Convection Currents Drawing
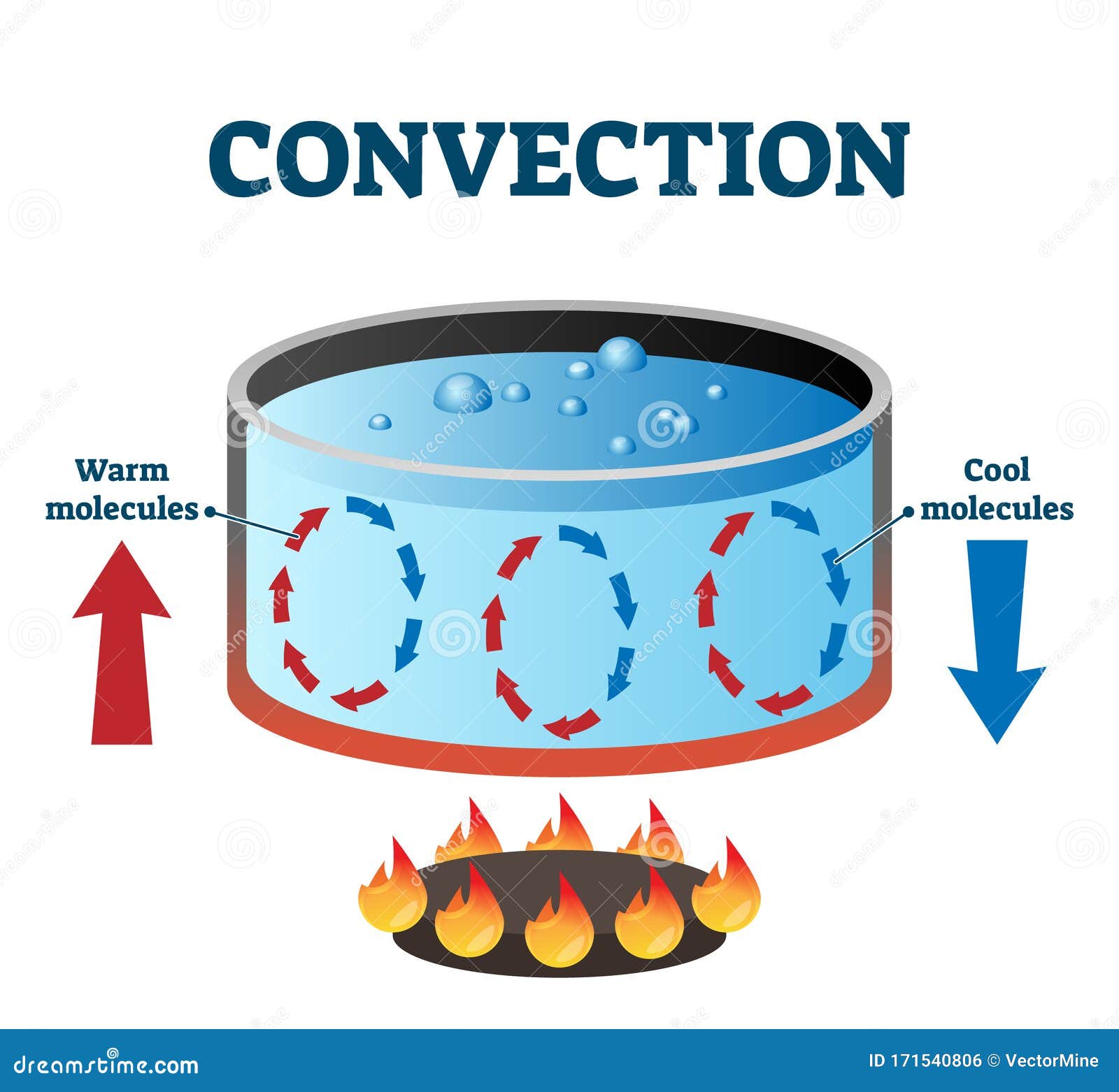
Convection Currents Drawing - (1) the heating and cooling of the fluid, (2)changes. Illustration of convection currents in heated water. Web convection is a process in which heat is carried from place to place by the bulk movement of a fluid and gases. Web an explanation of density and how to determine what floats. Diverging currents pull them apart. Here's a simple and visually appealing way to show convection currents in water. Web convection currents drive the movement of earth’s rigid tectonic plates in the planet’s fluid molten mantle. 4how does convection relate to. Web examples of convection. Conduction involves molecules transferring kinetic energy to one another through collisions. Web converging currents drive plates into each other. Changing the temperature of a fluid affects its. In the 1830s, in the bridgewater treatises, the term. Web the flow that transfers heat within a fluid is called convection current. Web when two plates rub against each other there is an earthquake. Diverging currents pull them apart. Differential heating causes convection currents, which transfer heat from one place to another in fluids like air and water. • identify earth’s outer core as the heat source driving convection currents in earth’s mantle; Web during this lesson students observe convection currents by performing a lab experiment. In places where convection currents rise up towards. > when you heat a fluid (i.e., water), the hotter material. In the previous lesson the students. Web convection currents drive the movement of earth’s rigid tectonic plates in the planet’s fluid molten mantle. Illustration of convection currents in heated water. In the 1830s, in the bridgewater treatises, the term. Primary means of transferring heat in liquids. Illustration of convection currents in heated water. Convection is the movement of fluid molecules from higher temperature to lower temperature regions. Web convection is heat transfer by the macroscopic movement of mass. In the 1830s, in the bridgewater treatises, the term. Web convection is a process in which heat is carried from place to place by the bulk movement of a fluid and gases. Web • explain convection currents can occur in any liquid substance; Convection can be natural or forced and generally transfers thermal energy faster than. Examples of convection currents in water, air, and the earth. What sets a. 4how does convection relate to. In the previous lesson the students. In the 1830s, in the bridgewater treatises, the term. What sets a convection current in motion? Convection is the movement of fluid molecules from higher temperature to lower temperature regions. Make your own heat waves in an aquarium. Web when two plates rub against each other there is an earthquake. As a result of this activity, students develop an understanding of the process of convection. Web the flow that transfers heat within a fluid is called convection current. Web there are three forms of thermal energy transfer: Changing the temperature of a fluid affects its. Conduction involves molecules transferring kinetic energy to one another through collisions. Diverging currents pull them apart. Web evaporation cools the surface enough to make some molecules sink back toward the bottom of the pan again. A simple example of convection currents is warm air rising. (1) the heating and cooling of the fluid, (2)changes. Convection can be natural or forced and generally transfers thermal energy faster than. Web examples of convection. > when you heat a fluid (i.e., water), the hotter material. Web convection is the process of heat transfer by the bulk movement of molecules within fluids such as gases and liquids. Web converging currents drive plates into each other. Convection can be natural or forced and generally transfers thermal energy faster than. Web • explain convection currents can occur in any liquid substance; Boiling water in a pot. Diverging currents pull them apart. Web an explanation of density and how to determine what floats. Make your own heat waves in an aquarium. Web convection is heat transfer by the macroscopic movement of mass. Web when two plates rub against each other there is an earthquake. 4how does convection relate to. What sets a convection current in motion? Boiling water in a pot. Web examples of convection. Convection currents transfer thermal energy through many fluids, not just hot water in a pot. • identify earth’s outer core as the heat source driving convection currents in earth’s mantle; Web evaporation cools the surface enough to make some molecules sink back toward the bottom of the pan again. Primary means of transferring heat in liquids. Convection is the movement of fluid molecules from higher temperature to lower temperature regions. Conduction involves molecules transferring kinetic energy to one another through collisions. In the previous lesson the students. Web convection is a process in which heat is carried from place to place by the bulk movement of a fluid and gases.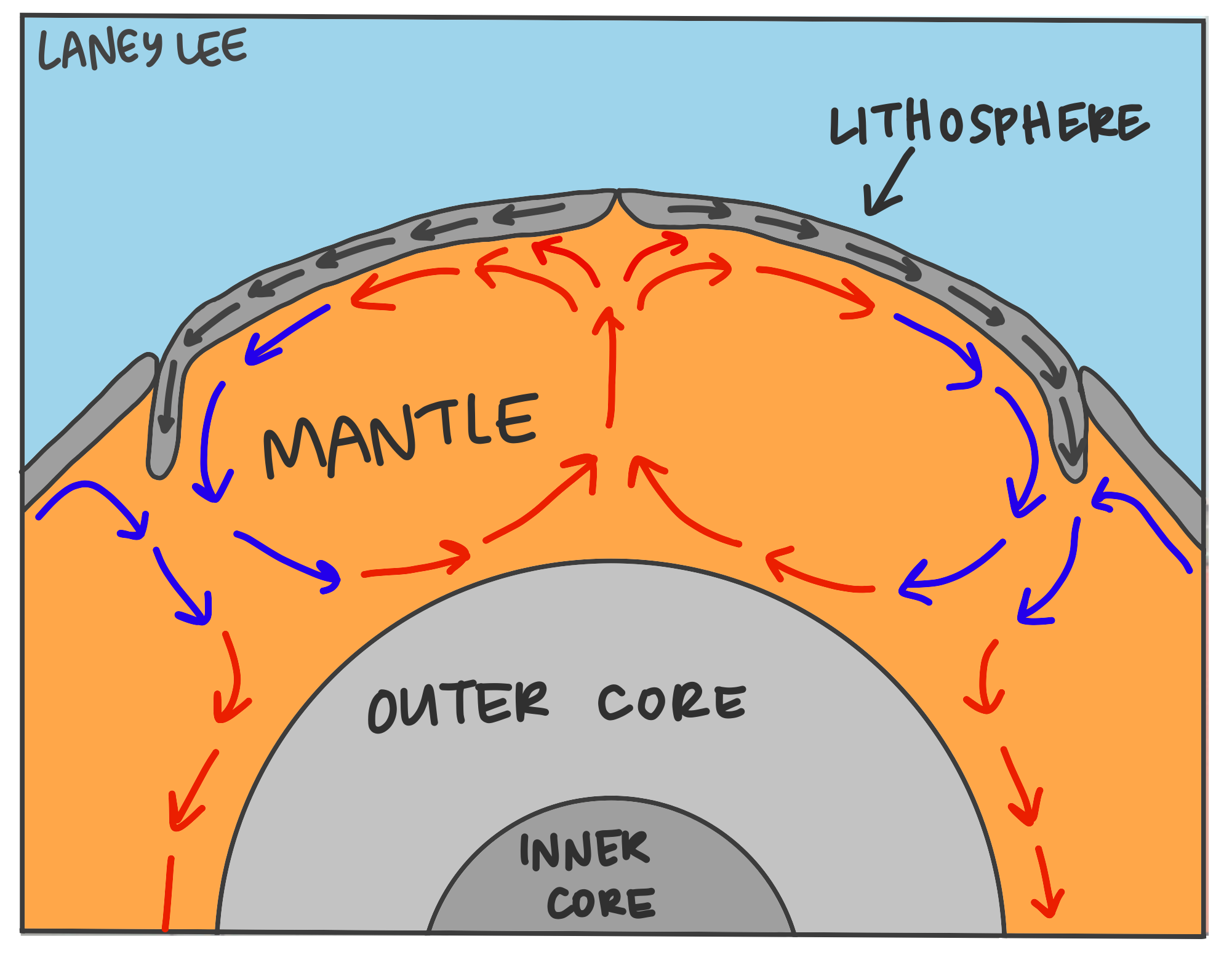
Convection Currents & Plate Tectonics Laney Lee

Convection currents in hot air balloon diagram 3500500 Vector Art at

How to draw convection currents in atmosphere Easy Drawings Dibujos

Plate Tectonics Convection Currents Convection currents, Plate
convection currents labeled diagram Coloso

Convection Currents Worksheet
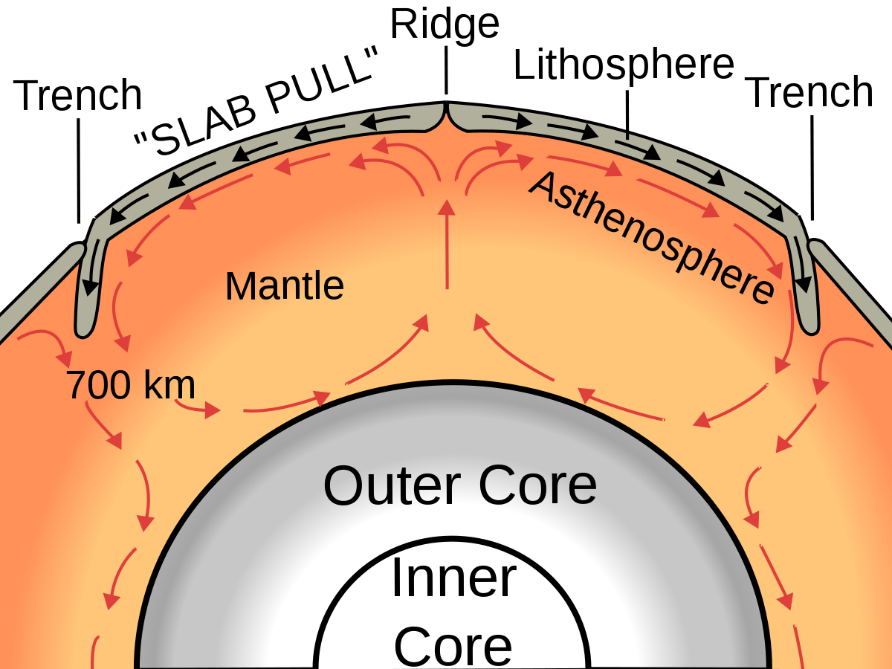
Convection Currents What, How A Level Geography Notes
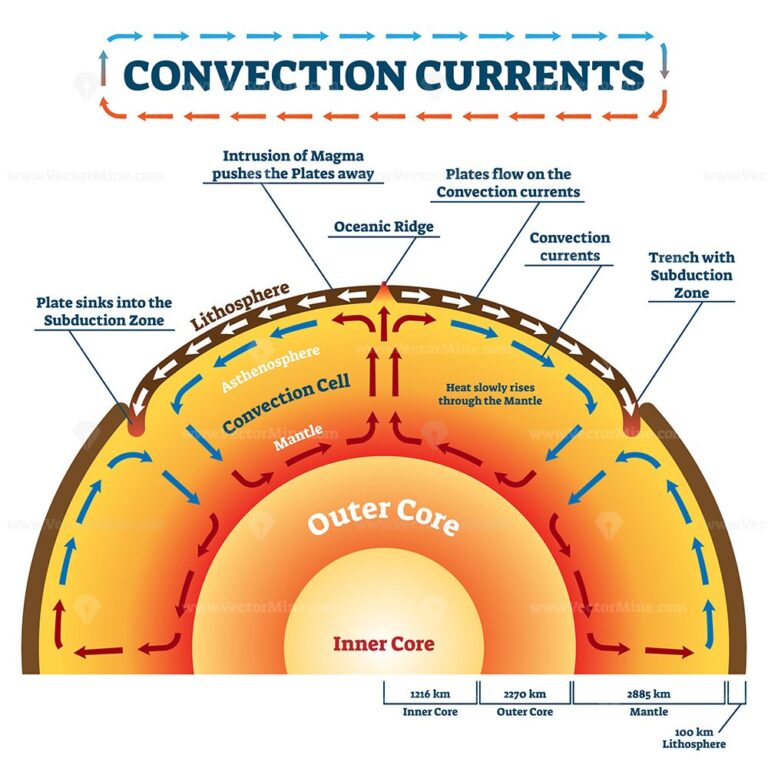
Convection Currents vector illustration VectorMine
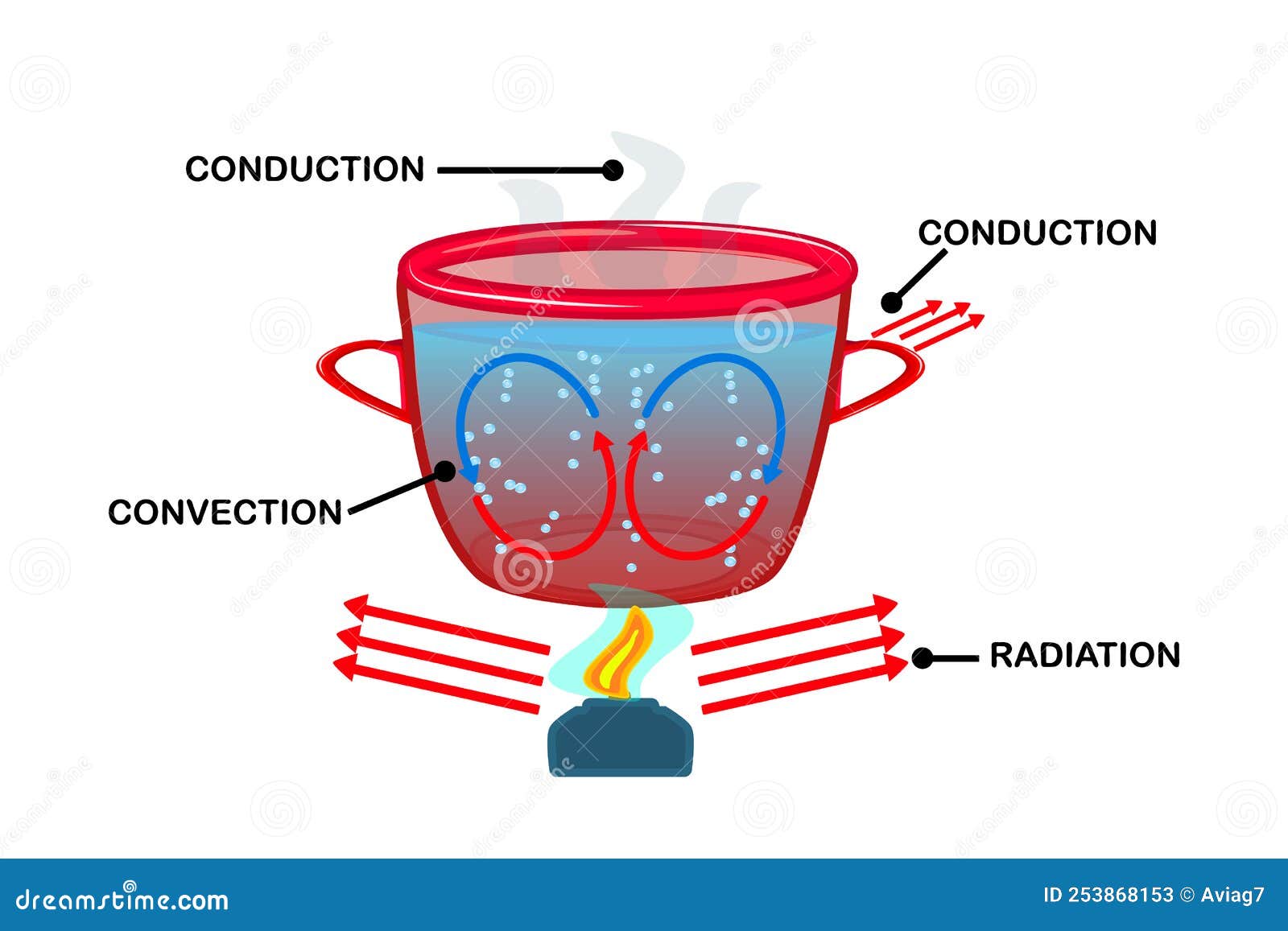
Heat Transfer. Convection Currents Labeled Diagram. Stock Vector

Convection currents Diagram Quizlet
Web 1What Is A Current?
(1) The Heating And Cooling Of The Fluid, (2)Changes.
Hot Mantle Rock Rises From The Core And Moves Along Under The Crust.
Web The Flow That Transfers Heat Within A Fluid Is Called Convection Current.
Related Post: