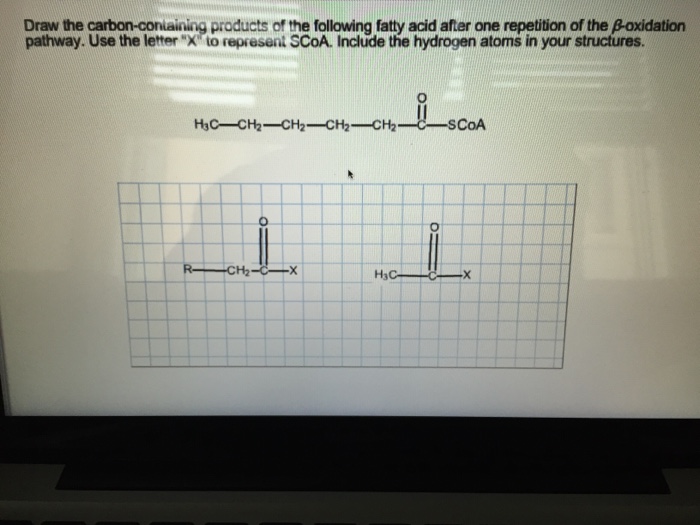
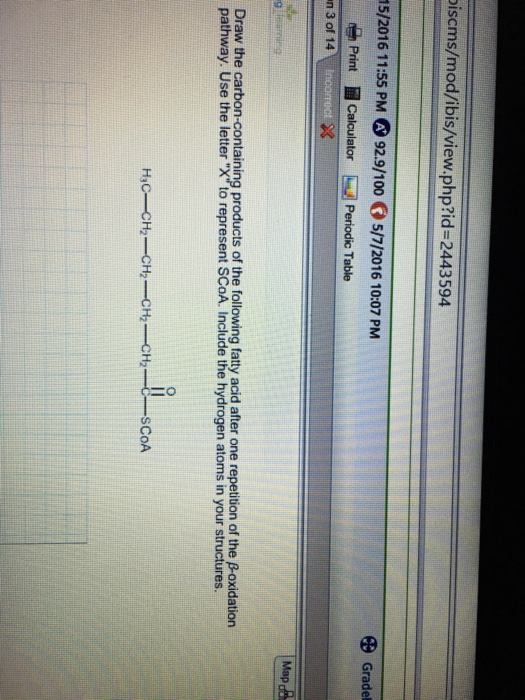
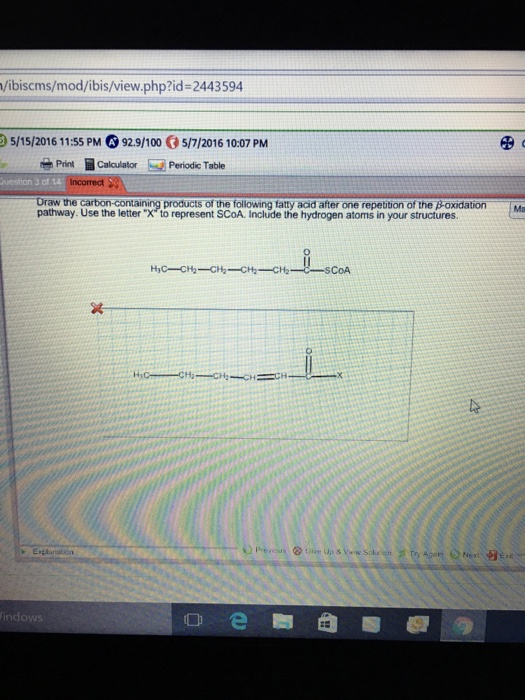
Draw The Carbon Containing Products Of The Fatty Acid
Draw The Carbon Containing Products Of The Fatty Acid - Include the hydrogen atoms in your structures. Most fatty acids are unbranched and. Web consider the fatty acid. The fatty acid has the formula c h 3 c h 2 c h 2 c h 2 c h 2 c o s c o a. Some fatty acids have double bonds, which changes the structure. The final reaction is cleavage of the β. Triglycerides are formed through dehydration reactions. It is said that a fatty acid will usually have an even number of carbons. 1 acetyl coa is released from the fatty acid carbon chain for each. Web fatty acids are carboxylic acids that are the structural components of many lipids. They may be saturated or unsaturated. The final reaction is cleavage of the β. It is said that a fatty acid will usually have an even number of carbons. Since there is only one double bond, oleic acid is an example of a. Web the overall structure of fatty acids is long hydrocarbon chains of various lengths and degrees of. Triglycerides are formed through dehydration reactions. Most fatty acids are unbranched and. They may be saturated or unsaturated. Most fatty acids are unbranched and. Since there is only one double bond, oleic acid is an example of a. Some fatty acids have double bonds, which changes the structure. Use the letter x to represent scoa. The final reaction is cleavage of the β. It is said that a fatty acid will usually have an even number of carbons. They may be saturated or unsaturated. They may be saturated or unsaturated. Use the letter x to represent scoa. Generally, a fatty acid consists of a straight chain of an even number of carbon atoms, with hydrogen atoms along the length of the chain and at one end of the chain and a carboxyl group (―cooh) at the other end. To recognize the structures of common. Most fatty acids are unbranched and. It is said that a fatty acid will usually have an even number of carbons. Web triglycerides, or fats, are formed from the combination of glycerol and three fatty acid molecules. Most fatty acids are unbranched and. Web fatty acids are carboxylic acids that are the structural components of many lipids. Web triglycerides, or fats, are formed from the combination of glycerol and three fatty acid molecules. The fatty acid has the formula c h 3 c h 2 c h 2 c h 2 c h 2 c o s c o a. Web fatty acids are carboxylic acids that are the structural components of many lipids. Most fatty acids. 1 acetyl coa is released from the fatty acid carbon chain for each. The fatty acid has the formula c h 3 c h 2 c h 2 c h 2 c h 2 c o s c o a. Use the letter x to represent scoa. To recognize the structures of common fatty acids and classify them as saturated,. Web fatty acids are carboxylic acids that are the structural components of many lipids. Web triglycerides, or fats, are formed from the combination of glycerol and three fatty acid molecules. Web fatty acids are carboxylic acids that are the structural components of many lipids. Web the overall structure of fatty acids is long hydrocarbon chains of various lengths and degrees. Since there is only one double bond, oleic acid is an example of a. Draw the carbon‑containing products of the fatty acid after one repetition of the. Web triglycerides, or fats, are formed from the combination of glycerol and three fatty acid molecules. Include the hydrogen atoms in your structures. Web the overall structure of fatty acids is long hydrocarbon. It is said that a fatty acid will usually have an even number of carbons. Web the overall structure of fatty acids is long hydrocarbon chains of various lengths and degrees of unsaturation terminated with carboxylic acid groups. Web fatty acids are carboxylic acids that are the structural components of many lipids. Most fatty acids are unbranched and. Generally, a. Most fatty acids are unbranched and. Use the letter x to represent scoa. Since there is only one double bond, oleic acid is an example of a. They may be saturated or unsaturated. Web fatty acids are carboxylic acids that are the structural components of many lipids. The final reaction is cleavage of the β. To recognize the structures of common fatty acids and classify them as saturated, monounsaturated, or polyunsaturated. 1 acetyl coa is released from the fatty acid carbon chain for each. Web your solution’s ready to go! It is said that a fatty acid will usually have an even number of carbons. Web the overall structure of fatty acids is long hydrocarbon chains of various lengths and degrees of unsaturation terminated with carboxylic acid groups. Web consider the fatty acid. Draw the carbon‑containing products of the fatty acid after one repetition of the. Include the hydrogen atoms in your structures. Generally, a fatty acid consists of a straight chain of an even number of carbon atoms, with hydrogen atoms along the length of the chain and at one end of the chain and a carboxyl group (―cooh) at the other end. Most fatty acids are unbranched and.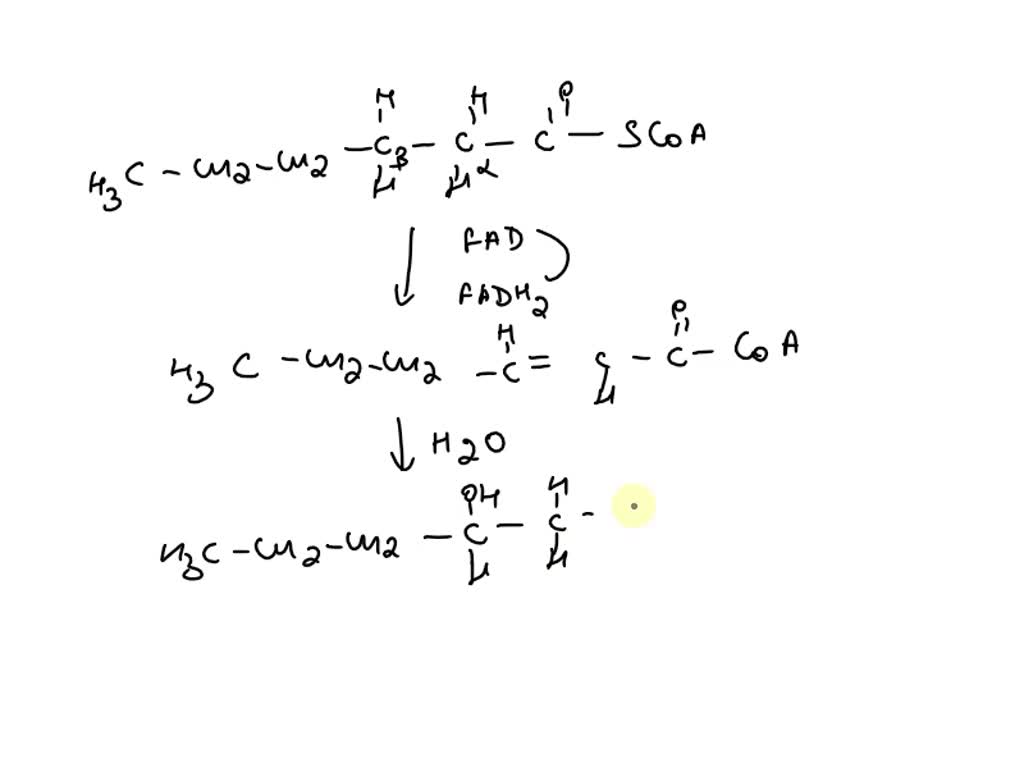
SOLVED Draw the carboncontaining products of the fatty acids after
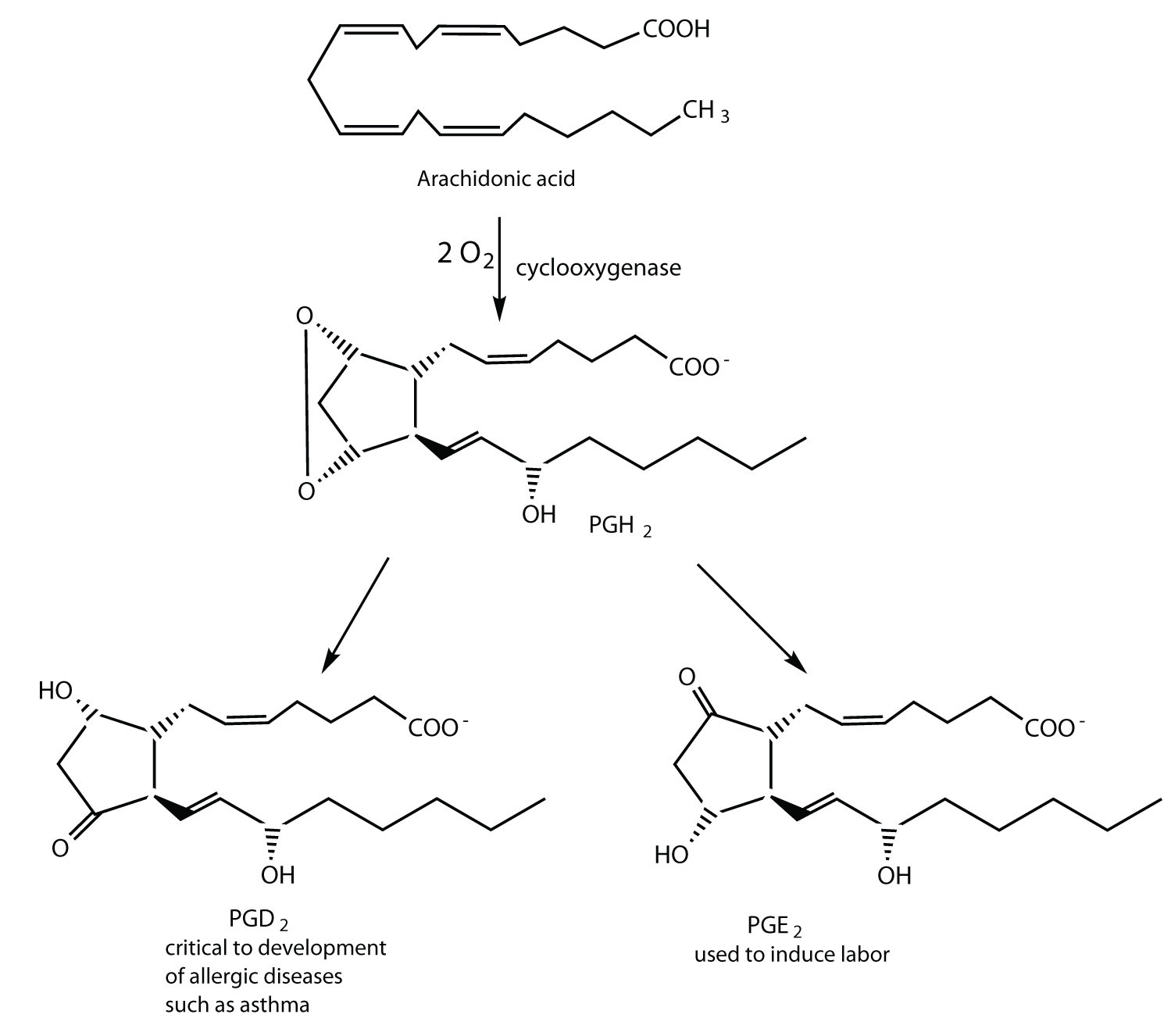
Fatty Acids
Solved Draw the carboncontaining products of the following
Solved Draw the carboncontaining products of the following
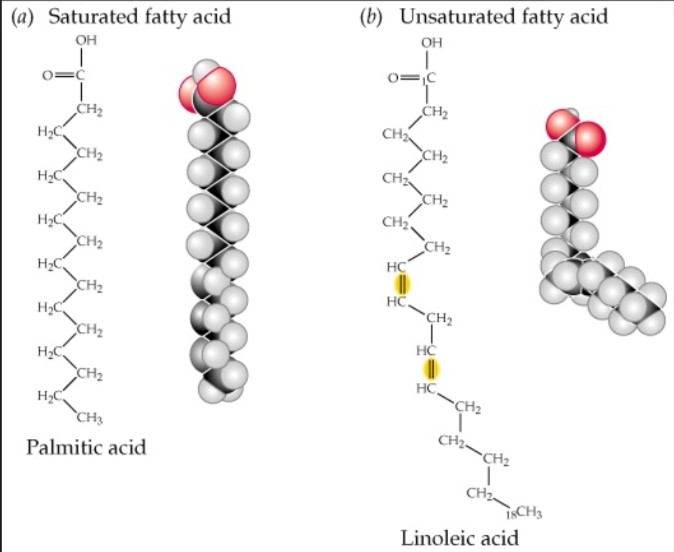
Fatty Acid General Structure

Fatty Acid Nomenclature Nutrition Course Hero
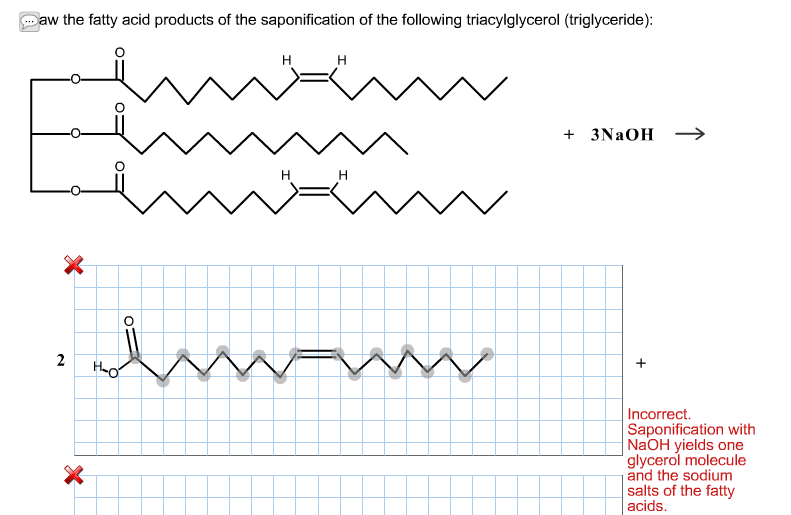
Solved Draw the fatty acid products of the saponification of
Solved Draw the carboncontaining products of the following

Fatty Acid Nomenclature Nutrition Course Hero
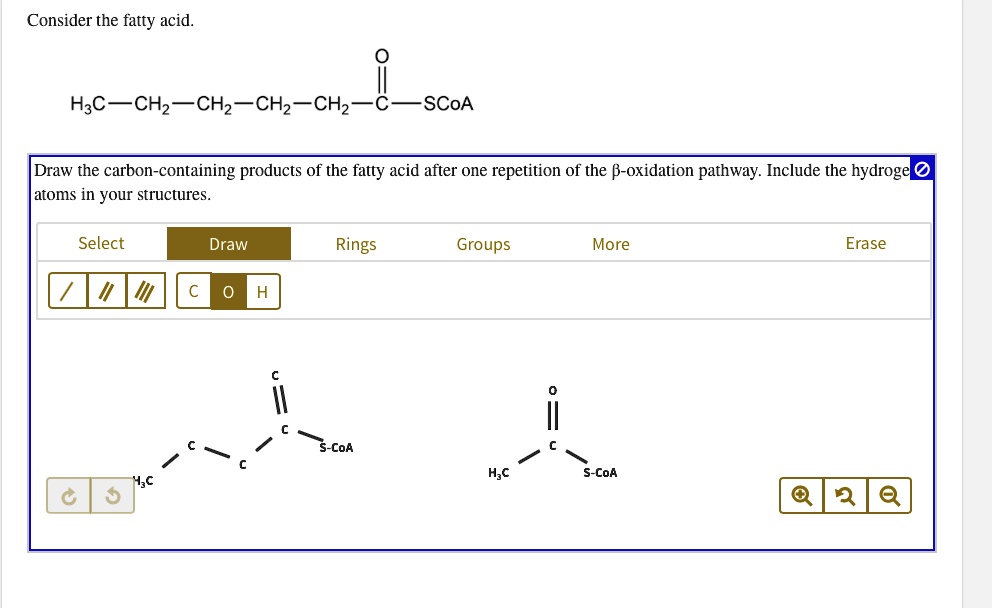
SOLVED Consider the fatty acid. H3CCH2CH2CH2 SCoA Draw the carbon
Triglycerides Are Formed Through Dehydration Reactions.
Some Fatty Acids Have Double Bonds, Which Changes The Structure.
They May Be Saturated Or Unsaturated.
The Fatty Acid Has The Formula C H 3 C H 2 C H 2 C H 2 C H 2 C O S C O A.
Related Post: