Emt Offset Chart
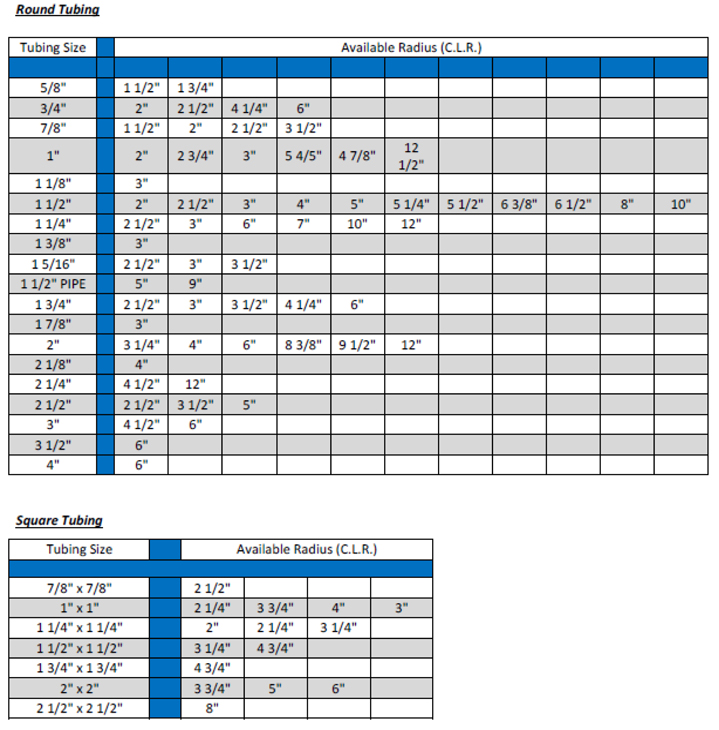
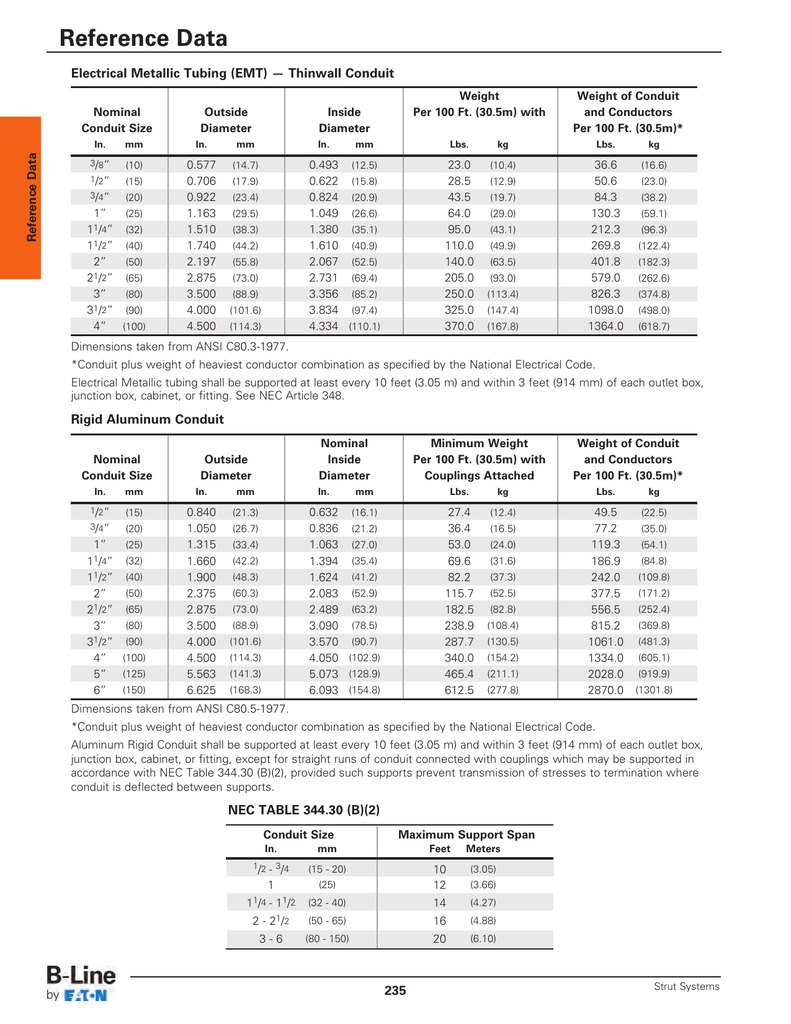
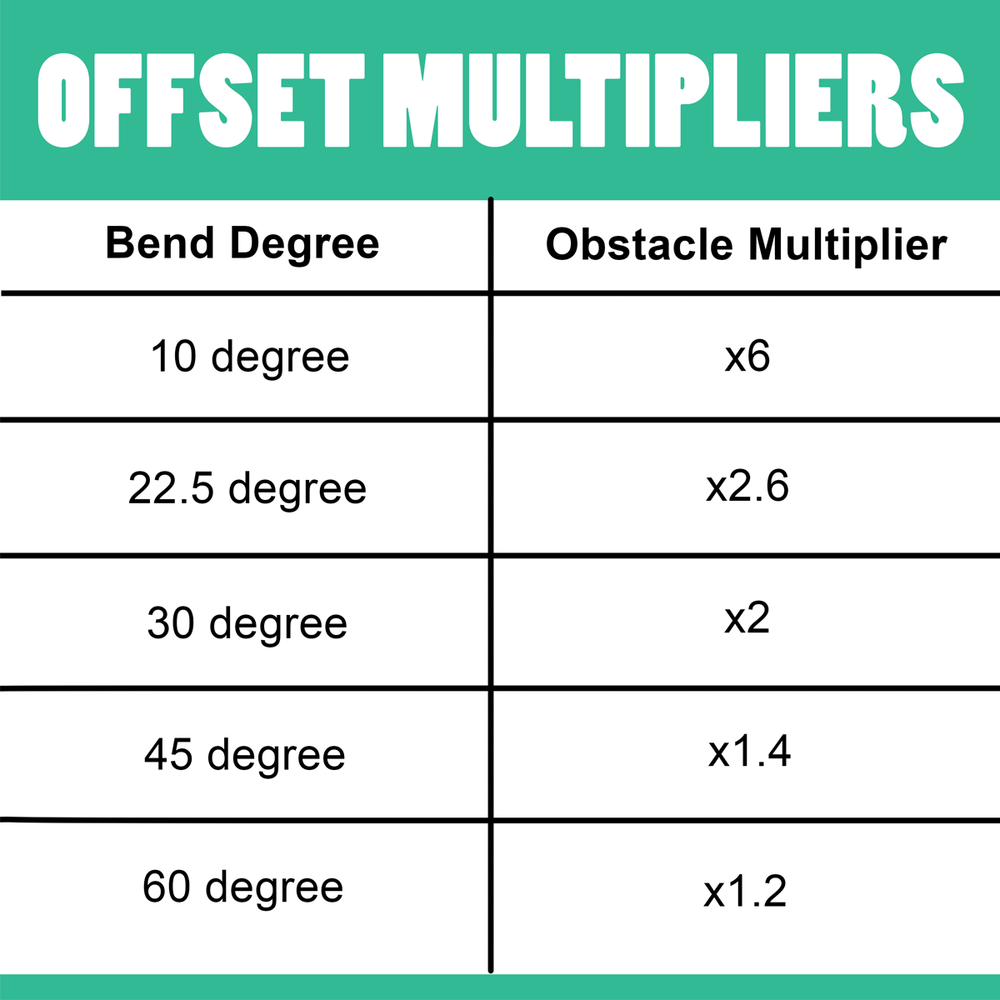
Emt Offset Chart - A conduit bending guide on how to bend an offset. Use this to shift the conduit to avoid an obstacle or change elevation, the continue in its original direction. Line up the bender's arrow (b) with the first mark. The choice of degree is Keep in mind that shallow bends make for easier wire pulling, steeper bends conserve space. The national electric code (nec) specifies a minimum radius for conduit bends in order to avoid damage to both the conduit and conductors. If bending at 10 degrees, the conduit will shrink 1/16 for every inch of rise. This page incorporates a comprehensive conduit bending guide and describes how to bend an offset using multipliers. An offset bend requires you to bend the conduit in two places at opposite angles, usually between 10 and 45 degrees. Web use offset bends to shift the position of the conduit. The angle d is the angle at which the conduit is bent. As an example, the offset distance of the obstacle is 6” and the distance to obstacle is 20”. Calculate the proper values to mark on the conduit to clear the obstacle and fit in the gap measured. This page incorporates a comprehensive conduit bending guide and describes how. Web in the diagram below, the heavy black line represents the bent piece of conduit; The code further specifies that the total of all bends in a conduit run must not exceed 360°. The choice of degree is Web how to make an offset bend the offset bend is used when an obstruction requires a change in the conduit’s plane.. The installation allows for a 45° x 45° offset bend. The green triangle shows some useful lengths and angles. The green triangle shows some useful lengths and angles. Calculate and mark where the conduit will be bent. Line up the bender's arrow (b) with the first mark. Use this to shift the conduit to avoid an obstacle or change elevation, the continue in its original direction. 15 degrees is 1/8 for every inch, 22.5 is 3/16, 30 is 1/4, 45 is 3/8 and 60 is 1/2. The green triangle shows some useful lengths and angles. Web one of the more common bends made in electrical conduit is. Use this to shift the conduit to avoid an obstacle or change elevation, the continue in its original direction. The angle d is the angle at which the conduit is bent. Web using a triangle to understand an offset the pipe above is bent into an offset. Web in the diagram below, the heavy black line represents the bent piece. Keep in mind, when bending offsets, the conduit will shrink. Calculate and mark where the conduit will be bent. A conduit bending guide on how to bend an offset. In the diagram below, the heavy black line represents the bent piece of conduit; An offset bend requires you to bend the conduit in two places at opposite angles, usually between. The green triangle shows some useful lengths and angles. Keep in mind, when bending offsets, the conduit will shrink. Use this to shift the conduit to avoid an obstacle or change elevation, the continue in its original direction. Calculate and mark where the conduit will be bent. In the diagram below, the heavy black line represents the bent piece of. In the diagram below, the heavy black line represents the bent piece of conduit; Necessary charts and tables for multipliers and decimal to fractions are included: Calculate and mark where the conduit will be bent. Web using a triangle to understand an offset the pipe above is bent into an offset. 15 degrees is 1/8 for every inch, 22.5 is. Keep in mind that shallow bends make for easier wire pulling, steeper bends conserve space. The choice of degree is The angle d is the angle at which the conduit is bent. The green triangle shows some useful lengths and angles. Web using a triangle to understand an offset the pipe above is bent into an offset. Keep in mind that shallow bends make for easier wire pulling, steeper bends conserve space. 15 degrees is 1/8 for every inch, 22.5 is 3/16, 30 is 1/4, 45 is 3/8 and 60 is 1/2. The angle d is the angle at which the conduit is bent. An offset bend requires you to bend the conduit in two places at. Necessary charts and tables for multipliers and decimal to fractions are included: This page incorporates a comprehensive conduit bending guide and describes how to bend an offset using multipliers. The installation allows for a 45° x 45° offset bend. Web in the diagram below, the heavy black line represents the bent piece of conduit; Web use offset bends to shift the position of the conduit. In the diagram below, the heavy black line represents the bent piece of conduit; Keep in mind that shallow bends make for easier wire pulling, steeper bends conserve space. Use this to shift the conduit to avoid an obstacle or change elevation, the continue in its original direction. If bending at 10 degrees, the conduit will shrink 1/16 for every inch of rise. The code further specifies that the total of all bends in a conduit run must not exceed 360°. The choice of degree is Calculate and mark where the conduit will be bent. Keep in mind, when bending offsets, the conduit will shrink. The angle d is the angle at which the conduit is bent. As an example, the offset distance of the obstacle is 6” and the distance to obstacle is 20”. The national electric code (nec) specifies a minimum radius for conduit bends in order to avoid damage to both the conduit and conductors.
1/2 Emt Offset Chart

1/2 Emt Offset Chart

Emt Offset Chart

How To Bend Conduit change comin
Emt Offset Bending Chart
How To Bend An Offset In 34 Emt

Emt Offset Chart
Emt Conduit Offset Chart
3/4 Emt Shrinkage Chart

1/2 Emt Offset Chart
Calculate The Proper Values To Mark On The Conduit To Clear The Obstacle And Fit In The Gap Measured.
Web One Of The More Common Bends Made In Electrical Conduit Is The Offset Bend.
The Green Triangle Shows Some Useful Lengths And Angles.
A Conduit Bending Guide On How To Bend An Offset.
Related Post: