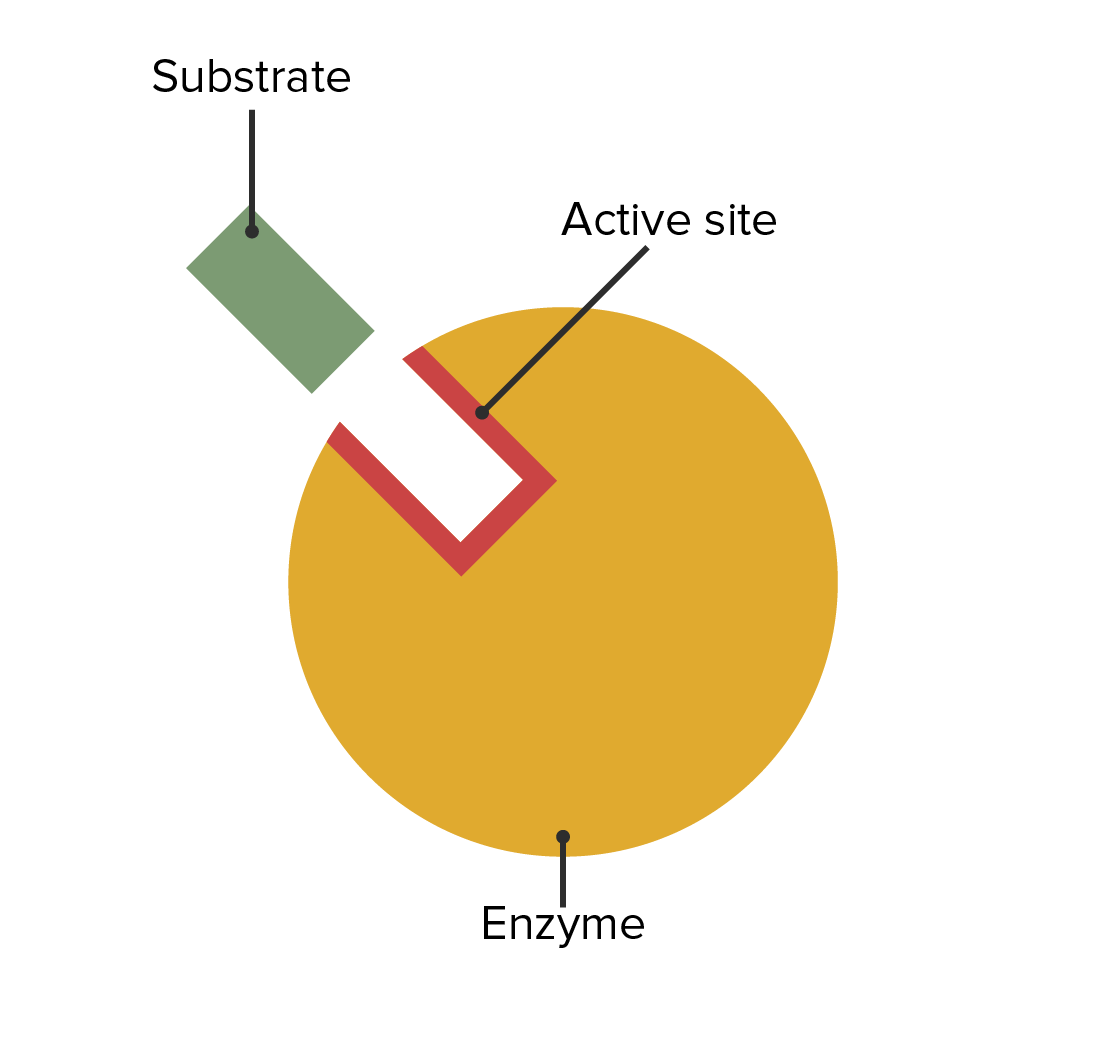
What Are Enzymes Structure And Location Hubpages

Enzyme substrates and active sites chemical Vector Image
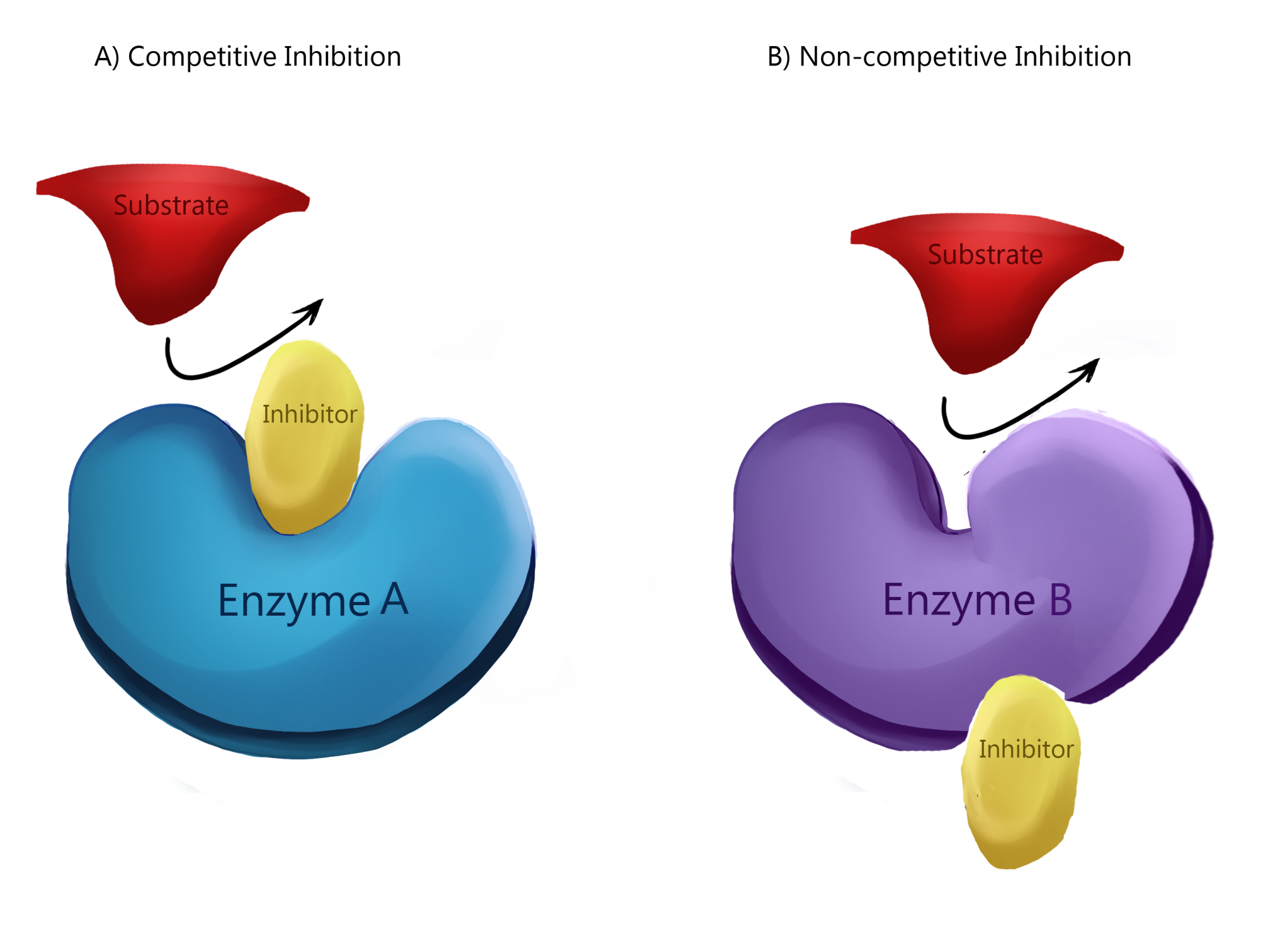
Enzymes AP® Biology Crash Course Review Albert.io

Enzyme vector illustration Full labeled cycle and diagram with
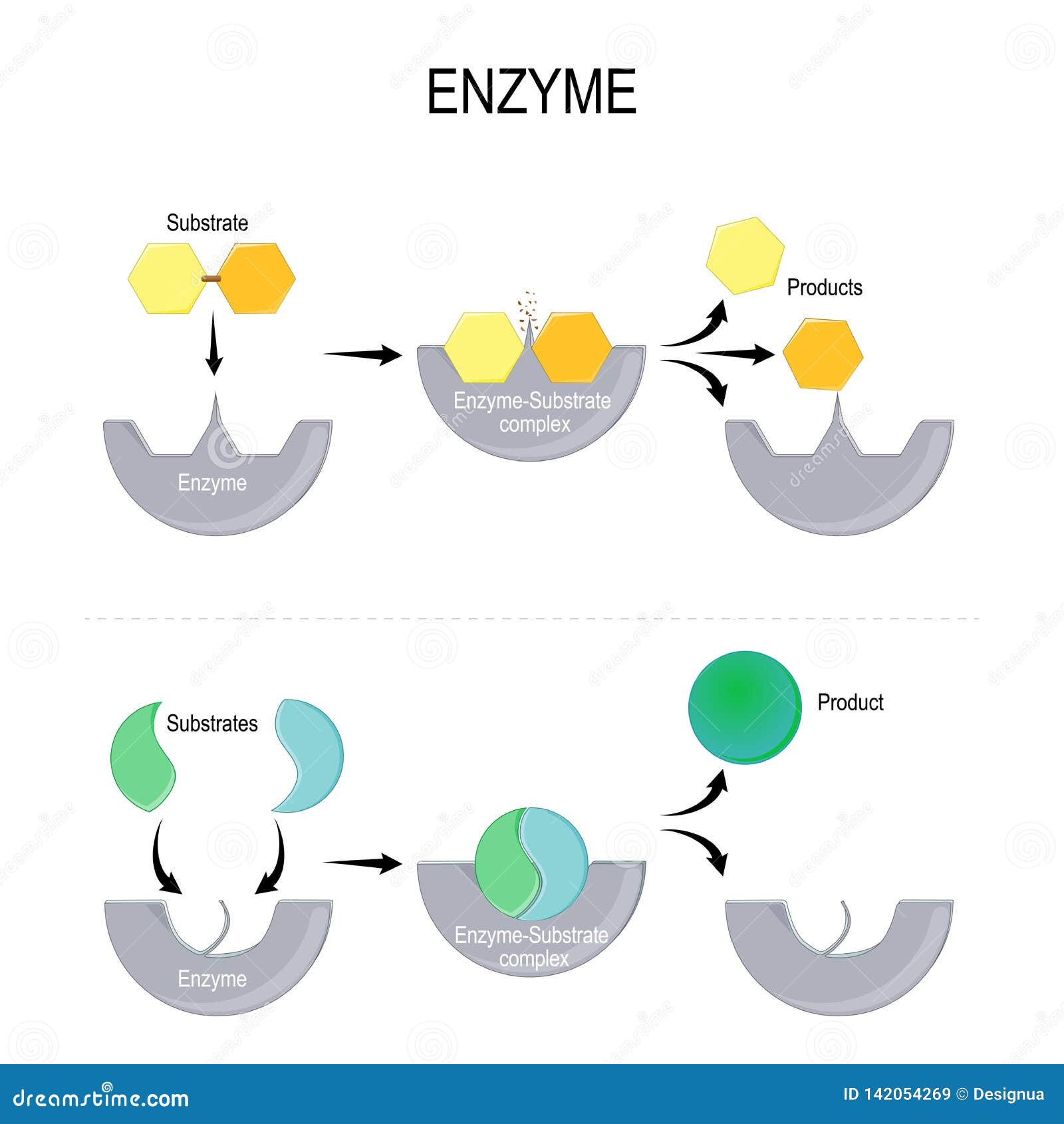
Enzyme function stock vector. Illustration of biological 142054269
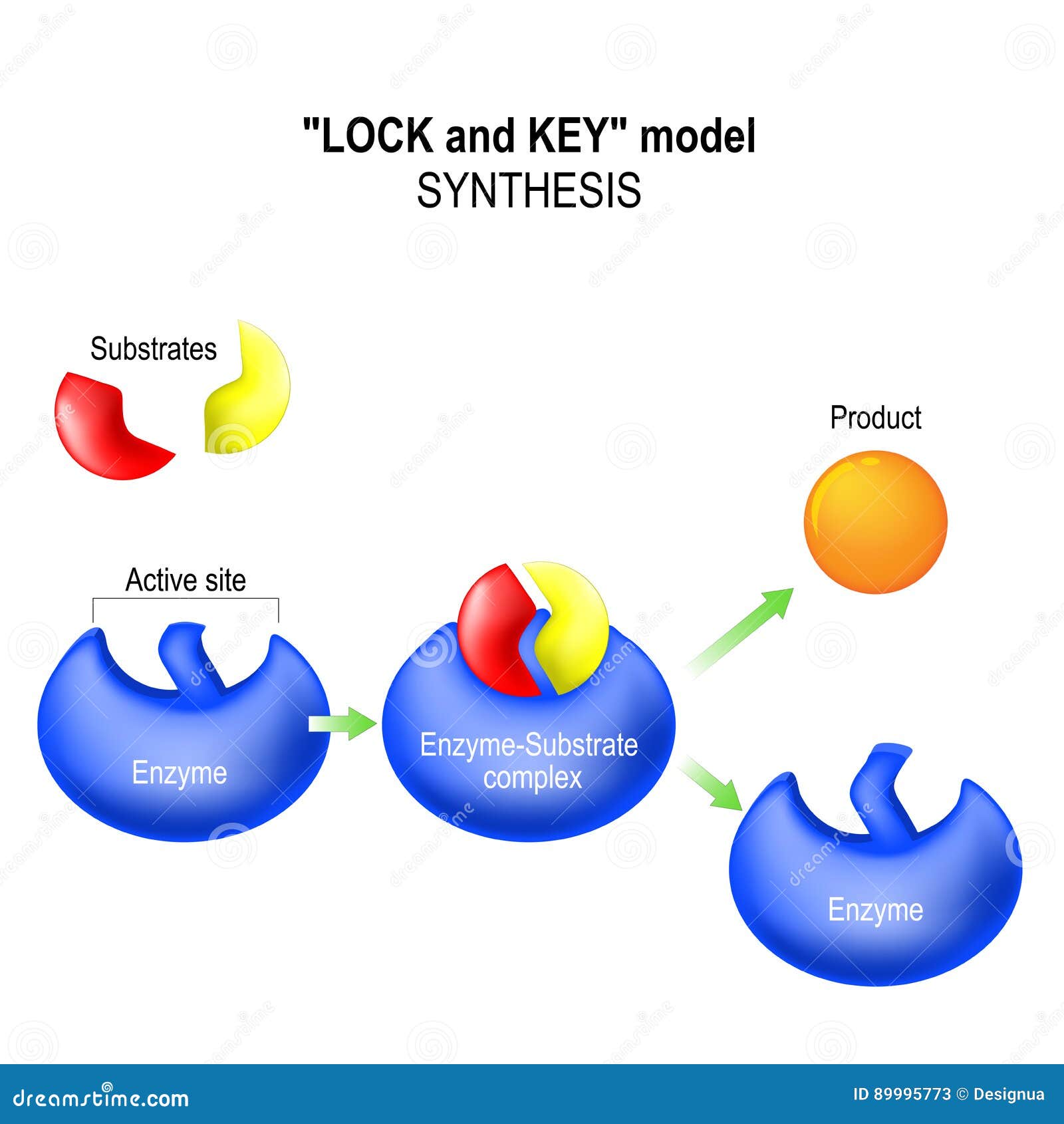
Enzyme. synthesis stock vector. Illustration of model 89995773
Web Get Editable Icons And Illustrations Of Enzymes.
Enzymes Are Proteins Consisting Of One Or More Polypeptide Chains.
We Will See That Enzymes Employ Various Chemical Strategies To Increase The Rates Of Reactions, In Addition To Physical Ones Like Reactant Proximity And The Introduction Of Strain.
The Area In Which Bonds Of The Reactant(S) Are Broken Is Known As The Active Site.
Related Post:
