Connective Tissue Flow Chart
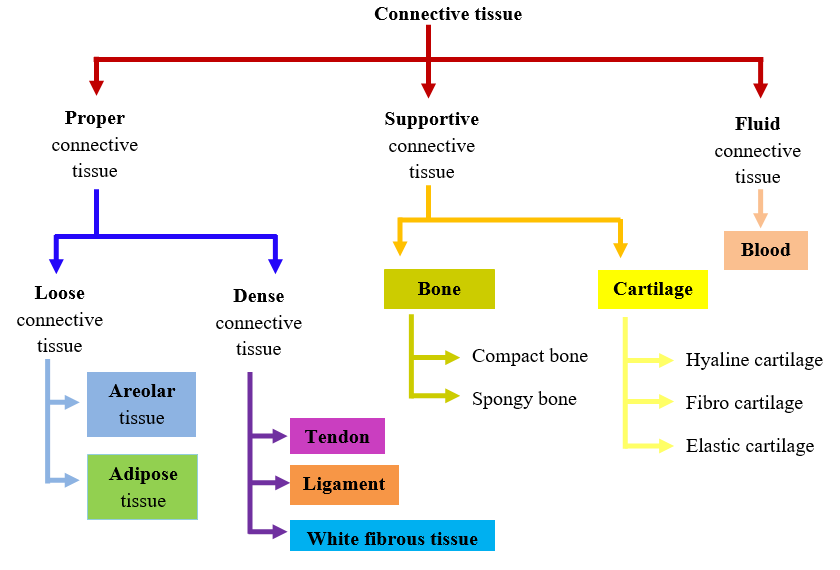
Connective Tissue Flow Chart - Web a connective tissue is responsible for connecting different parts of the body physically or by transporting substances from one part to another. Web connective tissue flow chart ( easy way) sunil kumar. Develop in the bone marrow, found in lymphatic system and in blood vessels. Humans—and other complex multicellular organisms—have systems of organs that work together, carrying out processes that keep us alive. Furthermore, it provides protection against infection, gives passage to nerve and blood vessels through other tissues and fixes organs together. Loose connective tissues can be found all over the body, providing both support and elasticity. This tissue is most widely distributed connective tissue in the animal body. We are going to discuss them in details. Web between areolar and reticular, dense regular and dense irregular, the beginner anatomy student is expected to tell the difference between a bunch of types of connective tissue. For example, ligaments connect 2 bones together and tendons connect muscles to bones and hence they are connective tissues. They are a loose array of random fibers that has a wide variety of cell type. Dense connective tissue is divided into 1) dense regular, 2) dense irregular, 3) elastic. The primary elements of connective tissue include a ground substance, fibers, and cells. Connective tissue proper has two subclasses: 32k views 5 years ago animal tissues. Video for connective tissue is divided into different parts each part. They are a loose array of random fibers that has a wide variety of cell type. The principal cell of connective tissues is the fibroblast. Connective tissue proper is further subdivided into loose and dense connective tissues. Web the following points highlight the three main types of connective tissues. Dense connective tissue is divided into 1) dense regular, 2) dense irregular, 3) elastic. Web connective tissue is made up of a few cells present in the intercellular framework of protein fibres secreted by the cells, known as collagen or elastin. Video for connective tissue is divided into different parts each part. This tissue is most widely distributed connective tissue. Tissues & histology introduction to connective tissue. (a) areolar tissue (= loose connective tissue): Connective tissue proper has two subclasses: Loose connective tissues can be found all over the body, providing both support and elasticity. The principal cell of connective tissues is the fibroblast. Flow chart of classification of connective tissue. Although connective tissue is diverse, all connective tissue consists of 3 main components: Web connective tissue is made up of a few cells present in the intercellular framework of protein fibres secreted by the cells, known as collagen or elastin. The principal cell of connective tissues is the fibroblast. Furthermore, it provides protection. (a) areolar tissue (= loose connective tissue): From the connective tissue sheath that surrounds a muscle, to the tendons that attach muscles to bones, and to. Explain the functions of connective tissues. Web a connective tissue is responsible for connecting different parts of the body physically or by transporting substances from one part to another. Web connective tissue is divided. Furthermore, it provides protection against infection, gives passage to nerve and blood vessels through other tissues and fixes organs together. Web connective tissue introduction connective tissue serve as a connecting link for binding, supporting and strengthening all other body tissues together. Like all tissue types, it consists of cells surrounded by a compartment of fluid called the extracellular matrix (ecm).. They are a loose array of random fibers that has a wide variety of cell type. In addition, they nourish and pillows epithelia. From the connective tissue sheath that surrounds muscle cells, to the tendons that attach muscles to bones, and to. Explain the functions of connective tissues. Web according to the nominator, isolated partial facetectomy and soft tissue release. Loose connective tissue is divided into 1) areolar, 2) adipose, 3) reticular. (a) areolar tissue (= loose connective tissue): Web unlike epithelial tissue, which has cells that are closely packed together, connective tissue typically has cells scattered throughout an extracellular matrix of fibrous proteins and glycoproteins attached to a basement membrane. The ground substance is made of an organic substance. This tissue is most widely distributed connective tissue in the animal body. (a) areolar tissue (= loose connective tissue): From the connective tissue sheath that surrounds muscle cells, to the tendons that attach muscles to bones, and to. Web between areolar and reticular, dense regular and dense irregular, the beginner anatomy student is expected to tell the difference between a. (a) areolar tissue (= loose connective tissue): Web connective tissues perform many functions in the body, most importantly, they support and connect other tissues: Web unlike epithelial tissue, which has cells that are closely packed together, connective tissue typically has cells scattered throughout an extracellular matrix of fibrous proteins and glycoproteins attached to a basement membrane. Web connective tissue introduction connective tissue serve as a connecting link for binding, supporting and strengthening all other body tissues together. The ground substance is made of an organic substance (usually a protein) and an inorganic substance (usually a mineral or water). Most connective tissues are highly vascular (contain blood vessels). Web connective tissue can be broken down into two primary categories: From the connective tissue sheath that surrounds a muscle, to the tendons that attach muscles to bones, and to. Tissues & histology introduction to connective tissue. Furthermore, it provides protection against infection, gives passage to nerve and blood vessels through other tissues and fixes organs together. The principal cell of connective tissues is the fibroblast. We are going to discuss them in details. Flow chart of classification of connective tissue. They are a loose array of random fibers that has a wide variety of cell type. The cells also secrete a thin gel of polysaccharides, which together with fibres make matrix or ground substance. Connective tissue proper is further subdivided into loose and dense connective tissues.
Connective Tissue Chart FullColor; 12 detailed micrographs; 44.45 x 59
Connective Tissue W3schools
Connective Tissue Flow Chart vrogue.co

Connective Tissue Flow Chart

Connective Tissue Flow Chart

Connective Tissue types Tissue types, Basic anatomy and physiology

Connective tissues and their functions

Structure And Function Of Connective Tissue And Bone Lab
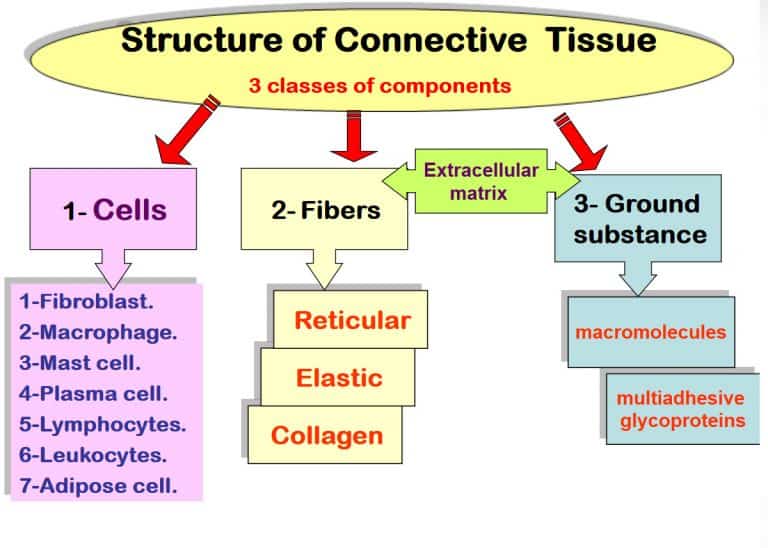
Connective Tissue Types (Examples) and Functions
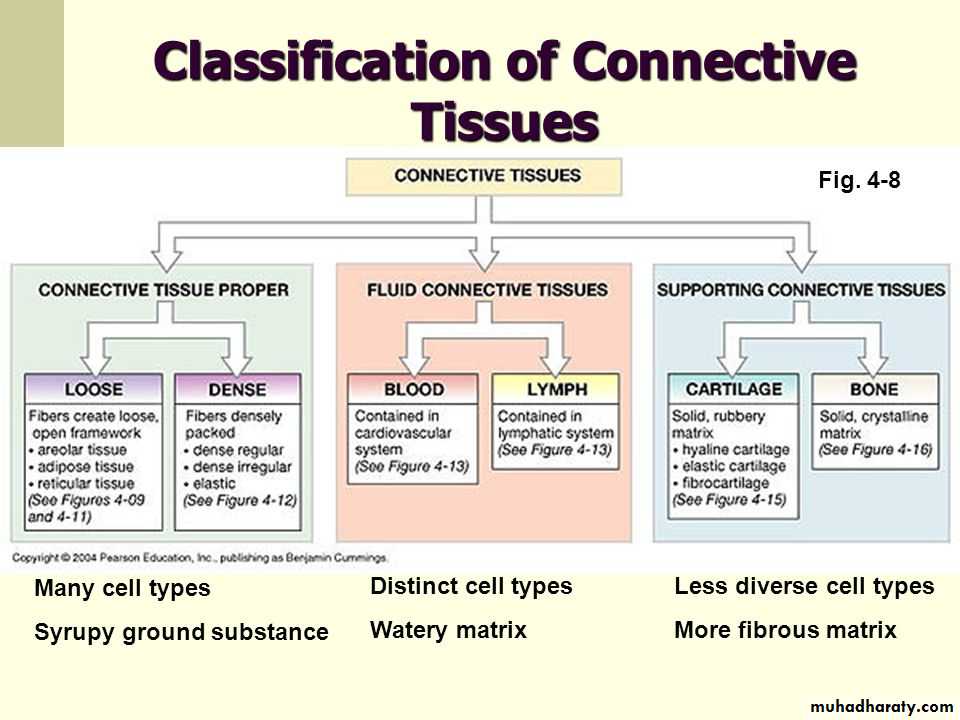
Connective tissue pptx D. Talib Muhadharaty
Web Connective Tissue Is Divided Into Four Main Categories:
Cells Make Up Tissues, Tissues Make Up Organs, And Organs Make Up Organ Systems.
Web According To The Nominator, Isolated Partial Facetectomy And Soft Tissue Release Are Already Included In Spinal Fusion Procedures And Should Not Be Separately Billed With An Osteotomy Code.
Develop In The Bone Marrow, Found In Lymphatic System And In Blood Vessels.
Related Post: