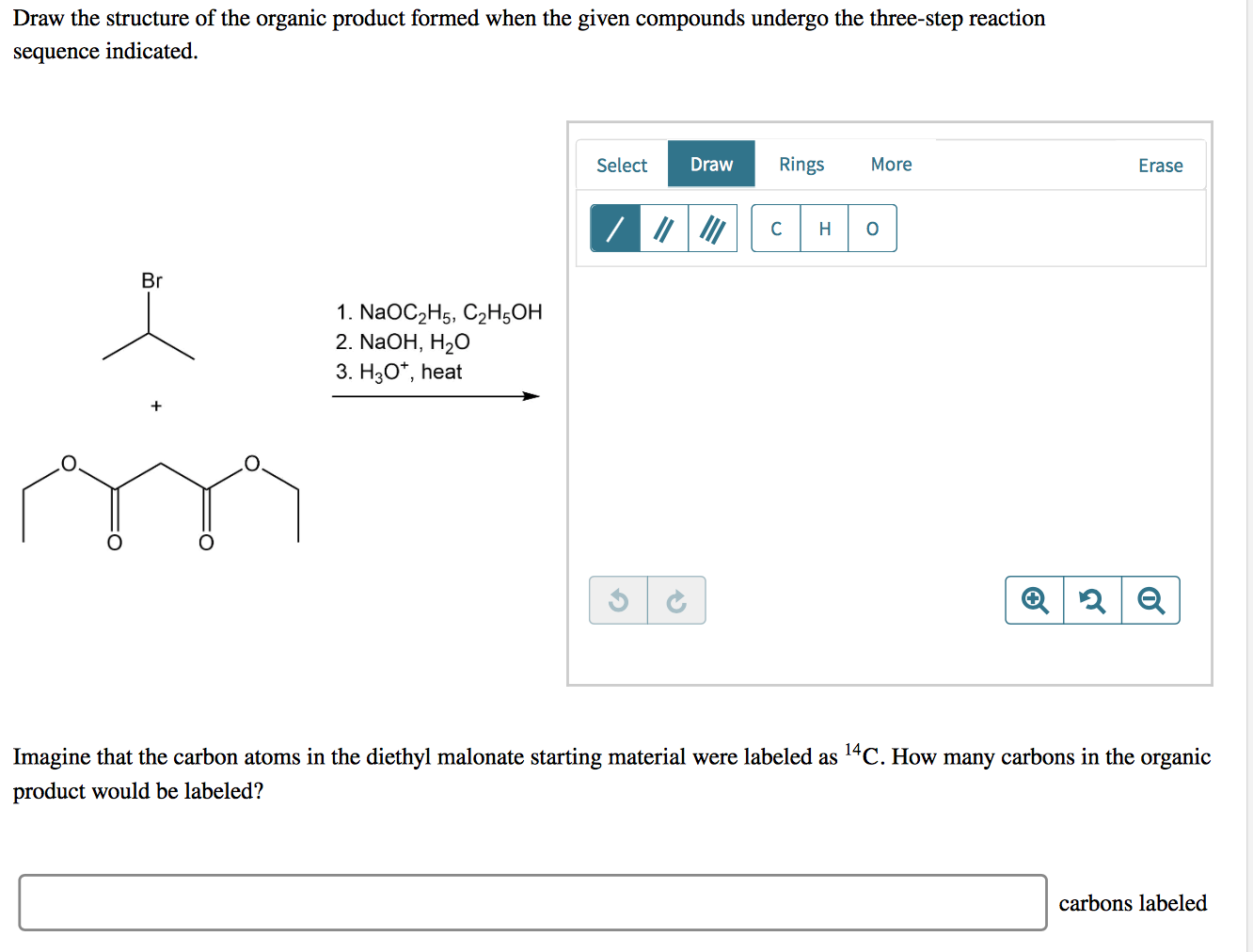
Draw The Remaining Product Of The Reaction
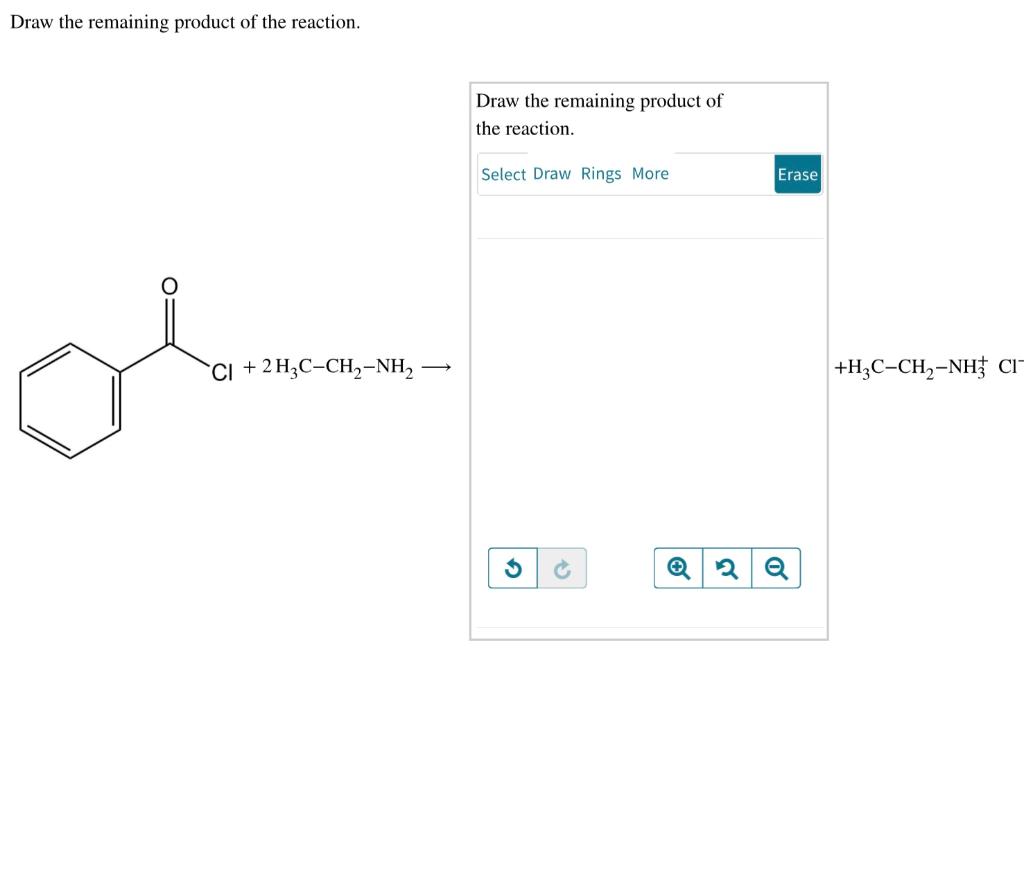
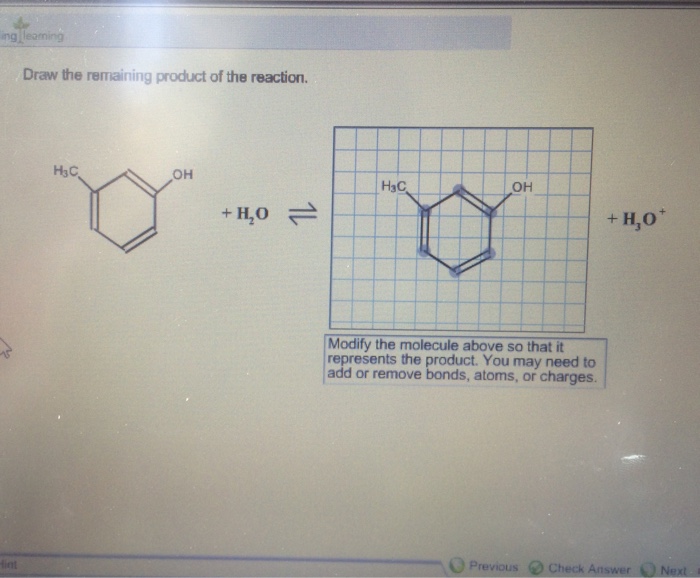
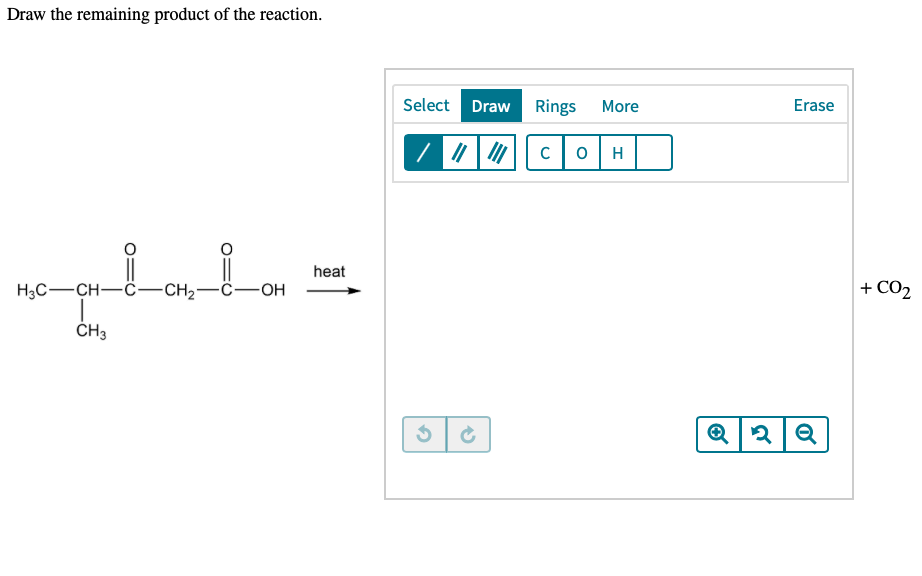
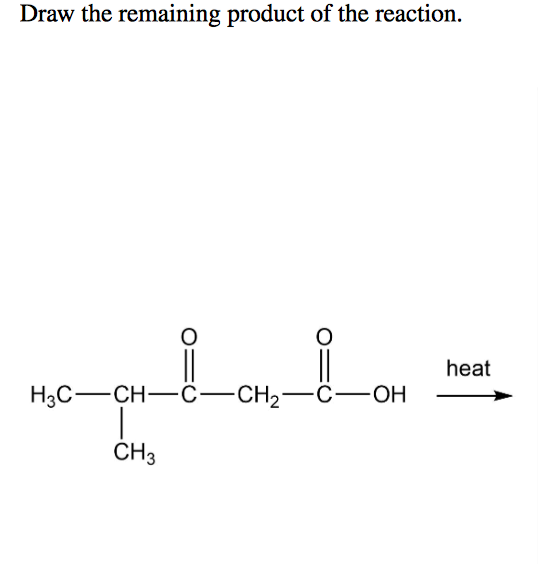
Draw The Remaining Product Of The Reaction - Select draw rings more erase c o h heat ཡོད་རིགས་བང་ཡི་ཡབ་ + co2 གྱི a ཞ. Modify the molecule so that it represents the product. Here in the above reaction acid chloride reacts with 2 mo. Web the product formed when the bond to h is broken is called the conjugate base. Derive the rate law consistent with a given reaction mechanism. Modify the molecule to show the product. Here’s the best way to solve it. Products are the end result of the. The product formed when the bond to h is formed is called the conjugate acid. Web to determine the remaining product of the given reaction, we first need to identify the reactants and the type of reaction taking place. Here in the above reaction acid chloride reacts with 2 mo. Select draw rings more erase c o h heat ཡོད་རིགས་བང་ཡི་ཡབ་ + co2 གྱི a ཞ. Web a chemical equation describes a chemical reaction. Web in a chemical reaction, the atoms and molecules that interact with each other are called reactants. Web draw the remaining product of the following reaction. Web 2ch3oh(l) + 3o2(g) → 2co2(g) + 4h2o(g) + energy. Modify the molecule to show the product. Web the remaining product will be ch3ch(ch3)coch3. If you need to reset your. Here in the above reaction acid chloride reacts with 2 mo. Draw the remaining product of the reaction. Web draw the remaining product of the following reaction. If you need to reset your. What type of reaction is this? Modify the molecule so that it represents the product. Sketch out an activation energy diagram for a multistep mechanism. Draw the remaining product of the following reaction. Draw the remaining product of the reaction. Derive the rate law consistent with a given reaction mechanism. Web draw the remaining product of the following reaction. What type of reaction is this? Draw the remaining product of the reaction. Web the remaining product will be ch3ch(ch3)coch3. Web write a balanced chemical equation for a process given its reaction mechanism. Products are the end result of the. Modify the molecule to show the product. View the full answer step 2. Draw the product(s) of the following reaction. Web the product formed when the bond to h is broken is called the conjugate base. Web in a chemical reaction, the atoms and molecules that interact with each other are called reactants. View the full answer step 2. If a covalent single bond is broken so that one electron of the shared pair remains with. Draw the remaining product of the reaction. Web write a balanced chemical equation for a process given its reaction mechanism. Modify the molecule so that it represents the product. Modify the molecule to show the product. Web write a balanced chemical equation for a process given its reaction mechanism. Web the product formed when the bond to h is broken is called the conjugate base. Draw the remaining product of the reaction. Web 2ch3oh(l) + 3o2(g) → 2co2(g) + 4h2o(g) + energy. Web write a balanced chemical equation for a process given its reaction mechanism. If you need to reset your. Web in a chemical reaction, the atoms and molecules that interact with each other are called reactants. Web define an elementary reaction, and state how it differs from an ordinary net chemical reaction. Decarboxylation is a chemical reaction that removes a. Web write a balanced chemical equation for a process given its reaction mechanism. Web a chemical equation describes a chemical reaction. Web the remaining product will be ch3ch(ch3)coch3. Derive the rate law consistent with a given reaction mechanism. The product formed when the bond to h is formed is called the conjugate acid. What type of reaction is this? Web the product formed when the bond to h is broken is called the conjugate base. Draw the remaining product of the reaction. Web ' predict the product of the following reaction: Sketch out an activation energy diagram for a multistep mechanism. Draw the remaining product of the reaction. Draw the remaining product of the following reaction. Here’s the best way to solve it. You may need to add or remove bonds, atoms, or charges. Decarboxylation is a chemical reaction that removes a carboxyl group. +h20'_—' h30 oh modify the molecule. Modify the molecule to show the product. If a covalent single bond is broken so that one electron of the shared pair remains with. Your solution’s ready to go! Draw the product(s) of the following reaction. Here in the above reaction acid chloride reacts with 2 mo.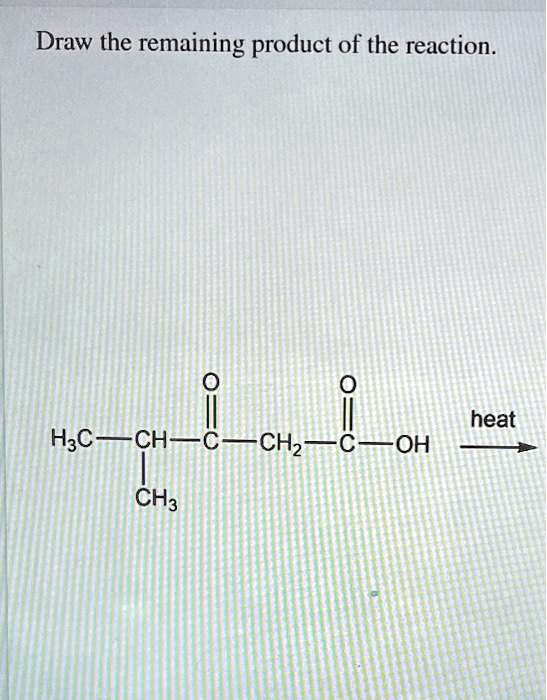
SOLVED Draw the remaining product of the reaction. heat H2C=CHOH CH3
Solved Draw the remaining product of the reaction. Draw the
Solved Draw the remaining product of the reaction. H3C. OH
Solved Draw the remaining product of the reaction. Select
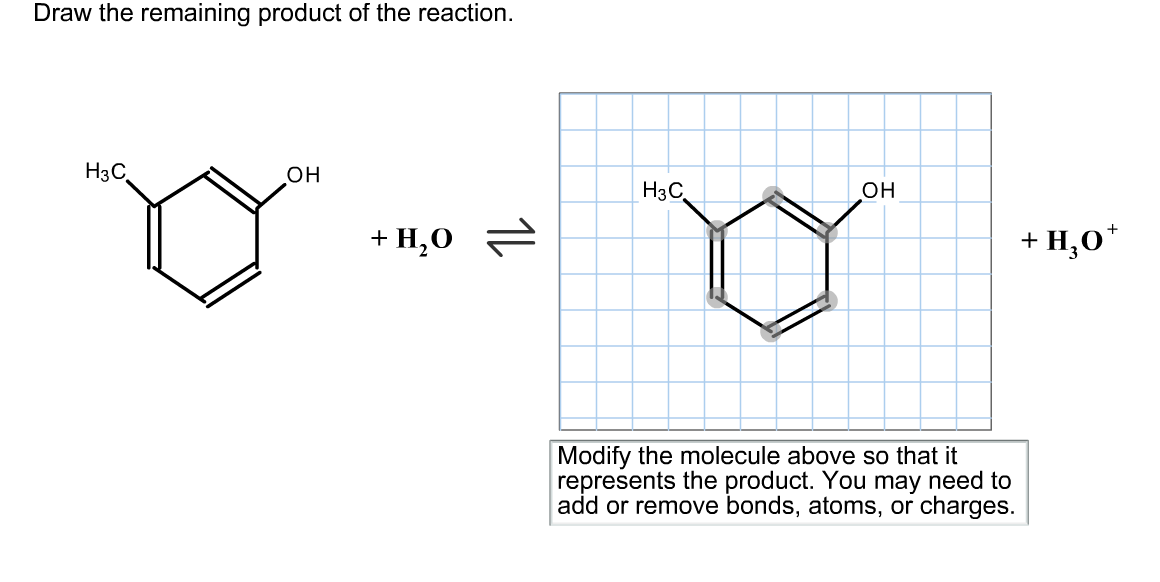
Solved Draw the remaining product of the reaction.
Solved Draw the remaining product of the reaction. 0 heat
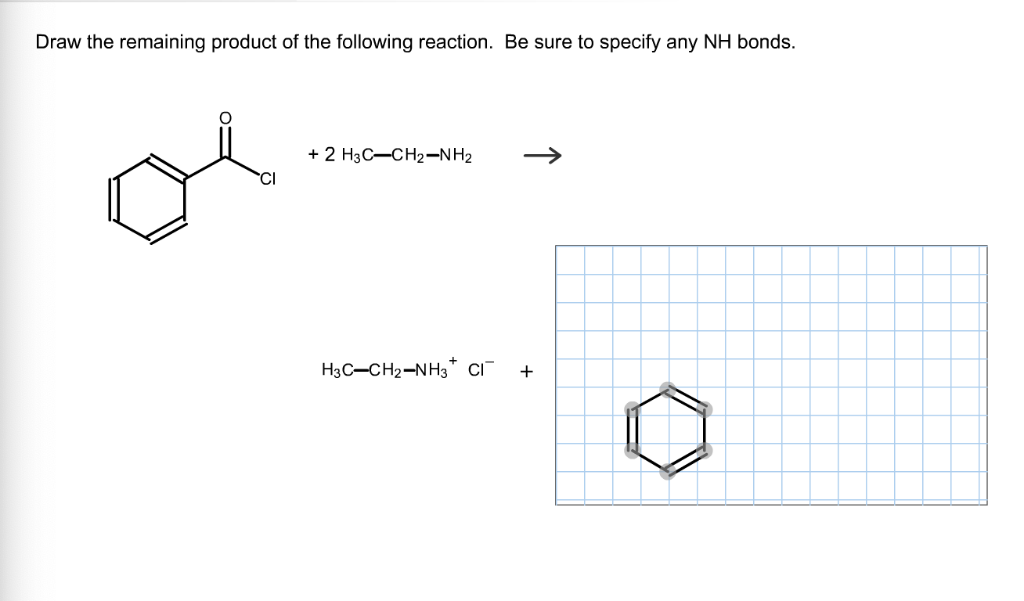
Solved Draw the remaining product of the following reaction.
Solved Draw the remaining product of the reaction. 0 heat

SOLVED Draw the remaining product of the reaction. heat H2C=CHOH CH3
Draw the Remaining Product of the Reaction OliverhasCharles
In A Chemical Reaction, The Atoms And Molecules Produced.
Web 2Ch3Oh(L) + 3O2(G) → 2Co2(G) + 4H2O(G) + Energy.
Derive The Rate Law Consistent With A Given Reaction Mechanism.
Web Draw The Structure For The Reactant (A), Intermediate Product (B), And The Final Product (C) In Each Of The Following Reactions.
Related Post: