Cranial Drawer Test Dog
Cranial Drawer Test Dog - Check for cranial drawer with multiple Web craniocaudal translation remains present under passive manipulation (cranial drawer test) and is possible with sufficient anterior shear loading. Place one hand on the distal femur with the thumb on the caudal aspect of the condyle and the index and middle fingers on the patella. Web cranial drawer test landmarks •lateral fabella •patella •tibial tuberosity •fibular head partial vs. Diagnosis is based on the demonstration of a specific test, called the cranial drawer test. By manipulating the knee joint, they can detect abnormal forward. Web dogs having partial crcl tears typically show a painful response when the affected stifle is hyperextended. Place the thumb of the other hand on the fibular head and the index and middle fingers on the tibial tuberosity. 2 unlike humans — whose acl can tear as a result of a traumatic injury — a dog's ccl tear is usually due. This abnormal forward movement of the lower leg bone (tibia) in front of the thigh bone (femur). Web craniocaudal translation remains present under passive manipulation (cranial drawer test) and is possible with sufficient anterior shear loading. Web specific tests to evaluate the integrity of the cranial cruciate ligament include a cranial drawer test or a tibial compression test, which are used to determine if there is increased movement in the joint. Web a physical exam. Web specific. In dogs with chronic cruciate injuries, scar tissue develops on the medial (inside) of the affected knee, which is easily palpated during an exam and is called a medial buttress. Web a physical exam. Web during the lameness examination, your veterinarian will try to demonstrate a particular movement, called a cranial or anterior drawer sign. Ccl injury is diagnosed through. Web dogs having partial crcl tears typically show a painful response when the affected stifle is hyperextended. Web diagnosis of cranial cruciate ligament rupture is usually made by a positive cranial drawer sign. Web the cranial drawer test is performed most commonly and tends to be the mainstay of testing for stifle instability by general veterinarians. Ccl injury is diagnosed. In a mature dog, a healthy, intact cranial cruciate ligament will not permit cranial tibial translation with the stifle held in extension or in flexion.3 in an immature dog, puppy laxity may permit a few millimeters of cranial and caudal tibial translation, but. When it ruptures, abnormal movement of the joint occurs, resulting in pain and lameness. Web specific palpation. By manipulating the knee joint, they can detect abnormal forward. Web pain upon forced full extension of the stifle is a simple test that is suggestive of early crcld. 1 the ccl helps connect the femur (thigh bone) to the tibia (shin bone). They might show signs of stiffness, especially after periods of rest. Web this study evaluated how well. Web the cranial drawer test is performed most commonly and tends to be the mainstay of testing for stifle instability by general veterinarians. The key to the diagnosis of the ruptured cruciate ligament is the demonstration of an abnormal knee motion called a drawer sign. They might show signs of stiffness, especially after periods of rest. 1 the ccl helps. When it ruptures, abnormal movement of the joint occurs, resulting in pain and lameness. Web welcome to our canine physiotherapy tutorial video, where we will guide you through two essential diagnostic tests for evaluating cranial cruciate ligament (. Veterinarians use this diagnostic test to check for acl integrity. Web pain upon forced full extension of the stifle is a simple. This is best performed with the dog lying on its side in a. Web difficulty in mobility: Web this study evaluated how well preoperative findings correlated with arthroscopic assessment of ccl fiber damage in 29 dogs with complete ccl tears. Patients were assessed while awake, under sedation, and under anesthesia. Web definitive diagnosis of rupture of the ccl demands an. A physical exam allows a veterinarian to isolate which leg and joint is affected. In order to feel this, you dog will be placed on his/ her side, and the veterinarian will feel the knee for cranial drawer motion. The key to the diagnosis of the ruptured cruciate ligament is the demonstration of an abnormal knee motion called a drawer. 1 the ccl helps connect the femur (thigh bone) to the tibia (shin bone). Web similar to the anterior cruciate ligament (acl) in humans, the canine cranial cruciate ligament (ccl) is an important structure that stabilizes your dog’s knee joint. Web the diagnosis of cclr is typically based on the presence of the “cranial drawer sign”. Web the cranial drawer. It is performed by applying a force to the tibia while holding the femur stable, thereby creating craniocaudal translation of. Web this study evaluated how well preoperative findings correlated with arthroscopic assessment of ccl fiber damage in 29 dogs with complete ccl tears. They might show signs of stiffness, especially after periods of rest. Web diagnosis of cranial cruciate ligament rupture is usually made by a positive cranial drawer sign. Web welcome to our canine physiotherapy tutorial video, where we will guide you through two essential diagnostic tests for evaluating cranial cruciate ligament (. Web laxity of the stifle can be detected by cranial drawer or cranial tibial thrust procedures. Web similar to the anterior cruciate ligament (acl) in humans, the canine cranial cruciate ligament (ccl) is an important structure that stabilizes your dog’s knee joint. 1 the ccl helps connect the femur (thigh bone) to the tibia (shin bone). In general, radiographic images are used to visualize the instability of the stifle joint by tibial compression, to detect effusion and secondary osteoarthritic changes. Web specific tests to evaluate the integrity of the cranial cruciate ligament include a cranial drawer test or a tibial compression test, which are used to determine if there is increased movement in the joint. In this test, the dog’s knee is slightly bent and anterior pressure is applied to the distal femur while posterior pressure is applied to the proximal tibia. In dogs with chronic cruciate injuries, scar tissue develops on the medial (inside) of the affected knee, which is easily palpated during an exam and is called a medial buttress. Web difficulty in mobility: Web craniocaudal translation remains present under passive manipulation (cranial drawer test) and is possible with sufficient anterior shear loading. Web veterinary school instruction has traditionally emphasized teaching subtle and difficult manipulative physical examination procedures, such as cranial drawer sign and cranial tibial thrust, to definitively diagnose crclr. Web specific palpation techniques that veterinarians use to assess the crcl include the ‘cranial drawer test’ and the ‘tibial compression test.’ these tests can confirm abnormal motion within the knee consistent with rupture of the crcl.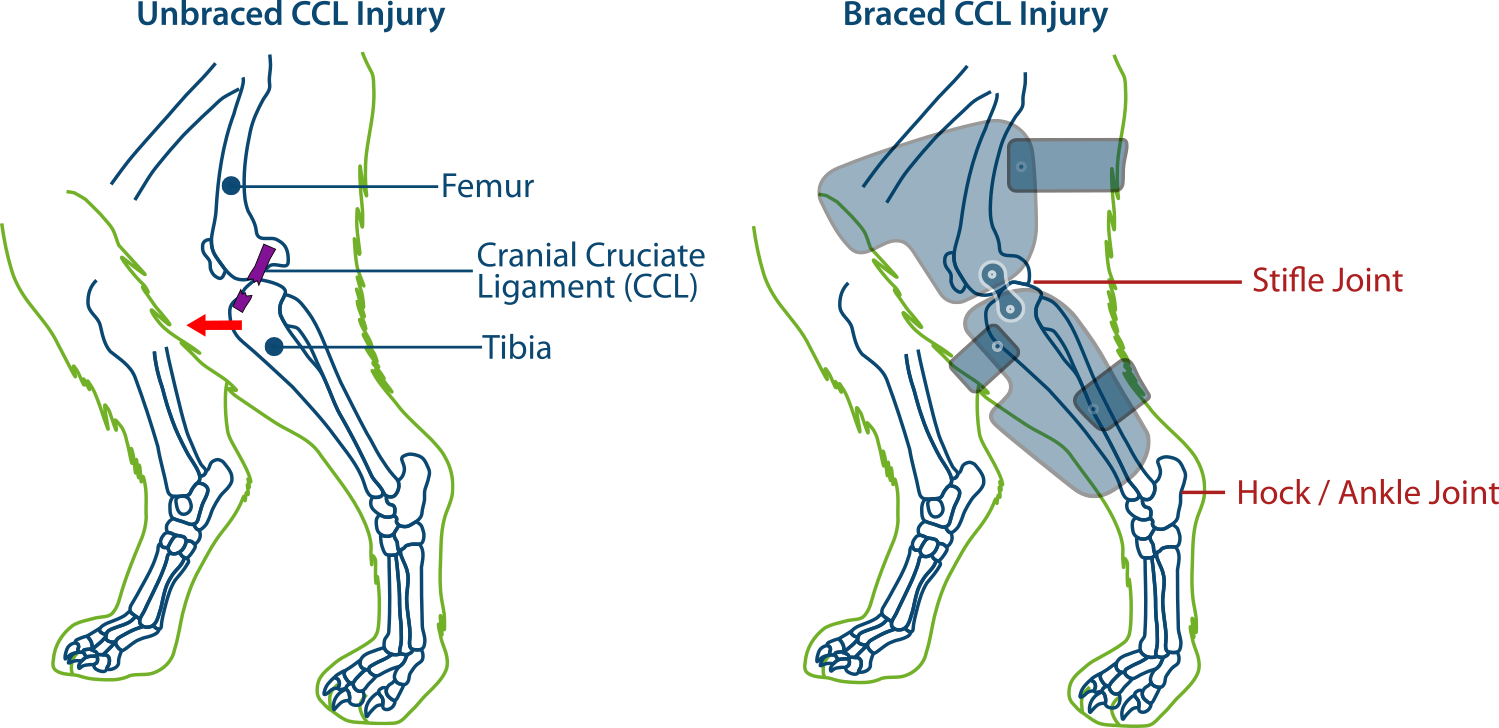
Dog Stifle CCL/ACL Injury Support Brace — PawOpedic

Canine Cruciate Ligament Damage — Impact Veterinary Physiotherapy

Cranial Cruciate Ligament Medical Diagram Torn Knee Ligament in Dogs

Cranial Nerve Assessment Cranial nerves, Pharmacology nursing, Vet school
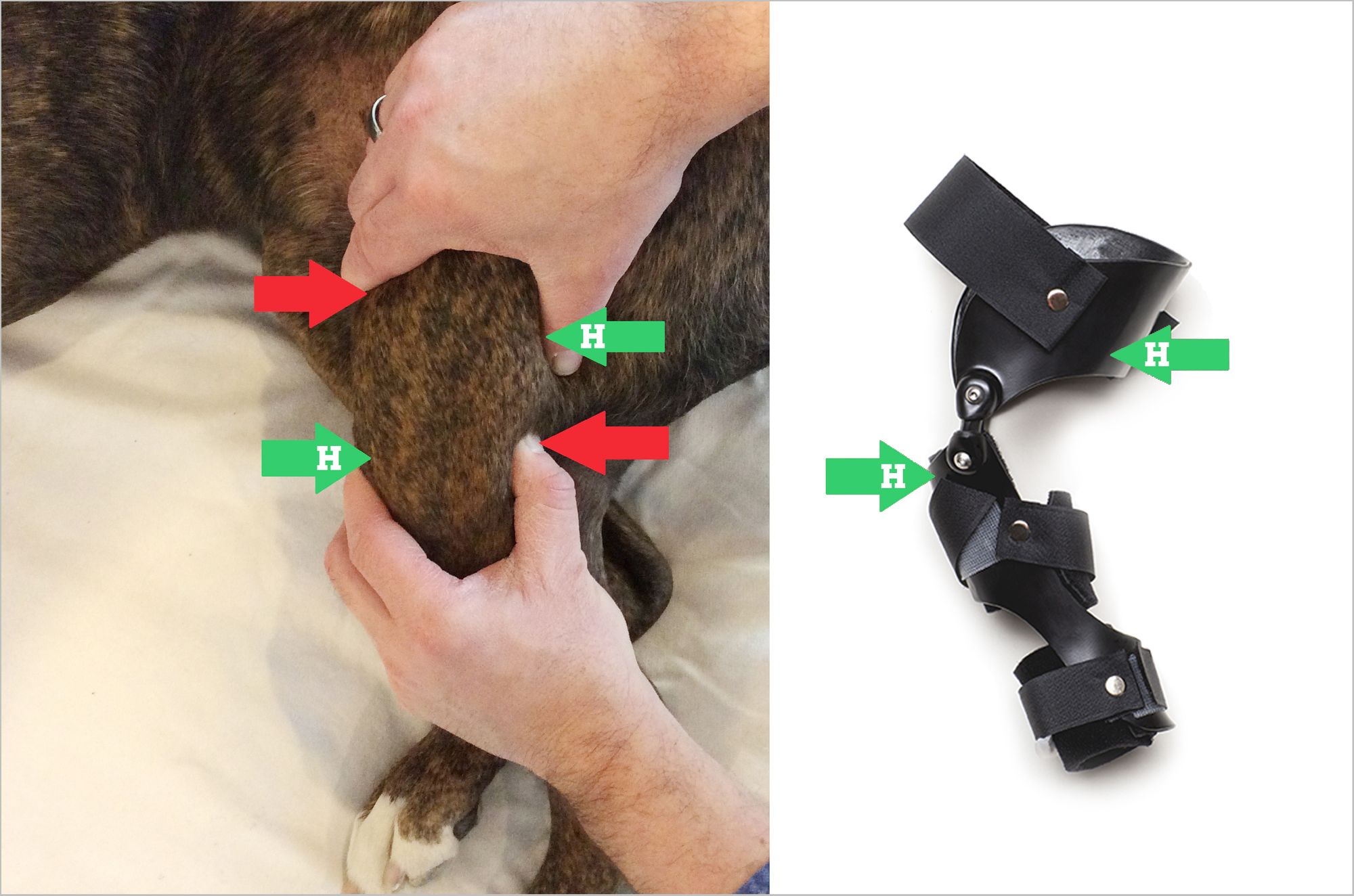
Torn ACL in Dogs How Braces Help

Dog with Cranial Drawer YouTube
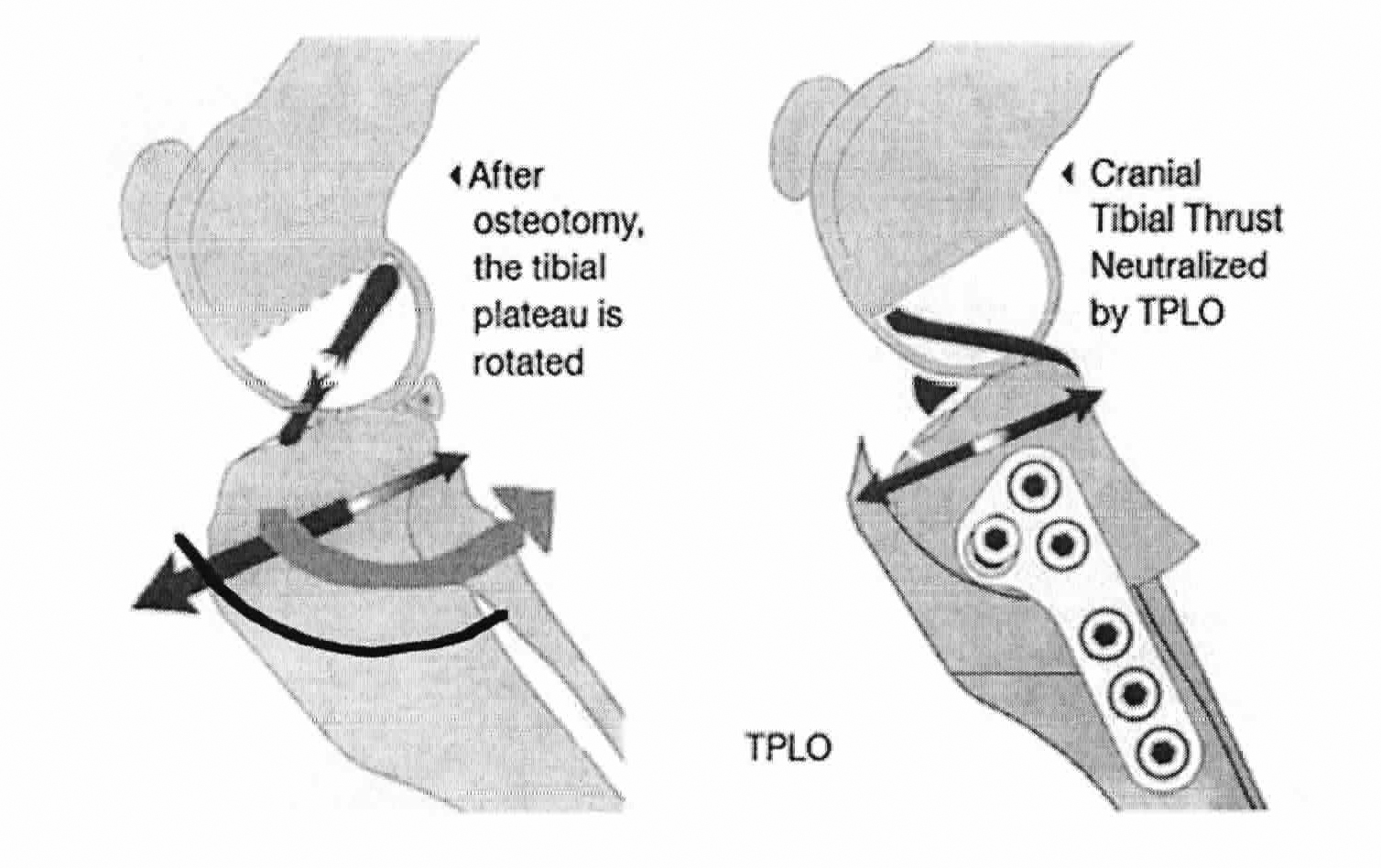
Tibial Plateau Leveling Osteotomy

Positive cranial drawer sign in a dog with a cranial (anterior

Cruciate Disease The Cranial Drawer Test YouTube

Pathology, Diagnosis, and Treatment Goals of Cranial Cruciate Ligament
Place One Hand On The Distal Femur With The Thumb On The Caudal Aspect Of The Condyle And The Index And Middle Fingers On The Patella.
Ccl Injury Is Diagnosed Through A Physical Exam And A Cranial Drawer Test, Which Functions To Elicit Instability Of The Joint.
Diagnosis Is Based On The Demonstration Of A Specific Test, Called The Cranial Drawer Test.
Web Dogs Are Often Seen By The Veterinarian In Either The Acute Stage Shortly After The Injury Or In The Chronic Stage Weeks Or Months Later.
Related Post: