Electron Energy Levels Chart
Electron Energy Levels Chart - Web each electron shell has a different energy level, with those shells closest to the nucleus being lower in energy than those farther from the nucleus. “coconut water is one of the highest sources of natural electrolytes,” says melissa mitri, rd, owner of melissa mitri nutrition. The 2s has lower energy when compared to 2p. How many orbitals are there at this energy level? Web we build electron configurations by filling the lowest energy orbitals first then filling progressively higher energy orbitals. This handy chart compiles the electron configurations of the elements up through number 104. In this lesson, they will focus on the arrangement of the electrons in each element. These stationary states/ energy levels for an electron are numbered as n = 1, 2, 3………. Drawing a shell model diagram and an energy diagram for hydrogen, and then using the diagrams to calculate the energy required to excite an electron between different energy levels. Web valence electrons chart for all elements. This is known as the aufbau principal. Web we build electron configurations by filling the lowest energy orbitals first then filling progressively higher energy orbitals. The 2s has lower energy when compared to 2p. But for most of the transition and inner transition elements, the valence electrons are the electrons present in the shells outside the noble gas core. Chemists. This chart clearly displays relative energy levels for all the electrons in the atom. Introduce students to the idea that electrons surround the nucleus of an atom in regions called energy levels. Web different orbits in which electrons revolve are known as stationary states or energy levels. Web the electron configurations and orbital diagrams of these four elements are: An. Web rank the energy levels of subshells based on the aufbau principle for filling electrons in orbitals ; Web different orbits in which electrons revolve are known as stationary states or energy levels. We can tell that the two electrons in the model above are at the same energy level because they are on the same ring. The 2s has. Web calculating electron energy for levels n=1 to 3. Web we build electron configurations by filling the lowest energy orbitals first then filling progressively higher energy orbitals. “it has an ideal ratio of potassium to sodium, two essential electrolytes for hydration,” she says. Web electron configuration chart and hund's rule. How many electrons can the fourth energy level have? The alkali metal sodium (atomic number 11) has one more electron than the neon atom. Because of the effects of shielding and the different radial distributions of orbitals with the same value of n but different values of l, the different subshells are not degenerate in. Explore book buy on amazon. Remember that the total number of electrons just equals. Web shown here is the first balmer transition, in which an electron jumps from orbit n = 3 to orbit n = 2, producing a photon of red light with an energy of 1.89 ev and a wavelength of 656 nanometres. “coconut water is one of the highest sources of natural electrolytes,” says melissa mitri, rd, owner of melissa mitri. Explain the ranking order of subshells using effective nuclear charge To write down the electron configuration of a given atom, we use general rules: Web different orbits in which electrons revolve are known as stationary states or energy levels. Web electrons can either jump to a higher energy level by absorbing, or gaining energy, or drop to a lower energy. The chart wipes clean with a damp cloth. According to bohr's theory, electrons of an atom revolve around the nucleus on certain orbits, or electron shells. Because of the effects of shielding and the different radial distributions of orbitals with the same value of n but different values of l, the different subshells are not degenerate in. Introduce students to. Remember that the total number of electrons just equals the total number of protons, and so the superscripts add up to 8, the atomic number of oxygen. Web shown here is the first balmer transition, in which an electron jumps from orbit n = 3 to orbit n = 2, producing a photon of red light with an energy of. It serves as a generic template for the atom, graphing electron energy level by orbit. The 2s has lower energy when compared to 2p. Web in this section we will discuss the energy level of the electron of a hydrogen atom, and how it changes as the electron undergoes transition. So we fill subshells in the order 1s 2s 2p. The 2s has lower energy when compared to 2p. Chemists sometimes use an energy level diagram to represent electrons when they’re looking at chemical reactions and bonding. Web the electron configuration of an atom of any element is the of electrons per sublevel of the energy levels of an atom in its ground state. According to bohr's theory, electrons of an atom revolve around the nucleus on certain orbits, or electron shells. Web electron configuration chart and hund's rule. To write down the electron configuration of a given atom, we use general rules: At energy level 2, there are both s and p orbitals. Web figure 2.5.10 orbital energy level diagram for a typical multielectron atom. An energy level diagram is more useful and easier to work with than quantum numbers in the quantum mechanical model. It serves as a generic template for the atom, graphing electron energy level by orbit. Web below is a blank energy level diagram which helps you depict electrons for any specific atom. Web rank the energy levels of subshells based on the aufbau principle for filling electrons in orbitals ; In this lesson, they will focus on the arrangement of the electrons in each element. Because of the effects of shielding and the different radial distributions of orbitals with the same value of n but different values of l, the different subshells are not degenerate in. We can tell that the two electrons in the model above are at the same energy level because they are on the same ring. These stationary states/ energy levels for an electron are numbered as n = 1, 2, 3……….
Electrons In Energy Levels Chart
Electron Energy Levels Chart
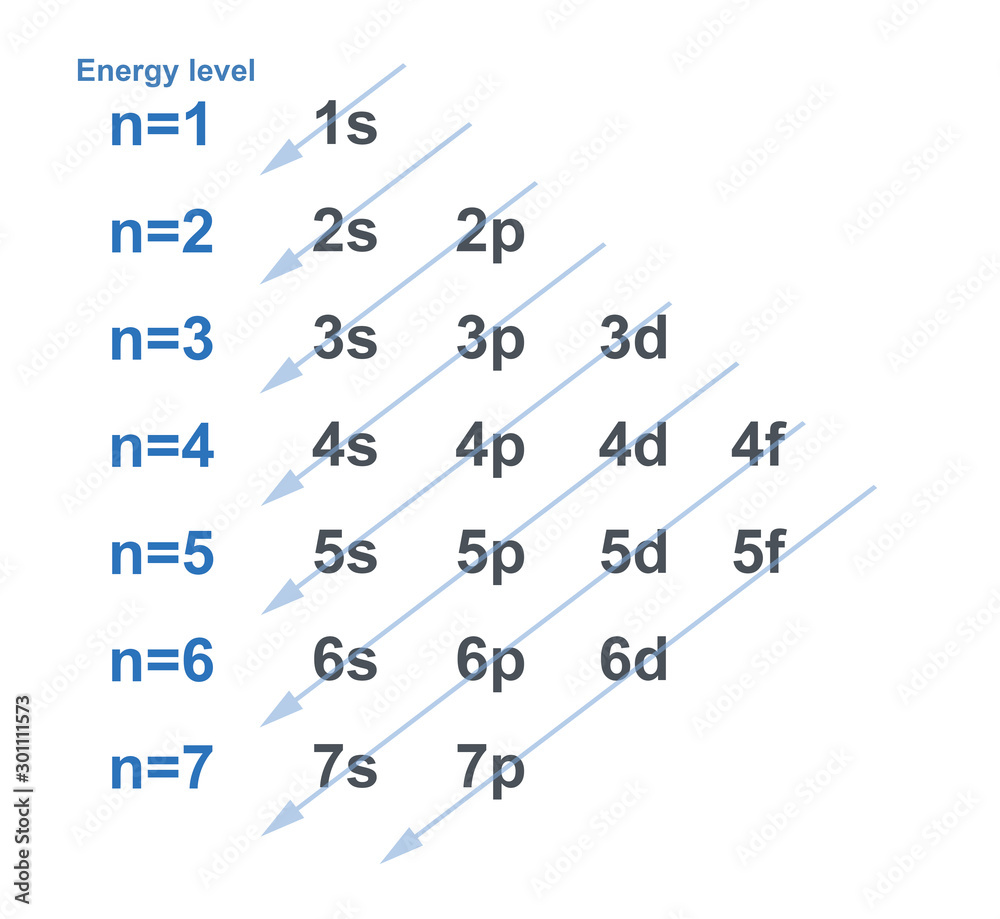
chart of electron configuration with each energy level for element in
/800px-Orbital_representation_diagram.svg-589bd6285f9b58819cfd8460.png)
Electron Configuration Chart

Atom Electrons, Orbitals, Energy Britannica

Electron Energy Levels Chart
Energy Levels, Sublevels, Electrons
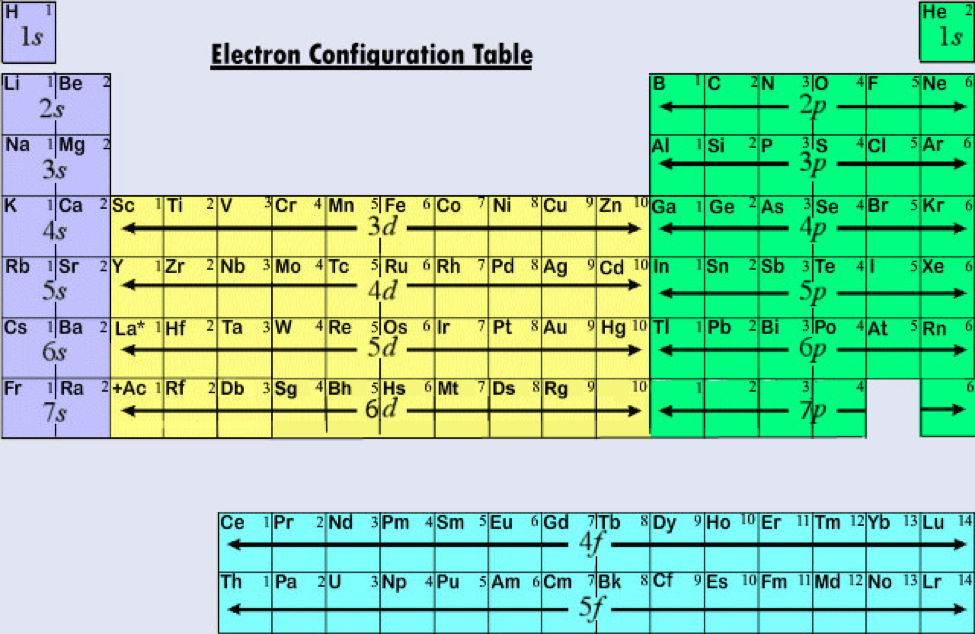
Electron Configurations Orbitals, Energy Levels and Ionisation Energy
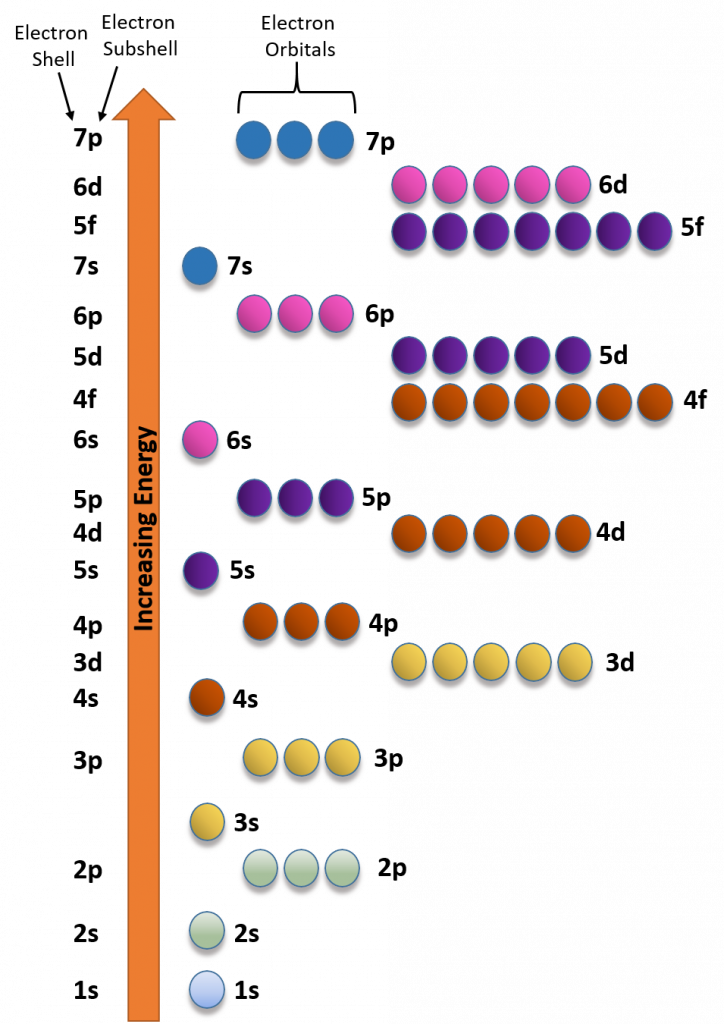
CH150 Chapter 2 Atoms and Periodic Table Chemistry

Chem Complete Electron Configurations Scientific Tutor
The Alkali Metal Sodium (Atomic Number 11) Has One More Electron Than The Neon Atom.
Web The Tiny Superscripts Say How Many Electrons Live In Each Orbital, The Letters Represent The Orbitals That Are Available, And The Big Numbers Say Which Energy Level The Orbitals Are Found In.
Web In This Section We Will Discuss The Energy Level Of The Electron Of A Hydrogen Atom, And How It Changes As The Electron Undergoes Transition.
This Chart Clearly Displays Relative Energy Levels For All The Electrons In The Atom.
Related Post:

.PNG)