Enthalpy Chart
Enthalpy Chart - Web enthalpy is defined as the sum of a system’s internal energy (u) and the mathematical product of its pressure (p) and volume (v): As intensive properties, the specific enthalpy, h = h / m , is referenced to a unit of mass m of the system, and the molar enthalpy, h m = h / n , where n is the number of moles. It is proportional to the size of the system (for homogeneous systems). Web enthalpy is an extensive property; Only enthalpy changes for chemical or For chemists, the iupac standard state refers to materials under a. The standard enthalpy of formation, \(δh^\circ_\ce{f}\), is the enthalpy change accompanying the formation of 1 mole of a substance from the elements in their most stable states at 1 bar (standard state). Web calculate the molar enthalpy of formation from combustion data using hess's law; Web enthalpy changes are typically tabulated for reactions in which both the reactants and products are at the same conditions. \[h=u+p v \nonumber \] enthalpy is also a state function. Enthalpy values for specific substances cannot be measured directly; To obtain gauge pressure, subtract atmospheric pressure. \[h=u+p v \nonumber \] enthalpy is also a state function. It is proportional to the size of the system (for homogeneous systems). Web calculate the molar enthalpy of formation from combustion data using hess's law; The standard enthalpy of formation, \(δh^\circ_\ce{f}\), is the enthalpy change accompanying the formation of 1 mole of a substance from the elements in their most stable states at 1 bar (standard state). Web enthalpy is defined as the sum of a system’s internal energy (u) and the mathematical product of its pressure (p) and volume (v): Only enthalpy changes for. Web enthalpy changes are typically tabulated for reactions in which both the reactants and products are at the same conditions. \[h=u+p v \nonumber \] enthalpy is also a state function. For chemists, the iupac standard state refers to materials under a. It is proportional to the size of the system (for homogeneous systems). Web examples of enthalpy changes include enthalpy. The standard enthalpy of formation, \(δh^\circ_\ce{f}\), is the enthalpy change accompanying the formation of 1 mole of a substance from the elements in their most stable states at 1 bar (standard state). Web enthalpy changes are typically tabulated for reactions in which both the reactants and products are at the same conditions. Web calculate the molar enthalpy of formation from. Using the enthalpy of formation, calculate the unknown enthalpy of the overall reaction; Web enthalpy is defined as the sum of a system’s internal energy (u) and the mathematical product of its pressure (p) and volume (v): The standard enthalpy of formation, \(δh^\circ_\ce{f}\), is the enthalpy change accompanying the formation of 1 mole of a substance from the elements in. Calculate the heat evolved/absorbed given the masses (or volumes) of reactants. To obtain gauge pressure, subtract atmospheric pressure. Web calculate the molar enthalpy of formation from combustion data using hess's law; The standard enthalpy of formation, \(δh^\circ_\ce{f}\), is the enthalpy change accompanying the formation of 1 mole of a substance from the elements in their most stable states at 1. It is proportional to the size of the system (for homogeneous systems). As intensive properties, the specific enthalpy, h = h / m , is referenced to a unit of mass m of the system, and the molar enthalpy, h m = h / n , where n is the number of moles. Calculate the heat evolved/absorbed given. Calculate the heat evolved/absorbed given the masses (or volumes) of reactants. Web enthalpy is defined as the sum of a system’s internal energy (u) and the mathematical product of its pressure (p) and volume (v): Web enthalpy changes are typically tabulated for reactions in which both the reactants and products are at the same conditions. The standard enthalpy of formation,. Web enthalpy is an extensive property; Enthalpy values for specific substances cannot be measured directly; Web enthalpy is defined as the sum of a system’s internal energy (u) and the mathematical product of its pressure (p) and volume (v): Web examples of enthalpy changes include enthalpy of combustion, enthalpy of fusion, enthalpy of vaporization, and standard enthalpy of formation. It. Web enthalpy is defined as the sum of a system’s internal energy (u) and the mathematical product of its pressure (p) and volume (v): Web enthalpy is an extensive property; It is proportional to the size of the system (for homogeneous systems). Using the enthalpy of formation, calculate the unknown enthalpy of the overall reaction; Enthalpy values for specific substances. Only enthalpy changes for chemical or Web calculate the molar enthalpy of formation from combustion data using hess's law; Enthalpy values for specific substances cannot be measured directly; Web examples of enthalpy changes include enthalpy of combustion, enthalpy of fusion, enthalpy of vaporization, and standard enthalpy of formation. As intensive properties, the specific enthalpy, h = h / m , is referenced to a unit of mass m of the system, and the molar enthalpy, h m = h / n , where n is the number of moles. A standard state is a commonly accepted set of conditions used as a reference point for the determination of properties under other different conditions. \[h=u+p v \nonumber \] enthalpy is also a state function. Calculate the heat evolved/absorbed given the masses (or volumes) of reactants. Web enthalpy changes are typically tabulated for reactions in which both the reactants and products are at the same conditions. Web enthalpy is an extensive property; It is proportional to the size of the system (for homogeneous systems). Web enthalpy is defined as the sum of a system’s internal energy (u) and the mathematical product of its pressure (p) and volume (v):
Pressure Enthalpy Chart
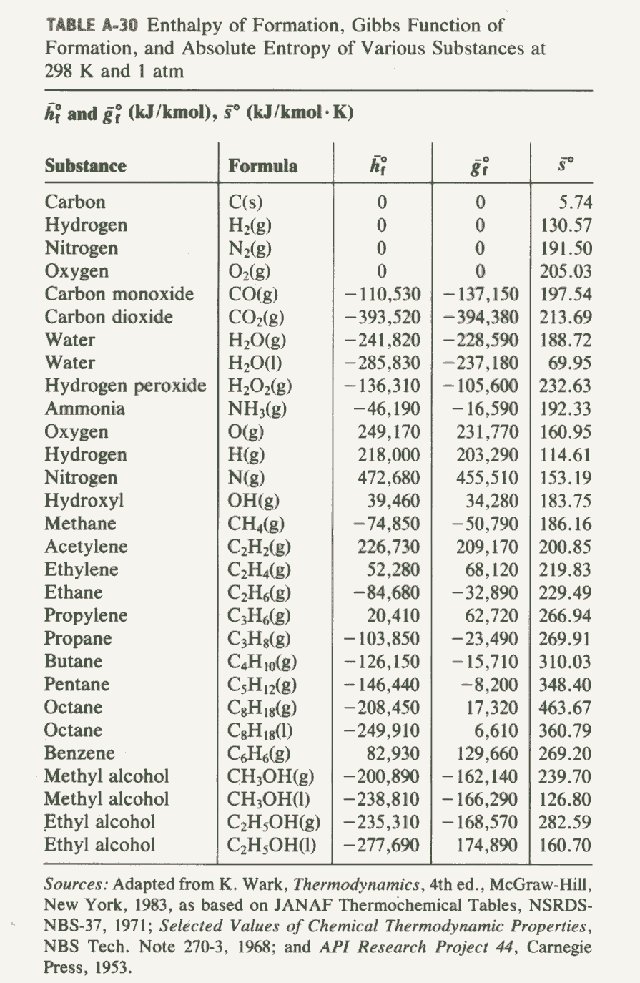
Standard Enthalpies of Formation SchoolWorkHelper

Pressure / Enthalpy Diagram Example HVAC School
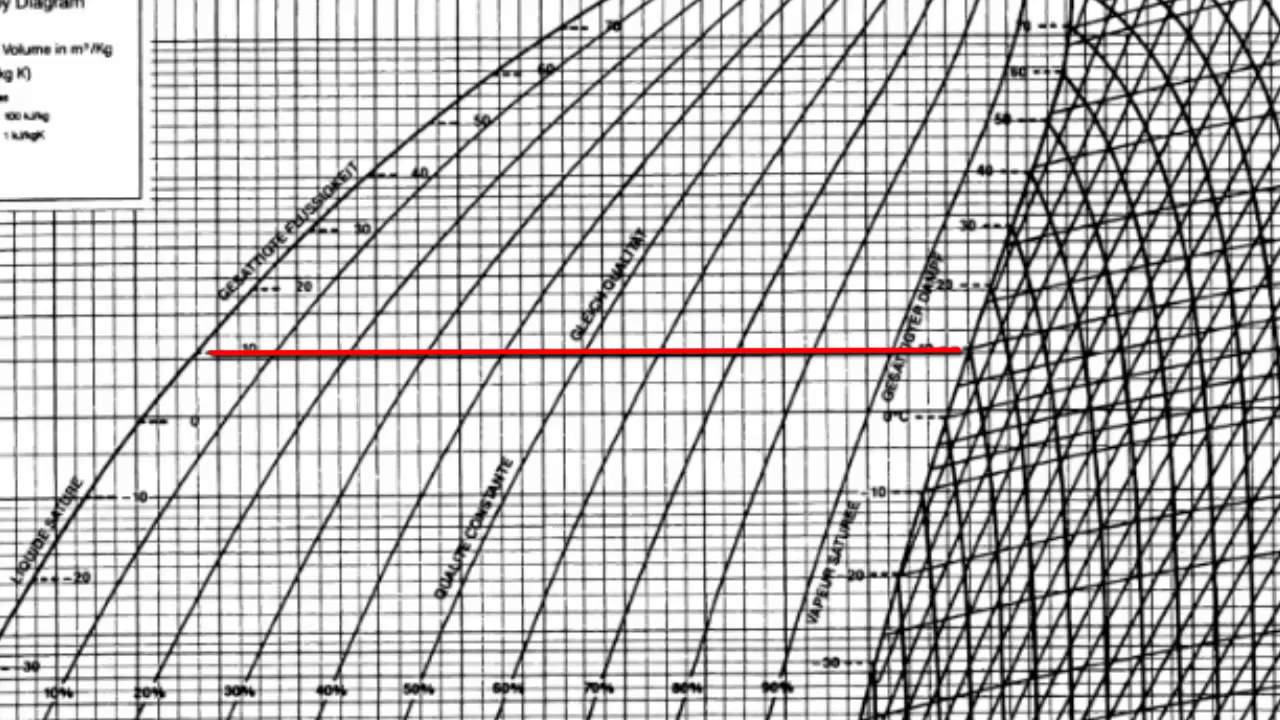
Refrigeration Cycle for Ideal conditions on a Pressure Enthalpy Chart

Enthalpy Diagram 101 Diagrams

Pressure Enthalpy Chart

Wet Bulb and Enthalpy The Left Side of the Chart HVAC School
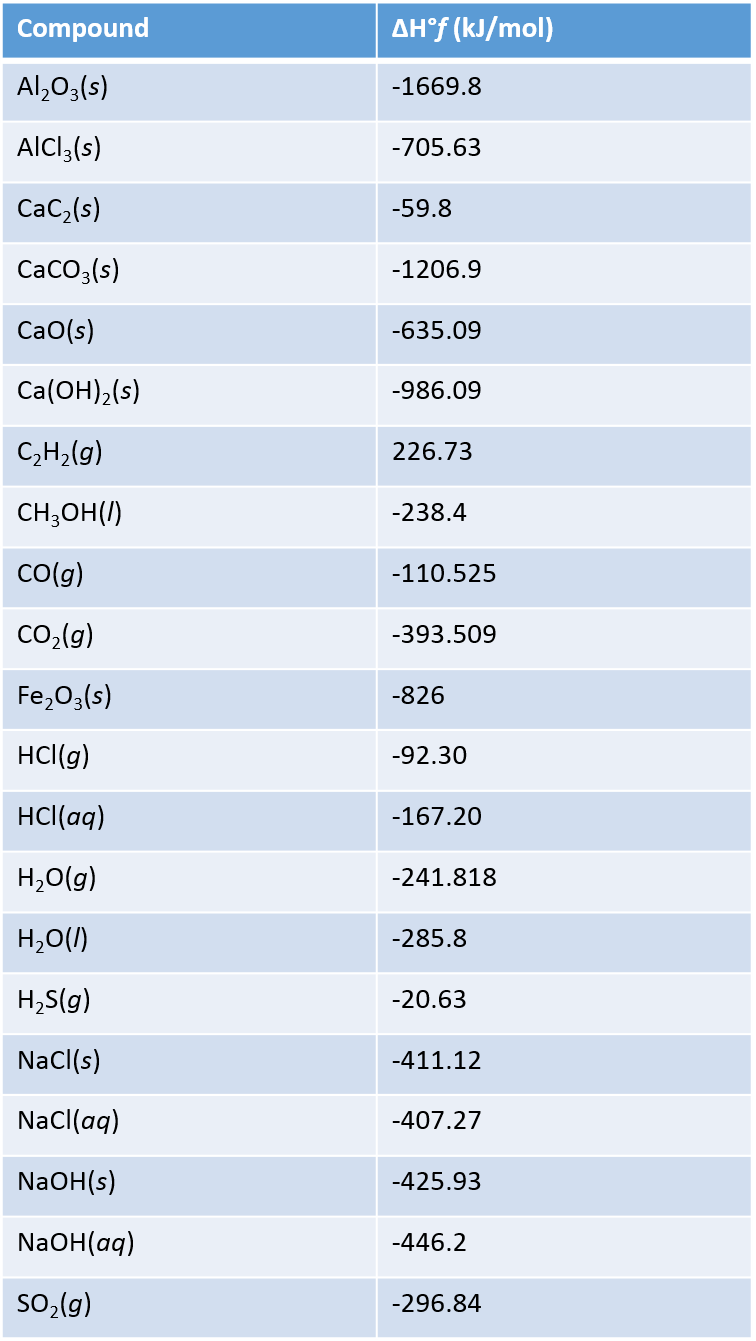
Solved Using the table of standard enthalpies of formation
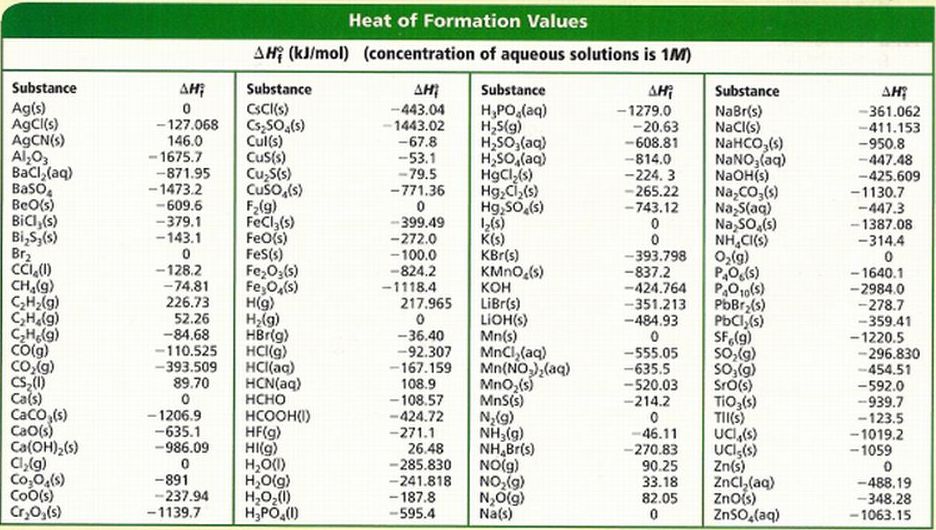
III Calculating Enthalpies STA Form IV Honors Chemistry

Wet Bulb to Enthalpy chart & Formulas SCAHACC
To Obtain Gauge Pressure, Subtract Atmospheric Pressure.
The Standard Enthalpy Of Formation, \(Δh^\Circ_\Ce{F}\), Is The Enthalpy Change Accompanying The Formation Of 1 Mole Of A Substance From The Elements In Their Most Stable States At 1 Bar (Standard State).
Using The Enthalpy Of Formation, Calculate The Unknown Enthalpy Of The Overall Reaction;
For Chemists, The Iupac Standard State Refers To Materials Under A.
Related Post: